Reproduction in humans
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Sexual reproduction in humans
involves the fusion of the male gamete (sperm) with the female gamete (egg)
Male Reproductive System
Testes: Produces sperm (male gamete) and testosterone (hormone)
Scrotum: Holds the testes outside of body to keep it colder than body temperature
Sperm Duct: Tube that carries sperm from the testes to the urethra
Prostate Gland: Secretes nutritive fluid which combines with sperm to form semen
Urethra: Tube which allows excretion of urine and semen from body
Penis: Passes urine out of the body & allows semen to pass into the vagina of a woman (during sexual intercourse)
The female reproductive system
Ovaries: Where egg cells (female gametes) are developed
Oviducts: Place where fertilisation takes place. Connects the ovary to the uterus, lined with ciliated cells to push the released ovum down it
Uterus: Place where the fetus develops
Cervix: Ring of muscle that keeps the fetus in place during pregnancy
Vagina: Entry point for the penis
Fertilisation
fusion of the nuclei from a male gamete (sperm) and a female gamete (egg cell)
Adaptive features of sperm
Adaptive features of sperm
1. Flagellum to swim towards egg cell 2. Mitochondria to provide energy for movement 3. Enzymes in the acrosome to break down egg cell’s protective layer
Adaptive features of egg cells
- Cytoplasm containing energy stores to support early development after fertilisation. 2. Jelly coat that changes after fertilisation to prevent multiple sperm from entering the egg
Sperm
very small, head region and flagellum, can move, produced in millions per day
Egg cell
large, round cell with jelly coating, can’t move on its own, only one released each month
Fertilisaiton process in humans
- Ovary releases egg and egg moves through oviduct with cilia. Sperm enters oviduct and if an egg is present, it may get fertilised. 2. Fusion of nucleus of a sperm and a nucleus of an egg cells.
Implantation
After gets fetilised with sperm, gamete becomes zygote. Zygote forms an embryo which is a ball of cells that implants into the lining of the uterus.
Pregnancy
Embryo grows into fetus by placenta, umbilical cord, amniotic sac, amniotic fluid
Placenta
- Develops during pregnancy and attaches to uterine wall. 2. Acts as an interface between the mother’s blood supply and the developing fetus. 3. Provides oxygen and nutrients to the fetus by diffusion across placenta due to difference in concentration gradients. 4. Removes waste products from the fetus eg. CO2, urea. 5. Produces estrogen and progesterone that help maintain the pregnancy. Some pathogens and toxins can pass across the placenta and affect the fetus.
Umbilical cord
Connects the developing fetus to the placenta 2. Provides the fetus with oxygen and nutrients from the mother’s blood via placenta 3. Removes waste products from the fetus and returns them to the mothers blood via placenta
Amniotic sac
- Surrounds and protects the developing fetus. 2. Contains amniotic fluid, which cushions and supports the fetus. 3. Helps regulate temperature around the fetus
Amniotic fluid
- Cushions and protects the fetus 2. Helps the fetus move and develop properly 3. Helps regulate temperature around the fetus
Puberty
Period when the body undergoes changes as a child progresses into adulthood. In males: testosterone. In females: estrogen.
Testosterone in males
- Growth of penis and testes. 2. Growth of fqcial and body hair. 3. Muscles develop 4. Voice deepens 5. Testes start to produce sperm
Estrogen in females
- Breasts develop 2. Body hair grows 3. Menstrual cycle begins 4. Hips get wider
Menstruation
- Ovaries release an ovum every 28 days. 2. Uterus lining thickens in preparation for embryo implantation 3. If ovum is not fertilized, uterine lining breaks down. 4. The unfertilised egg cells, together with the old uterus lining are passed out of the vagina.
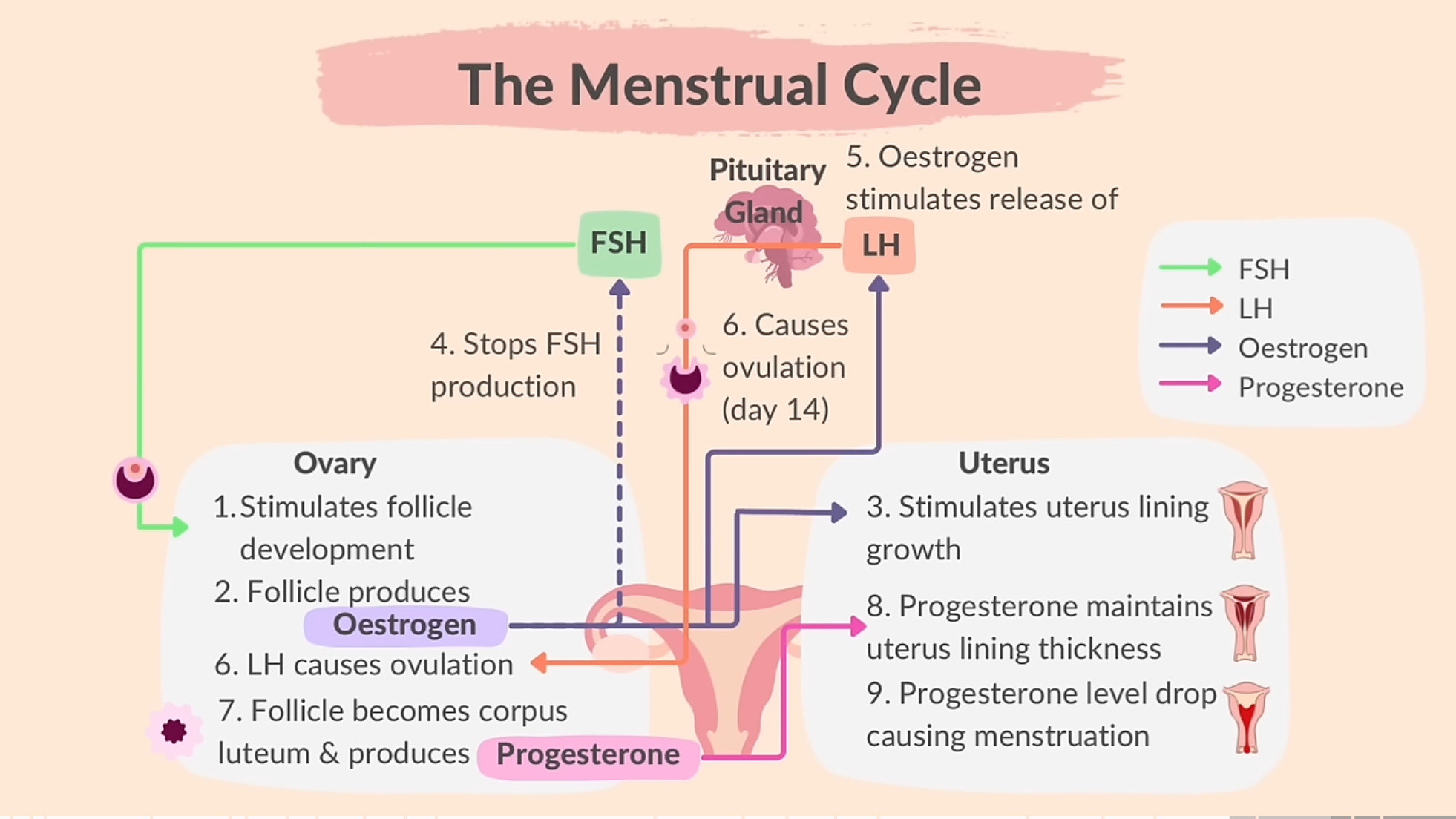
The menstrual cycle
The pituitary gland produces FSH which stimulates the development of a follicle in the ovary. 2. An egg develops in the follcile and 3. follicle releases estrogen 4. Stimulates uterus lining growth. 5 inhibits FSH 6. When estrogen rises to a high enough level, it stimulates release of LH from the pituitary gland which causes ovulation around day 14. 7. The follicle becomes corpus luteum and starts producing progesterone. 8. Progesterone maintains the thickness of uterus wall. 9. If egg is not fertilized, corpus luteum breaks down and progesterone levels drops, causing menstruation
Changes in ovaries
- Follicles in the ovaries begin to grow and mature. One follicle becomes dominant and continues to grow. 2. The dominant follicle ruptures and releases an egg around day 14. 3. The remaining cells form corpus luteum. If the egg is not fertilised, the corpus luteum degenerates and leads to menstruation
Sexual hormones in Humans
Estrogen
- Produced by the ovaries during menstrual cycle. 2. Produced by the placenta during pregnancy. 3. Stimulates growth of uterus lining, making it thicker 4. Causes the follicle containing the egg to mature. 5. Stimulates LH production 6. Decreases FSH production
Progesterone
Produced by the ovaries during menstrual cycle 2. Produced by the placenta during pregnancy 3. Maintains the thick uterus lining during menstrual cycle and pregnancy. 4. Decreases FSH production. 5. If egg is not fertilized, progesterone level drops, causing the uterine lining to break down
LH
When estrogen levels have reached their peak, it stimulates the pituitary gland to release LH.2. Stimulates ovulation which triggers an egg to be released. 3. Also stimulates progesterone production in the ovaries
FSH
1. Produced by pituitary gland 2. Causes a single follicle in the ovary to develop and mature 3. Also stimulates the ovaries to release estrogen
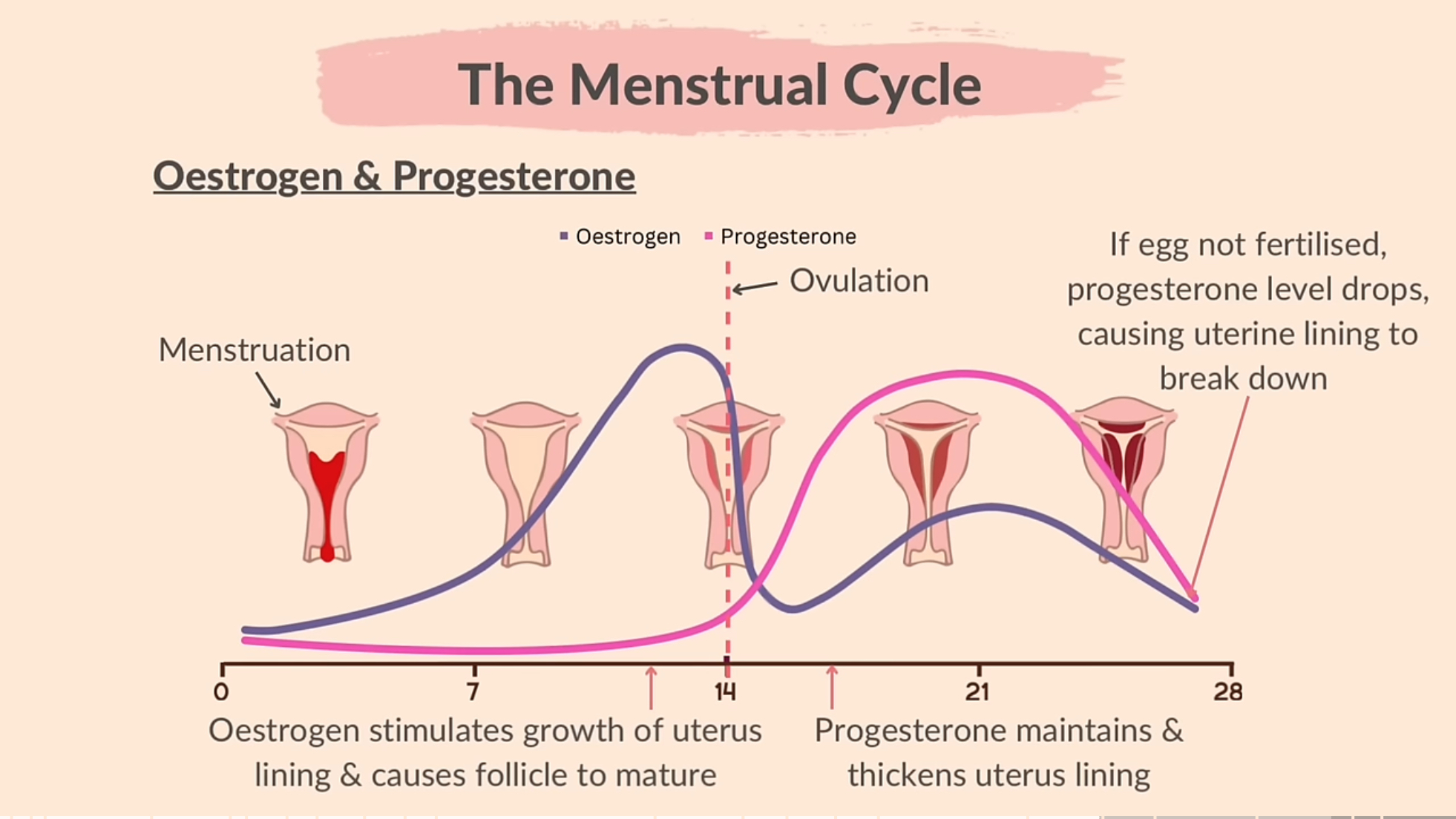
Estorgen and prograteron during mensgrual cycle
Days 1 to 14 Estrogen stimulates growth of uterus and causes follcile to mature. Days 14 to 28 progesterone maintains and thickens uterus lining. 2. First few days, low levels of estrogen and progesterone. 3. Afterwards, level of estrogen starts to increase, leading to the thickening of the uterine lining. Progesterone levels remain low during this time. 4. On day 14 ovulation takes place and causes sharp increase in estrogen levels and a little increase in progesterone levels. 5. Then follicle ruptures and forms corpus luteum, and produces high levels of progesterone to prepare the uterus for potential pregnancy. Estrogen levels also increase. 6. If pregnancy doesn’t occur, the corpus luteum breaks down, causing a drop in estrogen and progesterone levels, leading to menstruation
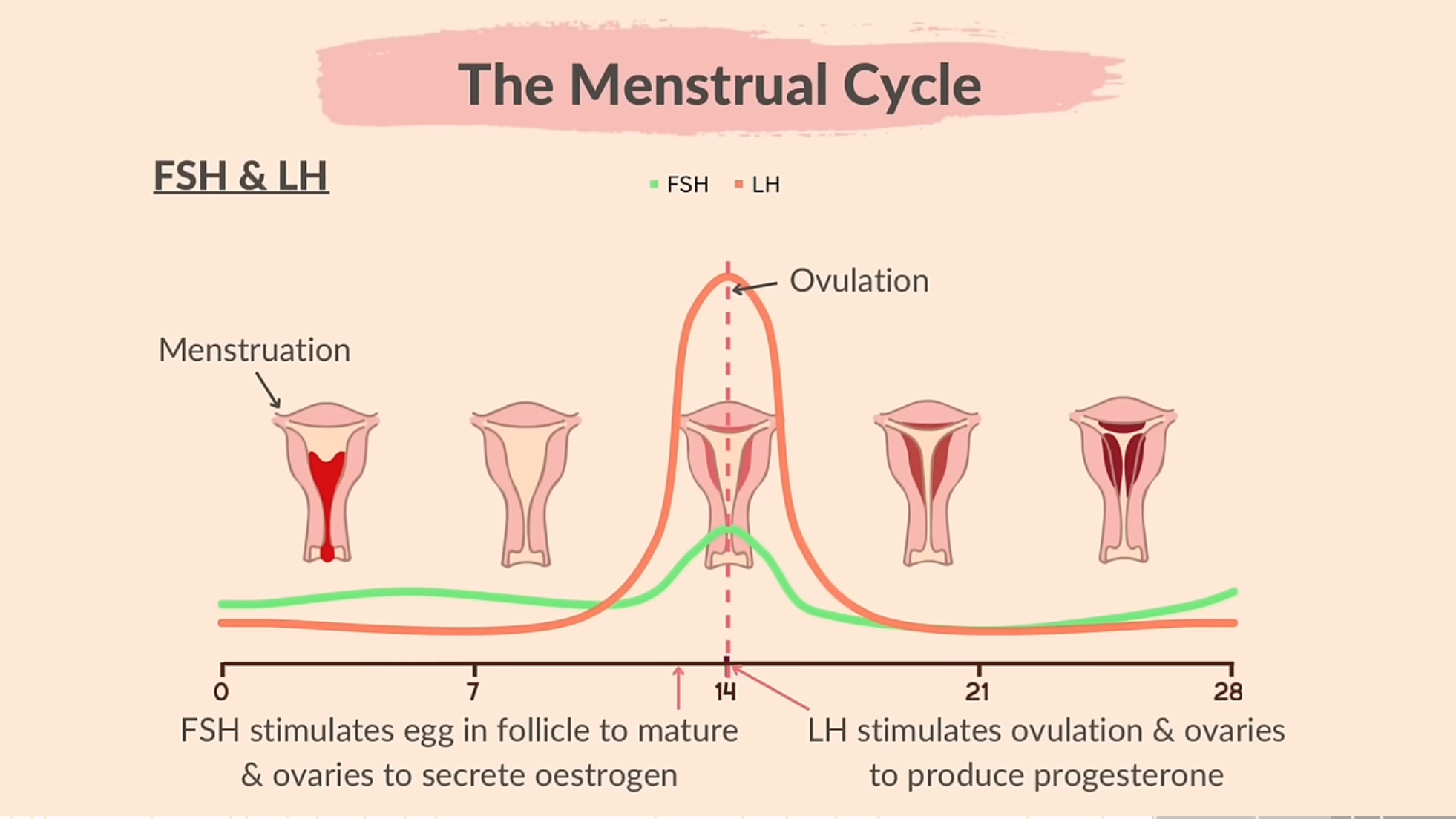
FSH and LH during menstrual cycle
First few days, low levels of FSH and LH. 2. FSH gradually increases and stimulates growth of follicles in ovaries. LH levels also begin to rise in response to increasing estrogen levels from the growing follicles. 3. Day 14 surge of LH triggers ovulation causing the dominant follicle to release an egg. 4. LH decrease after ovulation while FSH levels remain stable.
Sexually transmitted infections
an sti is an infection that is transmitted through sexual contact. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a pathogen that causes an STI.
HIV
HIV attacks and weakens the immune system by reducing the number of functioning lymphocytes and decreasing the body’s ability to produce antibodies to fight off infection, leaving the body more vulnerable to other infections and diseases.
AIDS
An HIV may lead to AIDS (Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) Makes an individual highly vulnerable to other pathogens as their white blood cells are unable to fight infection, potentially resulting in death.
Methods of HIV transmission
- Unprotected sexual intercourse 2. Sharing needles with an infected person 3. Vlood transfusions with infected blood 4. From mother to fetus through the placenta 5. Mother to baby via breast feeding
Controlling spread of HIV
- Limiting the number of sexual partners an individual has 2. Using condoms 3. Getting tested if unprotected sex or sex with multiple partners has occurred 4. Raising awareness through education programmes 5. Abstinence from sexual intercourse 6. Using sterile needles instead of sharing