Julissa's SET FOR US HISTORY!!!
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
Great Depression
economic hard times that lasted from 1929-1940s
Consumerism
Large purchasing of material goods.
Buying on Margin
Taking out a loan to invest in the stock market.
Black Tuesday
October 29, 1929; the day the stock market crashed
Hoovers Plan
Economy will work itself out

soup kitchens
set up by as a relief to help feed the poor, unemployed

Hoovervilles
nickname for the homeless communities
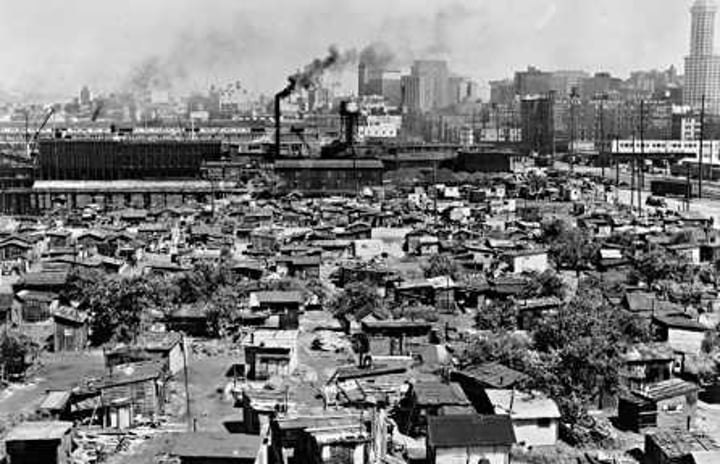

Hoboes
Traveled around the states looking for jobs

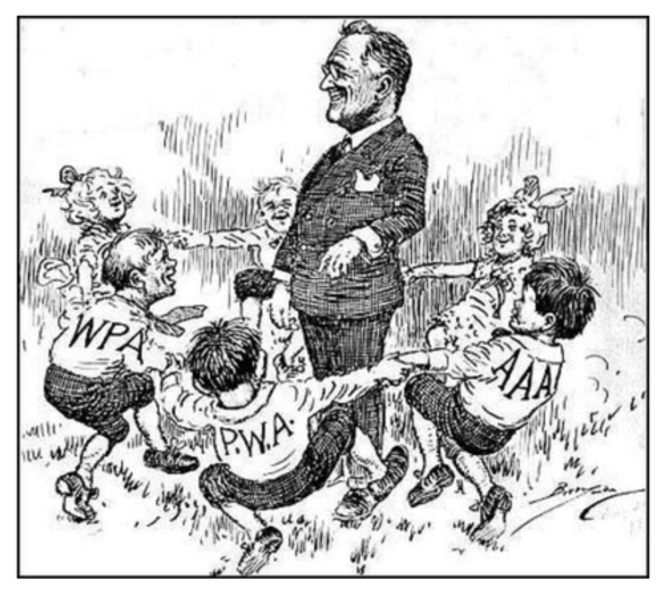
FDR's Plan
Relief programs, more government spending

New Deal
Roosevelt's plan to get people back to work

Alphabet Soup Programs
nickname for FDR's public works programs.

Social Security act
provides disability insurance and unemployment insurance

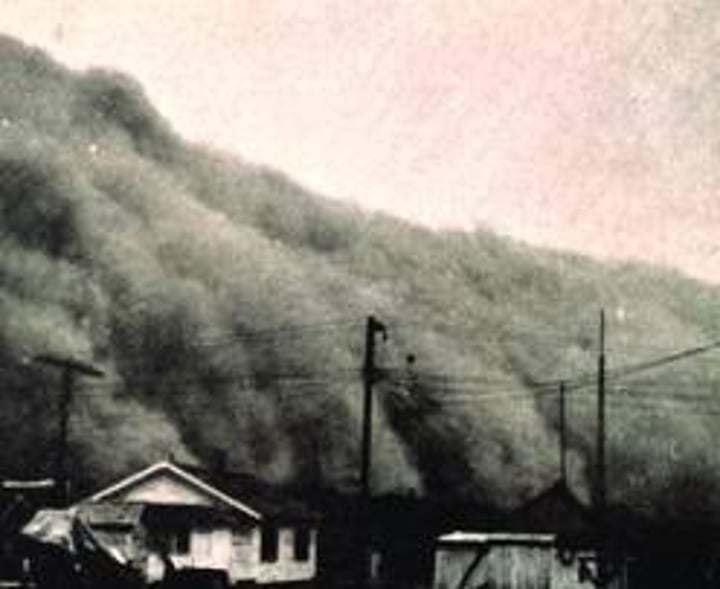
Dust Bowl
severe drought that worsened the Depression for people in the midwest

Red Scare
A fear of communism emerged. Fueled by (1) the recent Russian revolution, (2) Eugene Debs growing numbers, (3) strikes. Leads to anti-foreignism
Sacco and Vanzetti
Italian immigrants accused of murder. anarchists- utopida without government intervention
Ku Klux Klan
Against Catholics, Jewish, pacifists, communists, internationalists, revolutionists, bootleggers, gambling, adultery, and birth control.
pro-white Anglo-Saxon protestant
numerical peak during the 20's—about 5 million members
Emergency Quota Act
1921 cut the number of immigrants who could enter America to 3% of their nationality's U.S. population in 1910.
Immigration Act
In 1924, the Immigration Act sliced the number down to 2% of a group's U.S. population in 1890. (New Immigrants out, Old Immigrants in).
No Japanese immigrants.
Canadians and Latin Americans were not included in the law.
Problems with prohibition
not enough people to enforce
speakeasies
bootlegging
gangs
Immigrants effect labor unions
employers used racial difference to keep unions from getting stronger
Horace Kallen
keep old world traditions
Randolph Bourne
trans-nationality in america
Al Capone
bootlegging, public enemy #1, Chicago
Racketeering
"protection money"
Lindbergh Laws
make interstate childhood abduction punishable by death
John Dewey
"learn by doing" influential American philosopher, psychologist, and educational reformer. He believed in experiential learning, where education should be based on real-life experiences and problem-solving.
Scopes Trial
Evolution v. Fundamentalism
Charles Darrow
defended Scopes
William Jennings Bryan
lead prosecution
Nickelodeons
5 cent theaters
Movies
1st used as anti-german propaganda
now actors are highly paid
1920 census
more people live in urban than rural
Margaret Sanger
birth control movement
flappers
women who go against traditional terms
Modernists
God is a "good guy, in a chummy place
Sigmund Freud
helps flappers; sexual repression causes nervous and emotional ills
Modern art
surrealism, cubism, dadaism
Harlem Renaissance
racial pride
Langston Hughes- poetry
Marcus Garvey
United Negro Improvement Association
instill more black pride
Zora Hurston
"New Negro" She portrayed racial struggles in the early-20th-century American South and published research on hoodoo.
Signs of financial disaster
banks failing, natural disasters, investors losing money
1921 Bureau of the Budget
Andrew Mellon- in favor of low taxes : Problems with high taxes; rich invest in tax exempt securities, less revenue
Frederick Taylor
promoted efficiency in production
national womens party
equal rights
Social Gospel Movement
A social reform movement led by protestant ministers that developed within religious institutions and sought to apply the teachings of Jesus directly to society
Muckrakers
A group of investigative reporters who pointed out the abuses of big business and the corruption of urban politics; included Frank Norris (The Octopus) Ida Tarbell (A history of the standard oil company) Lincoln Steffens (the shame of the cities) and Upton Sinclair (The Jungle)
Initiative
A procedure by which voters can propose a law or a constitutional amendment.
Referendum
A state-level method of direct legislation that gives voters a chance to approve or disapprove proposed legislation or a proposed constitutional amendment.
Recall
procedure whereby voters can remove an elected official from office
Austrailian ballot system
A system that allows voters privacy in marking their ballot choices. Developed in Australia in the 1850s, it was introduced to the United States during the progressive era to counteract boss rule. (SECRET BALLOT)
Muller v. Oregon
1908 - Supreme Court upheld Oregon state restrictions on the working hours of women as justified by the special state interest in protecting women's health
Lochner v. New York (1905)
A setback for progressivists, it was ruled in this case that a law enforcing a 10-hour work day for bakers was unconstitutional.
Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire
(1911) 146 women killed while locked into the burning building (brought attention to poor working conditions)
Elkins Act (1903)
Strengthened the Interstate Commerce Act by imposing heavy fines on railroads offering rebates and on the shippers accepting them
Meat Inspection Act (1906)
Upton Sinclair's The Jungle heightened public awareness of the appalling and unsanitary conditions in the meat-packing industry. Public pressure forced a reluctant Congress to consider a Meat Inspection bill in 1906 which laid down binding rules for sanitary meat packing and government inspection of meat products crossing State lines. Changed the face of health care and food safety legislation in America from that point on.
Pure Food and Drug Act of 1906
1906 - Forbade the manufacture or sale of mislabeled or adulterated food or drugs, it gave the government broad powers to ensure the safety and efficacy of drugs in order to abolish the "patent" drug trade. Still in existence as the FDA.
Hetch Hetchy Valley
Site of a controversial dam built to supply San Francisco with water and power in the aftermath of the 1906 earthquake. The dam was built over the objections of preservationists such as John Muir.
Panic of 1907
A short financial panic in 1907 that caused "runs" on banks, suicides, and criminal indictments against speculators. Some in the financial world blamed President Roosevelt for his progressive reforms, such as corporate regulation, income taxes, and worker protections.
Dollar Diplomacy (Taft)
A policy for "substituting dollars for bullets" by William Howard Taft. It would link American business interests to diplomatic interests abroad without force, but with investments.
New Nationalism
Roosevelt's progressive political policy that favored heavy government intervention in order to assure social justice
New Freedom
Democrat Woodrow Wilson's political slogan in the presidential campaign of 1912; Wilson wanted to improve the banking system, lower tariffs, and, by breaking up monopolies, give small businesses freedom to compete.
Ida Tarbell, History of the Standard Oil Company
This 1904 book exposed the monpolistic practices of the Standard Oil Company. Strengthened the movement for outlawing monopolies. A muckraker novel.
Ida B. Wells (1862-1931)
An African-American woman who achieved nationwide attention as leader of the anti-lynching crusade.
Eugene V. Debs
Head of the American Railway Union and director of the Pullman strike; he was imprisoned along with his associates for ignoring a federal court injunction to stop striking. While in prison, he read Socialist literature and emerged as a Socialist leader in America.
Jacob Riis
Early 1900's muckraker who exposed social and political evils in the U.S. with his novel "How The Other Half Lives"; exposed the poor conditions of the poor tenements in NYC and Hell's Kitchen

Frances E. Willard (1839-1898)
This pious leader of the Woman's Christian Temperance Union wished to eliminate the sale of alcohol encouraged some women to take the leap toward more radical causes like woman suffrage, while allowing more conservative women to stick comfortably with temperance work.
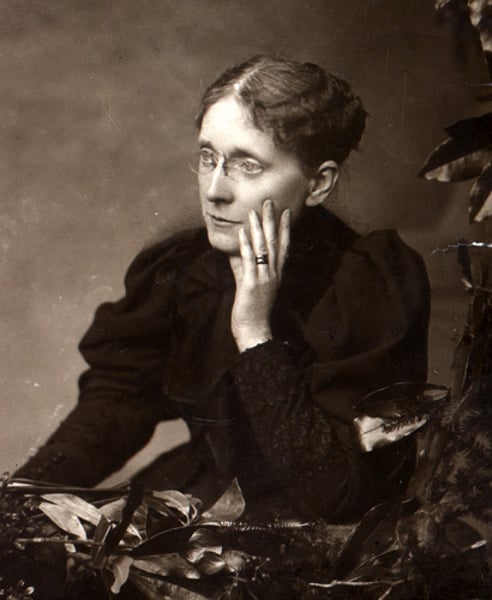

Gifford Pinchot (1865-1946)
A friend of Theodore Roosevelt, he was the head of the federal Division of Forestry and a noted conservationist who wanted to protect, but also use, the nation's natural resources,
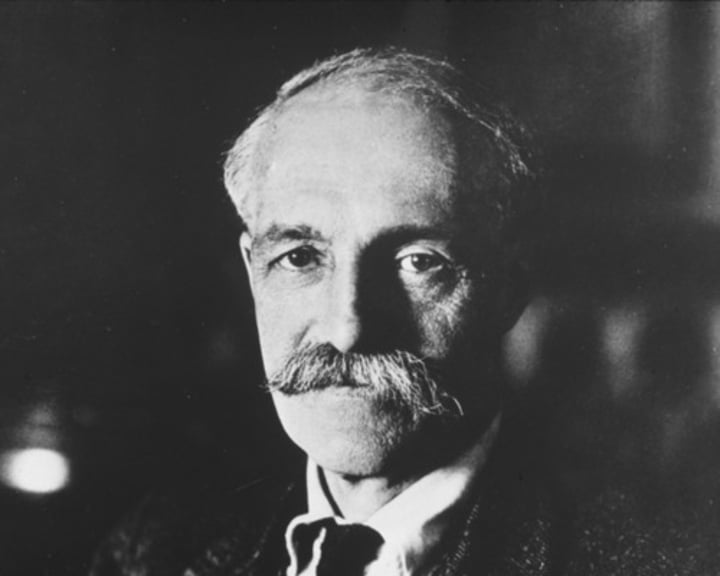

Theodore Roosevelt
26th president, known for: conservationism, trust-busting, Hepburn Act, safe food regulations, "Square Deal," Panama Canal, Great White Fleet, Nobel Peace Prize for negotiation of peace in Russo-Japanese War
Woodrow Wilson
28th president of the United States, known for World War I leadership, created Federal Reserve, Federal Trade Commission, Clayton Antitrust Act, progressive income tax, lower tariffs, women's suffrage (reluctantly), Treaty of Versailles, sought 14 points post-war plan, League of Nations (but failed to win U.S. ratification), won Nobel Peace Prize
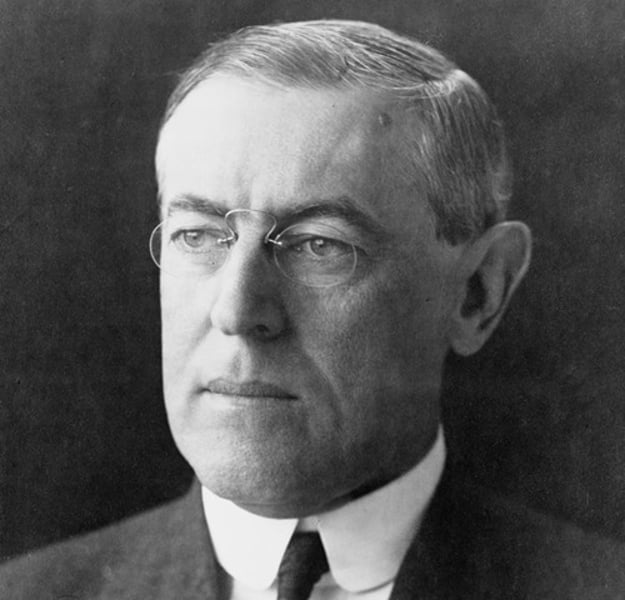

Susan B. Anthony and Elizabeth Cady Stanton
leading figures in the women's rights movement
16th Amendment
Amendment to the United States Constitution (1913) gave Congress the power to tax income.
Pendleton Act
1883 law that created a Civil Service Commission and stated that federal employees could not be required to contribute to campaign funds nor be fired for political reasons
Clayton Antitrust Act
1914 act designed to strengthen the Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890; certain activities previously committed by big businesses, such as not allowing unions in factories and not allowing strikes, were declared illegal.
Sherman Antitrust Act (1890)
First federal action against monopolies, it was signed into law by Harrison and was extensively used by Theodore Roosevelt for trust-busting. However, it was initially misused against labor unions
Interstate Commerce Act
Established the ICC (Interstate Commerce Commission) - monitors the business operation of carriers transporting goods and people between states - created to regulate railroad prices
Election of 1912
Presidential campaign involving Taft, T. Roosevelt, and Woodrow Wilson. Taft and Roosevelt split the Republican vote, enabling Wilson to win

Underwood Tariff
Pushed through Congress by Woodrow Wilson, this 1913 tariff reduced average tariff duties by almost 15% and established a graduated income tax (16th Amendment)
Upton Sinclair, The Jungle
revealed unsanitary nature of meat-packing industry, inspired Meat Inspection Act and Pure Food and Drug Act (1906)
Square Deal
Economic policy by Roosevelt that favored fair relationships between companies and workers
NAACP
Interracial organization founded in 1909 to abolish segregation and discrimination and to achieve political and civil rights for African Americans.
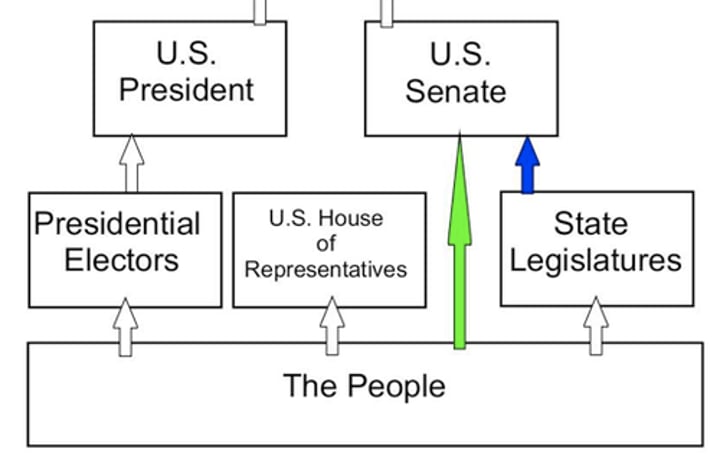
Seventeenth Amendment (1913)
Progressive reform from 1913 that required U.S. senators to be elected directly by voters; previously, senators were chosen by state legislatures.
League of Women Voters (LWV)
Successor to the National American Woman Suffrage Association, it promoted women's role in politics and dedicated itself to educating voters
19th Amendment (1920)
prohibits any United States citizen from being denied the right to vote on the basis of sex. The Constitution allows the states to determine the qualifications for voting,
Eighteenth Amendment
"Prohibition Law" declared it illegal to make, transport, or sell alcohol in the United States.

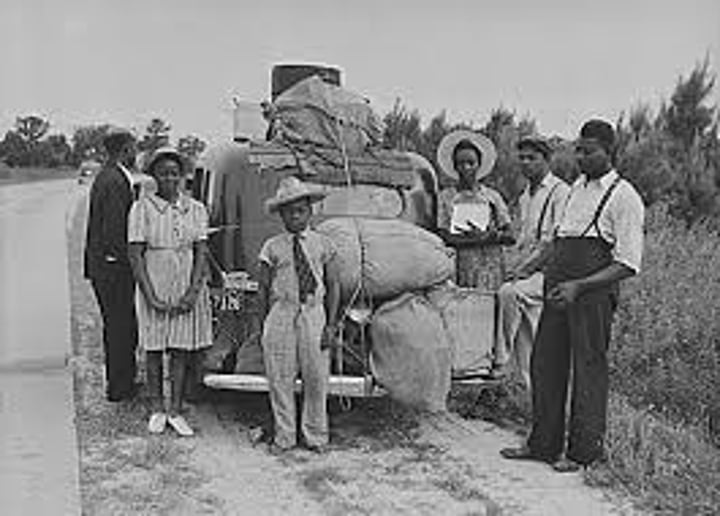
Great Migration
movement of over 300,000 African American from the rural south into Northern cities between 1914 and 1920

conservation
Protecting and preserving natural resources and the environment

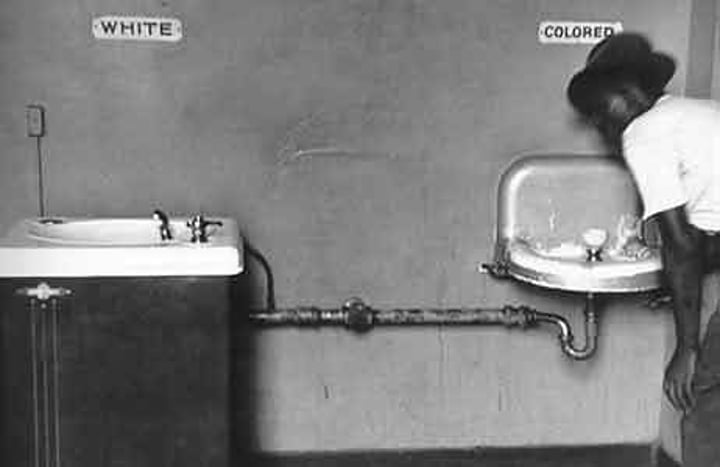
Plessey versus Ferguson
Supreme Court Case upholds segregation as legal using the rule of: separate but equal

17th Amendment
Passed in 1913, this amendment to the Constitution calls for the direct election of senators by the voters instead of their election by state legislatures.
Margaret Sanger
American leader of the movement to legalize birth control during the early 1900's. As a nurse in the poor sections of New York City, she had seen the suffering caused by unwanted pregnancy. Founded the first birth control clinic in the U.S. and the American Birth Control League, which later became Planned Parenthood.

Yellow Journalism
False or exaggerated reporting
Rough Riders
Group of actors, cowboys, Native Americans, college students, athletes, and ex-cops who were led by Theodore Roosevelt in the Spanish American War
Panama Canal
The United States built the Panama Canal to have a quicker passage to the Pacific from the Atlantic and vice versa. Columbians would not let Americans build the canal, but then with the assistance of the United States a Panamanian Revolution occurred.
USS Maine
Ship that exploded in Havana, Cuba killing 260 Americans.
Progressives
Reformers who worked to stop unfair business practices and to improve the way the government worked
Muckrakers
writers who uncovered shameful conditions in business and other areas of American life
Conservation (U.S. National Park Systems)
Protecting something natural from being used up or destroyed. Teddy established a system of parks.
jingoism
extreme, chauvinistic patriotism, often favoring an aggressive, warlike foreign policy
Teddy Roosevelt
Twenty-sixth president of the United States; he focused his efforts on trust busting, environment conservation, and strong foreign policy.
Pulitzer and Hearst
Rival newspaper publishers who used yellow journalism to sell papers
De Lome Letter
The Spanish ambassador insults President McKinley in this document; accused America of being weak.