Biology - DNA, Genes, Punnet square, Meiosis and Mutations
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Genome
All the DNA found within an organism
What is DNA made up of
DNA makes up genes and many genes make up a chromosome
What are chromosomes
Chromosomes are long, thin strings of genetic material made of DNA. They are located in the nucleus with 46 inside one human cell. They also come in pairs called Homologous pairs which means there is 23 homologous pairs in a human cell.
What is DNA and what are its functions
DNA is the molecule that carries genetic information for the development and functioning of an organism. Its 2 functions involve carrying genetic info from one gen to the next and containing the genetic info that codes for a protein.
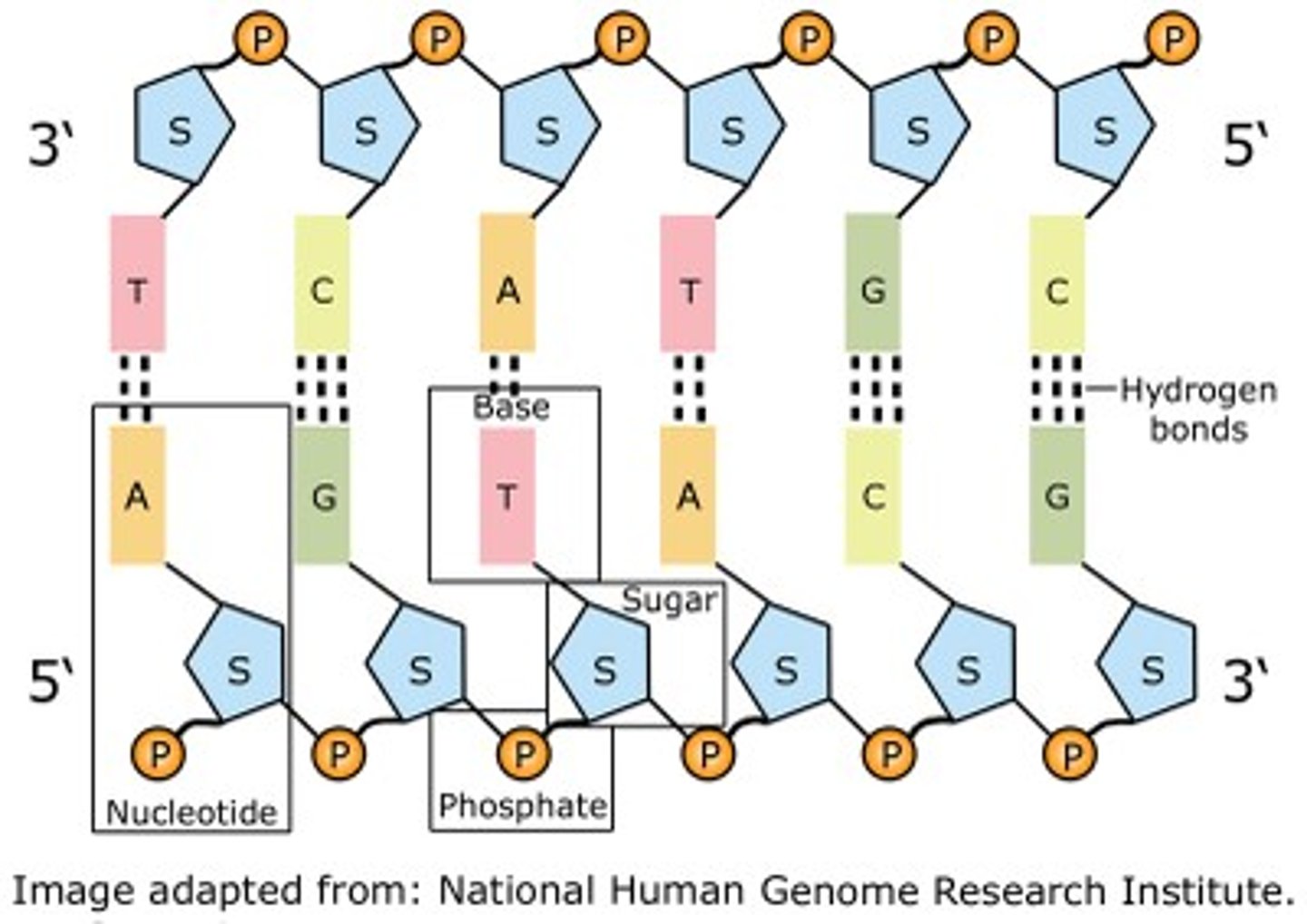
What is DNA made of
DNA is made up of a repeating unit called a nucleotide. These consist of
1. Sugar
2. Phosphate
3. And a Base which can either be A , C , T , G
What is complementary base pairing?
When base A always pairs up with base T, and base C always pairs up with base G.
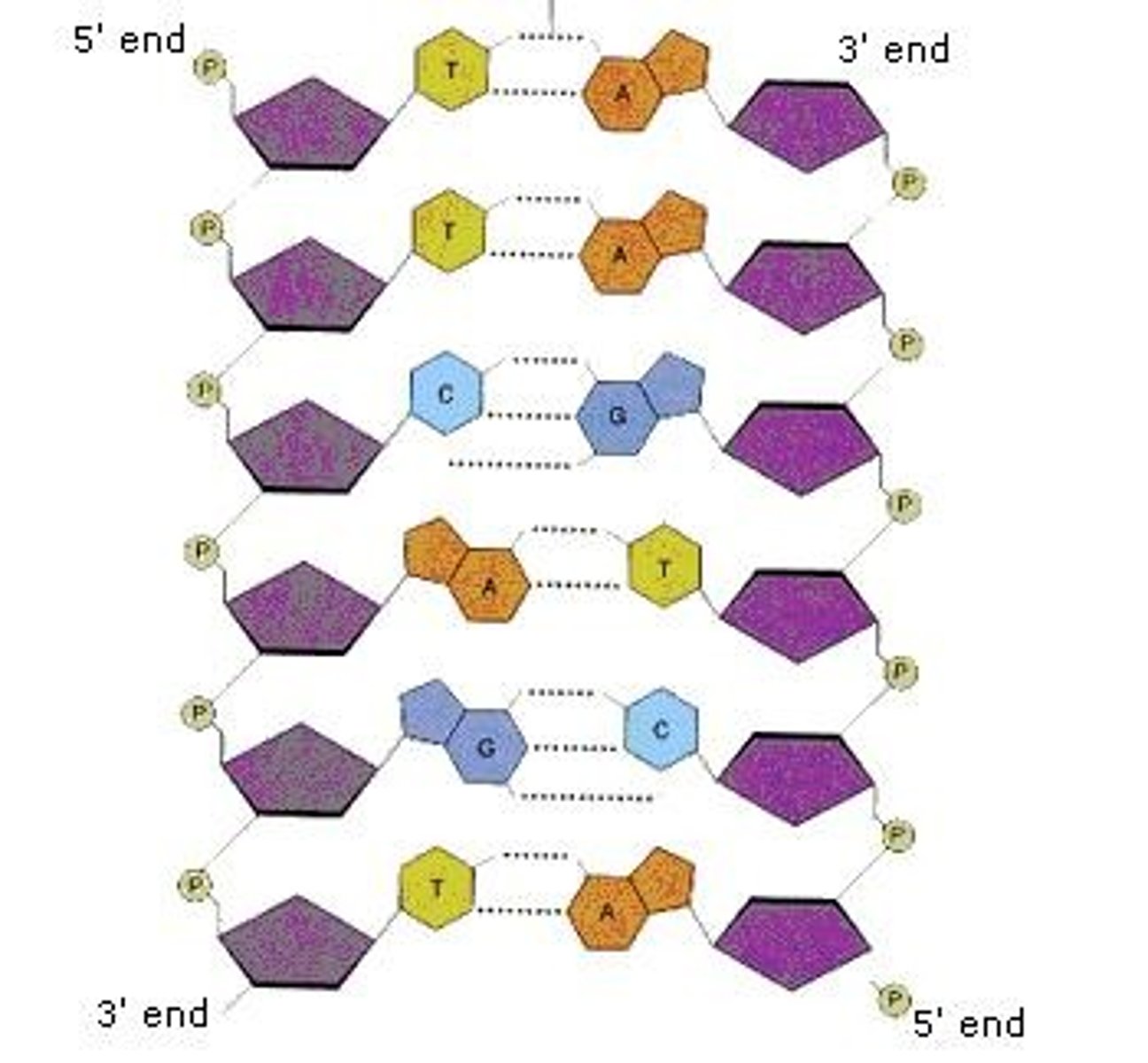
What shape is a DNA
DNA is double stranded molecule that twists to form a double helix
What are genes and what do they do?
Genes are sections of DNA that code for specific protein.
What are alleles
Alleles are different forms of a gene can take. In humans, for each gene there is 2 alleles, one from the mother and the other from the father. For example you can have a gene for hair color and alleles for brown and blond hair
How are proteins implemented in DNA
An allele is a specific version of a gene, made up of a unique sequence of DNA bases. This sequence determines the order of amino acids in a protein, which gives the protein its specific structure and function.
Genotype
The actual alleles an organism has (H,h) (H,H) (h,h)
Phenotype
physical expression of a gene
Homozygous
Pair of alleles for a gene that are the same (H,H) (h,h), also known as purebred
Heterozygous
Pair of alleles for a gene that are the different (H,h)
Dominant
An allele that is always expressed when present
Recessive
An allele that will only be expressed when a dominant allele is absent
How does an offspring inherits features from parents?
Offspring inherit features from their parents through genes, which are sections of DNA on chromosomes. Each parent gives one allele for every gene, and the combination of alleles determines how traits are expressed. Dominant alleles show even if only one is present, while recessive alleles only show if both are recessive. This is why children often resemble their parents but can also have unique traits.
What are gametes
sex cells (sperm and egg)
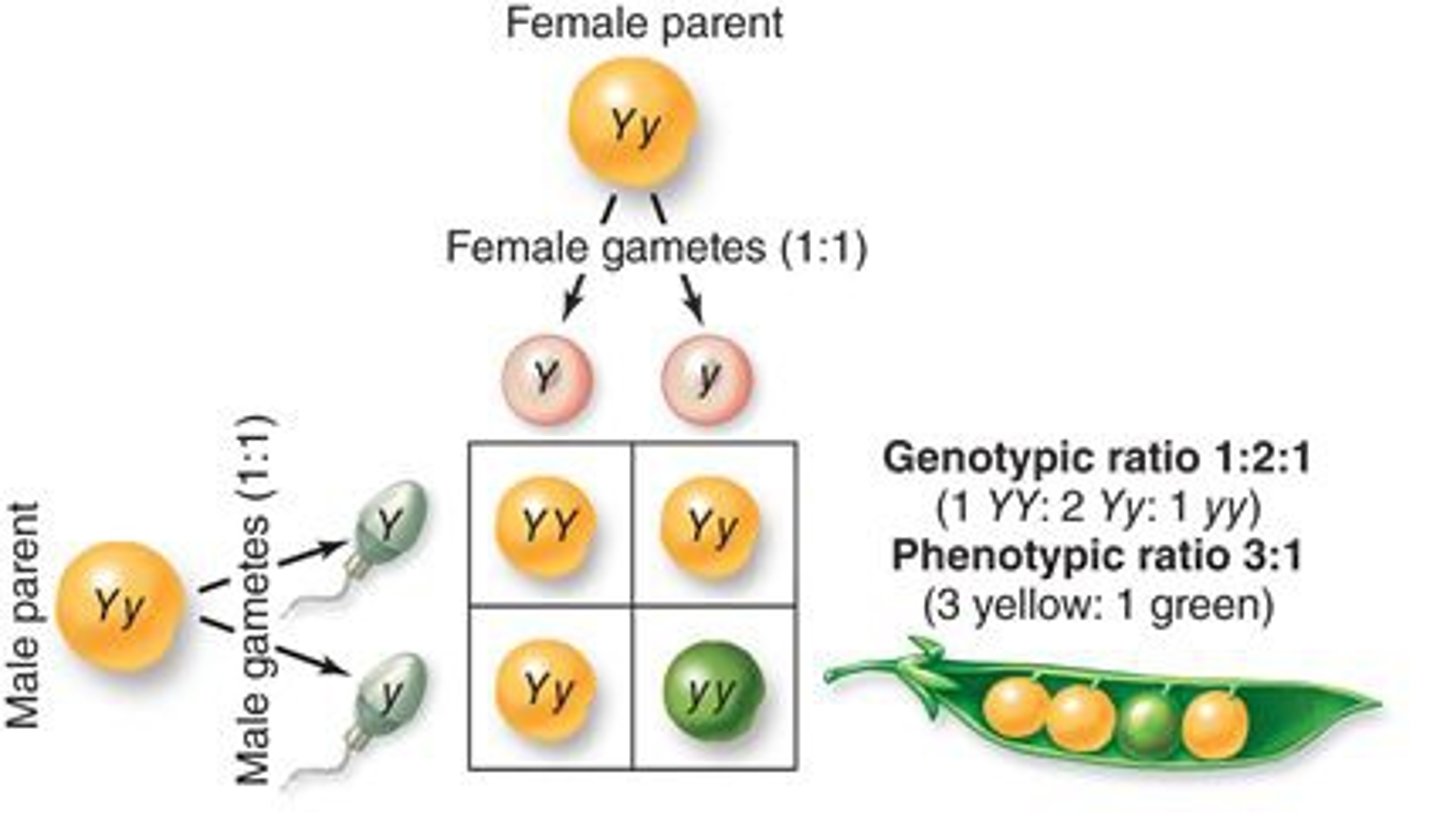
What are Punnett Squares and what do they do
Punnett squares are charts that are used to show the possible gene combinations in a cross between 2 organisms. They are only a prediction of the likely genotypes and phenotype of offspring because fertilisation is a random event.
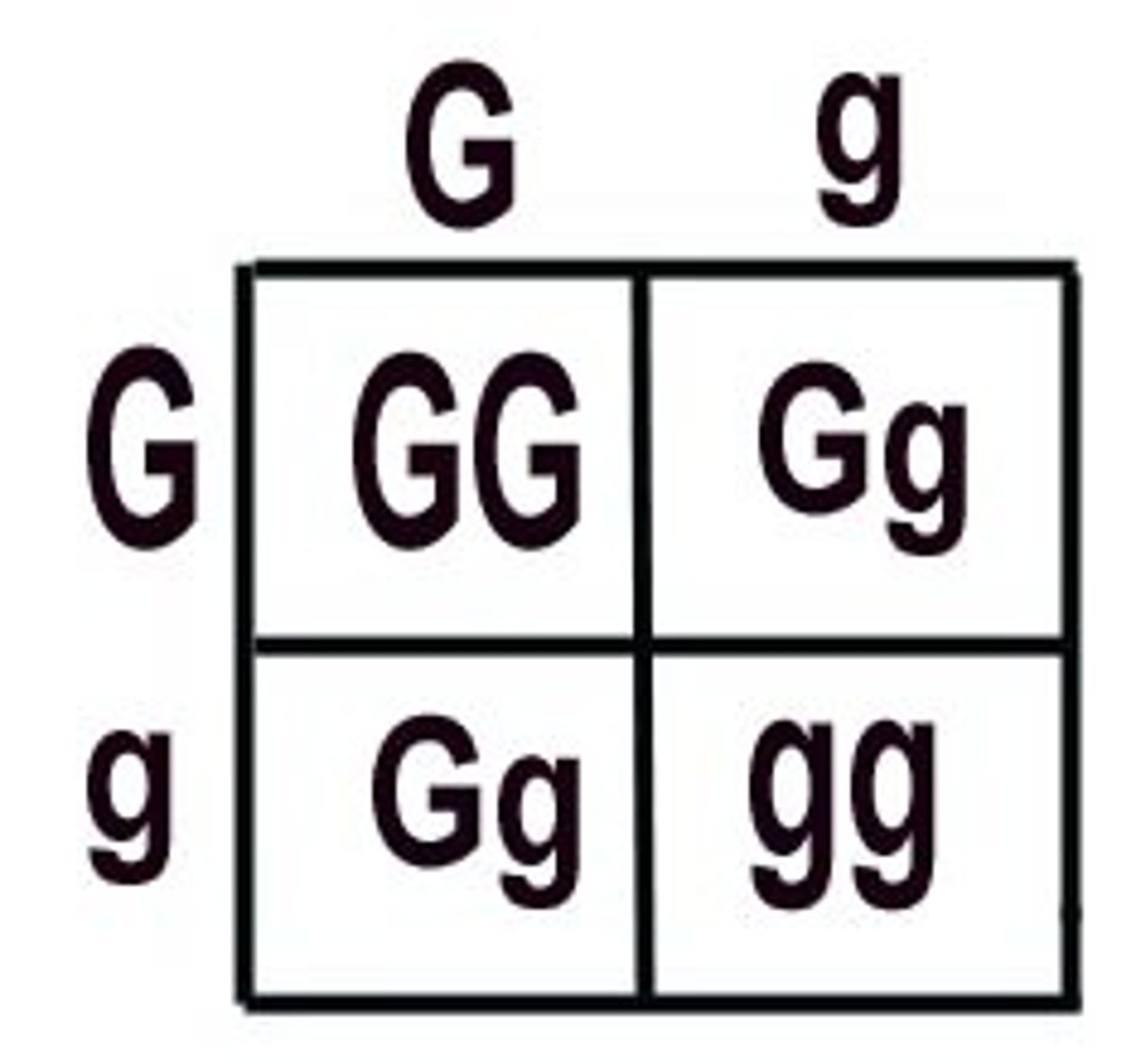
How do we get closer to the expected ratio in Punnett squares
Have more offspring which gives a larger sample
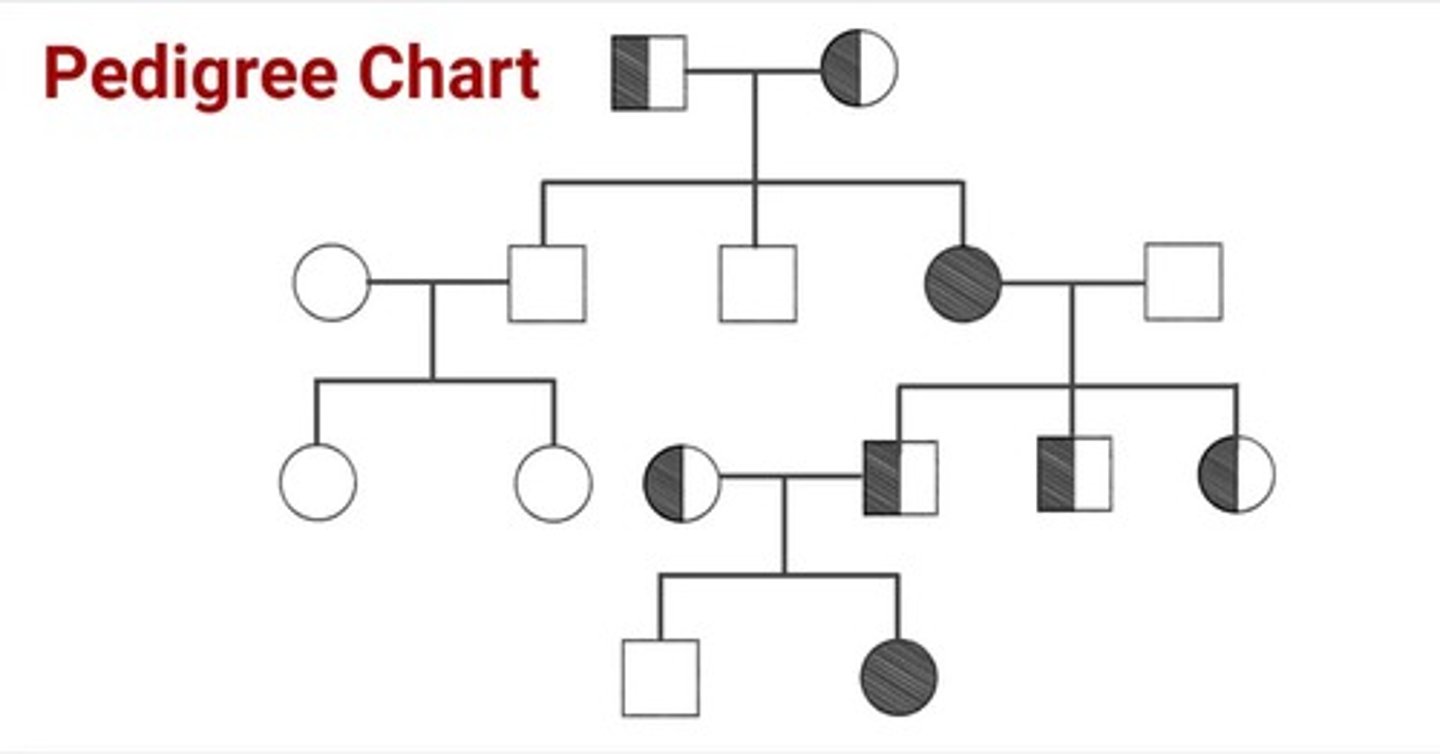
What are pedigree diagrams
used to trace the pattern of inheritance of a specific characteristic through generations of a family
Key tips
*When doing a Punnett square or Pedigree diagram, justify why they have that certain genotype and allele
*When stating the phenotype make sure to add percentage or fraction to show which phenotype
Sexual Reproduction
A reproductive process that involves two parents that combine their genetic material to produce a new organism, with a combination of traits from both parents
What is Meiosis
a type of cell division that produces gametes with half the normal amount of chromosomes
What are the benefits of meiosis
It shuffles the alleles to create new genetic combination in the offspring resulting in a diverse pool of traits. Overtime this diversity can increase the likelihood that some individuals will posses beneficial genes or alleles that improves their chances of survival in changing enviornments
What important qualities do the gametes receive through meiosis
shuffles alleles from your parents to make each gamete (egg or sperm) unique
Fertilisation
Fusing of a male sex cell with a female sex cell to create a zygote (fertilized egg). It is random which sperm and egg fuse which creates a huge amount of genetic variation in the offspring
Variation
when there is a range of different phenotypes possible for a specific characteristic
What is the importance of genetic variation
Very important to the survival of species because when environmental conditions change or new diseases occur hopefully at least some individuals will survive due to the species having genetic variation (some individuals having alleles that allow them to survive environmental change) This will allow the species to continue into the future.
What factors create genetic variation?
-Environment-(non-inheritable): This can influence how certain characteristics of an organism develop. eg. a person inherits an allele to grow tall but it fed very poorly for the years they are growing, they may grow to be short. This is not inherited by offspring
-Mutations-(inheritable): a permanent change in the DNA. It can only be passed down if it occurs in a gamete not in your own body. Mutation result in the formation of new alleles
-Meiosis-(inheritable): the process shuffles and creates new combination of alleles that were not present in the parents. Overtime this diversity can increase the likelihood that some individuals will posses beneficial genes or alleles that improves their chances of survival in changing enviornments
-Random fusion of gametes-(inheritable): It is random which sperm and egg fuse together and as each gamete is genetically unique this can create a endless variations in the offspring
What 3 factors alter allele frequency in populations
Mutations
Natural Selection
Bottleneck effect