Global Health: Key Concepts, SDGs, and Health Determinants
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
Global Health
Global Health transcends national boundaries.
International Health
The study of health issues that affect people living in the developing world or outside one's own country.
Domestic Public Health
Issues that affect people living in the US or within a country.
Environmental Health
The theory and practice of assessing, correcting, controlling, and preventing environmental factors that can adversely affect the health of present and future generations.
Health
Health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity.
Public Health Code of Ethics
Prevention of disease.
Public Health
Focus is on the population and public service.
Medicine
Focus is on the individual and personal service.
Neonatal Death
6,300 babies die every day in the world before they are four weeks old (2.3 million in 2022).
Maternal Mortality
287,000 women a year die in childbirth.
Measles Deaths
More than 136,000 people die every year of measles (2022).
Tuberculosis Deaths
1.3 million people die in the world every year (2022) from tuberculosis.
Low-income
<$1145.
Lower-middle income
$1146-4515.
Upper middle-income
$4516-14,005.
High-income
>$14,005.
Millennium Development Goals
Goals set forth by the United Nations Millennium Declaration in 2000.
Goal 1
Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger.
Goal 2
Achieve universal primary education.
Goal 3
Promote gender equality and empower women.
Goal 4
Reduce child mortality.
Goal 5
Improve maternal health.
Goal 6
Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria and other diseases.
Goal 7
Ensure environmental sustainability.
Goal 8
Develop a global partnership for development.
Sustainable Development Goals
Goals aimed at ending poverty and improving lives globally.
SDG 1
End poverty in all its forms everywhere.
Extreme poverty
Living on less than $1.25 a day.
SDG 2
End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition, and promote sustainable agriculture.
Food security
Access by all people at all times to enough food for an active, healthy life.
Food insecurity
Limited or uncertain availability of nutritionally adequate and safe foods.
Hunger
The uneasy or painful sensation caused by a lack of food.
Nutrient deficiencies
Lack of essential nutrients in the diet.
Hidden hunger
Nutrient deficiencies that are not immediately apparent.
Over-nutrition
Excess intake of nutrients, leading to obesity.
Obesity
Excess body weight due to over-nutrition.
Staple foods
Foods that are eaten regularly and constitute a dominant portion of a standard diet.
SDG3
Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages
Preventable diseases
11 children die every minute from preventable diseases
SDG4
Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all
Basic reading skills
170 million people could be lifted out of poverty if all students learned basic reading skills
Kerala state in India
Quality education, widespread healthcare access, strong nutrition programs
SDG5
Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls
Women's work hours
Women work 70% of the world's working hours, yet earn only 10% of the world's income
SDG6
Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all
Mobile phones vs toilets
More people have a mobile phone than have a toilet
SDG7
Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all
People without electricity
1.1 billion people live without electricity
SDG8
Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all
Minimum wage in Haiti
64¢ is the minimum hourly wage for garment workers in Haiti
SDG9
Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation
Foot bridge impact
Building a simple foot bridge between rural communities can increase new business growth by 15%
SDG10
Reduce inequality within and among countries
Wealth inequality
The 85 richest people in the world own the same amount as the 3.5 billion poorest people
SDG11
Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable
Urban population
½ of humanity lives in urban areas
SDG12
Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns
Earths needed
5: the number of earths it would take to support the world population if everyone lived like Americans
SDG13
Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts
Sea level rise
1-4 feet: how much sea levels will rise by 2100
SDG14
Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas, and marine resources for sustainable development
Seafood reliance
2.6 billion people rely on seafood as their main source of protein
SDG15
Protect, restore and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, and halt and reverse land degradation and halt biodiversity loss
Resource consumption
We are using 25% more resources than our planet can sustain each year
SDG16
Promote peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development, provide access to justice for all and build effective, accountable and inclusive institutions at all levels
Cost of violence
The world cost of violence is approximately $14 trillion/year
SDG17
Strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the global partnership for sustainable development
Extreme poverty reduction
½ the people living in extreme poverty in 1990 are not anymore
Infant mortality rate
The number of deaths of infants under age 1 per 1000 live births in a given year. Deaths < 1 year of age X 1000
Live births statistics
Zambia = 35.6/1000, Singapore = 1.5/1000, US = 5.4/1000
Life Expectancy at Birth
The average number of years a newborn baby could expect to live if current mortality trends were to continue for the rest of the newborn's life.
Maternal Mortality Ratio
The number of women who die as a result of pregnancy and childbirth complications per 100,000 live births in a given year.
Neonatal Mortality Rate
The number of deaths to infants under 28 days of age in a given year per 1000 live births in that year.
Under Five Mortality Rate
The probability that a newborn baby will die before reaching age five, expressed as a number per 1000 live births.
HALE (Health-Adjusted Life Expectancy)
Number of years to be lived in the equivalent of good health.
DALY (Disability Adjusted Life Year)
Measure of premature deaths and losses due to illness and disabilities in a population.
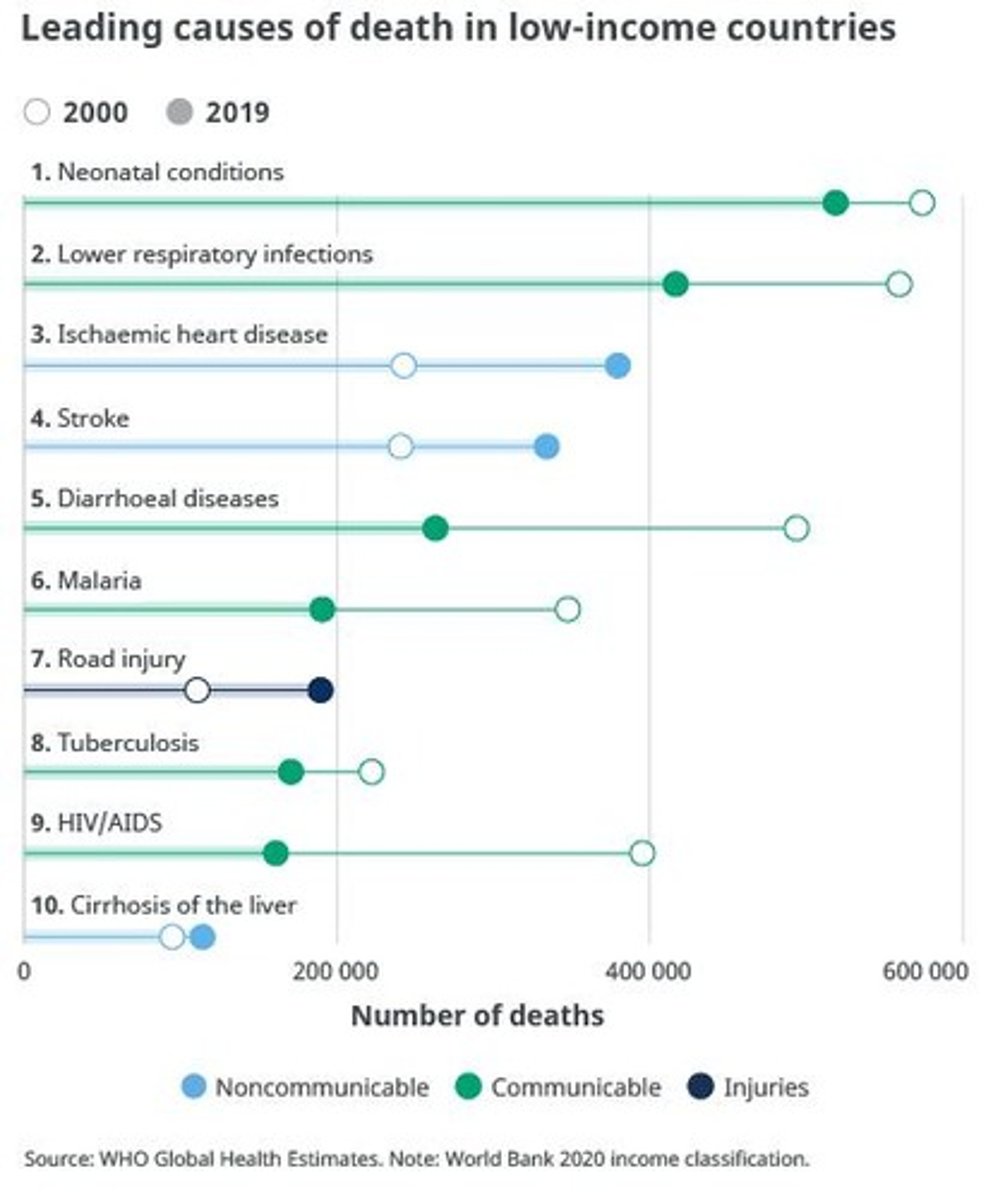
Leading causes of DALYs for low- and middle-income countries
Perinatal conditions, Lower respiratory infections, Ischemic heart disease.
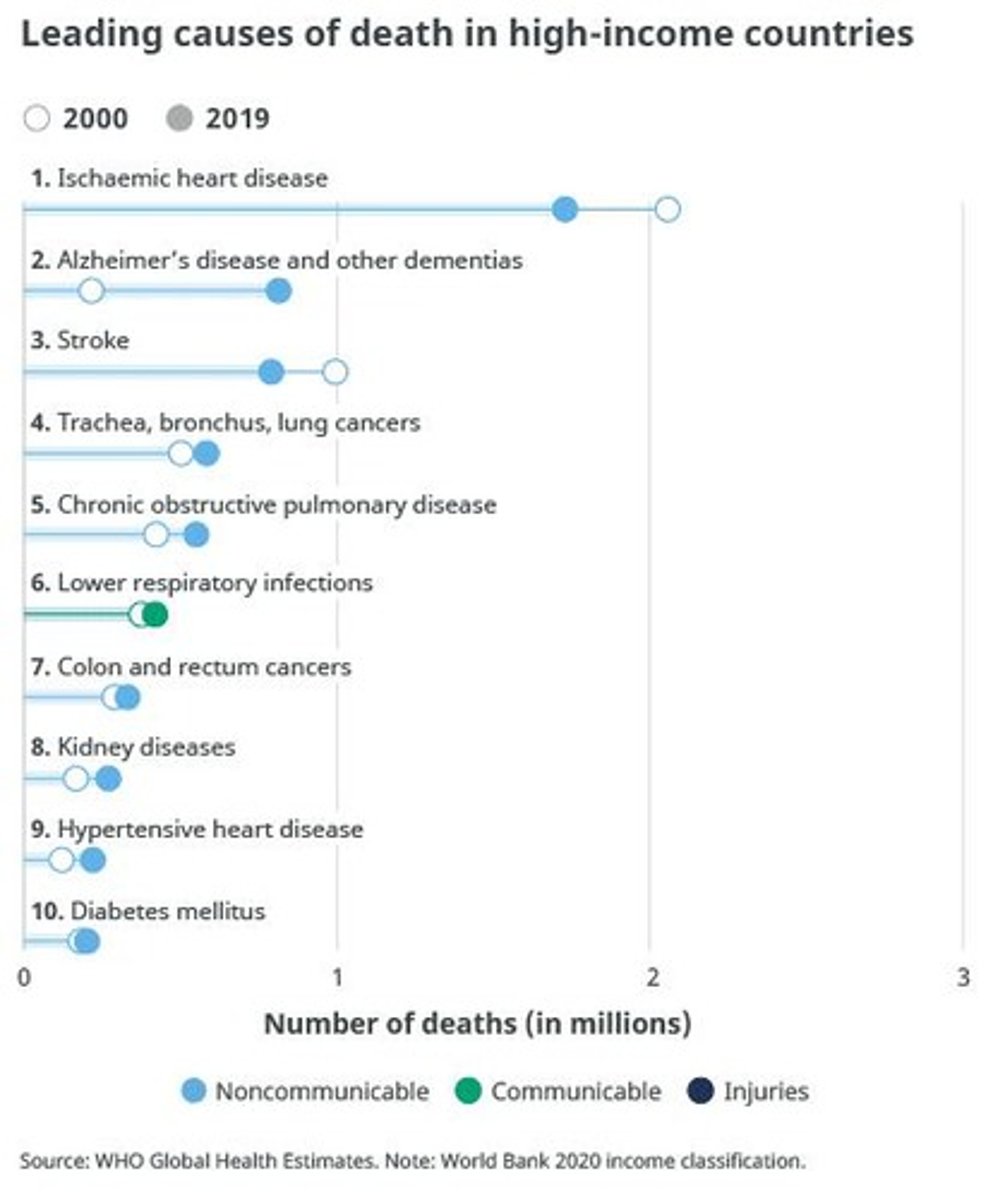
Leading causes of DALYs for high-income countries
Ischemic heart disease, Cerebrovascular disease, Unipolar depressive disorders.
Zambia's life expectancy in 2024
66.5 (UP FROM 52.5).
Japan's life expectancy in 2024
84.9 (UP FROM 84).
US life expectancy in 2024
79.5 (DOWN FROM 80).
South Sudan's Maternal Mortality Ratio
1223/100,000 (UP FROM 789).
Germany's Maternal Mortality Ratio
4/100,000.
US Maternal Mortality Ratio
21/100,000 (UP FROM 14).
Zambia's Neonatal Mortality Rate
24/1000.
Singapore's Neonatal Mortality Rate
1/1000.
US Neonatal Mortality Rate
3.2/1000.
Zambia's Under Five Mortality Rate
56/1000 (down from 61).
Singapore's Under Five Mortality Rate
2/1000.
US Under Five Mortality Rate
6/1000.
Cardiovascular disease
The leading cause of death worldwide.
Burden from communicable diseases
The poorest countries have a relatively larger burden from communicable diseases than from non-communicable diseases.