Unit 3 (Gas Exchange): Introducing Plant Parts and Stomata's Functions
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
plant organs
roots, stems, leaves
root system
parts of a plant below ground
shoot system
parts of a plant above ground
root
anchors a vascular plant in the soil and helps with absorption of minerals and water
taproot
the main vertical root that penetrates the soil deeply
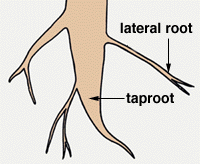
lateral roots
branches off the taproot and allows for better absorption

root hairs
thin, finger-like extensions of root epidermal cells
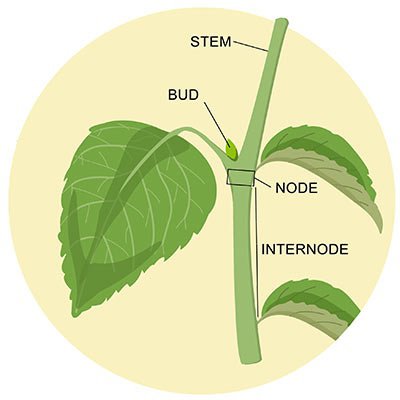
stem
connects leaves and buds, elongates the shoot
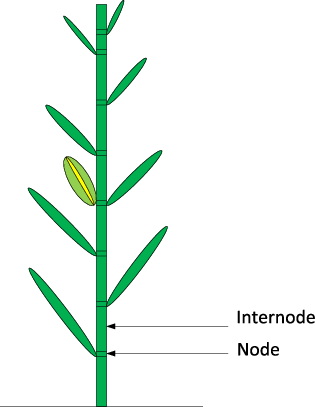
nodes
the points at which leaves are attached
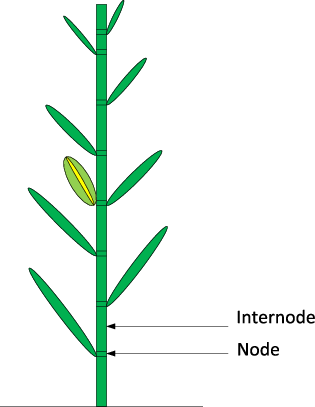
internodes
segments between the nodes (stem)

apical bud
located at the very top, responsible for continuous growth
axillary bud
can potentially form a branch, thorn, or flower
leaf
plant organ responsible for photosynthesis
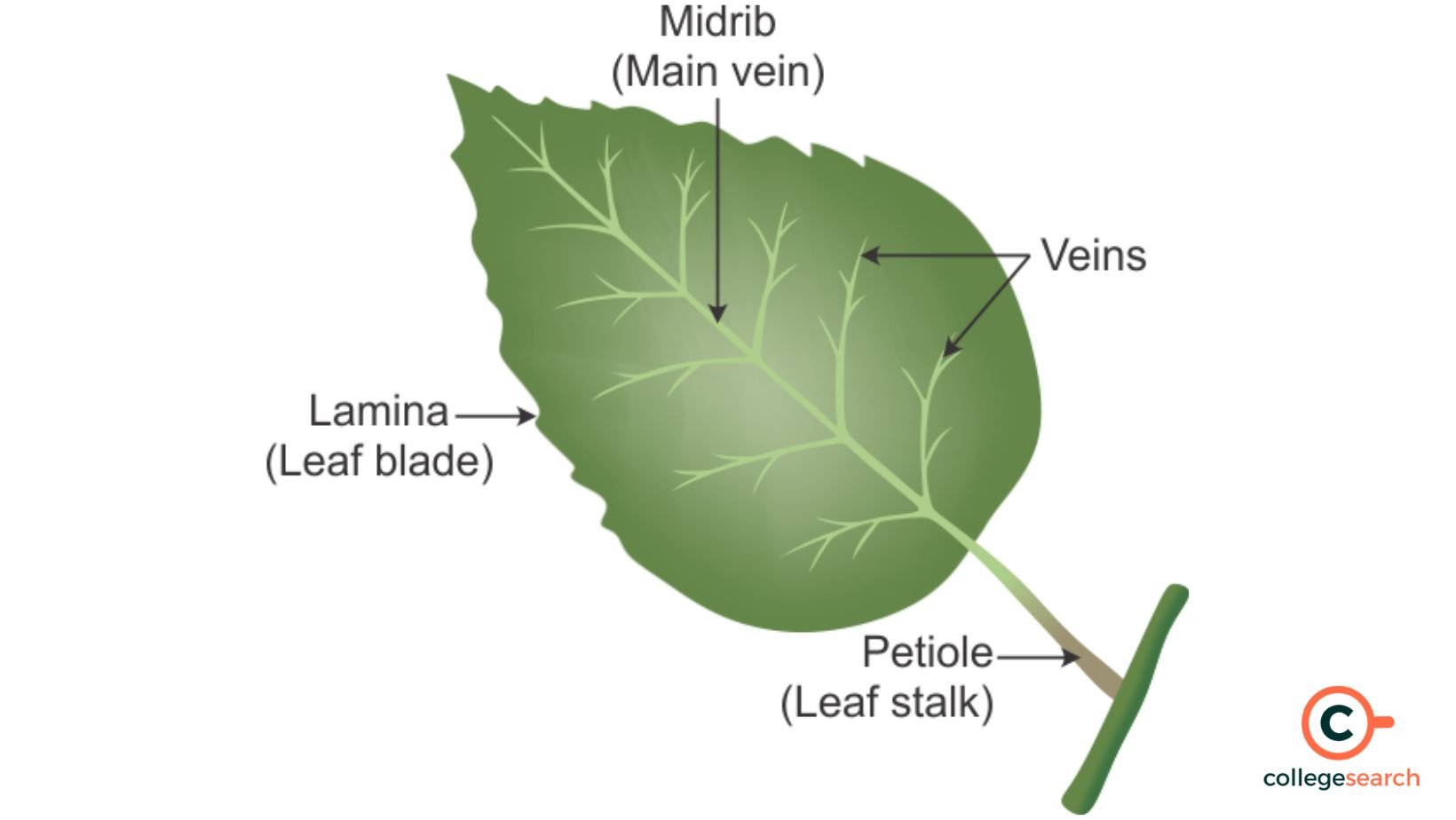
blade
the flat part of the leaf
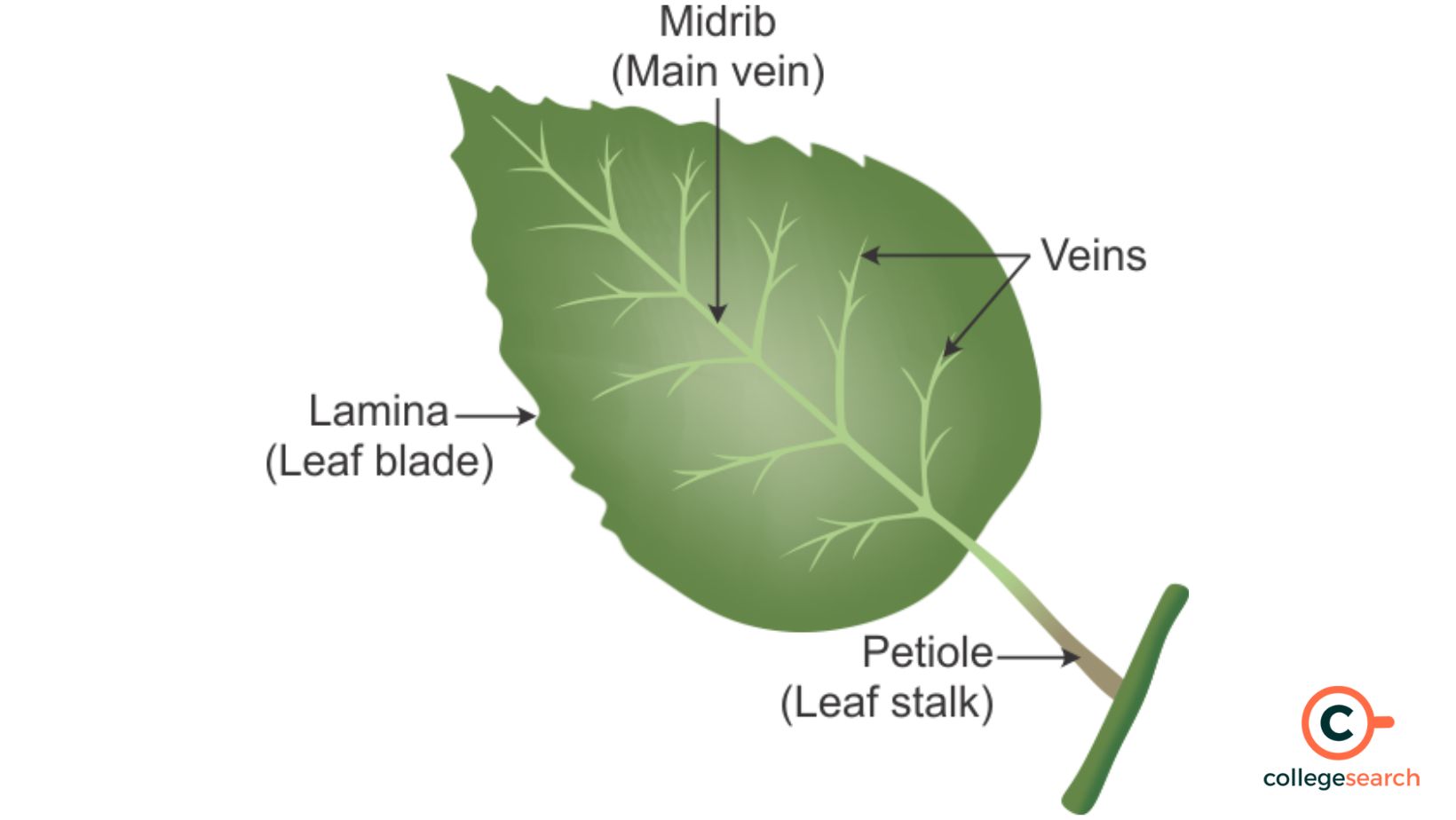
petiole
connects leaf to stem
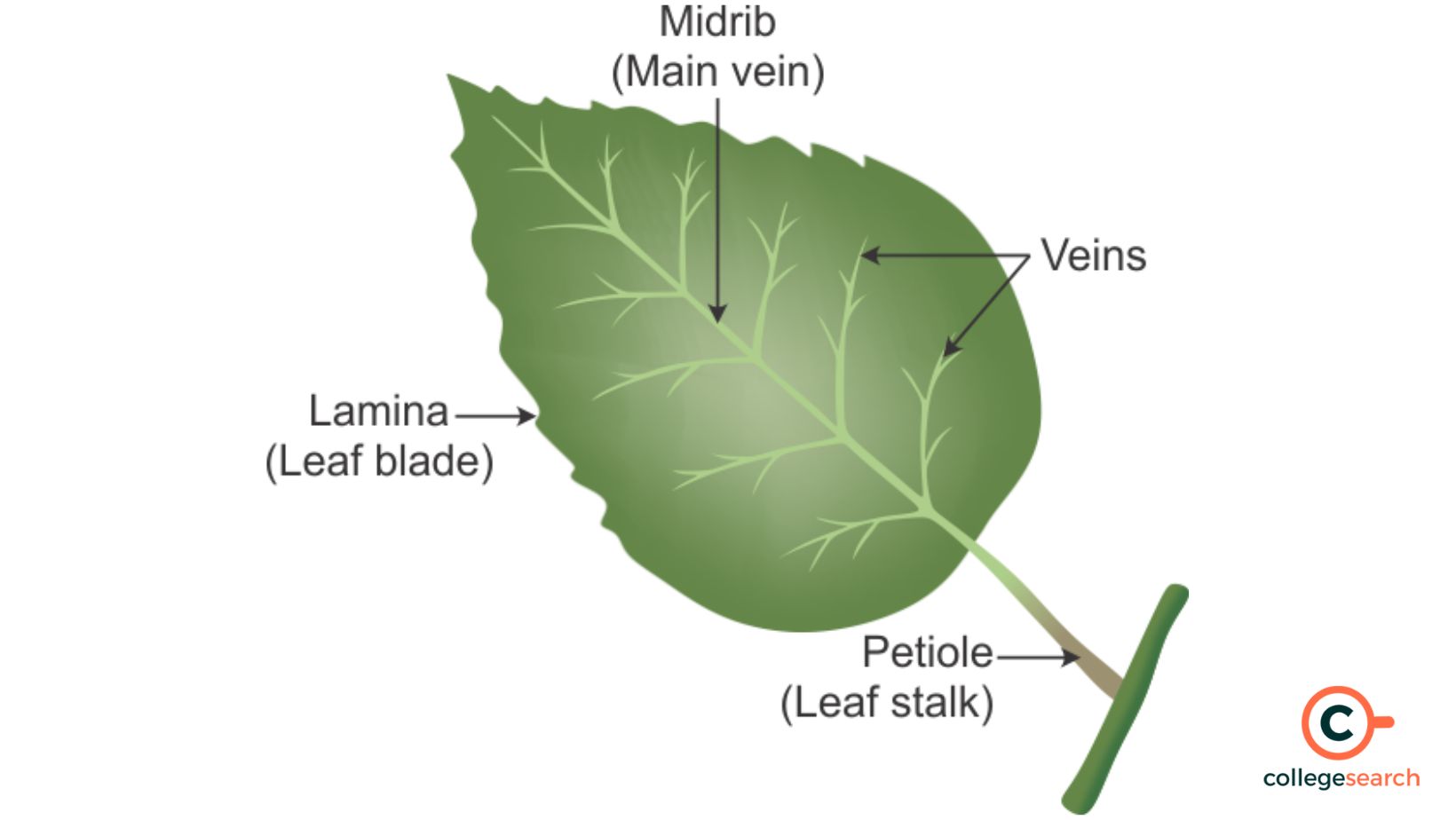
veins
vascular tissue of leaves
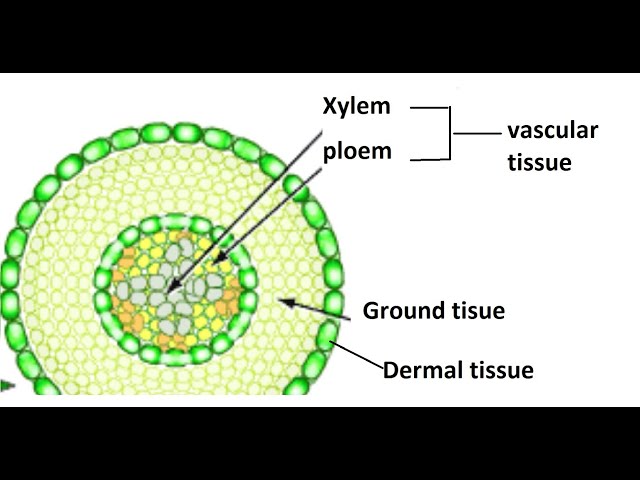
dermal tissue
plant’s outer-protective layer, first line of defense against damage
epidermis
makes up the dermal tissue in nonwoody plants, a single layer of cells
periderm
replaces epidermis as woody plants mature because it’s thicker/more protective
cuticles
secretes wax to prevent water loss
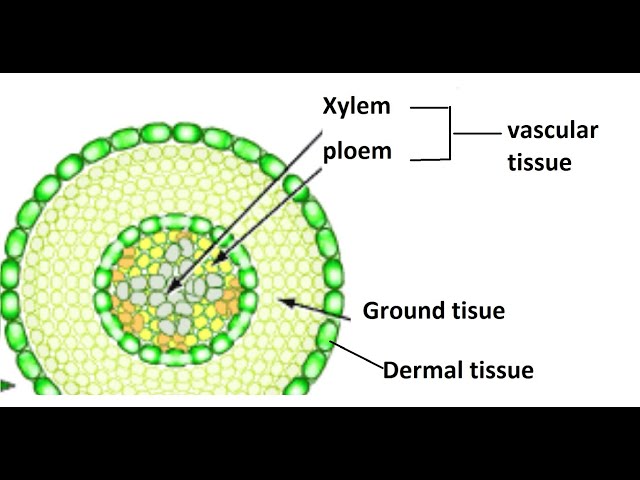
vascular tissue
xylem(water and minerals) and phloem(products of photosynthesis)
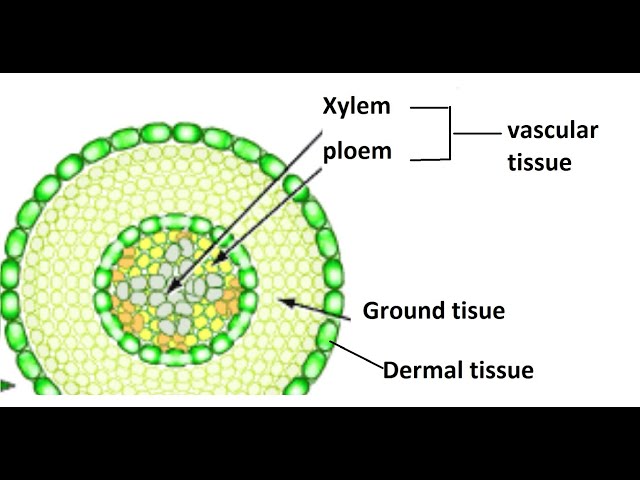
ground tissue
tissues that are neither dermal or vascular
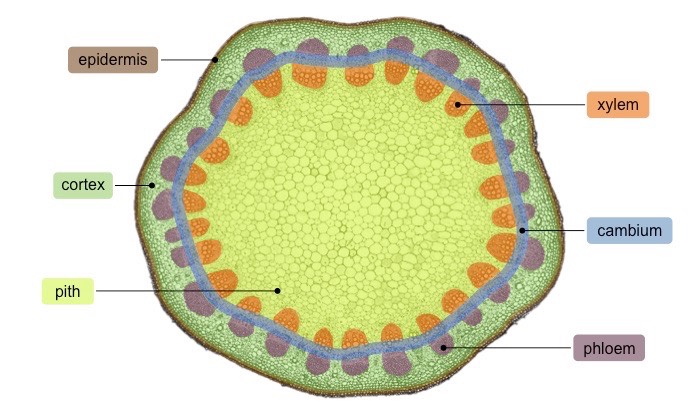
pith
ground tissue that surrounds vascular tissue
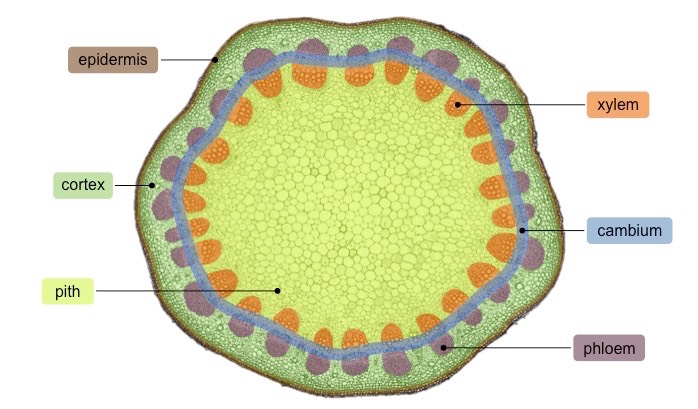
cortex
ground tissue external to the vascular tissue
stomata
aids in absorbing CO2 and releasing O2—also contributes to water loss
guard cells
control the diameter of the stomata by changing the shape
what does water loss depend on
number of stomata and size
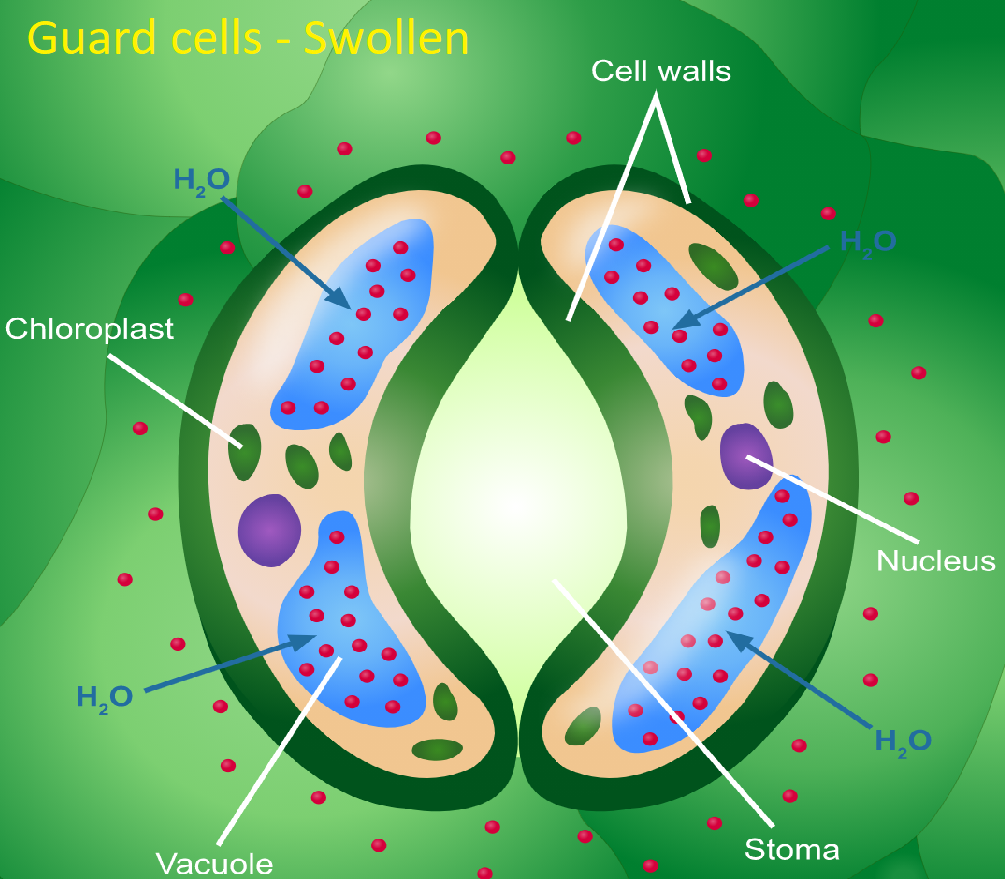
guard cells absorbing water
as guard cells absorb, they become more structured/turgid, bow-like
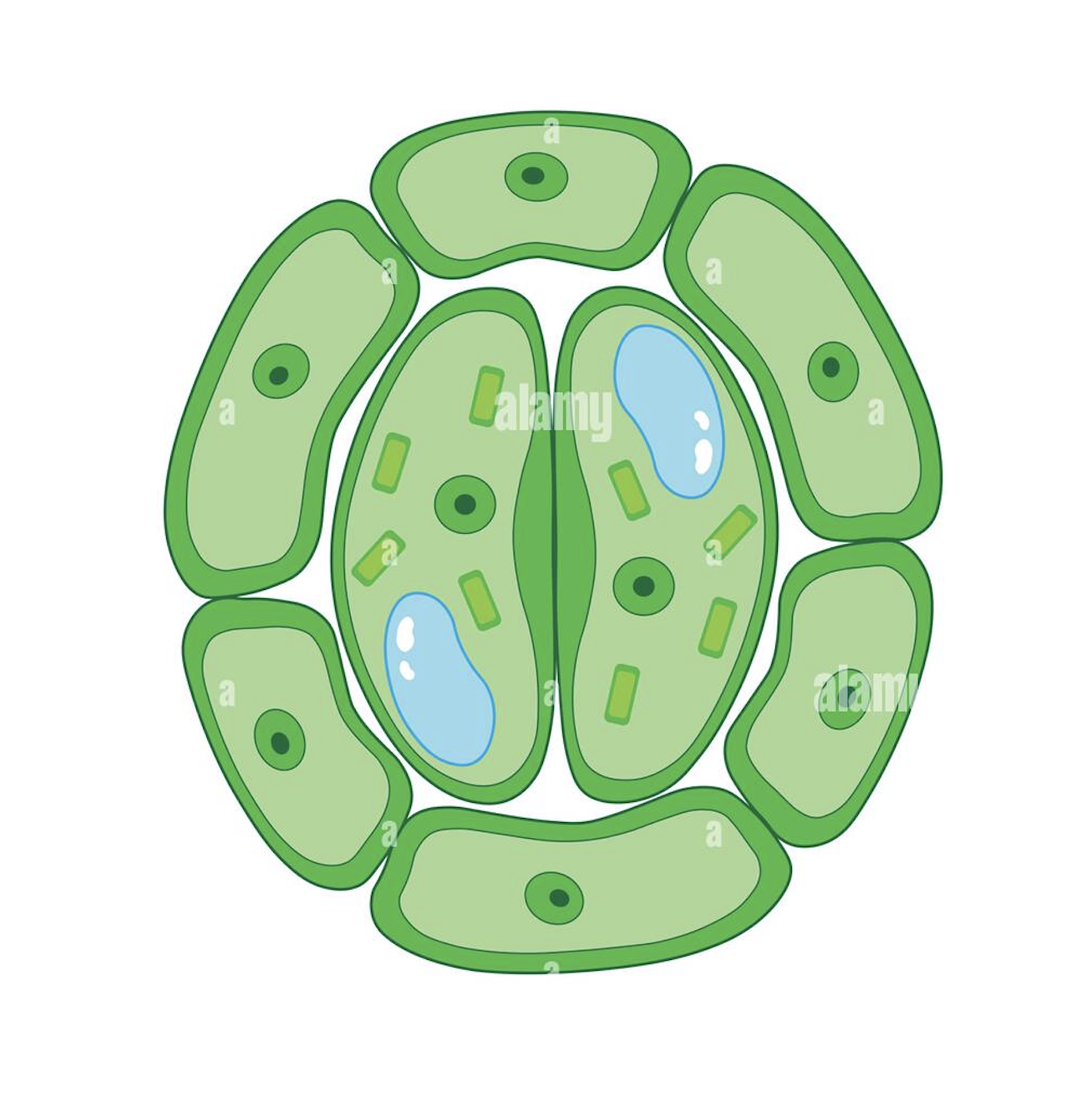
guard cells losing water
as guard cells release water , they become less bowed and close the pores
turgor pressure
pressure exerted by the fluid in the plant cell against its cell wall, gives the plant its rigidity
abiscisic acid (ABA)
produced in roots and leaves, signals guard cells to close stomata
xerophytes
plants adapted to arid environments
crassulaccean acid metabolism(CAM)
special photosynthesis found in succulents to take in CO2 at night and close stomata in the day where evaporation is more likely