Chapter 5-6: hypothesis testing
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Null hypothesis
default assumption that there is no significant effect, difference, or relationship between variables in a population, suggesting any observed results are due to chance
Types of tests
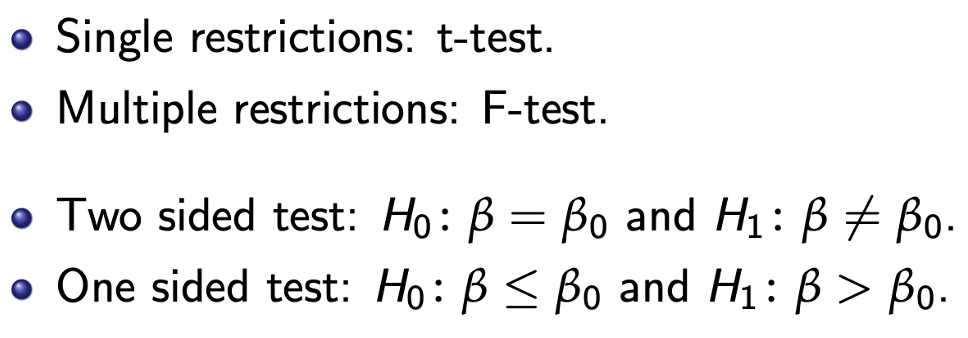
Rejection region Cα =
values of the test statistic that result in rejecting the null at the significance level α.
Rejection rule and Critical value(s)

Types of errors

Level and Power of a Test

Assumption A.5

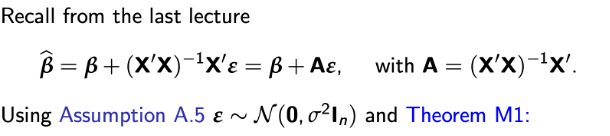




then …


We found that …
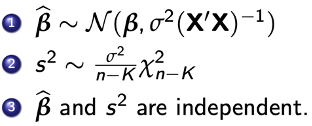
Testing single restrictions
Step 1
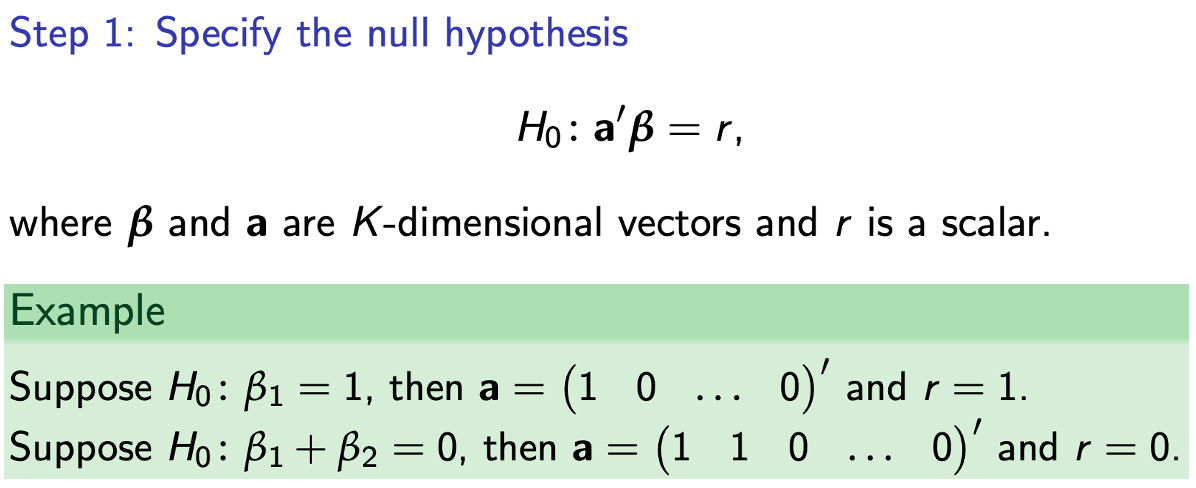
Testing single restrictions
Step 2
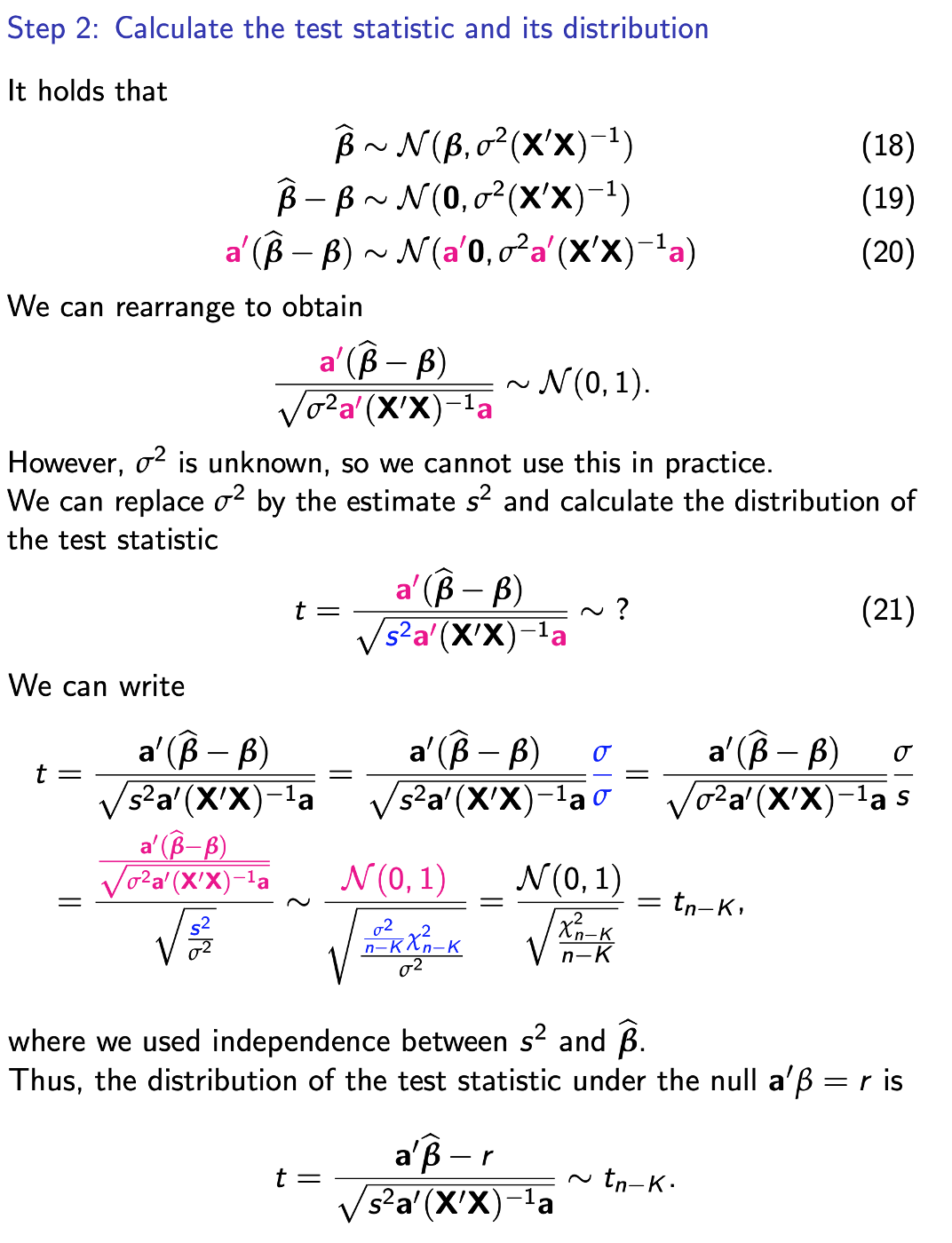
Testing single restrictions
Step 3
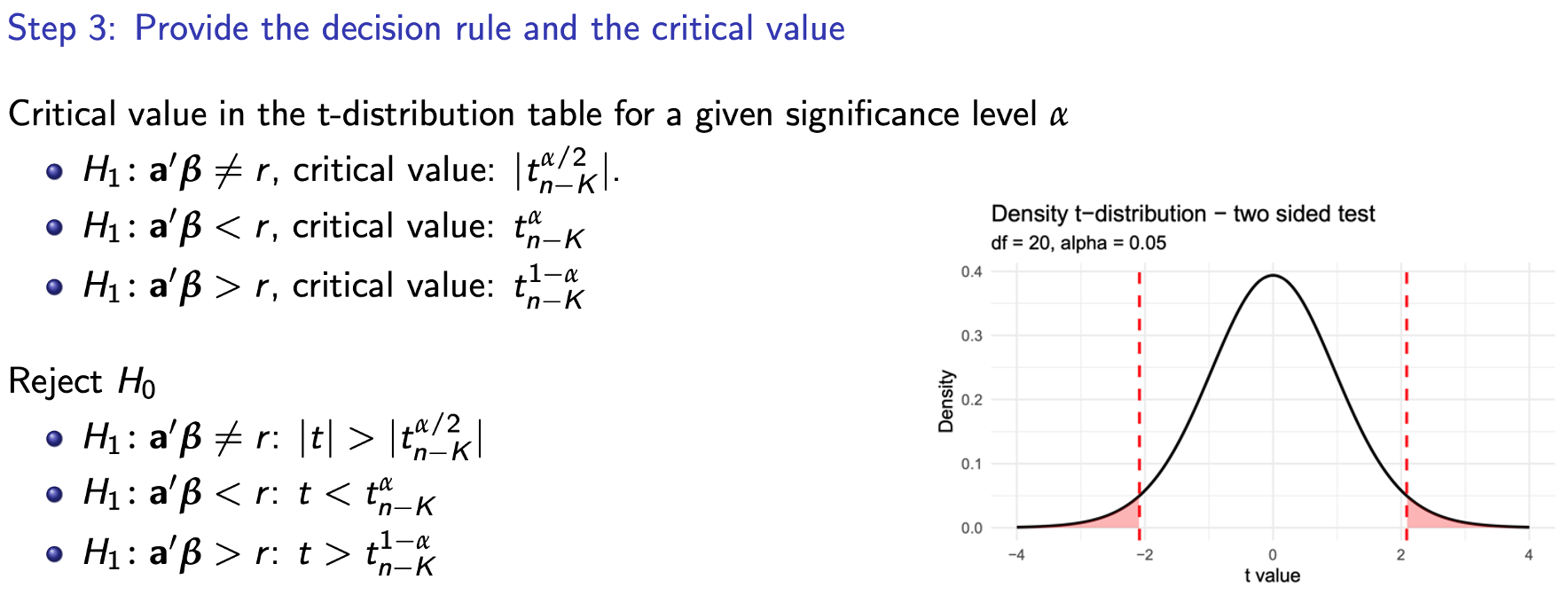
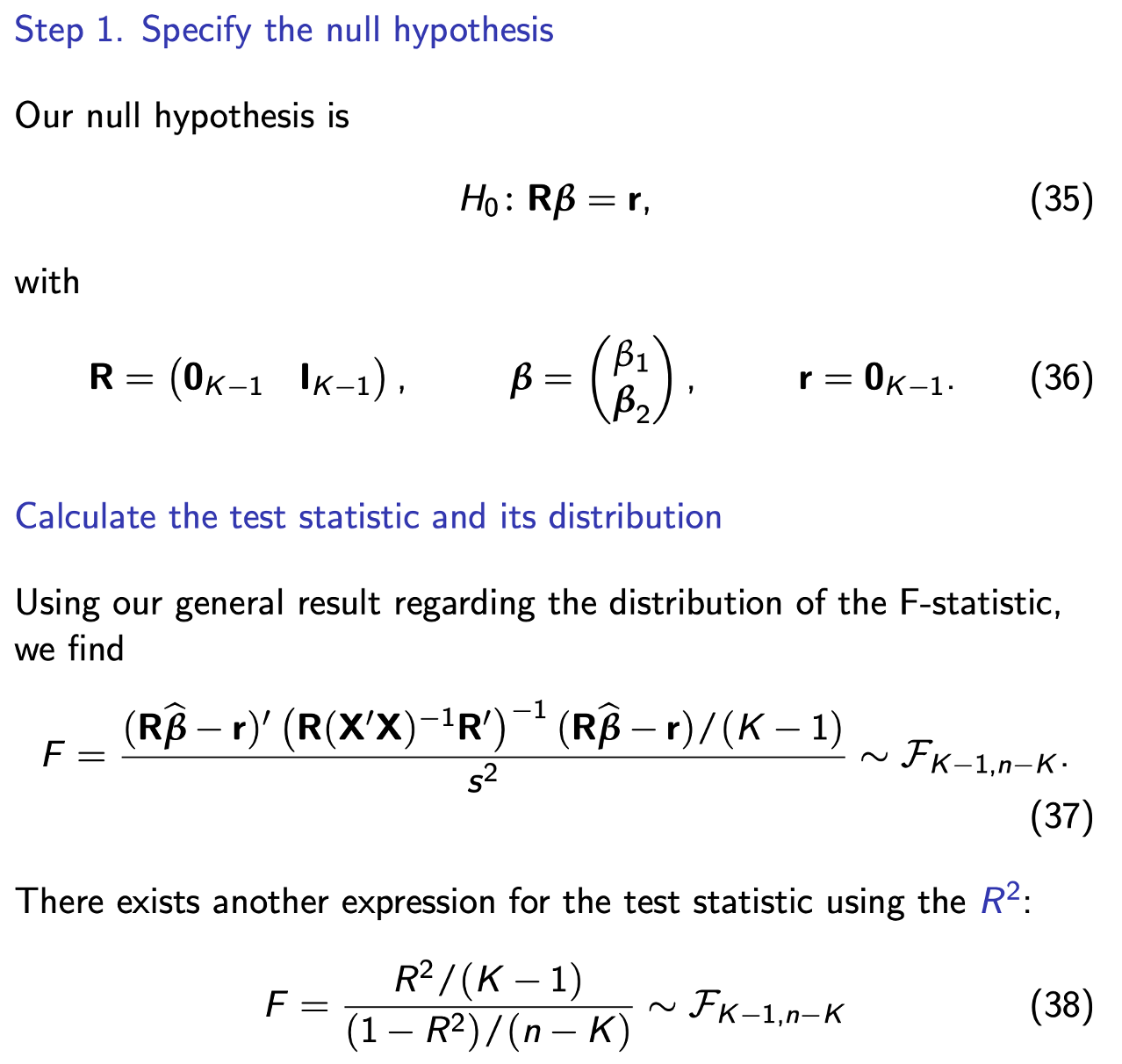
Testing multiple restrictions
Step 1
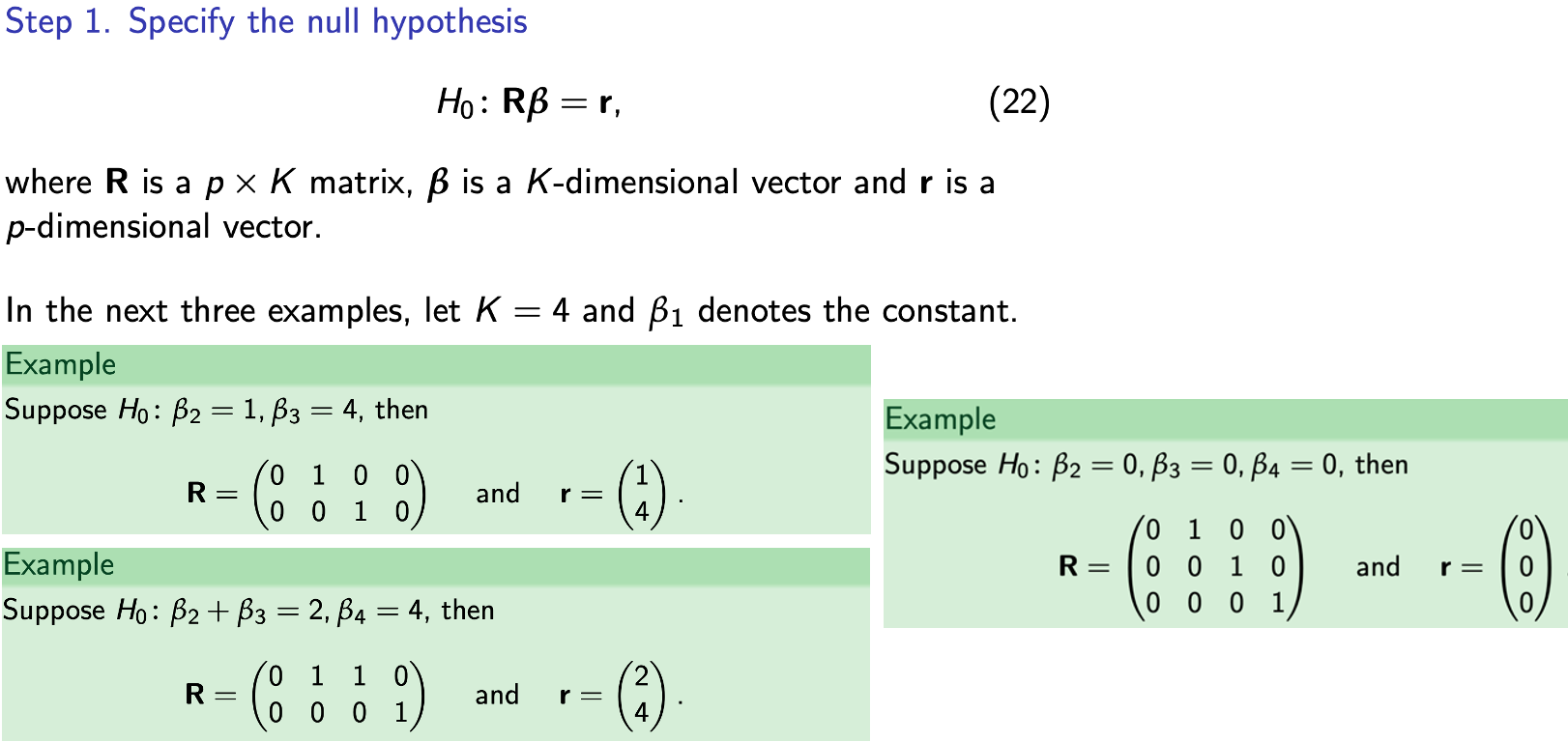
Testing multiple restrictions
Step 2.1
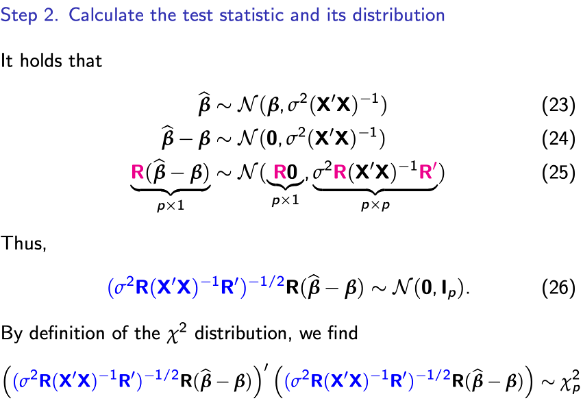
Testing multiple restrictions
Step 2
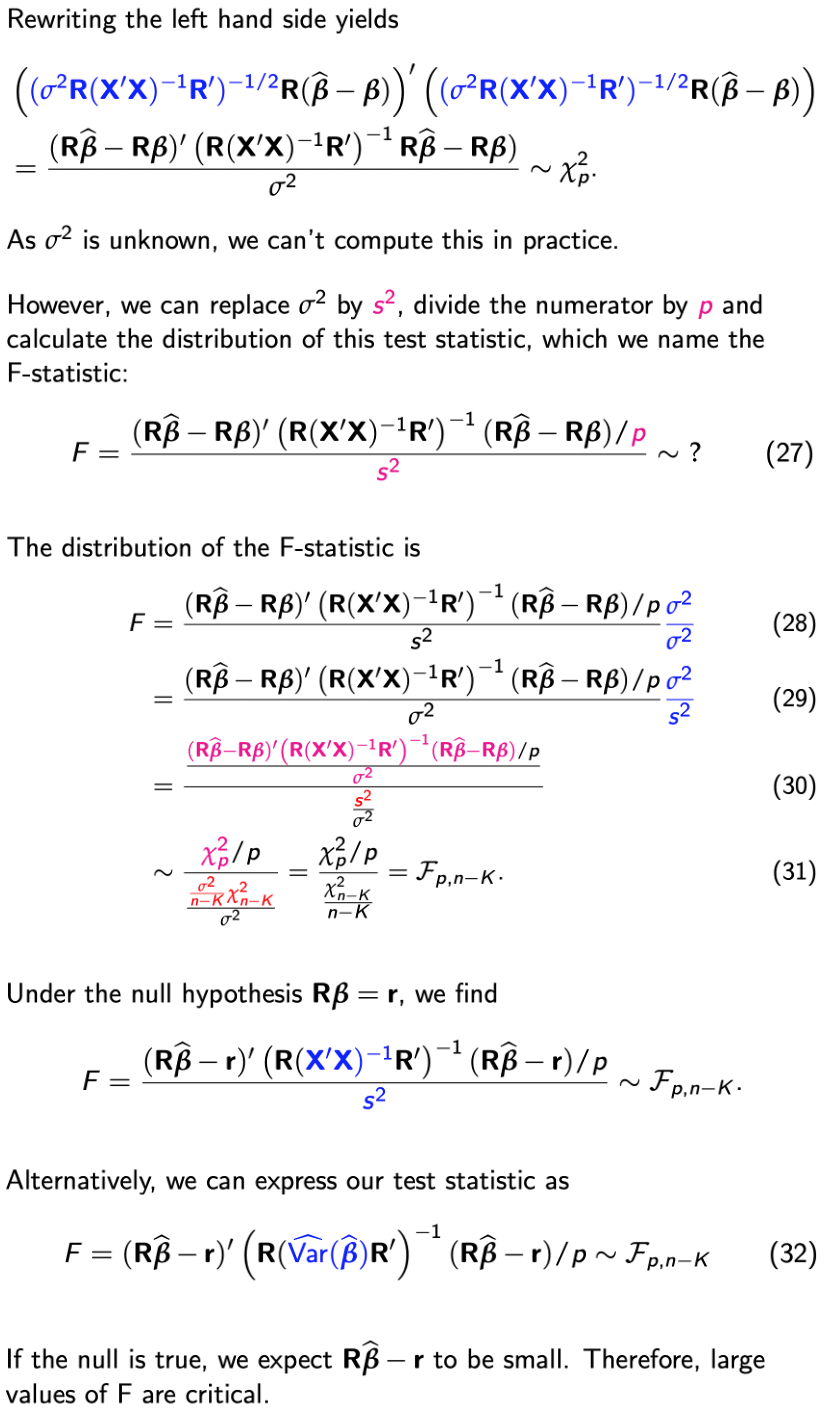
Testing multiple restrictions
Step 3
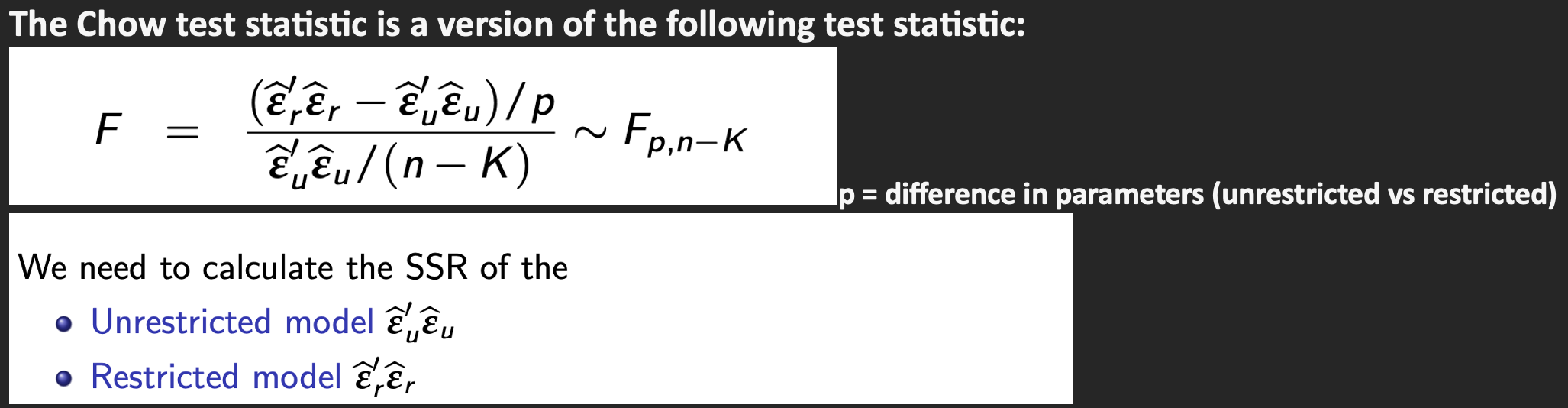
p is the number of restrictions being tested

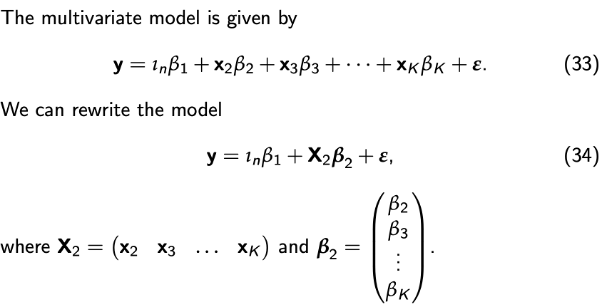
Goal: We want to test whether the parameters on the regressors are jointly equal to zero.
+ F test using R2
Restricted least squares (RLS) =
Example
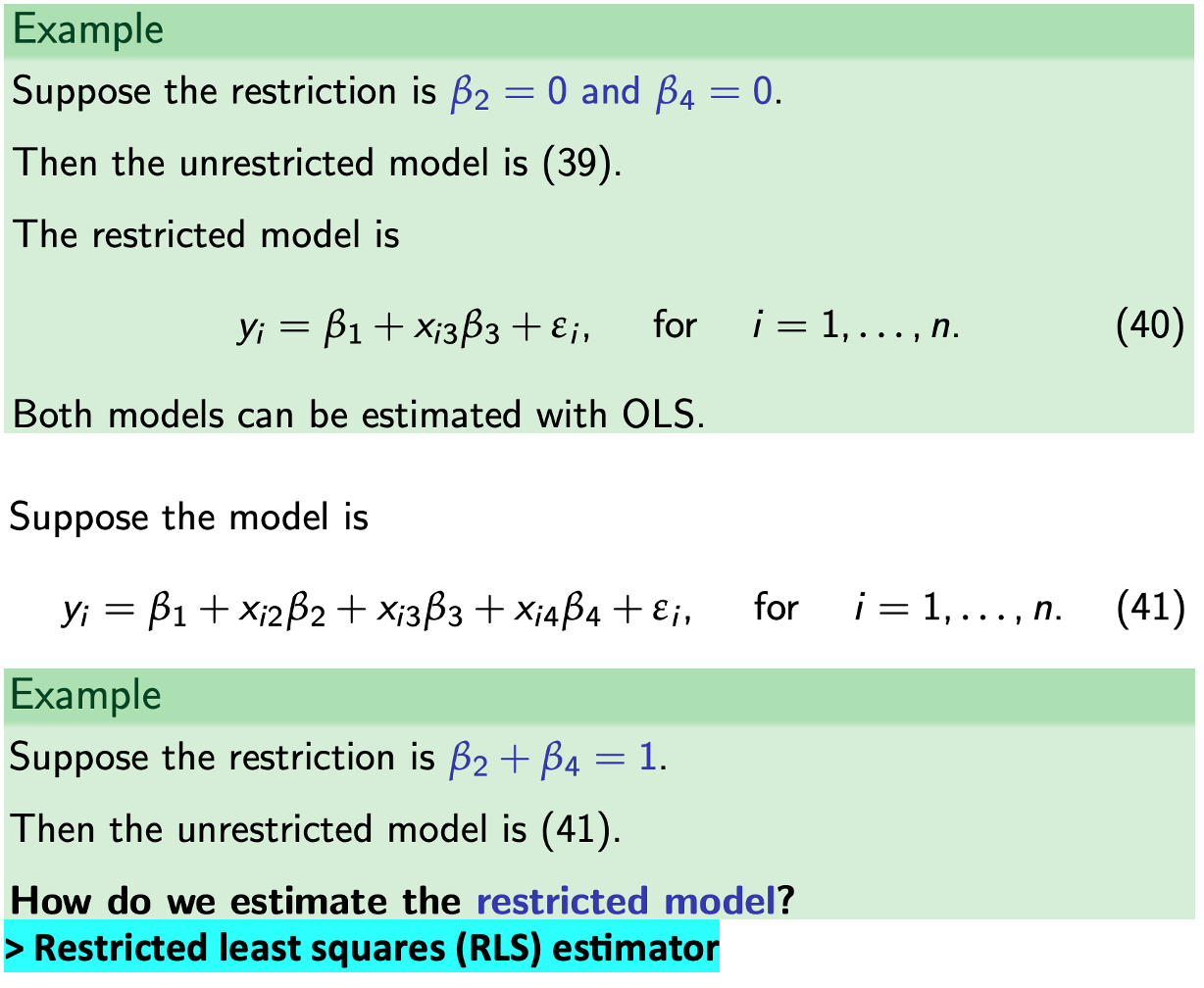
RLS estimator

We can analyse the properties of the RLS estimator - similar to our analysis of the OLS estimator. We find:
E(BRLS) =
Var(BRLS) =
sRLS2 =
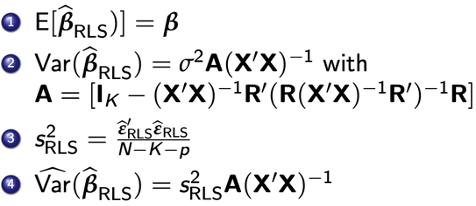


t statistic
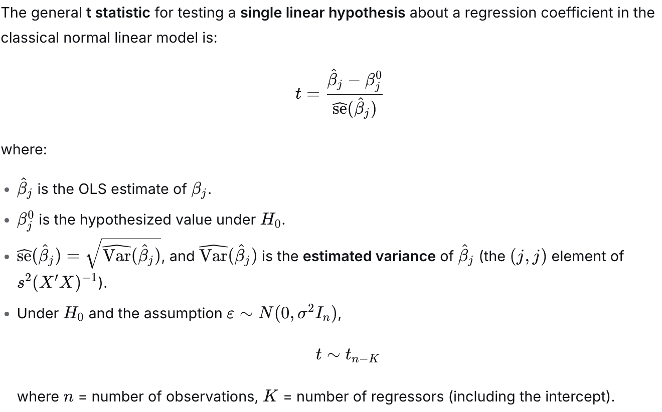
F-statistic using SSR
Used in Chow test
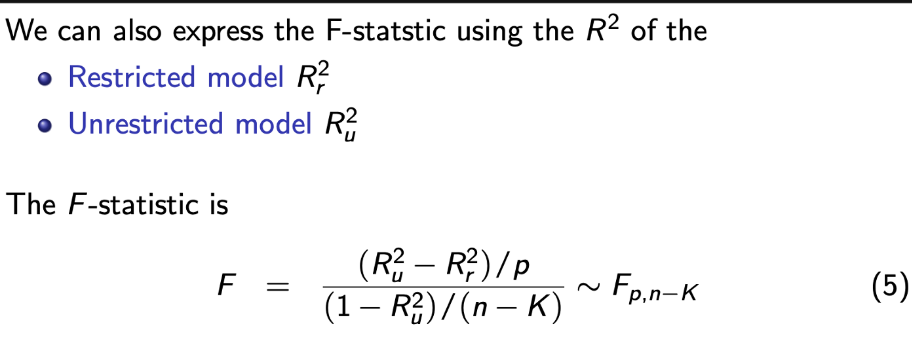
F-statistic using R2
Unrestricted vs Restricted
Chow test
Idea

The Chow test statistic is a version of the following test statistic:
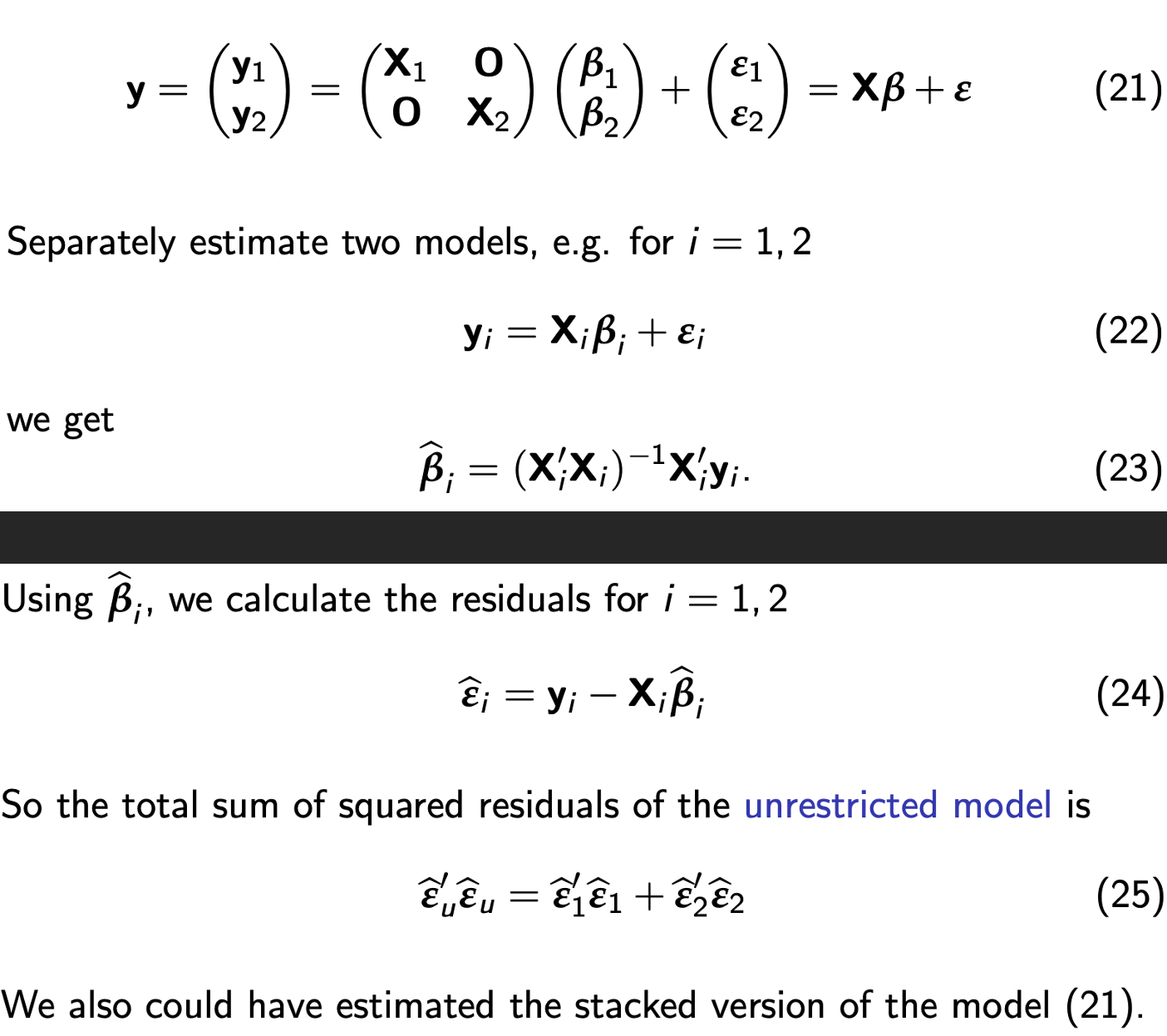
The unrestricted model:
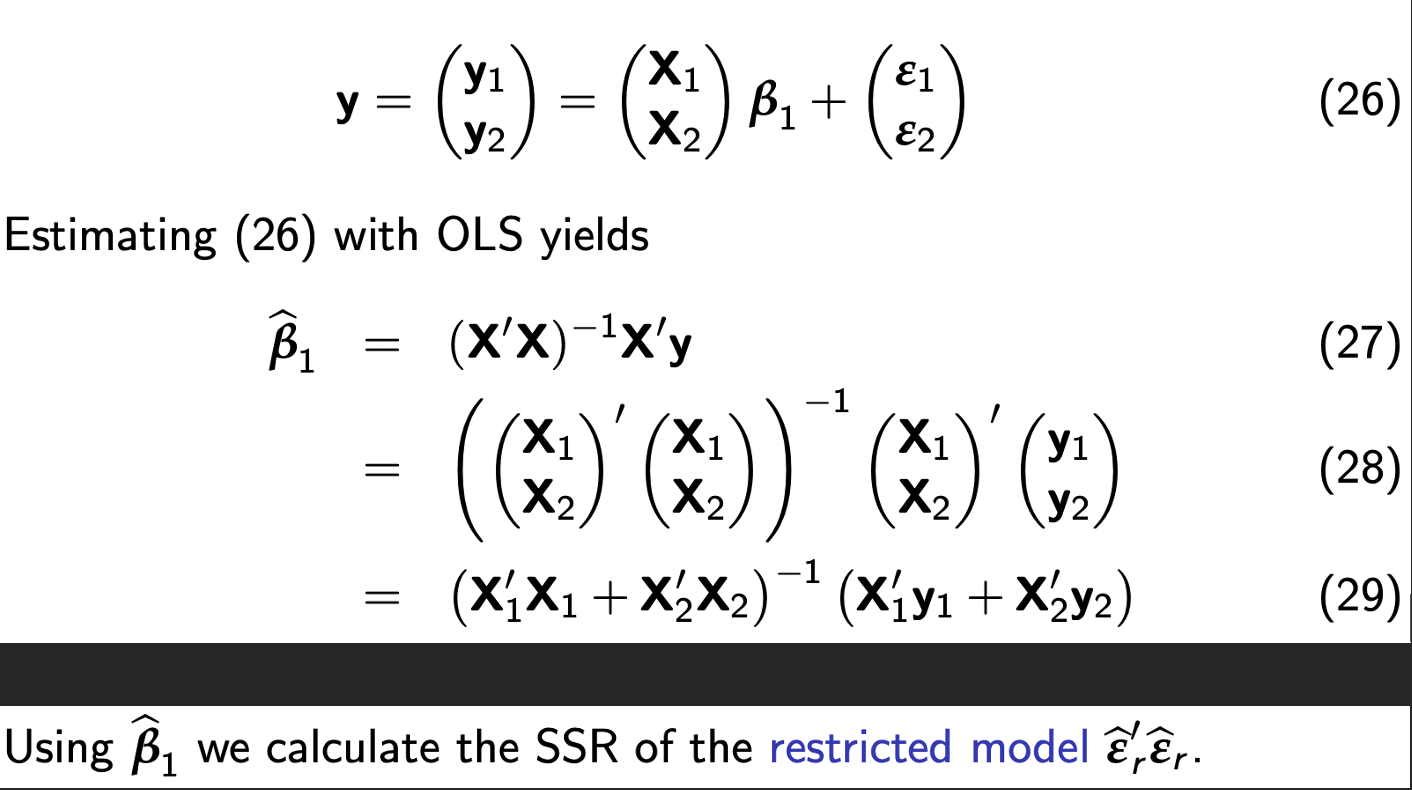
The restricted model (B1 = B2):
Chow test statistic
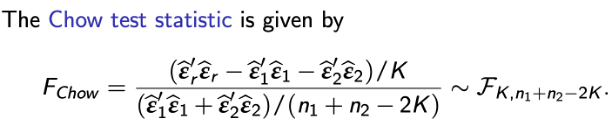
Confidence intervals

Due to the symmetry of the t-distribution we have that:
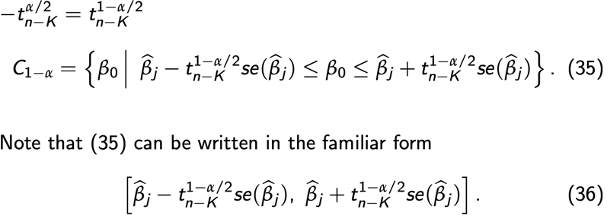
Maximum likelihood estimation - recap
Likelihood function
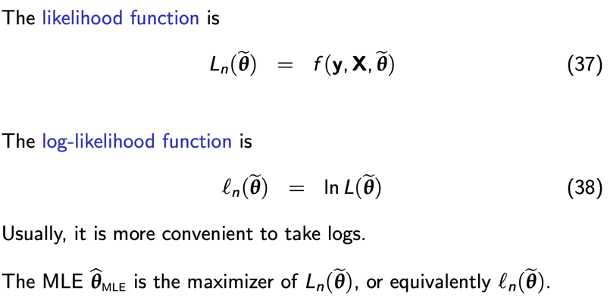
Log-likelihood function
Log-likelihood
First and second derivative

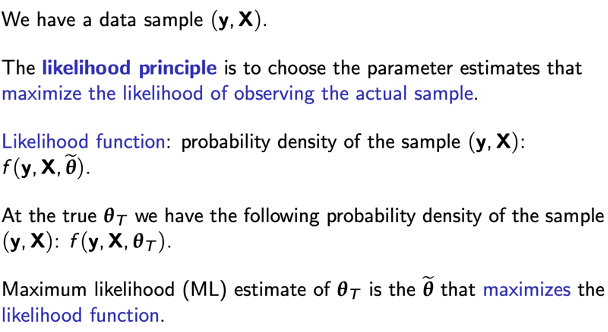
Maximum likelihood estimation
Model
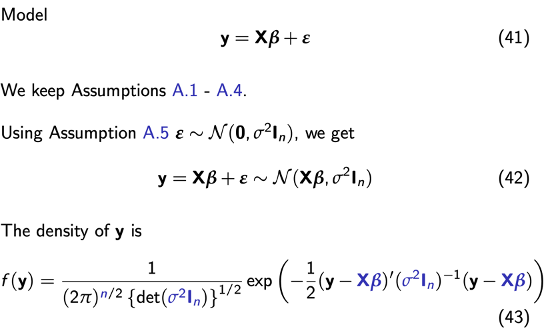
Likelihood function
Model

Log-likelihood function
Model
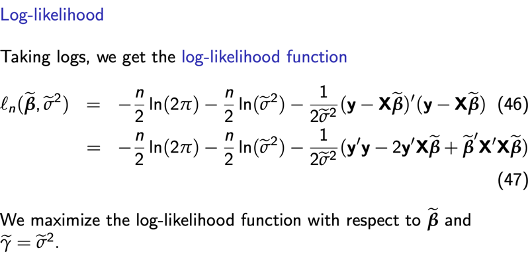
FOCs
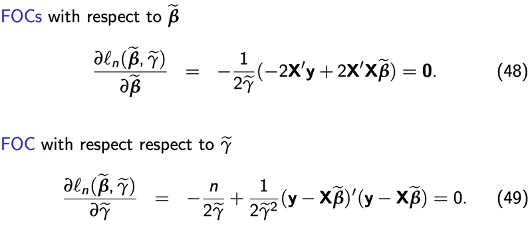
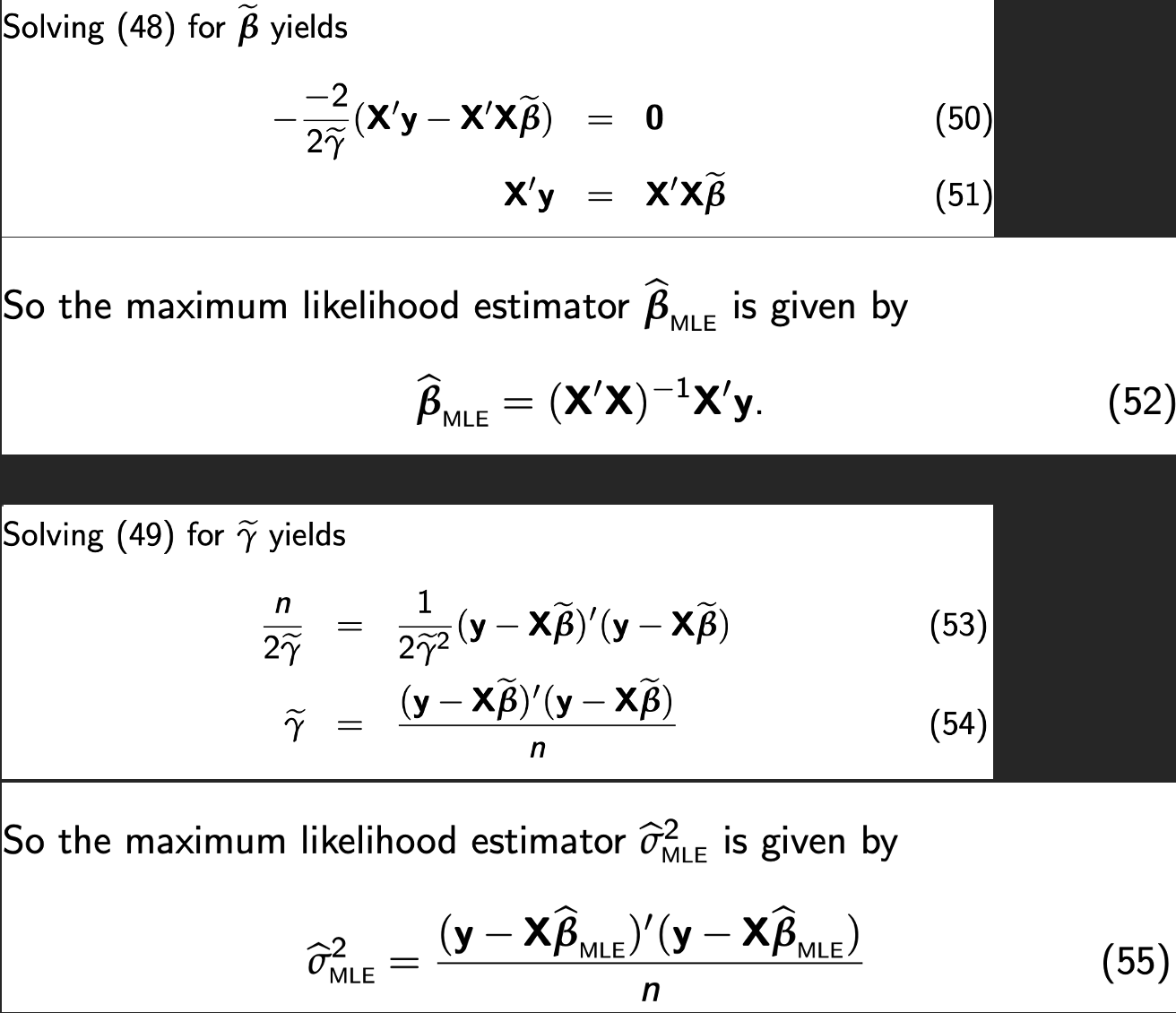
Solving FOCs

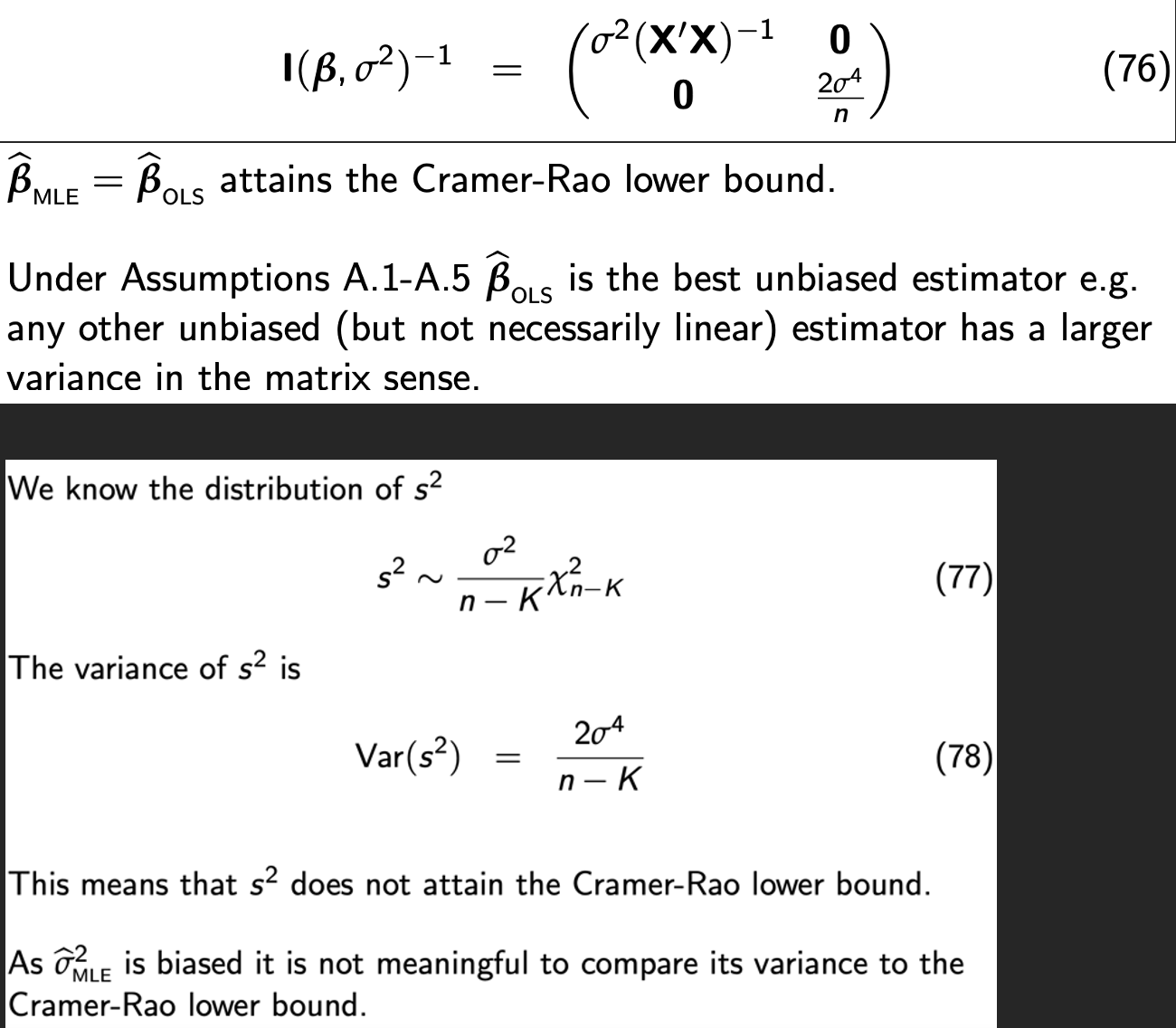
Biased or Unbiased?


Consistency


Expectation
Variance
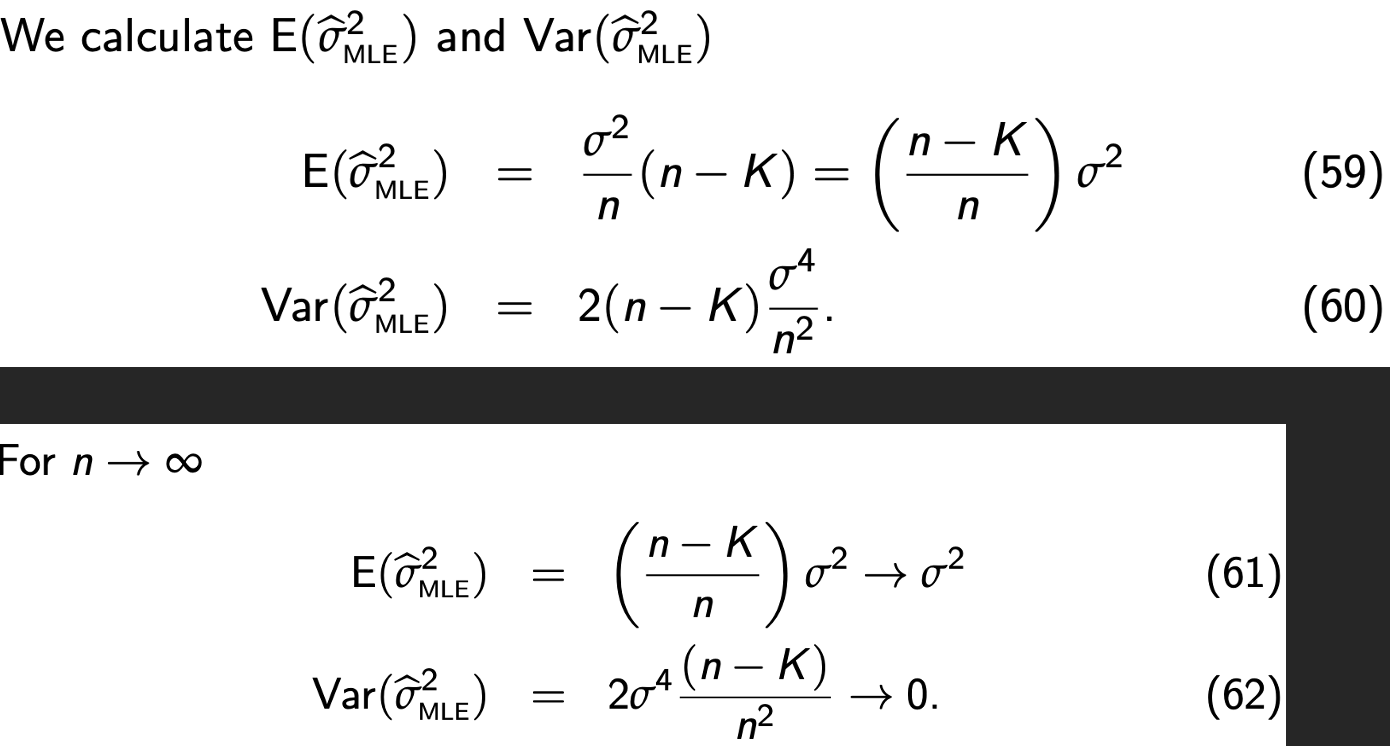
Cramer-Rao lower bound
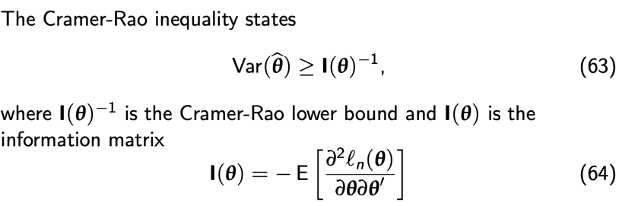
Information matrix
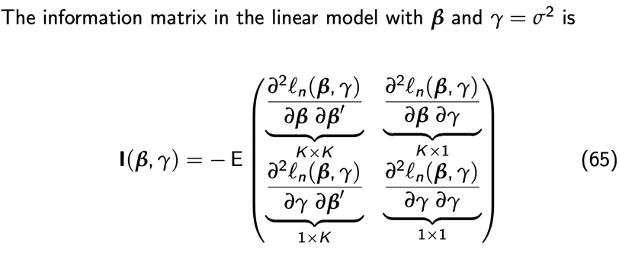
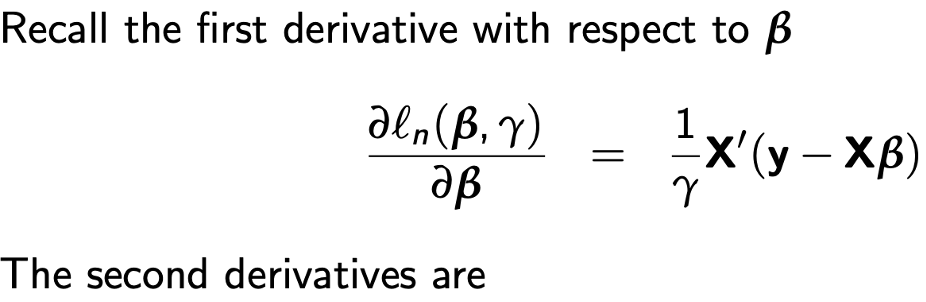
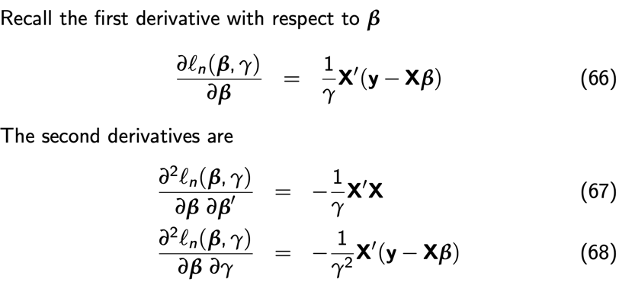
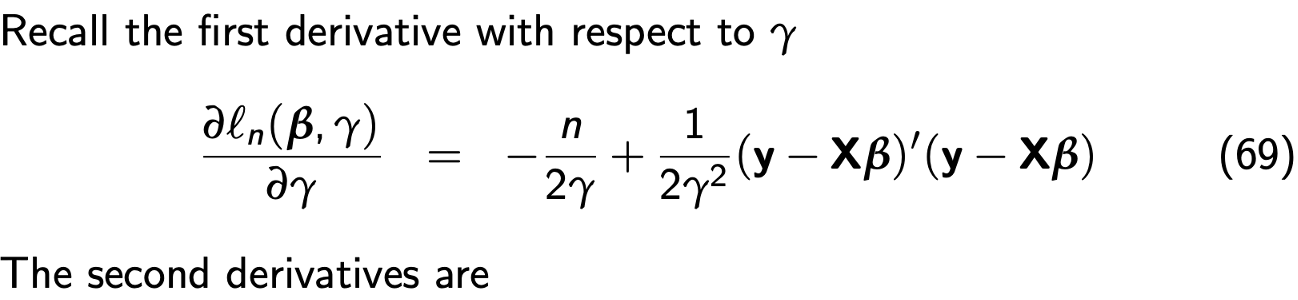
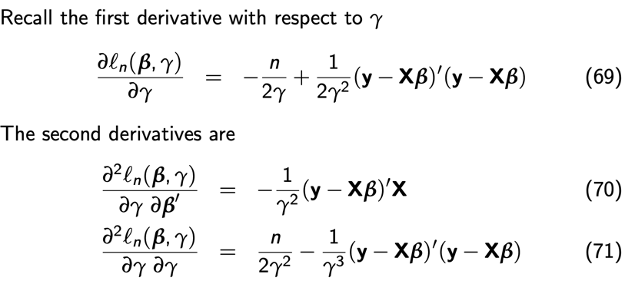
Derivation information matrix

The Cramer-Rao lower bound is
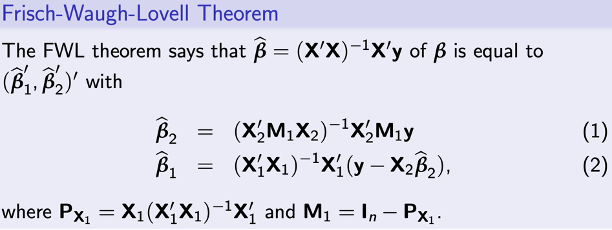
Frisch-Waugh-Lovell Theorem
Motivation and idea
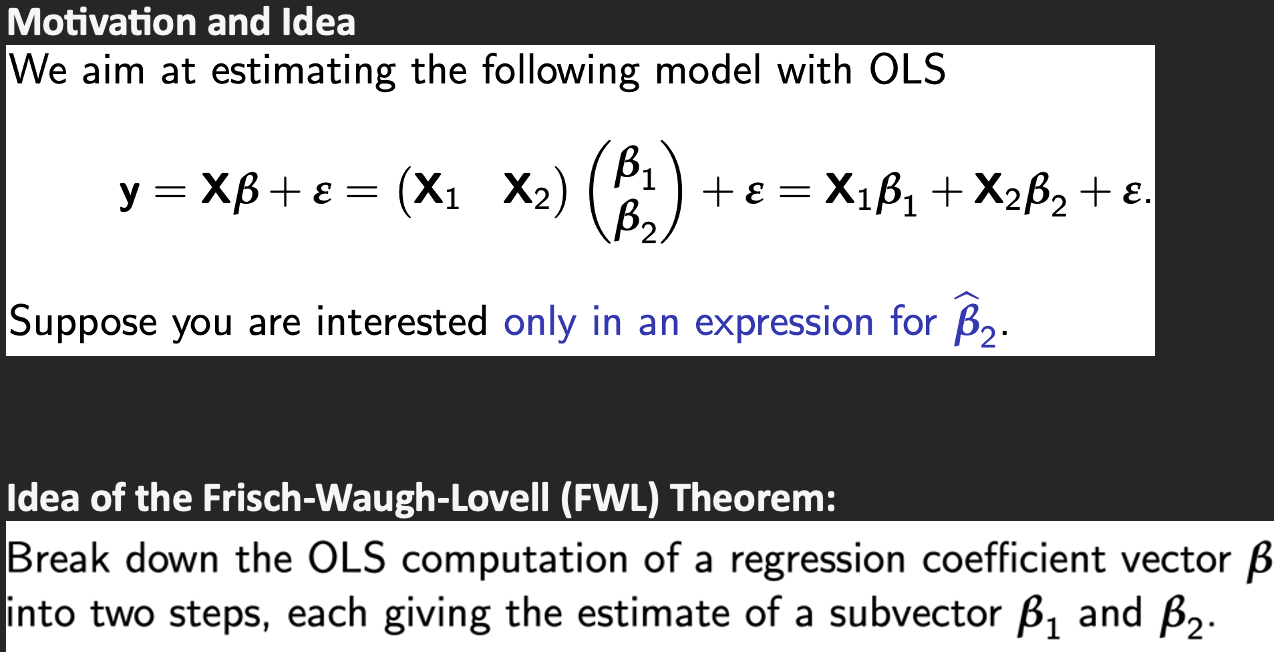
Frisch-Waugh-Lovell Theorem
Frisch-Waugh-Lovell Theorem Simplified

Frisch-Waugh-Lovell Theorem
Interpretation

In empirical research, the true specification of the regressor matrix is unknown:
The empirical researcher can make two mistakes:
1. Include irrelevant regressors
2. Omit relevant regressors
The empirical researcher can make two mistakes:
1. Include irrelevant regressors

The empirical researcher can make two mistakes:
2. Omit relevant regressors

The empirical researcher can make two mistakes
Summary table

Violation of Assumption A.2

Violation of Assumption A.4
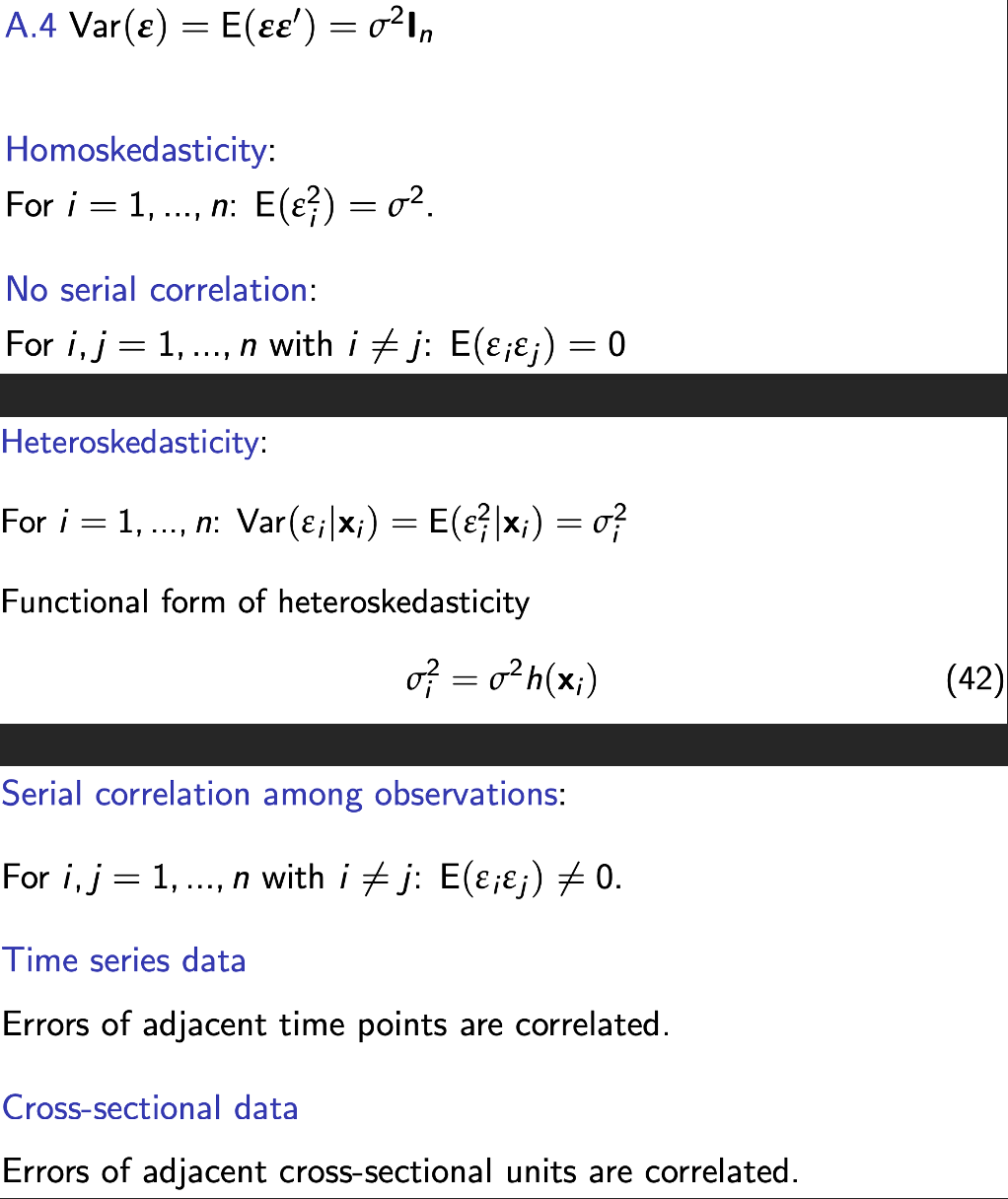
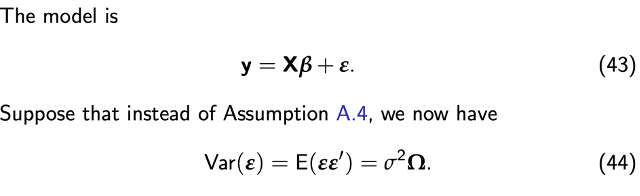
How does this affect the properties of the OLS estimator?

95% CI for β2−β3

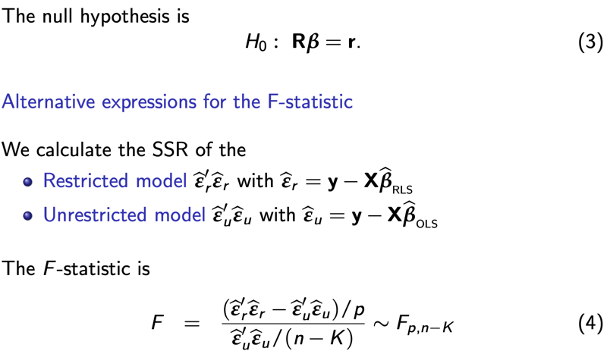
F-test formula for single restriction:
