Natural Selection
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Darwin and Wallace
independently came to the conclusion of natural selection
homologous structures
common ancestry; ex - forelimbs in whales, humans, and bats
analogous structures
convergent evolution; ex - flying in butterflies, birds, and flying squirrels
Hardy - Weinberg’s Five Conditions
(1) random mating
(2) large population
(3) no migration
(4) no natural selection
(5) no mutations
alleltic frequence (p is…q is..)
p is dominant, q is recessive
genotypic frequency
AA = p²
Aa = qp or pq
aa = q²
phenotypic frequency (how to see expression of dominant trait)
dominant trait showing is either AA or Aa, but if the recessive traits shows, it is only aa
how to find heterozygous frequency
2pq or 2qp
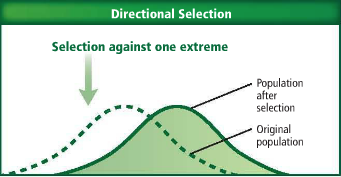
Directional Selection
favors traits that are at one extreme of a range of traits
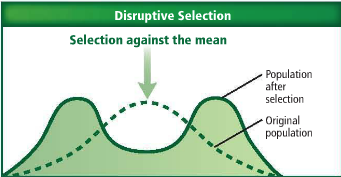
Disruptive Selection
occurs when environmental conditions favor individuals on both extremes
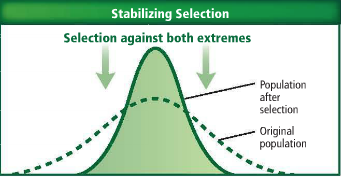
Stabilizing Frequency
eliminates individuals that have extreme or unusual traits
sexual selection
the idea that a certain fitness/characteristic about a mate that makes the candidate more desirable
intrasexual selection
fighting among the same sex for mates (ex: in lion packs, there is only one male with multiple female partners)
intersexual selection
mate choice (ex: birds of paradise female birds choose from the male birds)
sexual dimorphism
males and females have different appearances (ex: male lions have manes and female lions do not; male peacocks are beautiful and colorful while female peacocks are brown)
founder effect
small group of a population leaves original location to establish new, isolated population. leads to reduced genetic diversity and higher frequency rate of rare traits or diseases
bottleneck effect
population size is drastically reduced leading to loss of genetic diversity and increases the risk of inbreeding and expression of recessive traits
prezygotic barriers
(1) Habitat/Geographical Isolation
(2) Mechanical Isolation
(3) Gametic Isolation
(4) Temporal Isolation
(5) Behavorial Isolatiion
Postzygotic Barriers
(1) Reduced Hybrid Viability
(2) Reduced Hybrid Fertility
(3) Hybrid Breakdown
Habitat/Geographical Isolation
species live in different locations
Behavioral Isolation
different mating rituals
Temporal Isolation
different mating seasons; not active at the same time (up at night vs up at day)
Mechanical Isolation
physically cannot reproduce
Gametic Isolation
sperm and egg do not recognize each other as compatbile
reduced hybrid viability
miscarriage; development incomplete
reduced hybrid fertility
offspring is sterile (ex: mule)
hybrid breakdown
offspring have reduced viability or fertility (common in plants) over generations
hybrid zone
region where different species meet and mate
reinforcement
hybrids stop being produced
fusion
separate species fuse into one
stability
hybrids continue to be produced
allopatric speciation
occurs when there is a geographical barrier or habitat isolation that prevents the two species from interacting with one another (barriers)
sympatric speciation
usually due to sexual selection or mate choice. can also occur due to lack of or too much competition of a food source. occurs when there is a new species within the parents population (no barriers)
Miller - Urey Experiment (Abiotic Origin Theory)
began with inorganic substances (specifically ones that were present during the formation of the Earth’s atmosphere) and were able to form organic substances in a closed system
Extra - terrestrial origins
initial life form came to Earth from meteorites and asteroids (space rocks)
RNA World Hypothesis
RNA is the original genetic material and DNA came along later
Endosymbiont Theory
mitochondria and chloroplasts were free-living bacteria engulfed by a eukaryote and formed a symbiotic relationship