Training Principles in Sports: Specificity, Overload, Recovery & Periodization
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
What are training principles?
Fundamental rules that guide the design and execution of exercise programs.
Why are training principles important?
They ensure that the program is efficient, safe, and tailored to the athlete's goals.
What does specificity in training refer to?
Training must be directly aligned with the specific sport or fitness goals of an individual.
How does specificity affect exercise adaptations?
Exercise adaptations are specific to the type of activity being performed.
Give an example of specificity in training.
A sprinter focuses on explosive power, while a marathon runner emphasizes aerobic endurance.
What is progressive overload?
The gradual increase in training intensity or volume to avoid plateaus and ensure continuous improvement.
What are the elements of progressive overload?
Frequency, intensity, and duration of training.
Why is recovery important in training?
It allows the body to repair and adapt after training, preventing overtraining.
What are the two types of recovery?
Rest and active recovery.
What is the principle of variety in training?
Incorporating different exercises and methods to prevent adaptation and boredom.
What does reversibility mean in the context of training?
Fitness gains are lost when training is reduced or stopped.
What is periodization?
The systematic organization of training into phases to optimize performance and allow for recovery.
What are the phases of periodization?
Macrocycle, mesocycle, and microcycle.
What is the macrocycle in periodization?
The longest training period, typically lasting a year or more.
What is the mesocycle in periodization?
A smaller training cycle within the macrocycle, usually lasting 3-4 months.
What is the microcycle in periodization?
The smallest training cycle, lasting a week, involving detailed adjustments.
What distinguishes anaerobic training from aerobic training?
Anaerobic training involves short, high-intensity exercises, while aerobic training involves longer-duration, moderate-intensity exercises.
Give an example of anaerobic training.
Sprinting or high-intensity interval training (HIIT).
Give an example of aerobic training.
Long-distance running or cycling.
How should training programs be tailored?
They should be customized to the individual's current fitness level.
What should beginner athletes focus on in their training?
Aerobic fitness, flexibility, and basic strength with low to moderate intensity.
What should intermediate athletes incorporate into their training?
More specialized training such as speed, strength, or endurance development.
What is the focus for advanced athletes in their training?
Highly specialized programs targeting specific performance goals.
Why is it important for advanced athletes to follow a periodized program?
To ensure regular reassessment and progression.
What is the risk of not allowing proper recovery?
Athletes risk injury and burnout.
What role does sleep play in recovery?
It is essential for tissue repair and growth, crucial for recovery and adaptation.
Why must training programs for youth athletes be designed with caution?
Growing bodies require careful consideration to develop general physical literacy and safe exercise techniques.
What is recommended for adolescent athletes instead of intense weightlifting?
A focus on aerobic fitness and general strength.
What changes occur in older athletes that affect training?
Decreased muscle mass, lower bone density, and reduced cardiovascular capacity.
What should training programs for older athletes prioritize?
Strength training for bone health, balance exercises, and low-impact aerobic activities.
What hormonal factors influence training in men?
Men typically have higher levels of muscle mass, testosterone, and endurance capacity.
How does testosterone affect men's strength training progress?
Higher natural levels of testosterone enhance muscle hypertrophy, allowing quicker progress.
What are some characteristics of women's training compared to men's?
Women tend to have greater fat mass and lower muscle mass, and experience hormonal fluctuations affecting strength and recovery.
What is the menstrual cycle?
A recurring series of hormonal changes that prepares the body for potential pregnancy, consisting of four phases.
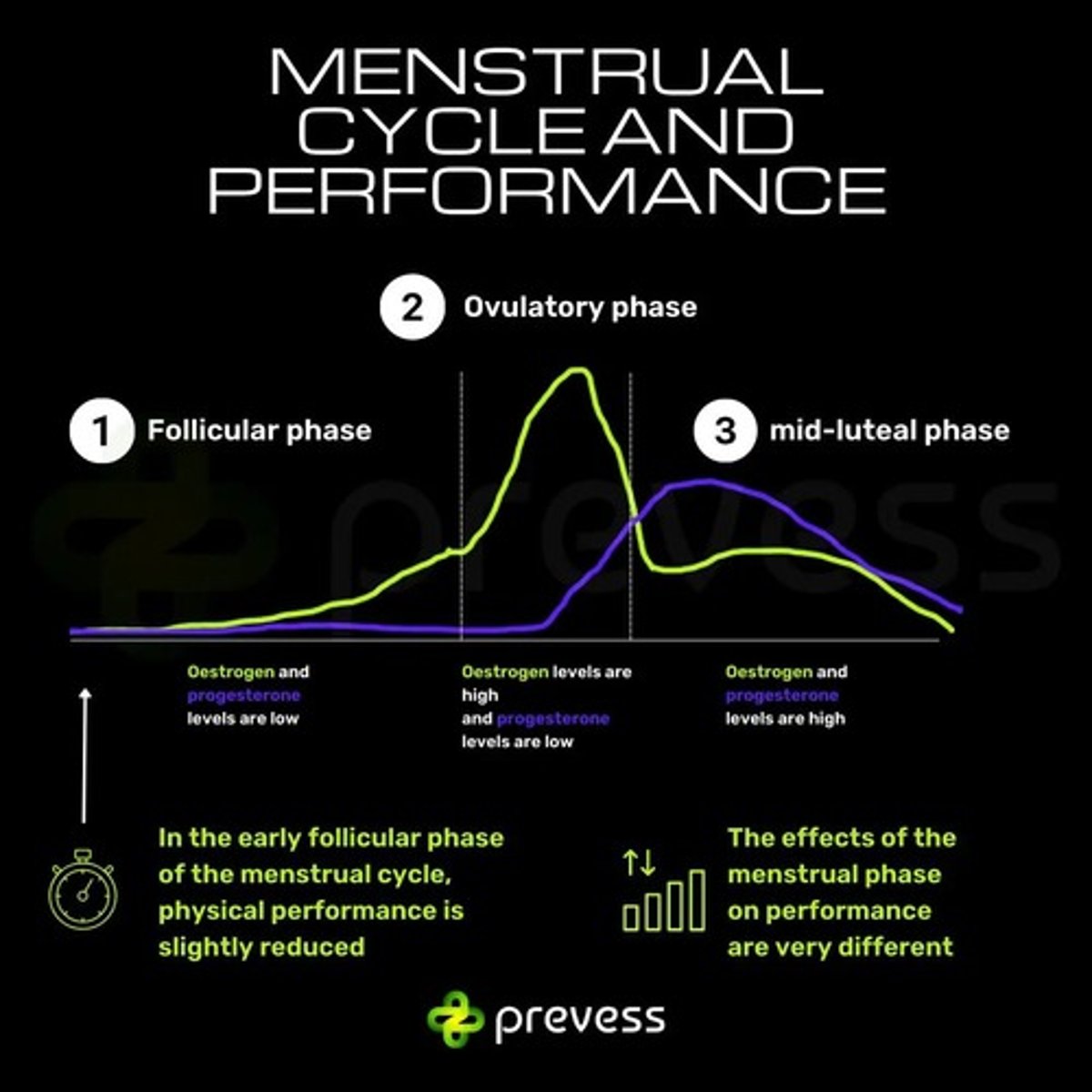
What occurs during the menstrual phase of the cycle?
Low estrogen and progesterone levels lead to fatigue, cramping, and decreased performance capacity.
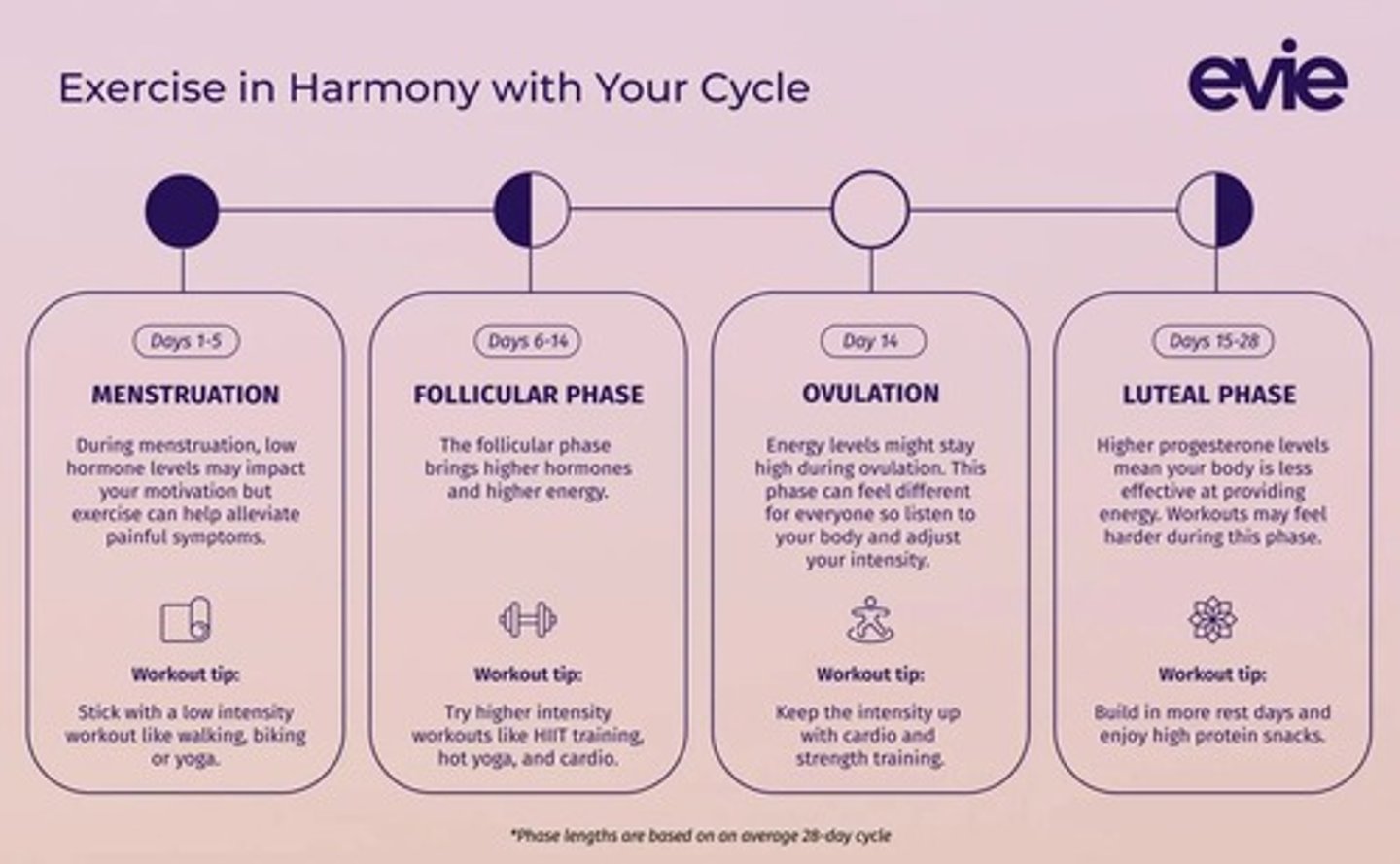
What type of training is recommended during the menstrual phase?
Light aerobic exercises and low-intensity activities.
What happens during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle?
Estrogen levels rise, increasing energy, muscle strength, and endurance capacity, making it optimal for intense training.
What is the optimal training focus during the ovulatory phase?
Maximal strength lifts, sprinting, and competitive efforts due to peak estrogen levels.
What changes occur during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle?
Progesterone rises, estrogen drops, leading to decreased performance, fatigue, and discomfort.
What type of exercises are beneficial during the luteal phase?
Low-to-moderate intensity exercises such as yoga, swimming, or low-intensity cycling.
How does the menstrual cycle affect glycogen utilization during exercise?
In the follicular phase, women rely more on fat as fuel, while in the luteal phase, reliance on carbohydrates increases.
What is thermoregulation?
The body's ability to maintain an optimal internal temperature during exercise.
How does the menstrual cycle influence thermoregulation?
During the luteal phase, elevated progesterone can increase body temperature, reducing thermoregulatory efficiency.
What is the optimal performance window in the menstrual cycle?
The follicular and ovulatory phases are when women generally experience the best performance due to higher estrogen levels.
What should athletes consider when planning workouts around their menstrual cycle?
Schedule harder workouts during the follicular and ovulatory phases, and focus on recovery during the luteal phase.
What is the significance of menstrual cycle tracking for athletes?
It helps identify patterns in energy levels, mood, and performance, allowing for better training planning.
What type of training is recommended for a 60-year-old marathon runner?
Strength training to maintain muscle mass and prevent injuries.
What is a potential benefit of periodized strength training for female athletes?
Adjusting intensity based on the menstrual cycle can optimize performance and recovery.
What is a common recommendation for training during the menstrual phase?
Engage in low-impact activities to maintain fitness without straining the body.
What is the impact of estrogen on fat oxidation during the follicular phase?
Estrogen enhances fat oxidation while sparing glycogen stores.
How should female athletes adjust carbohydrate intake during the luteal phase?
They should consider replenishing glycogen stores more quickly due to increased reliance on carbohydrates.
What type of training is optimal during the follicular phase?
Intense resistance training and cardiovascular conditioning.
What is the effect of progesterone on performance during the luteal phase?
It can increase fatigue and reduce overall energy levels, making high-intensity exercise more challenging.
What activities are suggested for maintaining fitness during the luteal phase?
Focus on aerobic training, flexibility, and recovery activities.
Why is understanding the menstrual cycle important for female athletes?
It helps design training programs that account for hormonal fluctuations affecting performance.
What can female athletes use to track their menstrual phases?
Apps or calendars.
During which phase of the menstrual cycle might a female athlete's performance peak?
The first half of the cycle.
What individual differences can affect female athletes' responses to their menstrual cycles?
Menstrual irregularities, PCOS, or endometriosis.
What is a potential consequence for athletes with irregular menstrual cycles?
They may need to monitor training loads and adjust intensity to prevent overtraining.
What did Chelsea F.C. Women implement in 2020 to optimize performance?
A specialist app to tailor training around players' menstrual cycles.
What is overreaching in the context of training?
Short-term overloading that exceeds the body's current capacity for recovery without causing long-term harm.
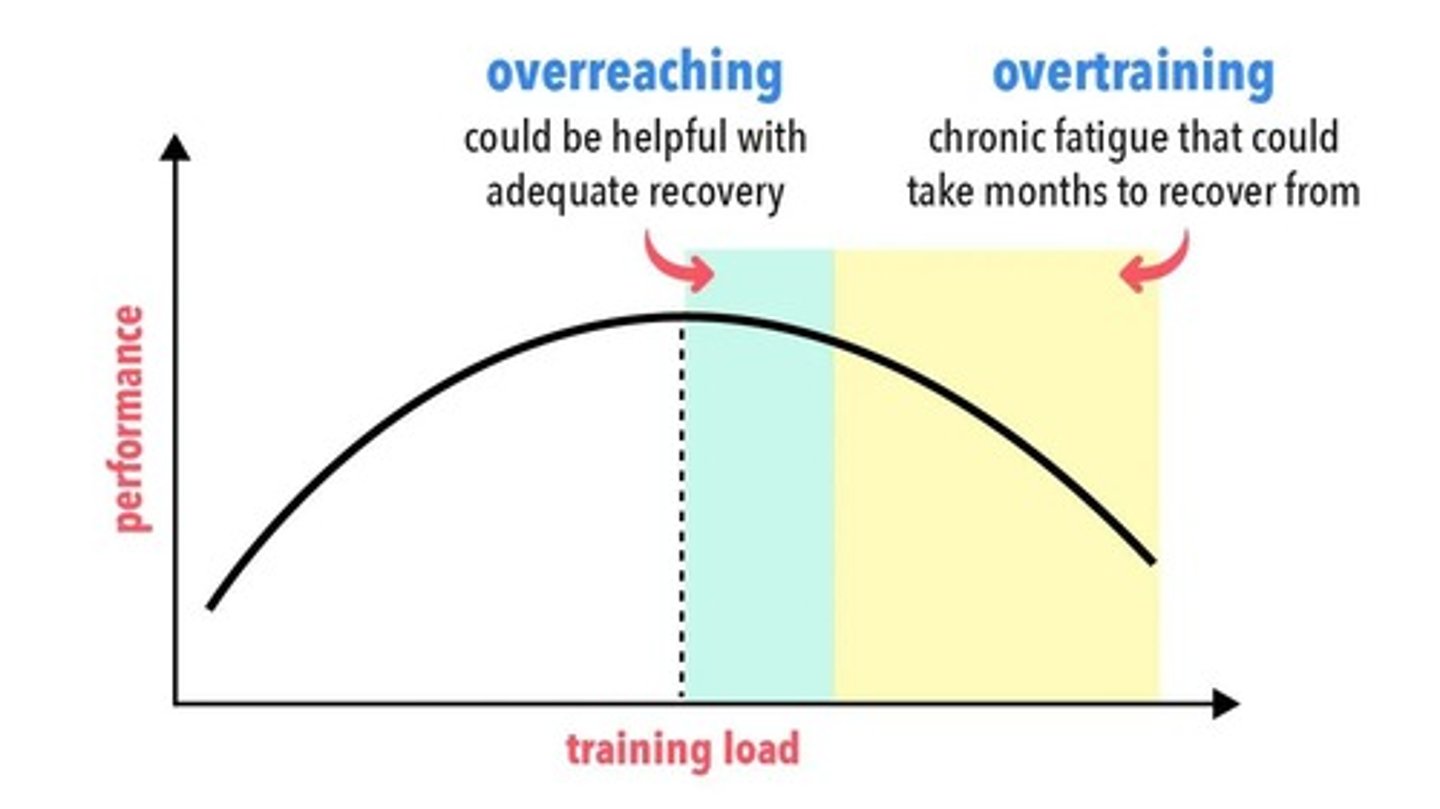
What can lead to overreaching?
Increased training intensity, lack of recovery, and inadequate nutrition.
What is the definition of overtraining?
A severe form of training stress resulting in chronic fatigue and decreased performance.
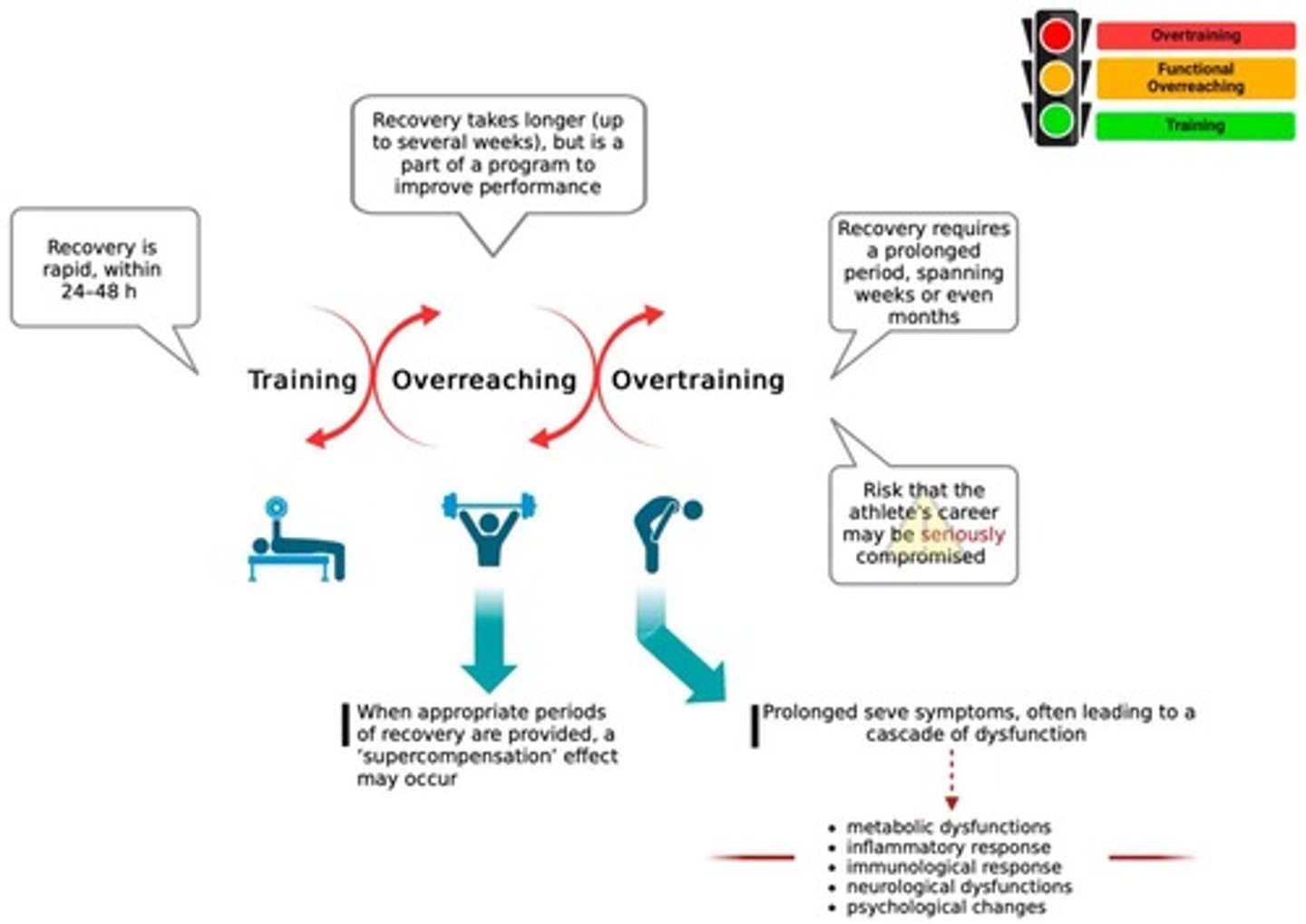
What are some causes of overtraining?
Excessive training volume, inadequate recovery, psychological stress, and nutritional deficiencies.
What physiological effect does overtraining have on strength and endurance?
It decreases muscle strength, endurance, and overall performance.
How does overtraining affect hormonal balance?
It can disrupt key hormones, leading to elevated cortisol levels and muscle breakdown.
What is DOMS?
Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness, muscle pain occurring after intense exercise due to microscopic muscle tears.
What psychological effects can arise from overtraining?
Mood disturbances, burnout, and increased perceived effort during exercise.
What is the importance of maintaining an appropriate training load?
It ensures athletes can adapt without crossing into overreaching or overtraining.
What is active recovery?
Low-intensity activities that promote blood circulation and muscle repair.
What is passive recovery?
Complete rest, including sleep, essential for muscle repair and energy replenishment.
Why is sleep critical for recovery?
Growth hormone is released during sleep, aiding muscle repair and improving immune function.
What hormone is released during sleep that aids in muscle repair?
Growth hormone
What can happen to an athlete who consistently gets less than 6 hours of sleep?
They may experience difficulty recovering from training, leading to fatigue and poor performance.
What is prehabilitation?
A proactive approach to injury prevention that prepares the body for the demands of training and competition.
What are the goals of prehabilitation?
To improve strength, flexibility, and mobility while reducing the risk of injuries.
How does prehabilitation help prevent injuries?
By addressing imbalances, weaknesses, or lack of flexibility in key muscle groups.
Give an example of a prehabilitation exercise for runners.
Hip flexor exercises to reduce the risk of muscle strains.
What are the benefits of prehabilitation?
Injury prevention, enhanced recovery, and optimized performance.
What is the purpose of a warm-up protocol?
To prepare the body for physical activity, reduce injury risk, and improve performance.
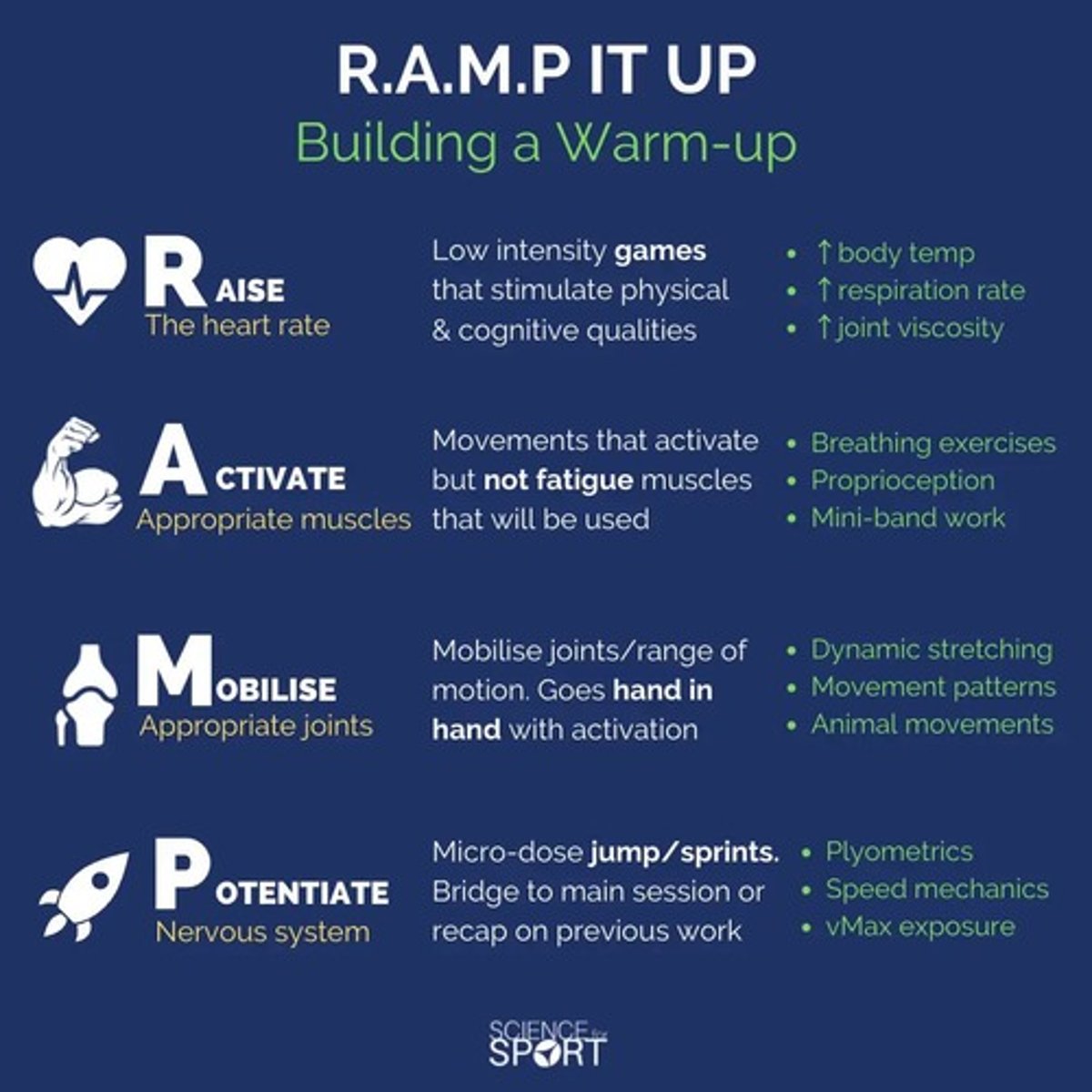
What does a general warm-up involve?
Low-intensity aerobic exercise aimed at gradually increasing heart rate and muscle temperature.
What is dynamic stretching?
Controlled, active movements that take joints and muscles through their full range of motion.
Why is dynamic stretching preferred over static stretching before exercise?
It is more effective for preparing the body for exercise and reducing injury risk.
What is a sport-specific warm-up?
Movements that mimic the actions of the actual activity or sport to prime the body.
What are activation exercises?
Exercises that target specific muscles to engage them before a workout.
How does a proper warm-up reduce injury risk?
By increasing muscle temperature and flexibility, improving joint mobility, and activating the nervous system.
What is the role of mental readiness in injury prevention?
Mental focus and awareness help athletes use proper technique and avoid risky movements.
What is the principle of specificity in training?
The idea that training should be tailored to the specific demands of the sport or activity.
How does progressive overload improve cardiovascular endurance?
By gradually increasing the intensity or volume of training to enhance the body's adaptation.
What happens to performance gains when training is stopped or reduced?
Performance gains may diminish, leading to a decline in fitness levels.
What is periodization in training?
A systematic planning of athletic training to peak at the right time.
What training considerations should be made for women due to hormonal fluctuations?
Adjustments in training intensity and carbohydrate intake during different phases of the menstrual cycle.
Why is the follicular phase considered optimal for strength and endurance training?
Hormonal levels during this phase support increased energy and performance.
Why might female athletes need to adjust carbohydrate intake during the luteal phase?
Due to increased reliance on glycogen and faster depletion of glycogen stores.
What is the impact of incorporating prehabilitation exercises into training?
It reduces the likelihood of developing common injuries.
What is an example of an activation exercise for leg workouts?
Glute bridges or clamshells.
What is the purpose of warm-up exercises?
To prepare the body physically and mentally for the demands of the workout.
What is the significance of neuromuscular activation during warm-up?
It improves coordination and reduces the risk of injuries caused by poor movement patterns.
What should be included in a beginner's training program?
Key components such as strength, flexibility, and endurance training tailored to the individual's needs.