SCH4U - U6 Organic Chemistry
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
1. Carbon is able to form large numbers of organic compounds because carbon can
a. | form 4 bonds. | d. | the carbon-carbon bond is very stable. |
b. | form single, double and triple bonds. | e. | All of a), b), c) and d). |
c. | form chains, rings, spheres and sheets. | ||
e. | All of a), b), c) and d). |
2. Which compound(s) cannot be classified with organic compounds?
a. | carbohydrates and sugars | d. | graphite |
b. | fats and protein | e. | none of the above |
c. | polyester, wool, and cotton | ||
d. | graphite |
3. What is the general formula for alkenes?
a.CnHn+2 | b.CnH2n+2 | c.CnH2n | d.CnH2n-2 | e.CnHn-2 |
c.CnH2n
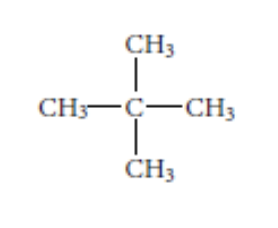
4. Which compound is a constitutional isomer of the compound shown below?
a.propane | b.butane | c.methane | d.pentane | e.hexane |
d.pentane
5. Isomers in which molecules form mirror images of each other around a carbon atom are _____________.
a. | enantiomers | d. | structural isomers |
b. | diastereomers | e. | none of the above |
c. | constitutional isomers | ||
a. | enantiomers |
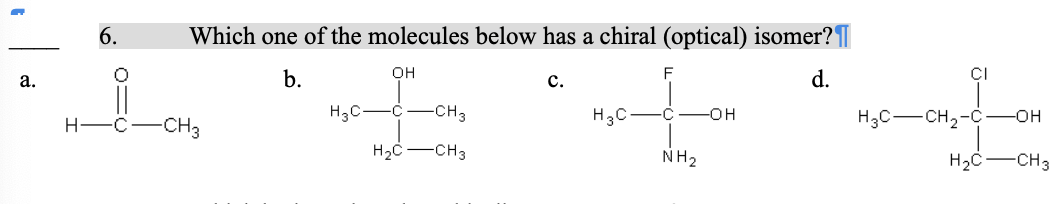
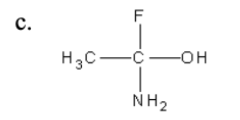
6. Which one of the molecules below has a chiral (optical) isomer?
c.
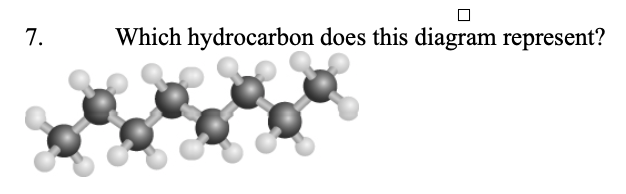
7. Which hydrocarbon does this diagram represent?
a. | pentane | c. | heptane | e. | decane |
b. | methylheptane | d. | octane | ||
d. | octane |
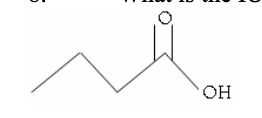
8. What is the IUPAC name of the following compound?
a. | pentanoic acid | c. | propyl methanoate | e. | 3-methylbutanol |
b. | butanoic acid | d. | 2 – oxy butan-1-ol | ||
b. | butanoic acid |
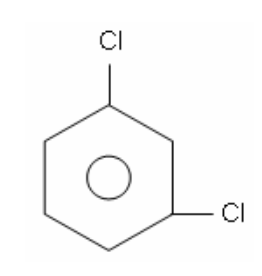
9. What is the IUPAC name of the following molecule?
a. | 1, 2-dichlorobenzene | c. | 1, 5-dibenzochloride | e. | 1, 5-dichlorobenzene |
b. | 1, 3-dichlorobenzene | d. | 1, 3-dibenzochloride | ||
b. | 1, 3-dichlorobenzene |
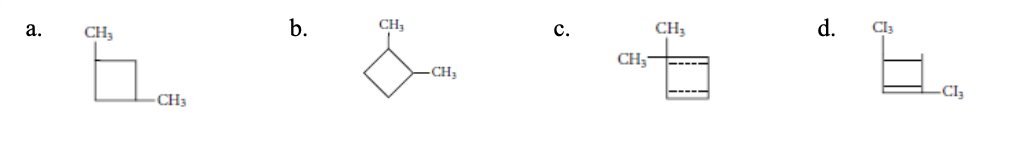
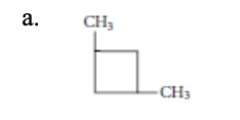
10. Which of the following molecular structures represents 1,3-dimethylcyclobutane?
a. | b. | c. | d. |
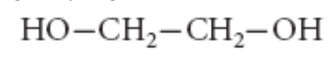
11. Ethylene glycol acts as antifreeze and is used in automobiles and computers. It is also used for preserving body organs and in the manufacture of capacitors. Its structure is shown below.
The IUPAC name of this compound is
a. | ethanol | d. | 2,2-dihydroxyethane-1,2-diol |
b. | ethane-1,2-diol | e. | diethane-1,2-diol |
c. | 1-hydroxyethane-1,2-diol | ||
b. | ethane-1,2-diol |
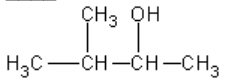
12. What is the correct name for the compound?
a. | 2-methyl-3-butanol | d. | 3-methyl-2-butanol |
b. | 2-pentanol | e. | none of these |
c. | isobutanol | ||
d. | 3-methyl-2-butanol |
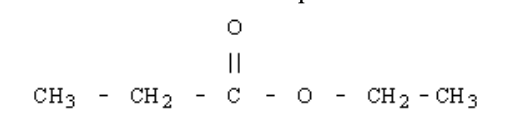
13. This fruit-scented compound is generally used in ice creams and other food stuffs as a flavouring agent. The IUPAC name of the compound is
a. | propyl ethanoate | c. | ethyl propanoate | e. | methyl propanoate |
b. | propane ethanoate | d. | ethane propanoate | ||
c. | ethyl propanoate |
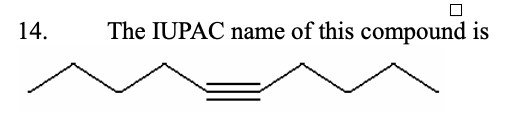
14. The IUPAC name of this compound is
a.non-5-yne | b.hept-3-yne | c.oct-4-yne | d.dec-5-yne | e.hex-4-yne |
d.dec-5-yne
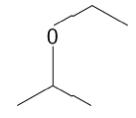
15. What is the IUPAC name for the following compound?
a.2-ethoxypropene | b.2-ethoxypropane | c.2-methoxyethene | d.2-methoxyethane |
b.2-ethoxypropane
16. What is the other name for methoxymethane?
a.2-methoxyethane | b.toluene | c.methyl alcohol | d.dimethyl ether |
d.dimethyl ether
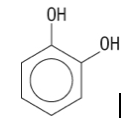
17. What is the name of the following molecule?
a.toluene-1,2-diol | b.hexen-1,6-diol | c.1,2-dihydroxybenzene | d.none of the above |
c.1,2-dihydroxybenzene |
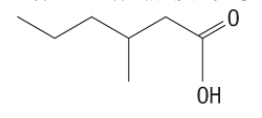
18. What is the IUPAC name for the following compound?
a. | 3-propylbutanoic acid | c. | 4-methylhexanoic acid |
b. | 3-methylhexanoic acid | d. | 4-propylbutanoic acid |
b. | 3-methylhexanoic acid |
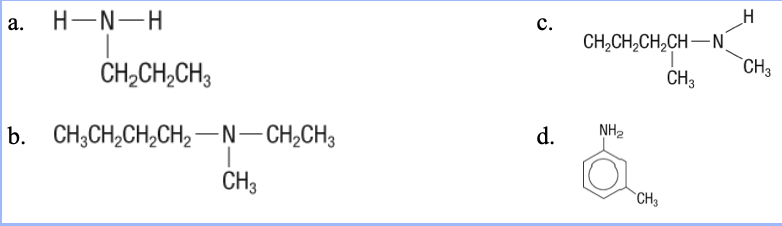
19. What is the structure of N-methylpentan-2-amine?
a. | c. |
b. | d. |
c.
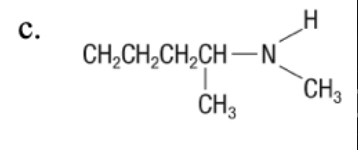
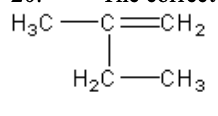
20. The correct name for the compound given is which of the following?
a. | 2-methyl-1-butene | c. | 2-ethyl-1-propene | e. | 2-ethyl-1-pentene |
b. | pentene | d. | 3-methyl-2-butene | ||
a. | 2-methyl-1-butene |
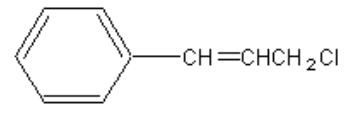
21. The correct name for compound shown is which of the following?
a. | chloropropylbenzene | c. | 1-chloro-3-phenyl-3-propene |
b. | 3-phenyl-1-choloropropyne | d. | 3-chloro-1-phenyl-1-propene |
d. | 3-chloro-1-phenyl-1-propene |
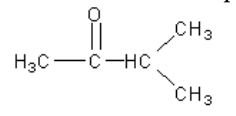
22. What is the proper name for the structure given below?
a. | 3-methyl-2-butanone | c. | 1-ethyl-1-propanone |
b. | 3-pentanone | d. | 1,1-dimethyl-1-propanone |
a. | 3-methyl-2-butanone |
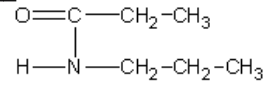
23. The correct name for the compound given is which of the following?
a. | 3-amino-3-hexanone | c. | N-propylpropanamide |
b. | ethyl ethanamide | d. | N-ethylethanamide |
c. | N-propylpropanamide |
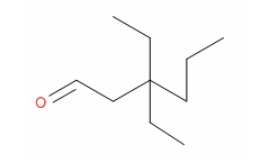
24. The correct IUPAC name for the following structure is
a. | 4,4-diethylheptanal | c. | 3-ethal-3-propylpentane |
b. | 3-ethyl-3-ethonehexane | d. | 3,3-diethylhexanal |
d. | 3,3-diethylhexanal |
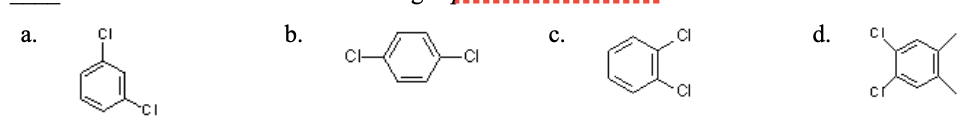
25. Which of the following is paradichlorobenzene?
a. | b. | c. | d. |
b.
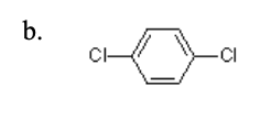
26. How many functional groups are there in this compound?
a.One | b.Two | c.Three | d.Four | e.Five |
b.Two
27. Which functional group does the compound CH3CH2NHCH(CH3)2 possess?
a. | aldehyde | c. | carboxylic acid | e. | alkyne |
b. | amine | d. | ether | ||
b. | amine |
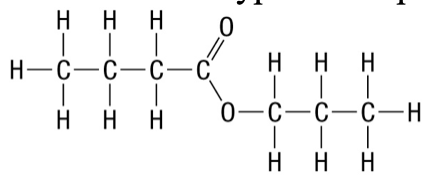
28. What type of compound is the following structure?
a. | ether | c. | ester | e. | amide |
b. | alcohol | d. | carboxylic acid | ||
c. | ester |
29. A carboxyl group is always ____________________.
a. | at the end of a chain | d. | on either side of a chain |
b. | at the beginning of a chain | e. | anywhere on the chain |
c. | in the middle of a chain | ||
a. | at the end of a chain |
30. Sodium benzoate is widely used as a preservative in food. Sodium benzoate is a(n) _______.
a. | ester | c. | amide | e. | alcohol |
b. | amide | d. | carboxylic acid | ||
a. | ester |
31. Which of the following carboxylic acids is the least soluble in water?
a. | CH3 COOH | c. | C3H7COOH | e. | HCO2H |
b. | C2 H5COOH | d. | C4 H9 COOH | ||
d. | C4 H9 COOH |
Why does the boiling point of an alkane increase as its chain length increases?
a.
There is more hydrogen bonding.
b.
There are hydrogen atoms available for hydrogen bonds to form.
c.
The molecules are highly branched.
d.
The strength of the dispersion forces increases with increased molecular size.
e.
None of the above are correct.
c. | The molecules are highly branched. |
33. Which of the following compounds has the lowest boiling point?
a. | pentane | c. | 2-methylpentane |
b. | 2,2-dimethylpropane | d. | hexane |
b. | 2,2-dimethylpropane |
34. The boiling points of alkanes and their associated substituted hydrocarbons can be compared. Differences are explained mostly by polarity and intermolecular forces. Assuming each compound has the same number of C atoms in the base chain, which is the correct arrangement in order from lowest boiling point to highest boiling point?
lowest b.p.---->---------------->---------------->---------------->---------------->----highest b.p | ||||
i) alkane | alcohol | carbonyl | amide | carboxylic acid |
ii) alkane | carbonyl | alcohol | carboxylic acid | amide |
ii) amide | carbonyl | carboxylic acid | alcohol | alkane |
iv) carbonyl | alcohol | carboxylic acid | amide | alkane |
a.i) is correct. | b.ii) is correct. | c.iii) is correct. | d.iv) is correct. |
b.ii) is correct.
ii) alkane | carbonyl | alcohol | carboxylic acid | amide |

35. Which statement is INCORRECT concerning these two molecules with the same formula, C2H6O?
a. | Compound (II) will more likely be soluble in water than compound (I). |
b. | Compound (I) will have a lower boiling point than compound (II). |
c. | Hydrogen bonding will be the most likely for compound (II). |
d. | Compound (II) will evaporate at a faster rate than that of compound (I) at a given temperature. |
d. | Compound (II) will evaporate at a faster rate than that of compound (I) at a given temperature. |
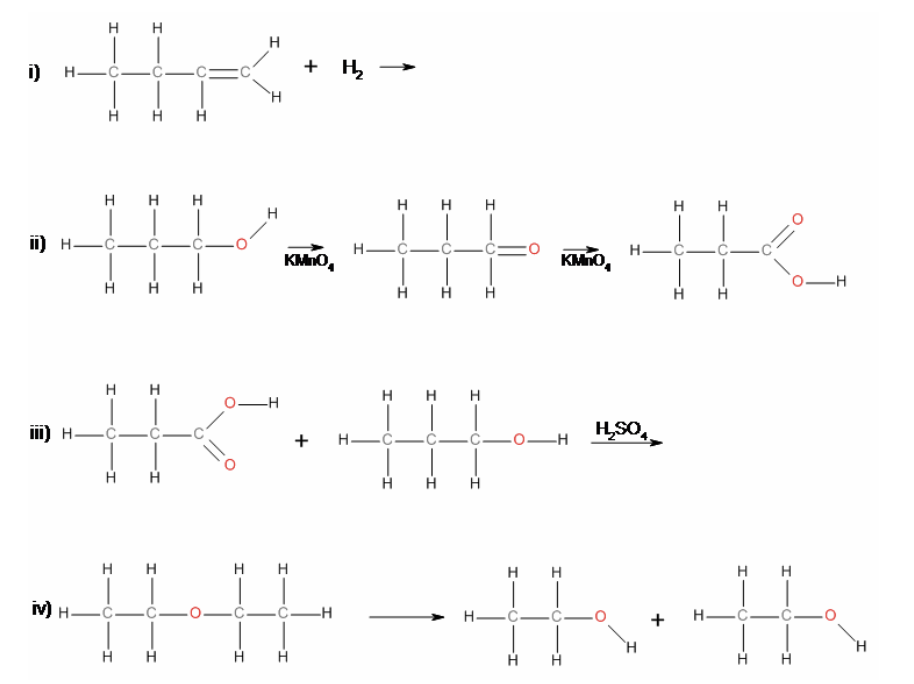
36. Reaction i) is an example of a
a. | elimination | c. | substitution | e. | hydrolysis |
b. | addition | d. | condensation | f. | oxidation |
b. | addition |
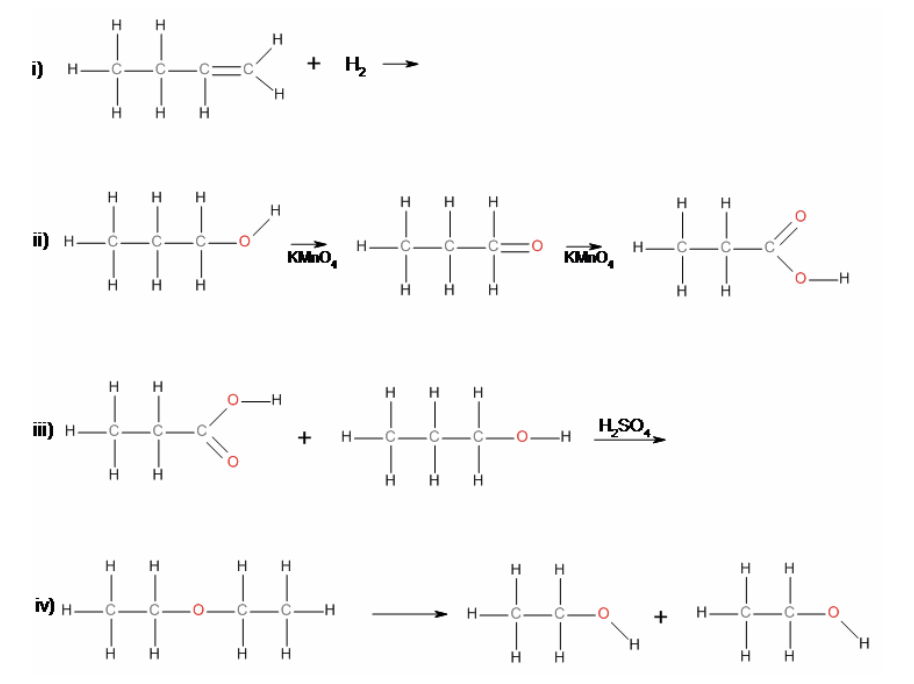
37. Reaction ii) is an example of a
a. | elimination | c. | substitution | e. | hydrolysis |
b. | addition | d. | condensation | f. | oxidation |
f. | oxidation |
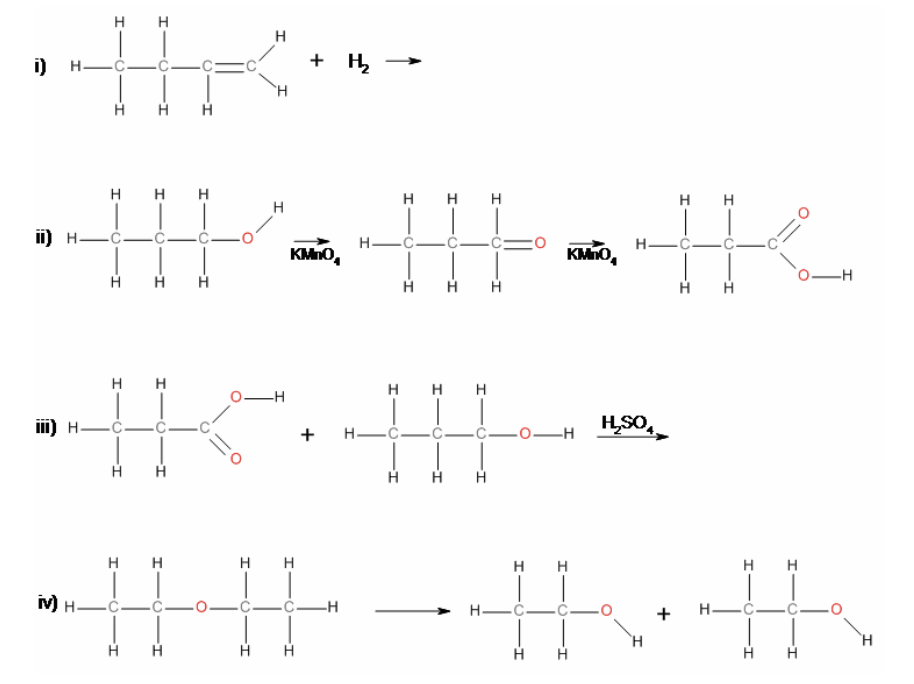
38. Reaction iii) is an example of a
a. | elimination | c. | substitution | e. | hydrolysis |
b. | addition | d. | condensation | f. | oxidation |
b. | addition |
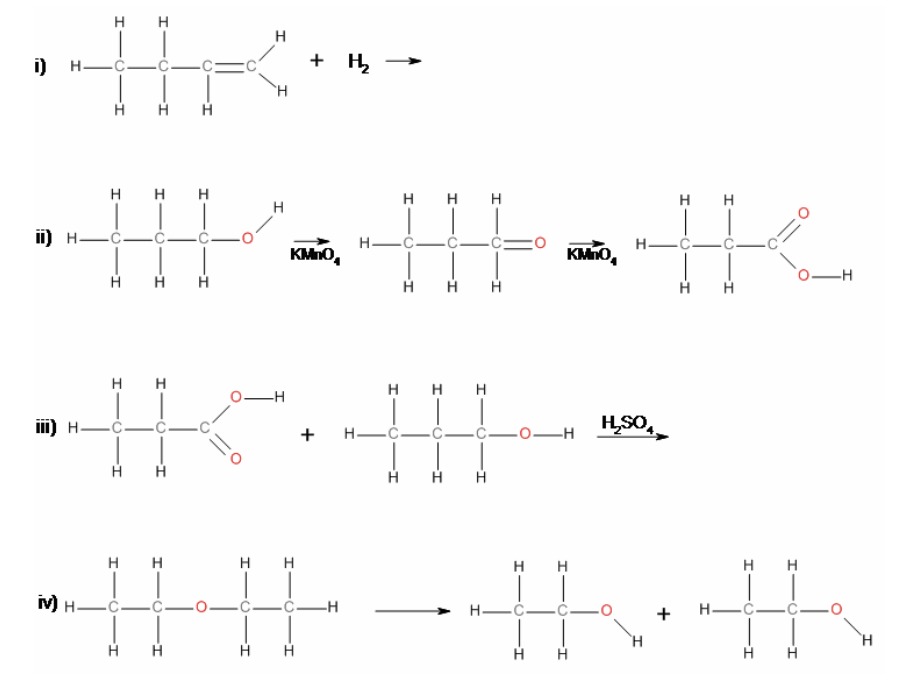
39. Reaction iv) is an example of a
a. | elimination | c. | substitution | e. | hydrolysis |
b. | addition | d. | condensation | f. | oxidation |
e. | hydrolysis |
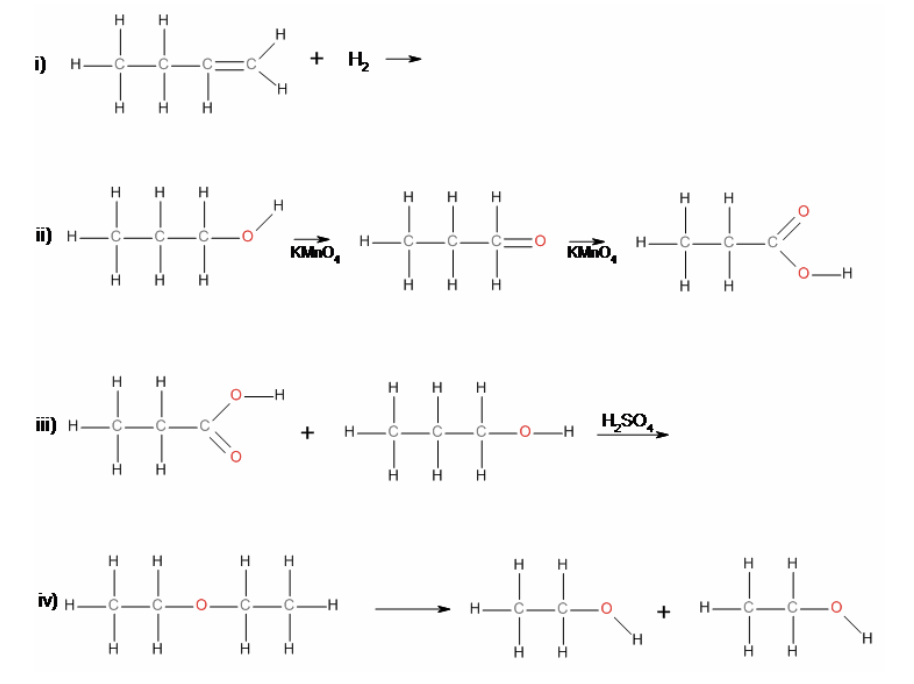
40. In reaction iii), the product is
a. | propyl butanoate. | c. | propyl propanoate. | e. | None of a), b), c) or d). |
b. | ethyl propanoate. | d. | butyl propanoate. | ||
c. | propyl propanoate. |
41. In the presence of UV light, the following reaction occurred:
CH4 + Cl2 ---> CH3Cl + HCl
What type of reaction does this represent?
a. | esterification | c. | hydrolysis | e. | elimination |
b. | substitution | d. | addition | ||
b. | substitution |
42. Which of these is NOT true regarding elimination reactions?
a. | They can be thought of as the reverse of an addition reaction. |
b. | Atoms are removed from an organic molecule to form a double bond. |
c. | Carbon atoms in the organic product are bonded to more atoms than were the carbon atoms in the organic reactant. |
d. | Alcohols can undergo elimination reactions to form alkenes. |
e. | Haloalkanes can undergo elimination reactions to form alkenes. |
c. | Carbon atoms in the organic product are bonded to more atoms than were the carbon atoms in the organic reactant. |
43. Which of these does NOT occur in a substitution reaction?
a. | two compounds react to form two different compounds |
b. | carbon atoms are bonded to a different number of atoms in the product than in the reactant |
c. | a hydrogen atom or functional group is replaced by a different atom or functional group |
d. | aromatic hydrocarbons will undergo substitution reactions with chlorine and bromine in the presence of a catalyst |
e. | a haloalkane can undergo a substitution reaction with a hydroxide ion to produce an alcohol |
b. | carbon atoms are bonded to a different number of atoms in the product than in the reactant |
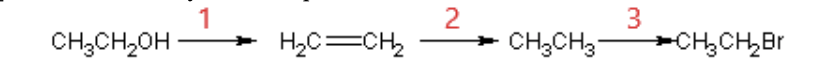
44. The synthesis sequence shown here is best described as which of the following?
a. | (1) Dehydration; (2) halogenation; (3) hydrogenation |
b. | (1) Hydrogenation; (2) dehydration; (3) halogenation |
c. | (1) Hydrogenation; (2) halogenation; (3) dehydration |
d. | (1) Halogenation; (2) hydrogenation; (3) dehydration |
e. | (1) Dehydration; (2) hydrogenation; (3) halogenation |
e. | (1) Dehydration; (2) hydrogenation; (3) halogenation |
45. In a hydration reaction, an alkene is converted to what type of compound?
a.an amide | b.an alkyne | c.an alcohol | d.an aldehyde |
c.an alcohol
46. When two alcohols undergo a condensation, what is formed?
a. | liquid alcohol | c. | an ester | e. | an ether |
b. | a ketone | d. | an aldehyde | ||
e. | an ether |
47. Which reaction is the “reverse” of a condensation reaction?
a. | esterification | c. | addition | e. | oxidation |
b. | hydrolysis | d. | substitution | ||
b. | hydrolysis |
48. The reaction below is catalized by H2SO4.
CH3COOH + CH3CH2OH ----> CH3COOCH2CH3 + H2O
As well as being a dehydration synthesis, which reaction does this represent?
a. | esterification | c. | addition | e. | elimination |
b. | hydrolysis | d. | oxidation | ||
a. | esterification |
49. When propene is treated with bromine water, Br2(l), in the presence of carbon tetrachloride as a catalyst, the product is:
a. | 1,2–dibromopropane | c. | 2–bromopropane | e. | none of these |
b. | 2,2–dibromopropane | d. | 1–bromopropane | ||
a. | 1,2–dibromopropane |
50. In an oxidation reaction, a carbon atom forms ___i___ bonds to oxygen atoms or ___ii___ bonds to hydrogen atoms. The statement given above is completed by the information in row
Row | i | ii |
A | more | the same |
B | more | fewer |
C | fewer | more |
D | fewer | the same |
E | fewer | fewer |
a. | b. | c. | d. | e. |
b.
B | more | fewer |
51. In a chemical equation, the symbol [O] represents _____________.
a. | an oxidizing agent | d. | catalysis by a strong acid |
b. | a reducing agent | e. | the presence of a base |
c. | an oxygen molecule | ||
a. | an oxidizing agent |
52. Which reactions can be used to characterize addition polymerization?
a. | addition | c. | substitution | e. | substitution |
b. | oxidation | d. | condensation | ||
a. | addition |
53. Nylons are condensation polymers with _________ .
a. | amide linkages | c. | amine linkages | e. | alpha linkages |
b. | ester linkages | d. | beta linkages | ||
a. | amide linkages |
54. Many polymers are more familiarly known by there common names (such as polypropylene), acronyms (such as PVC), or by their patented names (as in Kevlar). The polymerization of which monomer produces PVC?
a. | chloroethene | c. | ester | e. | acrylamide |
b. | styrene | d. | glucose | ||
a. | chloroethene |
55. A copolymer is a polymer in which
a. | all of the monomers are identical. |
b. | there are two or more different monomers. |
c. | the monomers are held together only by ionic bonds. |
d. | there is cross-linking between molecules. |
b. | there are two or more different monomers. |
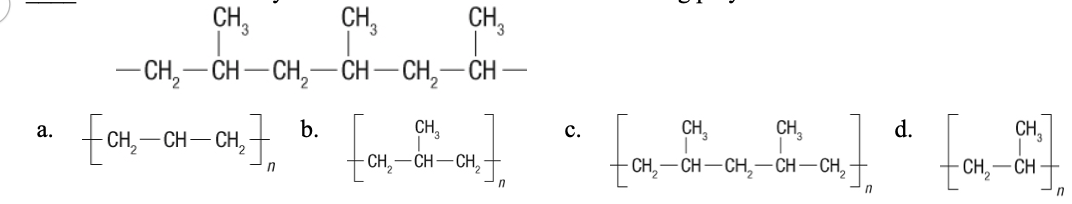
Identify the shorthand notation for the following polymer.
d.
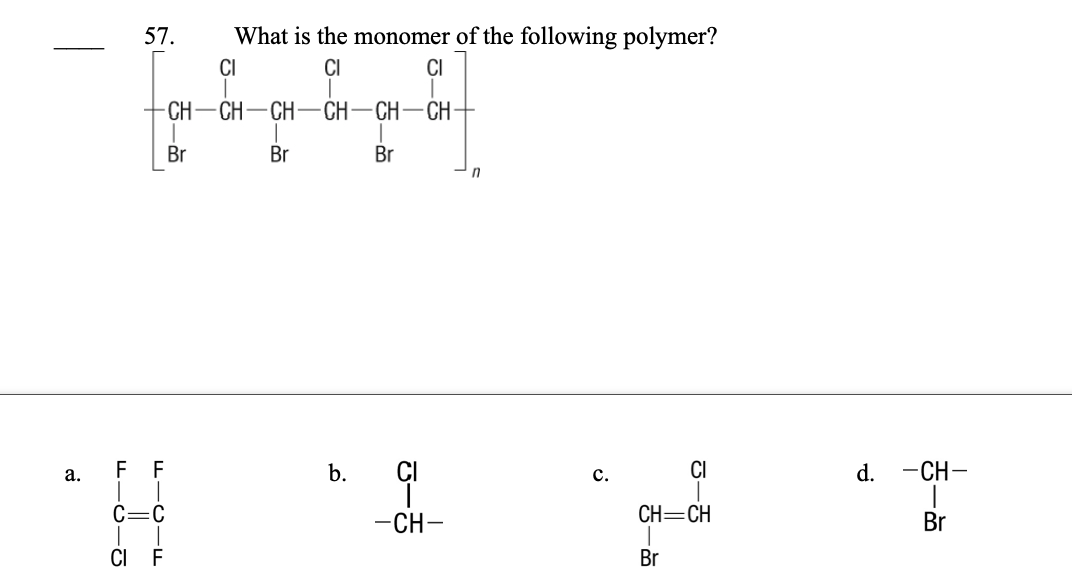
57. What is the monomer of the following polymer?
c,
____ 58. The properties of which of the following makes them excellent substances for making formed products?
a. | natural polymers | c. | copolymers | e. | thermoplastic polymers |
b. | addition polymers | d. | condensation polymers | ||
e. | thermoplastic polymers |

Matching:
59. Aldehydes
60. Ether
61. alkenes
62. amines
63. amides
64. thiols
65. alkyl halides
66. ketones
67. ester
68. alcohols
H
E
F
D
B
J
C
G
I
A
69. Ethane serves as the parent chain for several common organic compounds. Write the structural formulas and give the IUPAC name for the alcohol, the aldehyde, and the carboxylic acid derivatives of ethane. (3 marks)
Bonus (upto 3 marks): Give the common names.
alcohol | aldehyde | carb. acid | |
structural formula | |||
IUPAC name |
1.alchohol: CH3CH2OH ethanol alchohol/booze
aldehyde: CH3CH2O ethanal acetaldehyde
carboxylic acid: CH3CHOOH ethanoic acid acetic acid/vinegar
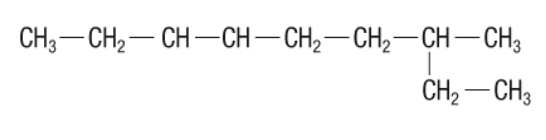
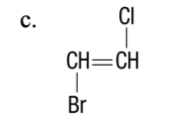
70. Why is 2-ethyl octane NOT an acceptable IUPAC name for the structure provided? Explain and provide the correct IUPAC name for the structure. (2 marks)
because it does not take into account the longest chain for the molecule. The proper name is 3-methyl nonane.
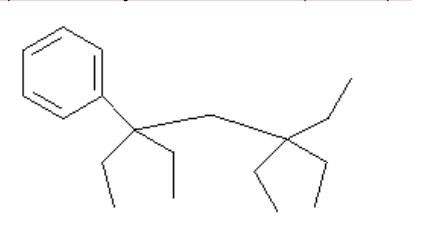
71. The common name for this strucure might be Spot.
a) On the diagram, circle the substituent groups and name them. Do the same for the base chain. (2 marks)
b) Give the systematic name. (2 marks)
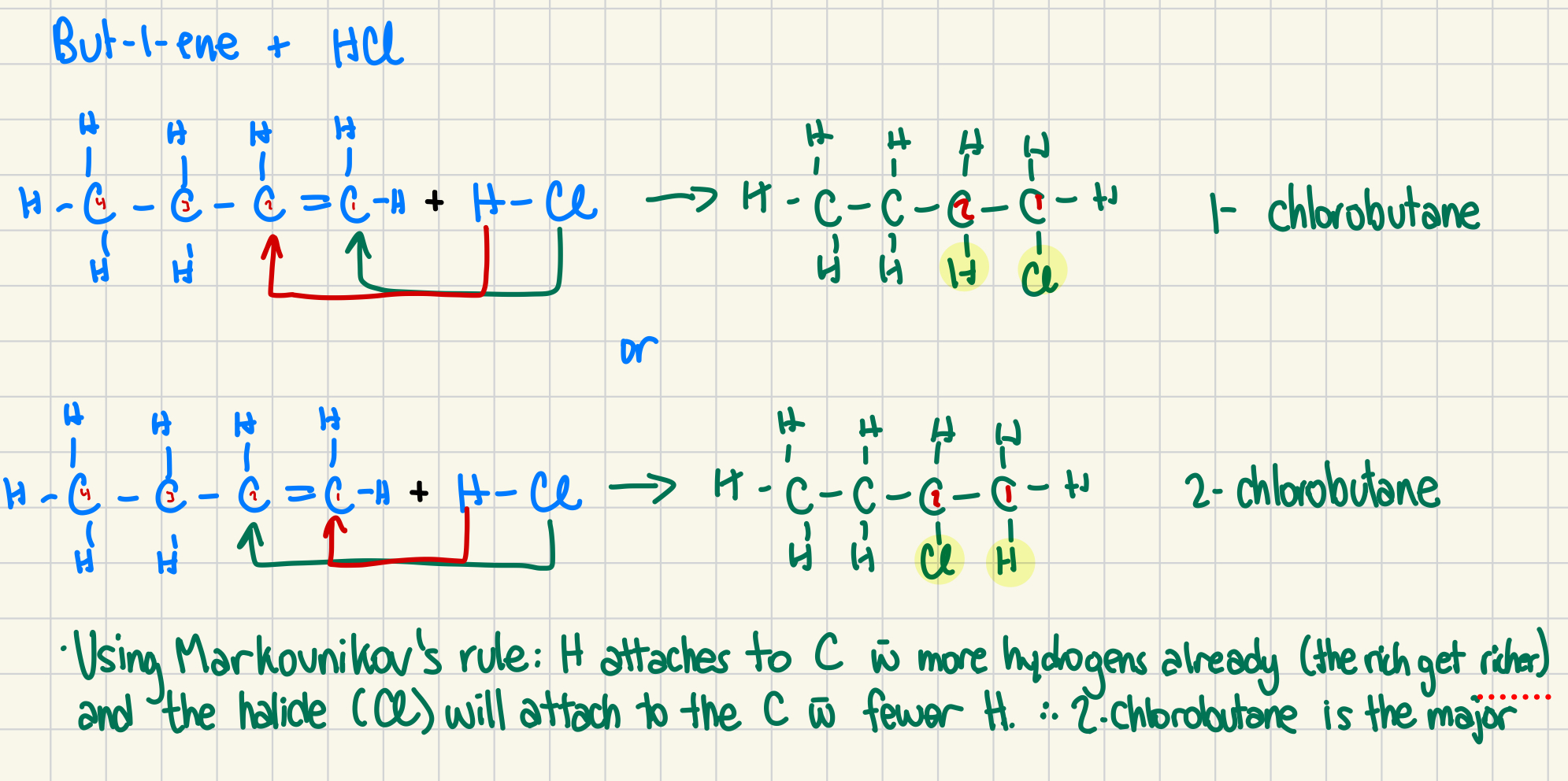
B) 3,5,5-triethyl-3-phenylheptane
72. An addition reaction occurs between but-1-ene and hydrochloric acid. Give the structural diagram for the reaction and both possible products, and indicate which product should be the major one. (4 marks)
73. Draw the structural formula for the following compounds. For C-H, show only the C- (omit the H atoms). (4 marks)
(a) butanoic acid
(b) 1,3-dibromopentane
(c) 3-isopropylhex-1-ene
(d) cis-pent-2-ene
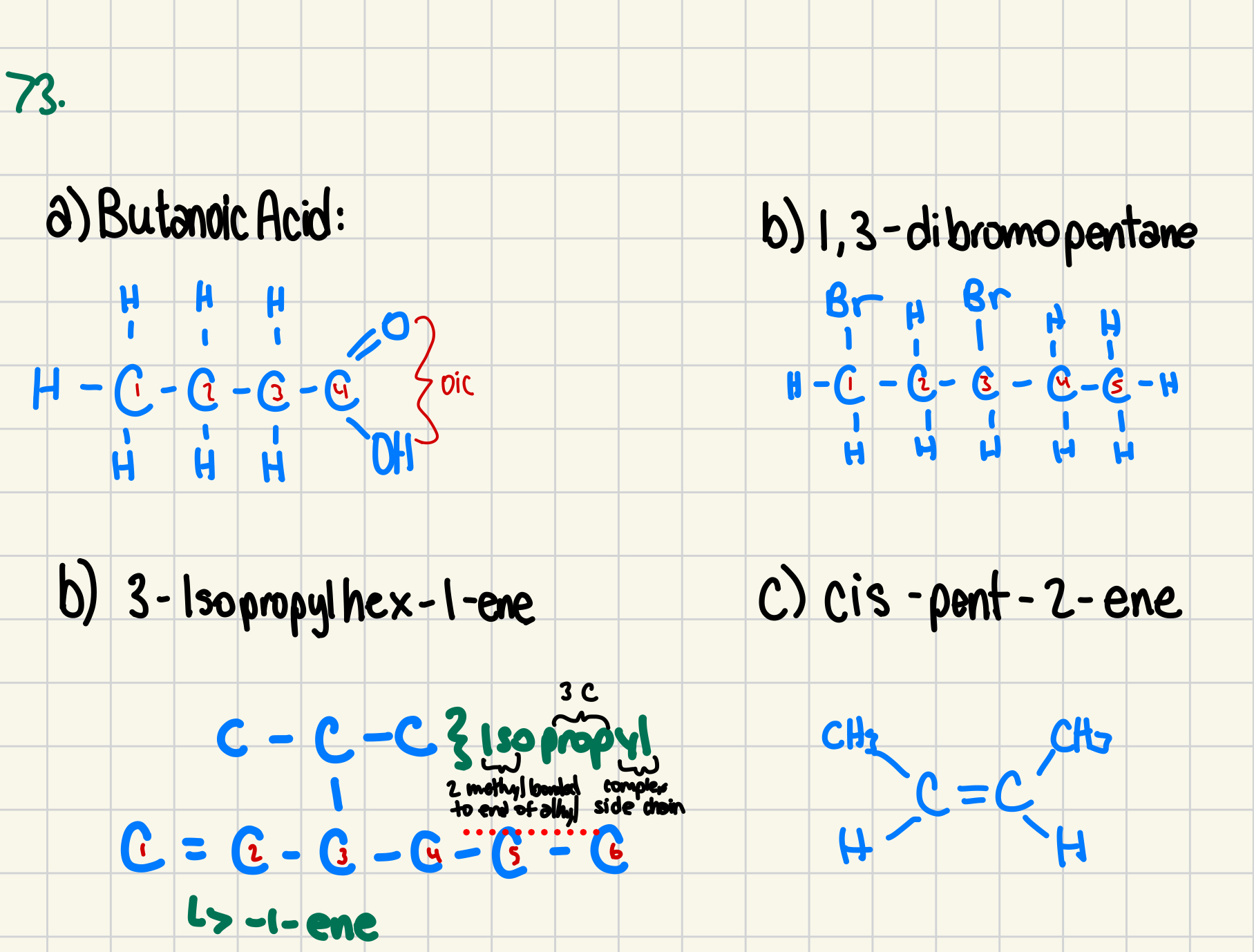
74. When a hydrocarbon burns in an excess of oxygen, it produces carbon dioxide and water. Write the balanced chemical equation for the complete combustion of pentene. (2 marks)
2C5H10(g) + 15O2(g) → 10CO2(g) + 10H2O(g)
b) incomplete combustion: products such as CO or C form in addition to water and carbon dioxide
-water gets first crack at the oxygens
75. Organic chemists tend to look at redox reactions in terms of oxygen and hydrogen and the localized electron density around the carbon backbone. Explain how an oxidation reaction is different from a reduction reaction. (3 marks)
In organic chemistry, an oxidation reaction occurs when a carbon atom forms more bonds to oxygen or fewer bonds to hydrogen. This means the carbon becomes more electron-deficient. In contrast, a reduction reaction takes place when a carbon atom forms fewer bonds to oxygen or more bonds to hydrogen, increasing the electron density around the carbon. Organic chemists focus on these changes in bonding and electron density to track redox processes in carbon-based molecules.
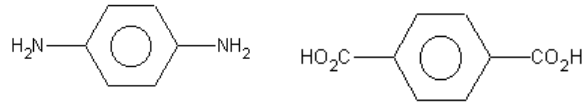
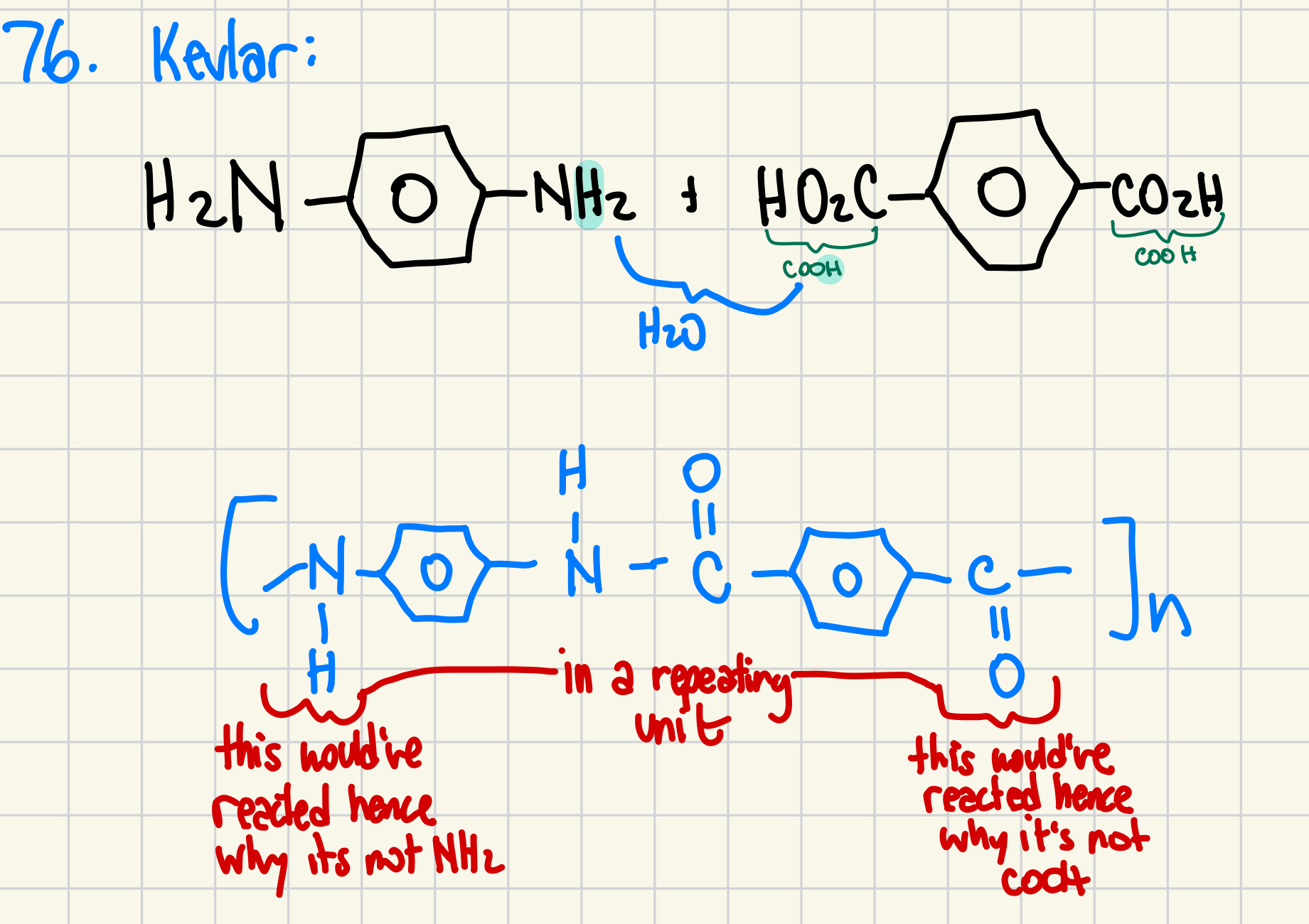
76.
a) Differentiate between an addition polymerization and a condensation polymerization.(2 marks)
b) Kevlar, a strong polymer used in bulletproof vests, is made by the condensation of two monomers:
and
Draw the structure of one subunit of the Kevlar polymer. (2 marks)
c) F2C=CF2 is used to produce the polymer commonly know as Teflon. What kind of polymerization reaction occurs and what is the IUPAC name of the polymer? (2 marks)
a) Addition polymerization is a process where monomers containing carbon-carbon double bonds (C=C) react to form long polymer chains. The double bonds break, and the monomers link together without producing any by-products.
Condensation polymerization involves monomers with two functional groups (such as –COOH and –NH₂ or –OH) that react to form covalent bonds (typically ester or amide bonds). During each bond formation, a small molecule like water (H₂O) is released — this is often a dehydration reaction.
These polymers are typically copolymers, formed from two or more different types of monomers.
c)
An addition polymerization reaction occurs because the monomer F₂C=CF₂ (tetrafluoroethene) contains a carbon–carbon double bond. During the reaction, these double bonds open up and link together to form a long chain, without producing any by-products.
The IUPAC name of the polymer formed is polytetrafluoroethene.
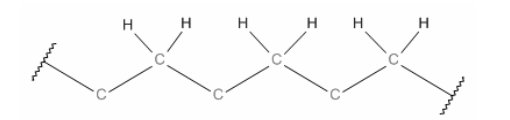
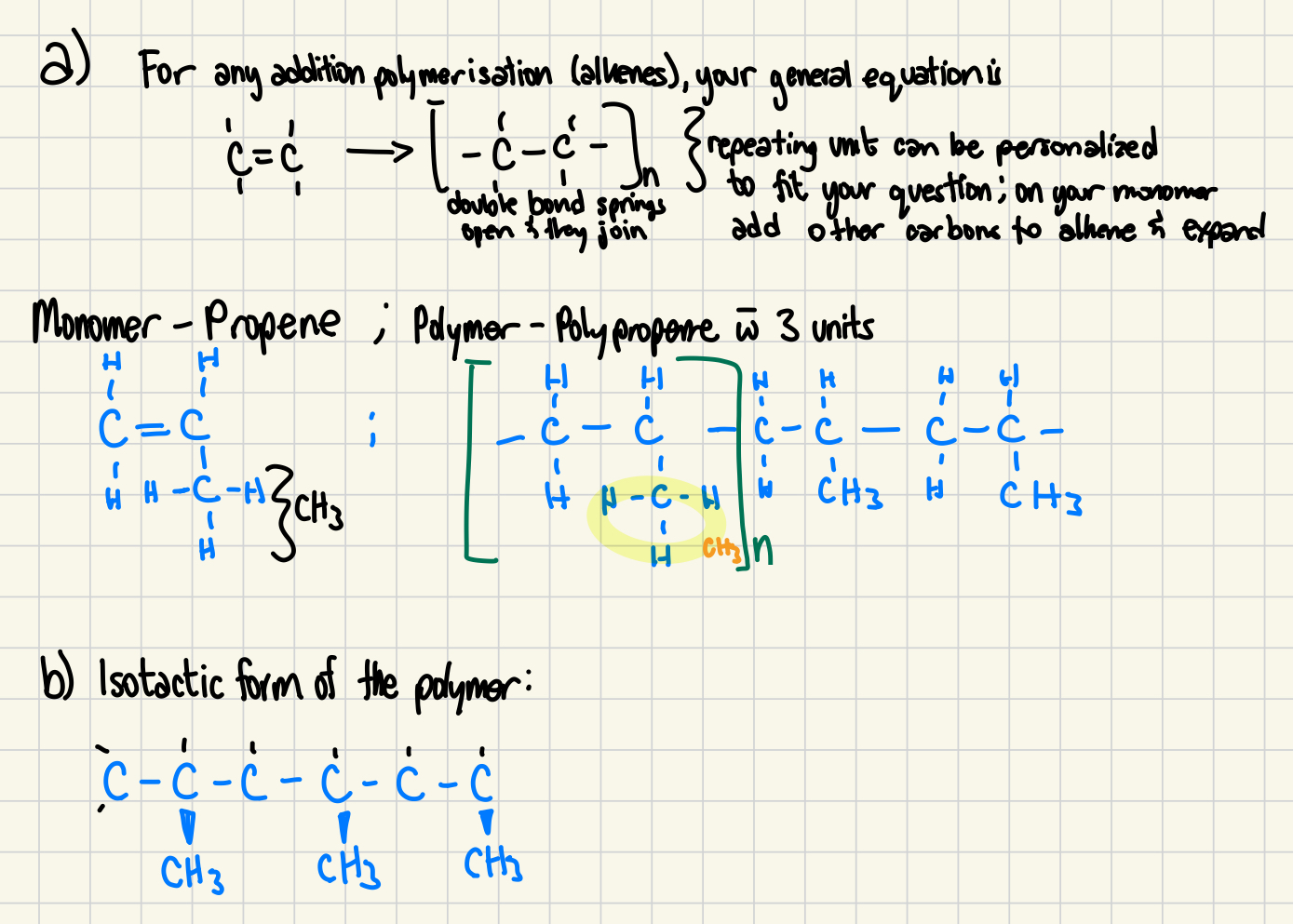
77. Propene (common name propene) is the basis of various polymers used in textiles (fabrics).
a) Draw the structural diagram for the monomer and a section of the polymer with three monomer subunits. (3 marks)
b) Tacticity refers to the arrangement of the substituent groups along the molecule: isotactic, syntactic and atactic polymers exist. Complete the drawing using 3D wedges to show the isotactic form of the polymer. (2 marks)
C-C=C , b) all on the same plane c )intermolecular bonding: isotactic bond is better, atactic poorest
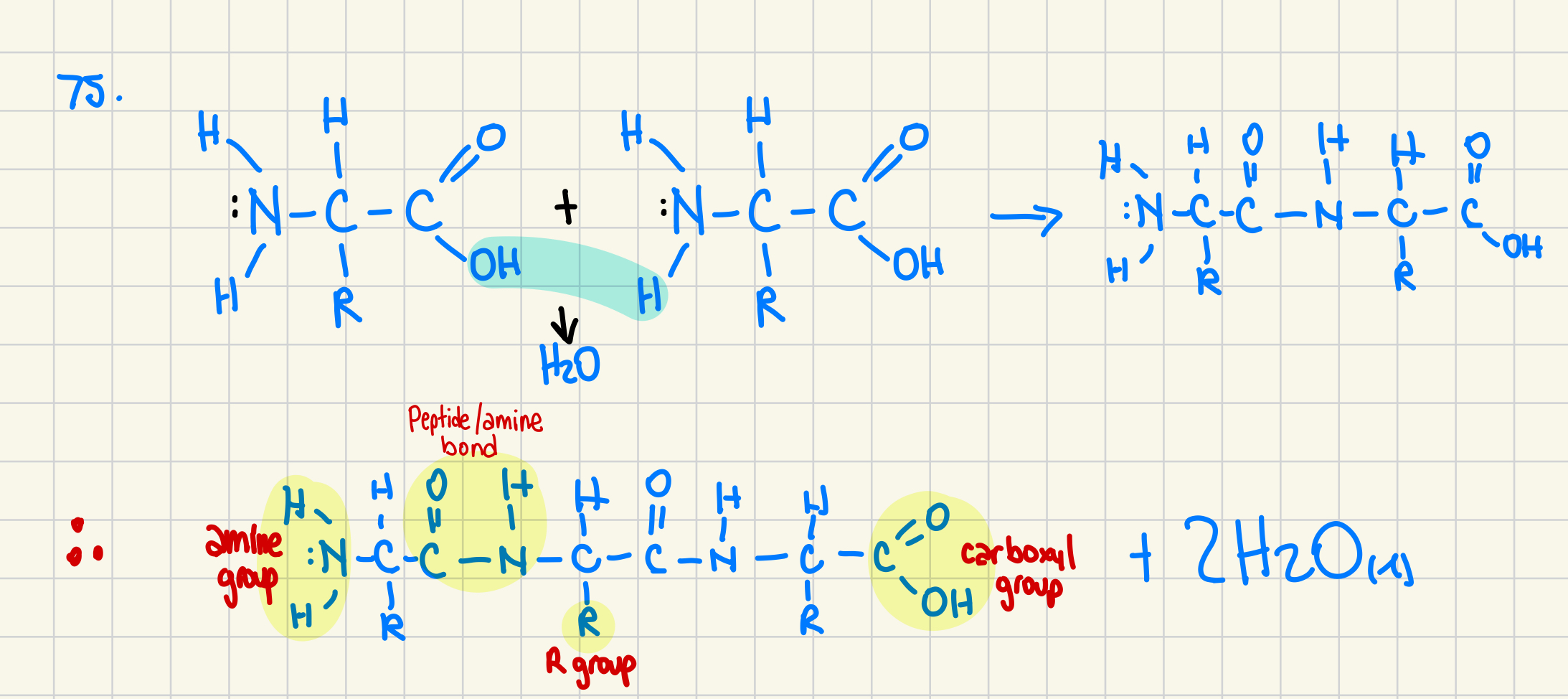
78. There are 20 common amino acids that can be combined in an extraordinary number of combinations to make up all the proteins that are necessary for biological functions in living organisms. Using the generic backbone to the 20 common amino acids, draw a protein that is three amino acids long and identify the functional groups on amino acids. (4 marks)
All 20 amino acids have a carboxyl group (-COOH) and an amino group (-NH2), with a different R group, giving them their distinct properties
that should say amide bond