HAN 364 Final Study Guide: EHR, Telehealth, Privacy, and Informatics
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Request for Proposal (RFP)
Formal detailed document that should include information about organization, requirements for proposed system, request for information from vendor, including company profile, sample contracts, system testing and training requirements, and process for evaluating responses.
Request for Information (RFI)
May start with a Request for Information to obtain basic information about products and narrow to whom RFP is sent.
Key Components of Security Design
Access Controls, Device Security, Software Updates, Cloud or Local, Antivirus/Firewalls, Security Training for Staff, Threat Detection/Awareness, How to Handle Breaches, Regulatory Compliance.
Unit Testing
Directed at EHR modules or subunits.
Integration Testing
Information flow between the EHR and external systems such as lab.
Regression Testing
Fixing one thing that didn't break another.
Performance Testing
Speed is within expected boundaries.
Hardware, Software, and Interface Testing
Testing of the hardware, software, and interfaces involved.
Application-Meets-Requirements Testing
All subunits working together.
Volume Testing
Many numbers & types of users.
'At the Elbow' User Support
Someone physically nearby to help.
SuperUsers & Clinical Champions
People from a clinical unit given more training and charged with helping colleagues through the transition.
Parallel Go-Live Model
Keep new and old systems running; very expensive.
Phased Go-Live Model
Add modules sequentially across organization.
Pilot Go-Live Model
Install full system in one unit at a time; may overlap.
Big Bang Go-Live Model
All at once; has risks but has been used successfully with proper planning.
Post-Implementation Considerations
How is it working? Did it cause other issues? Is the workflow being followed? What happens in a downtime situation? Any metrics being tracked? Collect Feedback from Users? Define Check Points? Lessons Learned and Handoff?
Reasons Telemedicine has become popular
Rising cost of healthcare worldwide, shortages of specialists in rural areas, rise in chronic disease, improved collaboration among physicians, raising patient satisfaction.
Store-and-Forward Transmission Mode
Images/videos saved and sent later; asynchronous communication.
Real-Time Transmission Mode
A specialist views video images transmitted from a remote site and discusses the case with another physician.
Remote Monitoring
Monitor patients at home or in nursing homes; usually part of disease management.
Goal of Teleconsultations
Improving access to services in rural/underserved areas.
Teleradiology
Radiologists can be home at night, read an image, dictate a report via voice recognition and host it all in the cloud for others to view.
Teleneurology
Remote neurologist can read the CAT scan of the brain and see the neurological exam being conducted on the patient.
Telemental Health/Telepsychiatry
Remote/virtual sessions with therapists/psychiatrists.
Teledermatology
Practical as images of skin conditions are diagnostic.
Teleophthalmology
Practical as retinal images can now be obtained without pupil dilation.
Barriers to Telemedicine
Limited reimbursement, limited research showing reasonable benefit, high initial cost, limited availability of high speed telecommunications, bandwidth issues, need for high resolution images, licensure laws, lack of standards, fear of malpractice, ethical and legal challenges.
Telemedicine & COVID-19
CMS allowed telemedicine for all Medicare visits, rapid update/increase of patients, improved communications with some patients.
Three Pillars of Data Security
Confidentiality, Availability, Integrity.
Administrative Safeguards of HIPAA
Security management processes, security personnel, information access management, workforce training, background checks, evaluation of security policies.
Physical Safeguards of HIPAA
Limit physical access to facilities, workstation and device security policies.
Technical Safeguards of HIPAA
Access control, audit controls, integrity controls, transmission security, unique usernames and passwords.
Consumer Rights under HIPAA
Ask to see and get a copy of their health records
Organizations That Do Not Need to follow HIPAA Privacy Rule
Life insurers
Threat Actors
Insiders, Hackivists, Organized Crime, Nation States
Social Engineering
Phishing: attackers deceive people into revealing sensitive information or installing malware (via email or text messaging)
Denial of Service (DOS)
Website is flooded with traffic, shutting it down
Brute Force
Random credentials are rapidly thrown at website hoping to gain access
Doxing
Gathers info about a victim and publishes that to harass or embarrass the individual
Clinical Research Informatics (CRI)
Application of informatics principles and techniques to support the spectrum of activities and business processes that instantiate clinical research
Challenges in Clinical Research Informatics
Patient Matching & Recruitment
US Common Rules
Guide the protection of research subject
Bioinformatics
Computational biology or the field of science in which biology, computer science, and information technology merge to form a single discipline
Transformational Bioinformatics
Specialization of bioinformatics for human health
Genomics
Field that analyzes genetic material from a species
Proteomics
Study at the level of proteins (through gene expression)
Pharmacogenomics
Study of genetic material in relationship with drug targets
Metabolomics
Study of genes, proteins, or metabolites
Metagenomics
Analysis of genetic material derived from complete microbial communities harvested from natural environments
Phenotype
Observable characteristic, structure, function, behavior of living organism
Genotype
Based on the genetic information associated with a phenotype or regulation of biological function
Genome
Total of genotypic traits
Challenges of Translational Informatics
Consent; Specimen/Protocol Tracking; Standards/Interoperability; Data Provenance; Optimal EHR Use; Precision Medicine Knowledge Capture & Application; Patient/Consumer Engagement
Precision Medicine
Diagnosis & treatment targeted to individual patients on basis of genetic/biomarker/phenotypic/psychosocial characteristics that distinguish them from other patients with similar clinical presentations.
Goals of Precision Medicine
Diagnosing hereditary diseases
Clinical Care Provided by Nurses
Monitoring; Maintenance; Prevention; Comfort; Instruction in ADLs; Patient Education & Self-management; Family Care; Delivery of Medical Plan; Case Management & Care Coordination
Indirect Care Provided by Nurses
Teaching students; Attending staff/committee meetings; Continuing education; Informatics/Quality/Safety
Nursing Workflow Includes
Patient care responsibilities; Planning; Supervision; Patient scheduling; Medications & treatment; Teaching; Admission, transfer, & discharge
Nursing workflows task relevance
Most time devoted to nursing practice, with three areas most promising for improving efficiency: Documentation (35.3%), Care coordination (20.6%), Medication administration (17.2%)
Consumer Health Informatics
The field devoted to informatics from a consumer view, often with a focus on mobile health
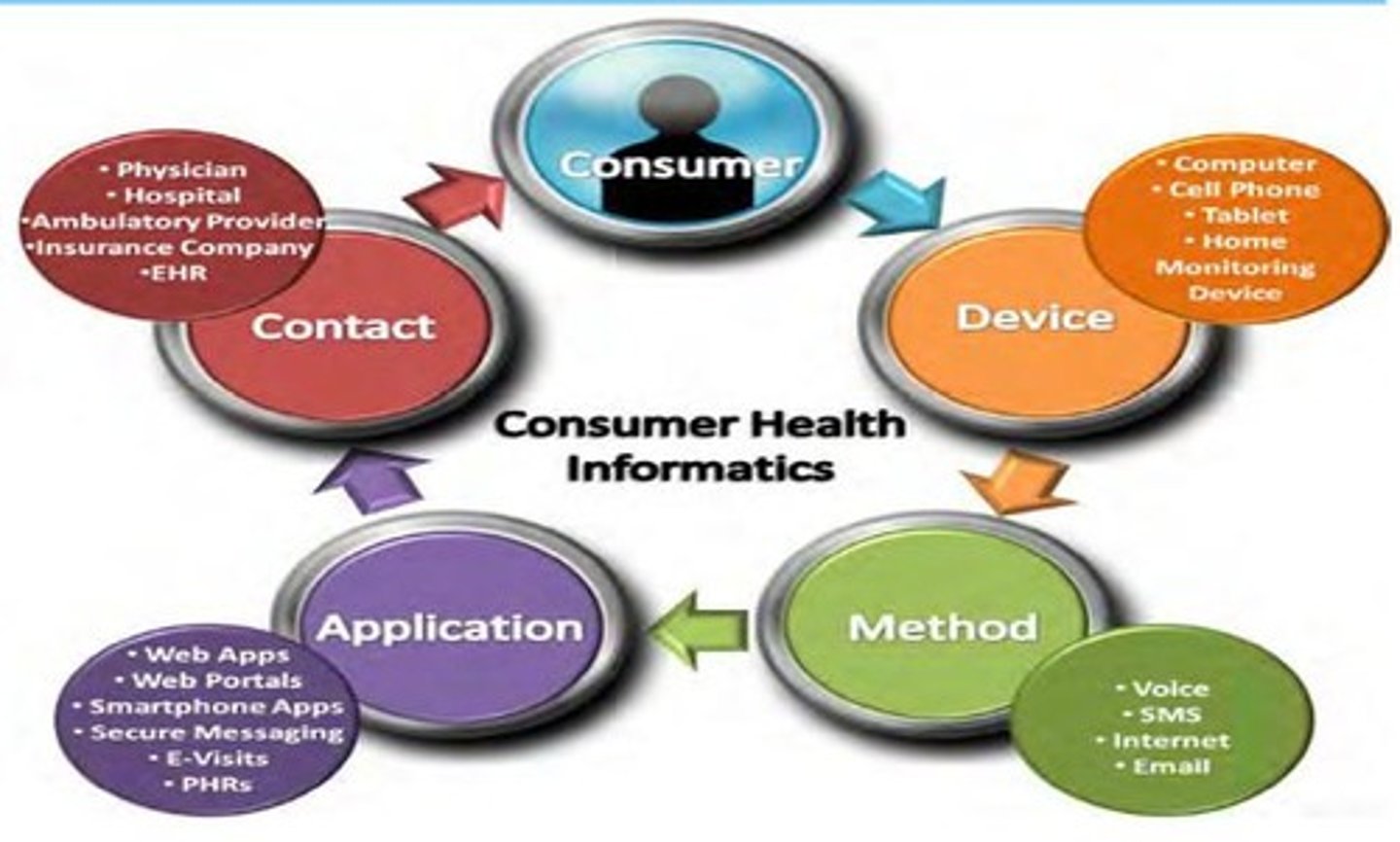
Mobile Health (mHealth)
Digital practice of medicine and public health supported by the use of smartphones and other mobile devices
Digital Health
Digital aspects of health & healthcare; technologies that empower consumers to make better-informed decisions about their health and provide new options for prevention/treatment/management of diseases
Participatory Medicine
A movement in which patients & health professionals actively collaborate and encourage one another as full partners in healthcare
Clinician Electronic Communication Challenges
Patient unwillingness to receive email notifications of test results
Patient Portals
Personal health records (PHRs) tethered to institutional EHRs, often providing additional functionality for engagement.
Additional functionality of Patient Portals
Securely message physician and others
Consumer Health Bill of Rights
Look at your health information and/or get a paper or electronic copy of it
Guidelines for Patient-Clinician Email
Establish turnaround time
Public Health
Science of protecting and improving the health of people and their communities.
Public Health Core Functions
Assessment, Policy Development, Assurance.
Assessment
Public health agencies investigate potential threats to the public's health.
Policy Development
Public health agencies create policies and regulations to protect health.
Assurance
Public health agencies ensure compliance with health laws and regulations.
Public Health Achievements in the 20th Century
Vaccination, motor-vehicle safety, safer workplaces, control of infectious diseases.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
System of hardware, software, and data used for mapping and analysis of geographical data.
Evidence-Based Medicine
Approach to medicine where decisions are based on well-conducted research.
PICO(T) Method
Framework for formulating clinical questions: Patient, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome, Type of Study.
Internal Validity
Believability of a study.
External Validity
Generalizability of study results to the population of interest.
Randomized Controlled Trials (RCT)
Subjects are randomly assigned to treatment or control groups.
Double-Blind
Both investigators and subjects do not know who received active medication or placebo.
Number Needed to Treat (NNT)
How many people must be treated for one individual to benefit.
Clinical Practice Guidelines
Systematically developed statements to assist decisions about health care.
Medical Imaging Informatics
Study and application of information technology for medical image data.
Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS)
Medical imaging technology for storage and access to images from multiple modalities.
Digital Imaging
Transitioned to PACS starting in the 1970s, with the first filmless hospital in 1999.
PACS Advantages
Allows remote viewing, expedites incorporation into electronic health records.
Nuremberg Code
Established voluntary consent and right to withdraw from experiments.
World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki
Added right to privacy and confidentiality for research subjects.
Pertinent Ethical Principles
Right to privacy, security of data, informed consent, sharing data appropriately.
Electronic Communications with Patients
Guidelines for communicating with patients via email.
Experimental Event Rate (EER)
Risk for people in the experimental group.
Control Event Risk
Risk for people in the control group.
Relative Risk (RR)
Rate of risk relative to the control: EER/CER.
Relative Risk Reduction (RRR)
Indicates how much the risk is reduced in the treatment group compared to control.
Absolute Risk Reduction (ARR)
Calculated as EER-CER.
Clinical Practice Guidelines Steps
Involves expert panel evaluation, evidence review, and local applicability assessment.
Zoom-in Feature in PACS
Allows close-up detail viewing of medical images.
Mark-up Tool in PACS
Adds text, measures size, angles, and areas on images.