Cholesterol Metabolism
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
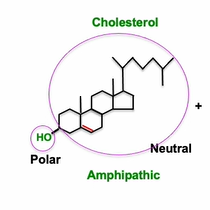
Structure of cholesterol
3 fursed hex rings and 1 pent ring
sterol → OH on thrid carbon of A ring
FA is added to chol in ER → less polor and more hydrophobic - better for travel
Overveiw of cholesterols function
regulates membrane fluidity as cell membrane component
precursor of hormones (test and est), bile acid, and vitamin D
be used for bile synthesis
main source of cholesterol is through synthesis, not diet
all nucleated cells can synthesize cholesterol from acetyl CoA through the Mevalonate pathway
however, main synthesis organs are the liver, intestine, adrenal cortex, ovaries, testes, and placenta
First stage of cholesterol synthesis
occurs in cytosol
3 acetyl CoAs are condensed to geterate 1 HMG-CoA
HMG-CoA can be converted into mevalonate acid
irreversible and rate limiting step
Cholesterol converted to hormones
occurs in mitochondira
makes aldosterone, cortisol, testosterone, and estradiol
Cholesterol → bile acid synthesis
Bile/bile salts released from liver
go into gut/intestine and converted into bile acid
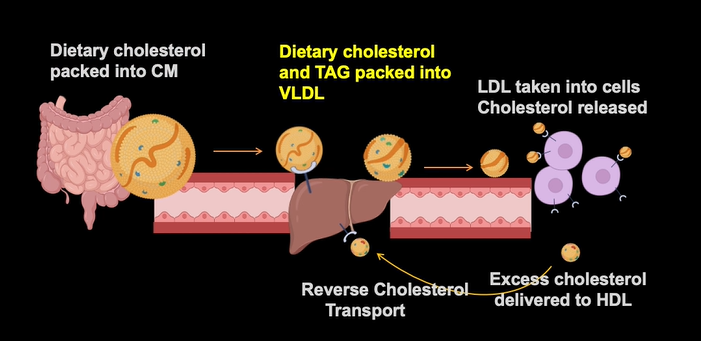
Cholesterol transport pathway
dietary cholesterol packed into CM (released from intestine)
Dietary cholesterol and TAG packed into VLDL and released from liver
LDL is taken into cells through endocytosis and cholesterol is released
excess cholesterol delivered to HDL
reverse cholesterol transport back to liver
liver will bake bile or new VLDLs
Regulation of cholesterol in first pathway
negative feedback control by HMG-CoA reductase in Mevalonate synthesis
inhibited by high levels of cholesterol (rate limited step)
Control biosynthesis of cholesterol by SREBP
high levels of cholesterol → blocks SREBP from translocating from ER to Golgi → cholesterol synthesis is inhibited
Low levels of cholesterol → SREBP is located at the ER by SCAP. SCAP holds SREBP into ER
SCAP then releases SREBP, SREBP is transported to golgi via COPII transport system
in golgi, 2 proteases cleave SREBP resulting in release of SREBP (active transcription factor)
SREBP moves to nucleus and initates transcription of target genes like HMG-CoaAR
Regulation: protosomal degradation of HMG-CoA reductase
high level of cholesterol
binding/inhibition of HMG CoA accelerates
degradation of HMG CoA reductase through proteasome degradation pathway
inhibits cholesterol synthesis
Lower cholesterol level through drugs (3)
inhibition of cholesterol synthesis statin
competatively inhibits HMG-CoA reductase
inhibition of cholesterol absorption
Ezetimbe- inhibitor of NPC1, major regulator of cholesterol absorption → lowering plasma cholesterol level
often used with statin together
increase LDL clearance - best
PSCK9 secreted from the kidneys, livier, and intestine
binds to LDLR, results in degradation of LDLR receptor
PCSK-9 inhibitor decreased LDLR degradation results in increased LDLR receptor level, therefore more LDLR bound LDLs are endocytosed by liver cells which reduces plasma level of LDL