Ionic equilibria
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What is a solute?
-the dissolved substance
What are strong electrolytes? Give examples
-Substances which when dissolved in a solvent are completely ionized.
-e.g. NaCl in water
-mineral acids in water e.g. HCl, HNO3, HClO4
What are weak electrolytes? Give an example
-Substances which when dissolved in a solvent are not completely ionized. Thus, the solution contains ions and molecules of the solute.
-Acetic acid in water: H3CCOOH + H2O ⇌ H3CCOO- + H3O+ The solution will contain un-dissociated molecules of the solute (CH3COOH) as well as acetate and hydrogen ions.
-Most organic acids and bases are weak electrolytes. e.g. R-NH2 + H2O ⇌ R-NH3 + + OH-
What are non-electrolytes?
-Substances which when dissolved in a solvent do not ionize. Such solutions do not conduct an electric current and hence contain no ions.
e.g. glucose in water, urea in ethanol
Are ions in solution able to move freely? Why?
no, not completely
-due to electrostatic interactions between charged particles. There will be both:
• Attractive forces between oppositely charged ions
• Repulsive forces between similarly charged ions
-These interactions affect ion mobility and reactivity, making their "effective concentration" different from their actual concentration.
What is another word for ‘effective concentration’? what is effective concentration?
the activity of the ions
how the ion actually behaves in solution rather than its analytical concentration.
Explain ionic atmosphere
-Due to electrostatic interactions, ions of opposite charge will tend to cluster together, and so in the area near any particular ion there will be a dominance of ions of opposite charge (counter ions). The environment of a particular ion therefore carries an opposite charge, and this charged environment=ionic atmosphere.
-For example, around a Na+ ion, there will typically be more Cl- ions than other Na+ ions. This atmospheric shell of counter-ions partially shields the central ion's charge. The strength of this effect depends on the total ionic concentration in the solution.
What is ionic strength? What is the equation for it?
-a measure of the total ion concentration, accounting for both concentration and charge
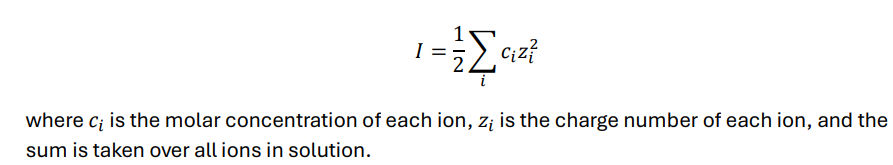
Calculate the ionic strength of a 0.1 M NaCl solution.
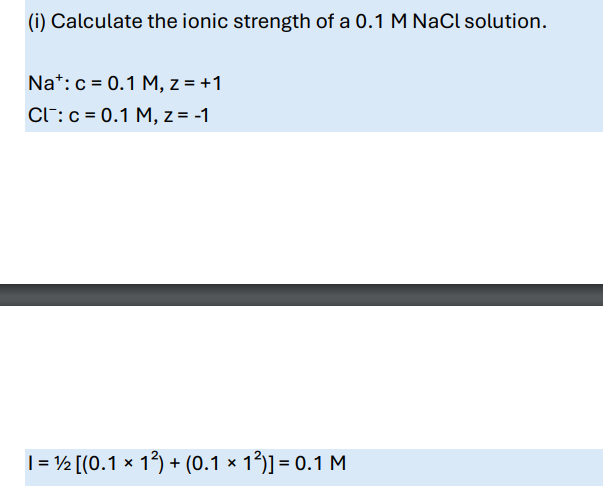
Calculate the ionic strength of a 0.1 M CaCl₂ solution:
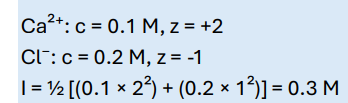
When is the ionic strength of a solution greater (i.e. with which type of ions)?
The ionic strength of solutions containing divalent or trivalent ions is much greater than for solutions of monovalent ions.
How do you calculate effective concentration?
𝑎 = 𝛾 ⋅ c
a=effective concentration
y=activity coefficient
c=concentration
What happens to activity coefficient and activity in very dilute ionic solutions? (i.e. when there is low ionic strength)
y approaches 1 and activity=concentration
-ionic strength and activity coefficient ‘inversely proportional’ not literally though
What happens to activity coefficient as ionic strength increases? What does this mean?
it typically decreases
-in more concentrated solutions. The ions interact and are less "free" to react, so the effective concentration is lower, thus activity coefficient decreases
How do you calculate pH of strong acids?
pH = −log[H +] where [H+ ] (or [H3O+ ] in aqueous solutions) is expressed in mol dm-3 or M.
for strong acids, [H+]=[H3O+]
Show how water acts as both an acid and a base
2H2O ⇌ H3O+ + OH-
How do you calculate Kw (ionic product of water)?
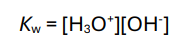
In dilute aqueous solutions, what is the concentration of water?
essentially constant ([H2O] ≈ 55.5 M)
What is the ionic product of water at 298K? What about pKw?
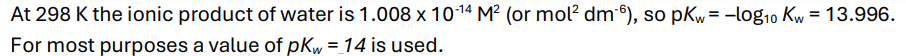
Explain, in terms of ionic equilibria, why water has a pH of 7

Explain how to calculate the pH of a strong base by doing this example question:
Calculate the pH of a 0.0050 M sodium hydroxide solution.

Are weak electrolytes partially or completely dissociated in solution?
partially
What is the dissociation constant for acetic acid in water?
H3CCOOH + H2O ⇌ H3CCOO- + H3O+
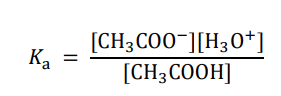
What value usually expresses the values of the dissociation constant? What is the equation for this?
pKa

How do you calculate the pH of a weak acid? Explain by answering this question:
What is the pH of a 0.1 M solution of acetic acid? The pKa of acetic acid = 4.76.
Ka= [H3O+]2 /cHA
![<p>Ka= [H3O+]<sup>2</sup> /cHA</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/52808275-3a43-4a83-81fc-92ede21a643f.png)
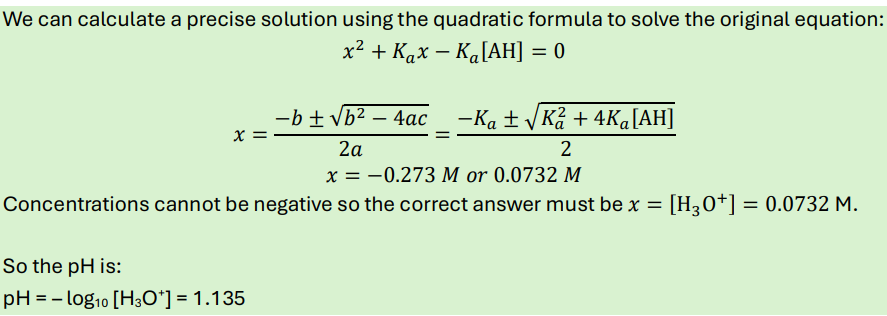
What is the pH of a 0.1 M solution of trichloroacetic acid (pKa = 0.7)?
-first do weak acid equation. If your H+ concentration is higher than the cHA, you must do quadratic formula
so must do quadratic formula
write down answer to everything under square root so that you don’t have to re-write
Explain how to calculate the pH of a weak base
In aqueous solution a base, B, will be a substance which reacts with water to give hydroxyl ions
B + H2O ⇌ BH+ + OH–
memorise BOTH equations as you may need 1 over the other.
cB= e stoichiometric concentration of the base
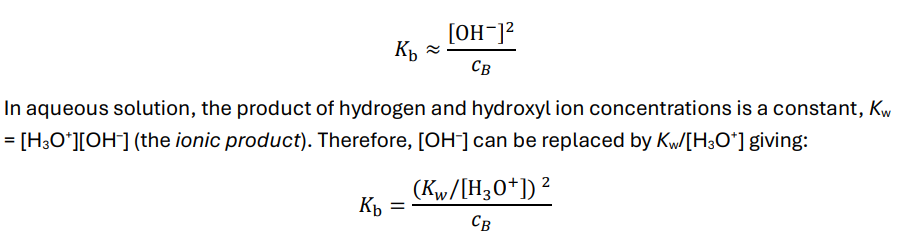
What is the acid dissociation constant (Ka) of a conjugate acid?
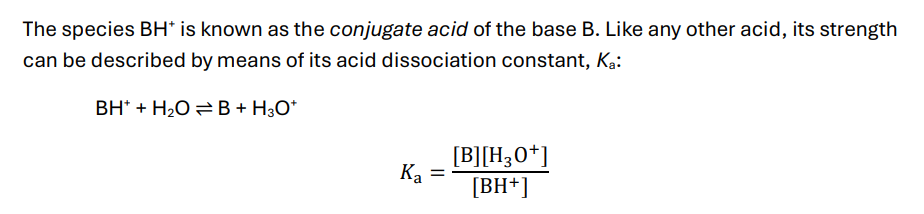
Kb constant
can rearrange to get [BH+]
![<p>can rearrange to get [BH+]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/58419a0a-554a-411d-97b0-c90d40d30c11.png)
Relationship between Ka and Kb drawn out
alternatively:
pKw = pKa + pKb
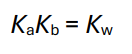
What is a conjugate acid vs a conjugate base?
A conjugate acid is what forms when a base accepts a proton (H+ ), while a conjugate base is what remains after an acid donates a proton. You can think of conjugate acid-base pairs as chemically related species that differ by a single proton, like NH4 + (conjugate acid) and NH3 (conjugate base).
What type of conjugate bases to strong acids have?
weak (doesn’t accept H+ ions easily)
weak conjugate acids don’t deprotonate easily
The pKb for aqueous ammonia is 4.74. What is the pKa for its conjugate acid NH4 +?
pKa = pKw – pKb = 14.00 - 4.74 = 9.26
How to calculate pKb using Kb
-logKb
Kb= [OH-] squared/stoichiometric conc. of the base
Units for Ka
M or mol L-1
What type of salt is produced when it’s strong acid+strong base
neutral salt
E.g. HCl+NaOH produces NaCl
What type of acid is produced when a strong acid reacts with weak base?
Acidic salt
E.g. HCl+NH3 makes ammonium chloride
What type of salt is produced when a weak acid reacts with a strong base?
Basic salt
E.g. H3CCOOH+ NaOH makes Na+ H3CCOO-
What type of salt is produced when a weak acid reacts with a weak base?
Neutral salt
e.g. ammonium acetate (NH4+ H3CCOO-) is the product of H3CCOOH and NH3
Are solutions of salts of weak acids acidic or alkaline? Why?
Alkaline due to salt hydrolysis
e.g. H3COO- +H2O (eq arrow) H3CCOOH+ OH-
What are buffer solutions?
-a solution that resists a change in pH when either an acid or base is added to it.
-A buffer is typically a mixture of a weak acid and its salt, e.g. acetic acid and sodium acetate.
pH of blood
7.4
pH of small intestine
8-9 approx.
What does the pH of a buffer solution depend on?
-the ratio of protonated/deprotonated species
How do you calculate the pH of a buffer solution containing a mixture of a weak acid (HA) and its salt (the conjugate base, A– )?
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
or you can use [salt]/[weak acid] instead if that is available
![<p>Henderson-Hasselbalch equation</p><p>or you can use [salt]/[weak acid] instead if that is available</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/dd6066a1-0e36-482f-83a8-36d1f39c0a89.png)
What are the 2 approximations we make when using the Henderson Hasselbalch equation for pH buffers?
1. The concentration of A– can be assumed to equal the initial amount of salt added to the solution.
2. The concentration of HA (the acid) can be assumed to equal the initial amount of acid added because: o Very little of the acid dissociates (because it is a weak acid) o Very little of the A– from the salt converts back to HA
A solution contains 0.01 M acetic acid and 0.02 M sodium acetate. Calculate the pH of the buffer. pKa(acetic acid) = 4.76.
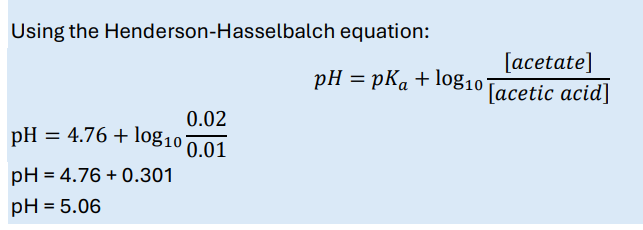
What happens when a strong acid is added to a buffer solution?
it will react with the salt to form more weak acid: 𝐻+ + 𝐴 − → 𝐻A
What happens when a strong base is added to a buffer solution?
the base will react with the weak acid to form more salt: 𝑂𝐻− + 𝐻𝐴 → 𝐴 − + 𝐻2O
Calculate the effect on the pH of adding 5 mL 0.1 M hydrochloric acid to 100 mL of a buffer solution which is 0.01 M with respect to both weak acid and salt. pKa(weak acid) = 4.00.
A-= salt HA=weak acid
-ALWAYS check if equation is balanced to check for correct molar ratio

What is buffer capacity? How do you calculate it?
-the number of moles of strong acid or strong base needed to change the pH of 1 litre of buffer solution by 1 unit.
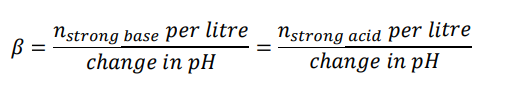
What does amphoteric mean?
they behave both as acids and as bases.
What is isoelectric point?
-the pH at which the net charge on the amino acid is zero and at which the amino acid shows minimum migration in an electric field.
-For glycine the isoelectric point is therefore the pH at which [+H3NCH2COOH] = [H2NCH2COO– ] and the concentration of the zwitterion is a maximum.
How to find/work out isoelectric point
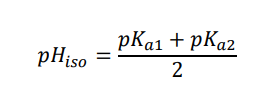
Calculate the value of pI for 2-aminopropanoic acid, given that Ka1 = 4.27 x 10-3 M and Ka2 = 1.29 x 10-10 M.

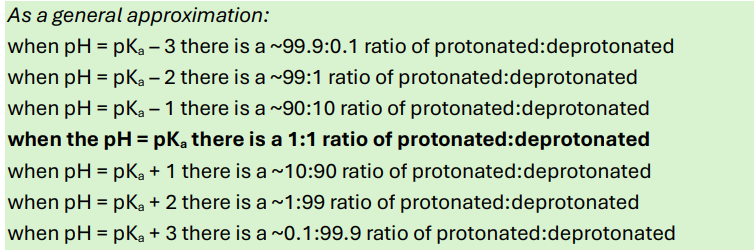
What are the fractions of deprotonated and protonated species for a weak mono-basic acid HA with a pKa of 6, at pH = 6?
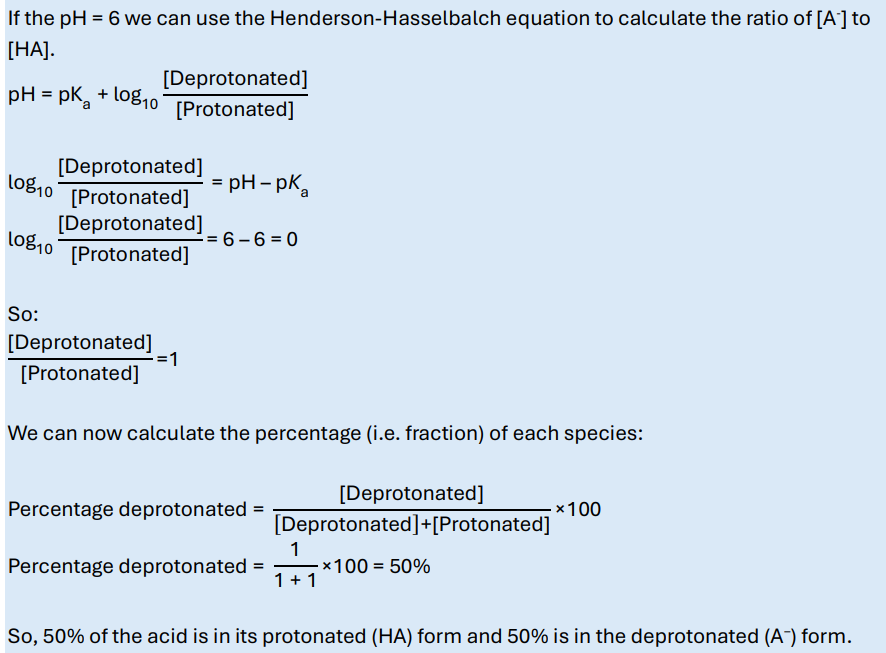
General approximations you MUST know for pH, pKa and ratio ionisation
e.g. when pH=pKa+2= 1% ionisation of acid/protonation and 99% deprotonation/ionisation of base (i.e. in its ion form)
Aspirin has pKa = 3.49. Calculate the percentage protonated/deprotonated in the blood, stomach and small intestine.
opposite of log is 10^ NOT 10^-

Imipramine has pKa = 9.50. Calculate the percentage protonated/deprotonated in the blood, stomach and small intestine.
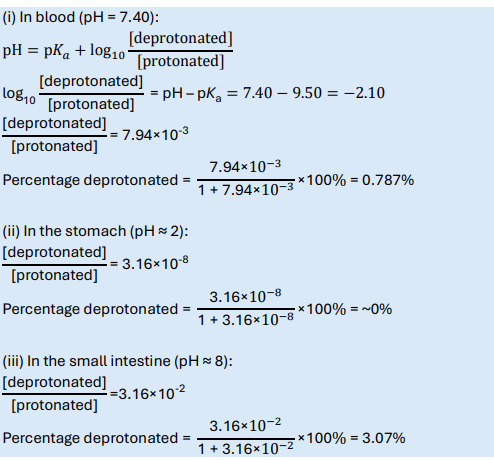
Lidocaine has pKa = 7.94. Calculate the percentage protonated/deprotonated in the blood (pH 7.4)

How do you work out pKw?
-logKw
state how to calculate:
pKa
pH
Kw
pKw
pH of weak acids
pH of weak bases
buffers
pI
pKw= pKa + pKb
