PATHO Ch. 18 Disorders of the CNS + PNS + Neuromuscular junction
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
traumatic brain injury
mild or severe trauma that can result from a violent impact to the head
focal tbi
specific, local observable lesions. Includes contusions and hematomas.
diffused tbi
multiple areas of the brain are compromised or damaged
closed tbi
the brain is injured but the skull is NOT BROKEN, fractured, or penetrated
- the dura is NOT torn
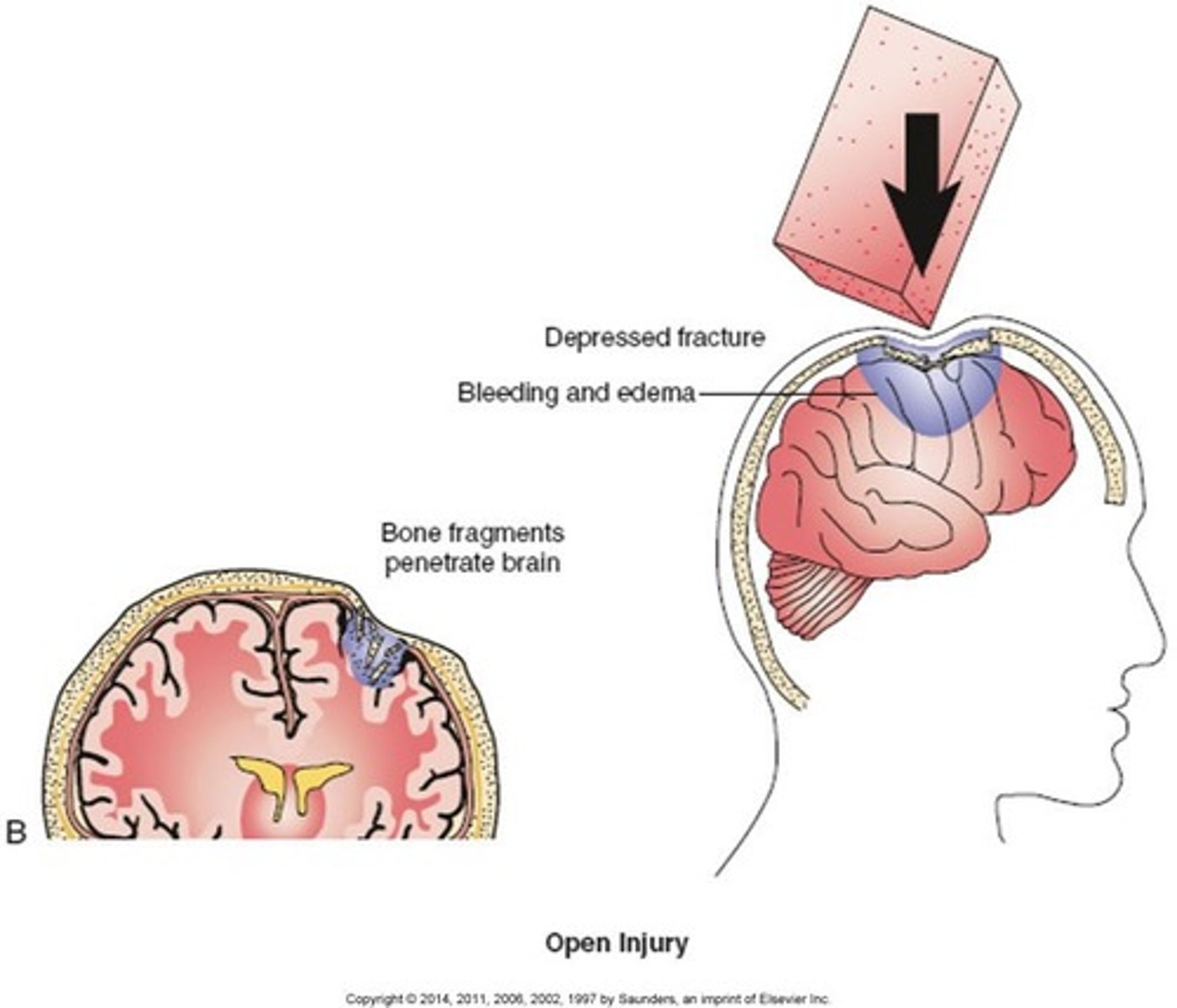
open tbi
brain injury where the skull is broken, fractured, or penetrated.
- the dura is torn in a penetrating injury
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS)
a scale used to assess the consciousness of a patient upon physical examination, typically in patients with neurological concerns or complaints
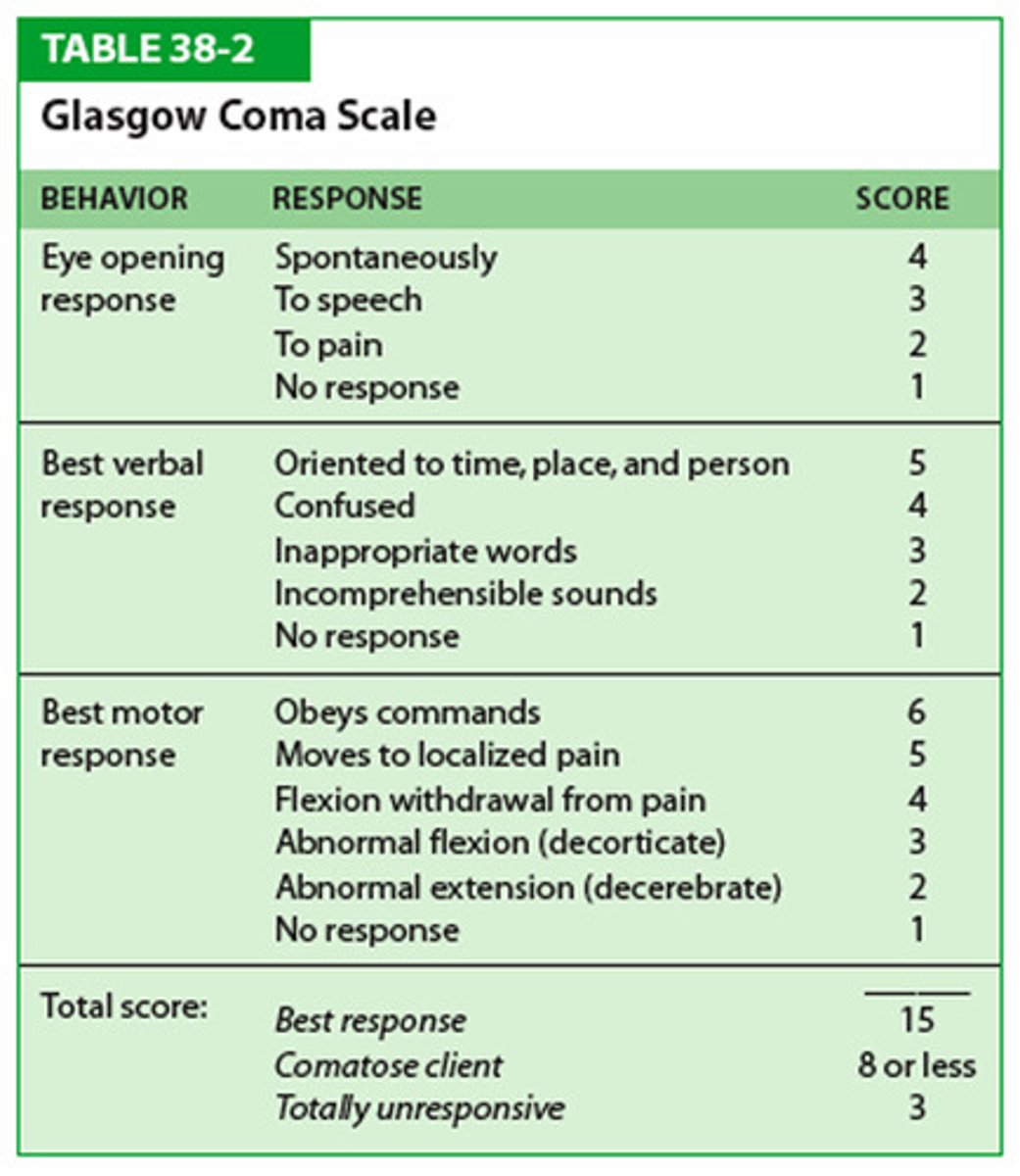
high GCS
better

lower GCS
severe brain injury
hallmark of brain injury
loss of consciousness more than 6 hours
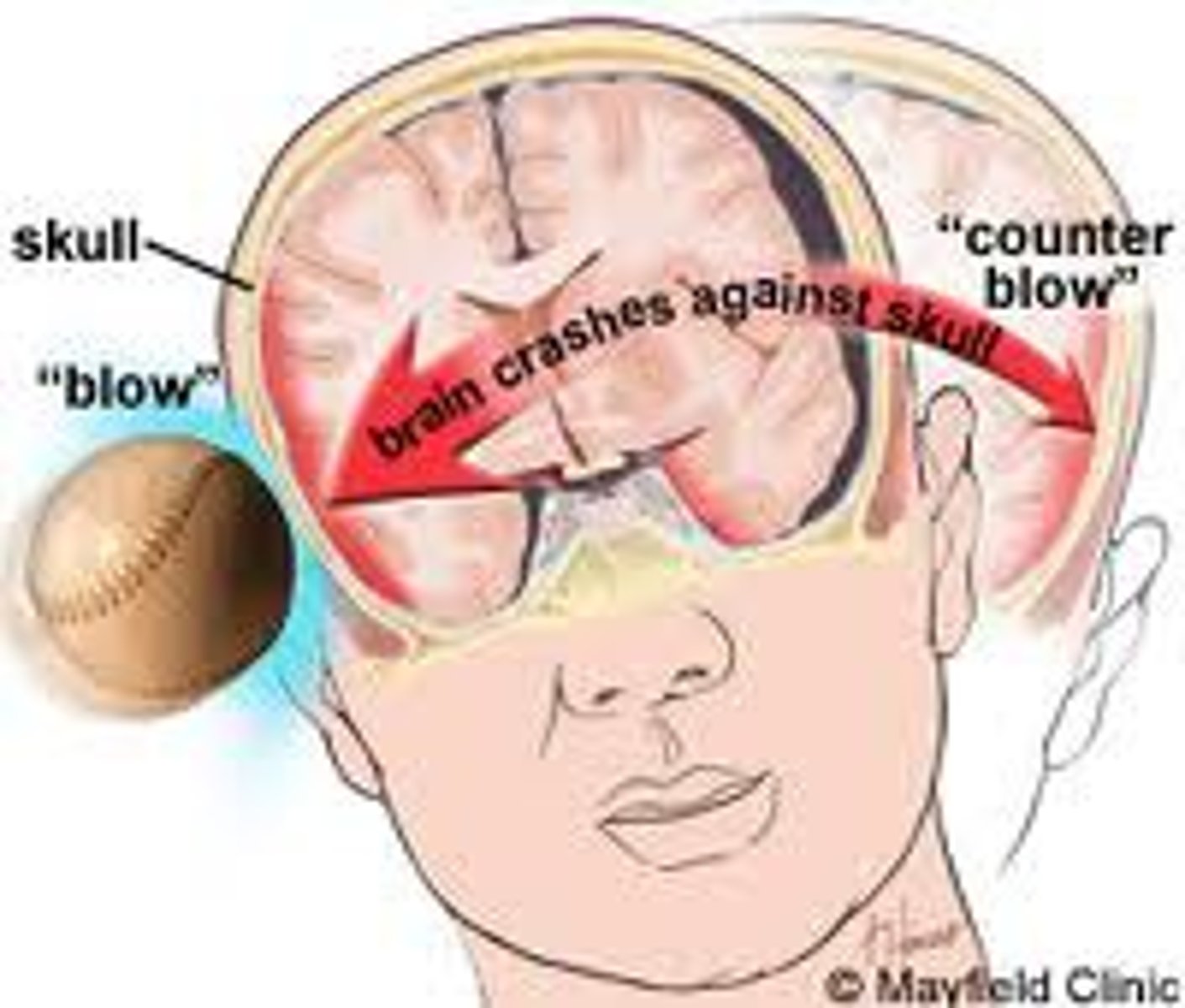
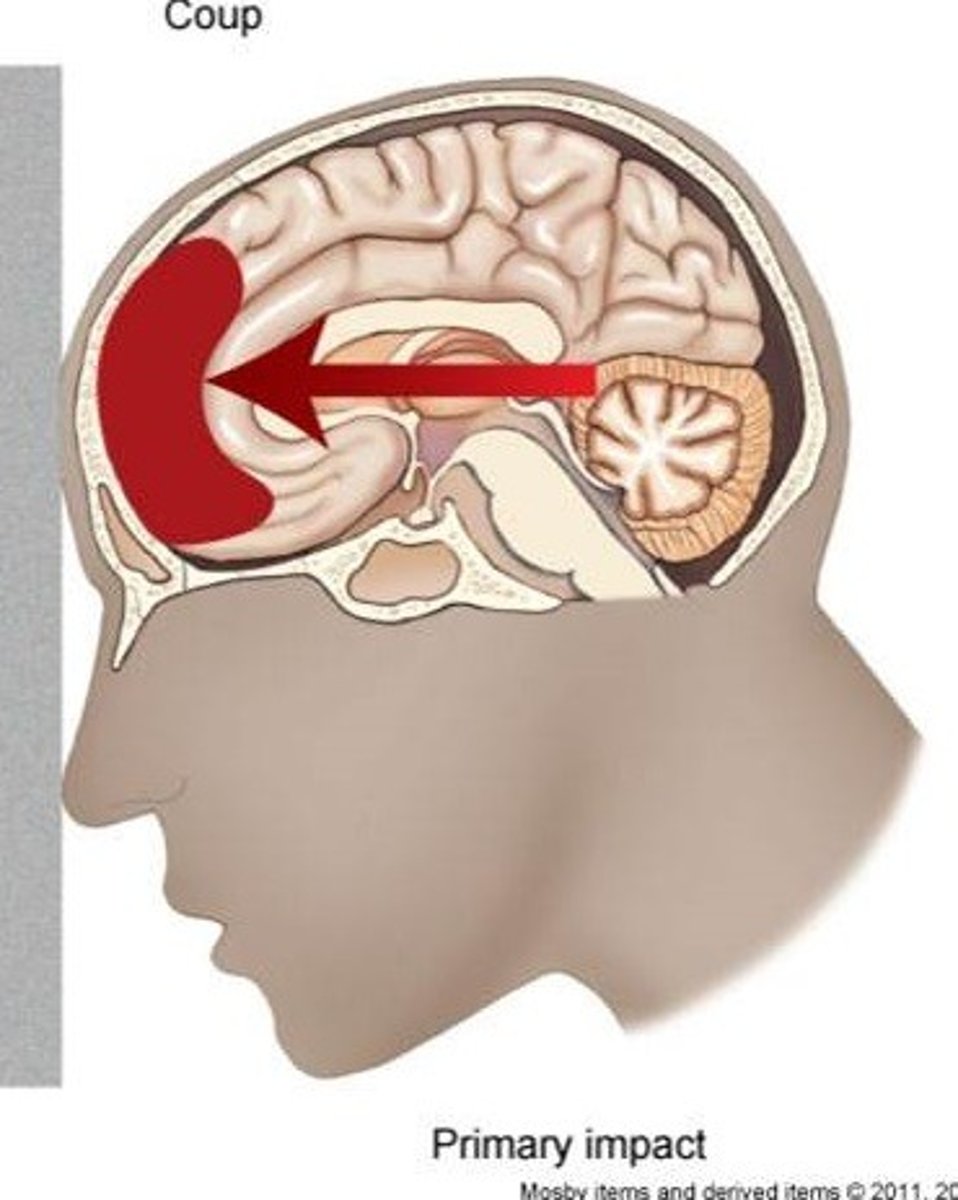
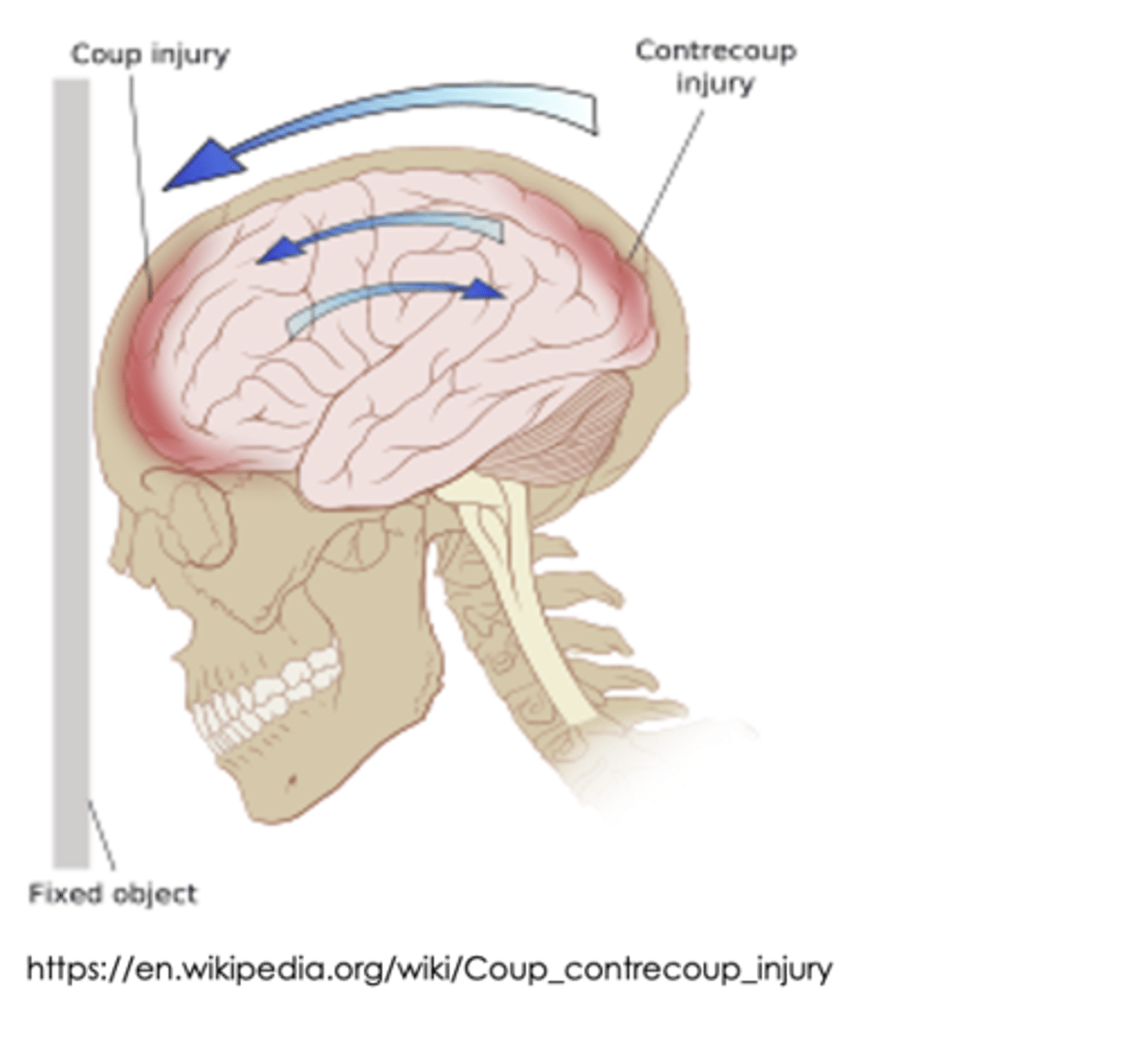
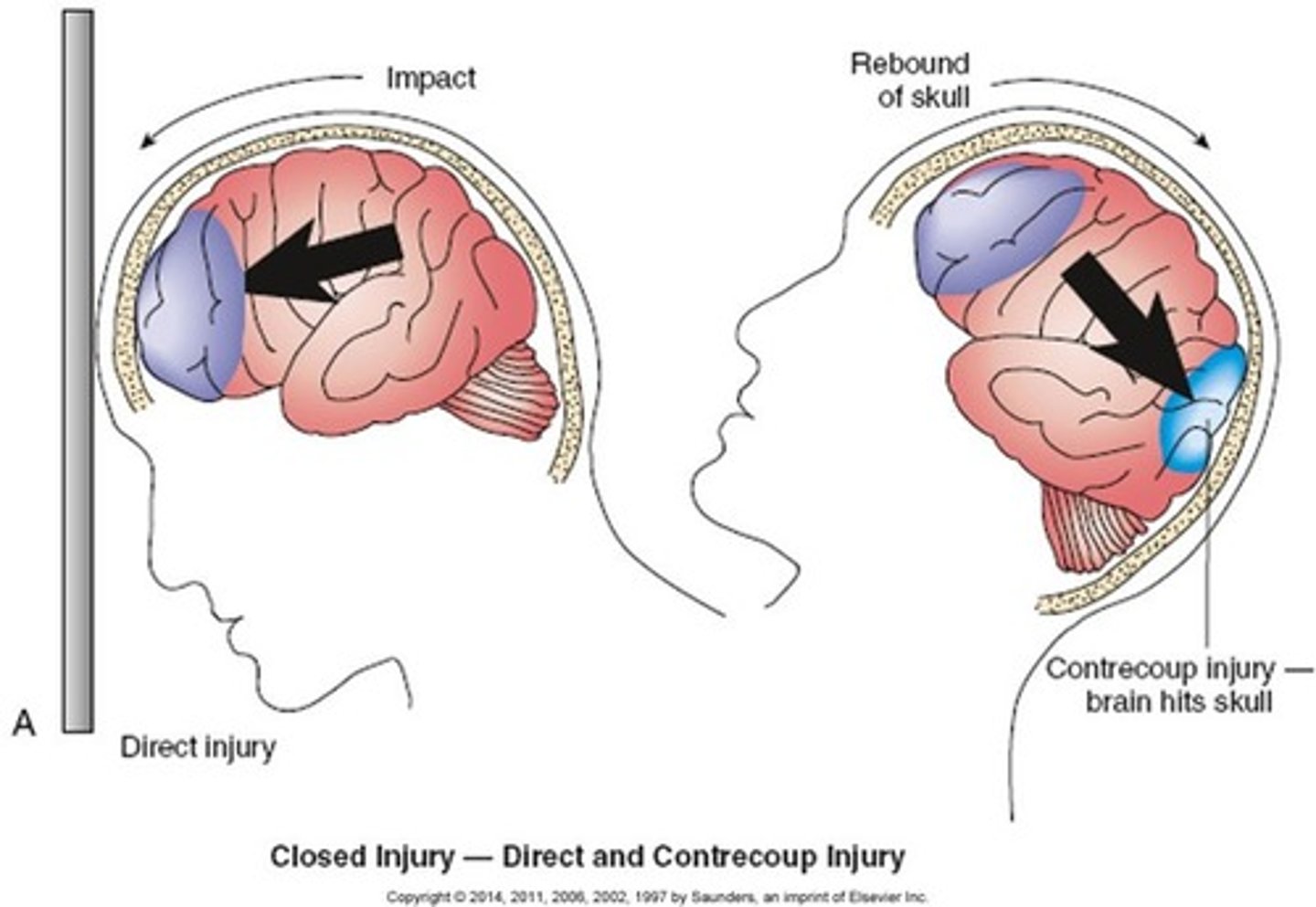
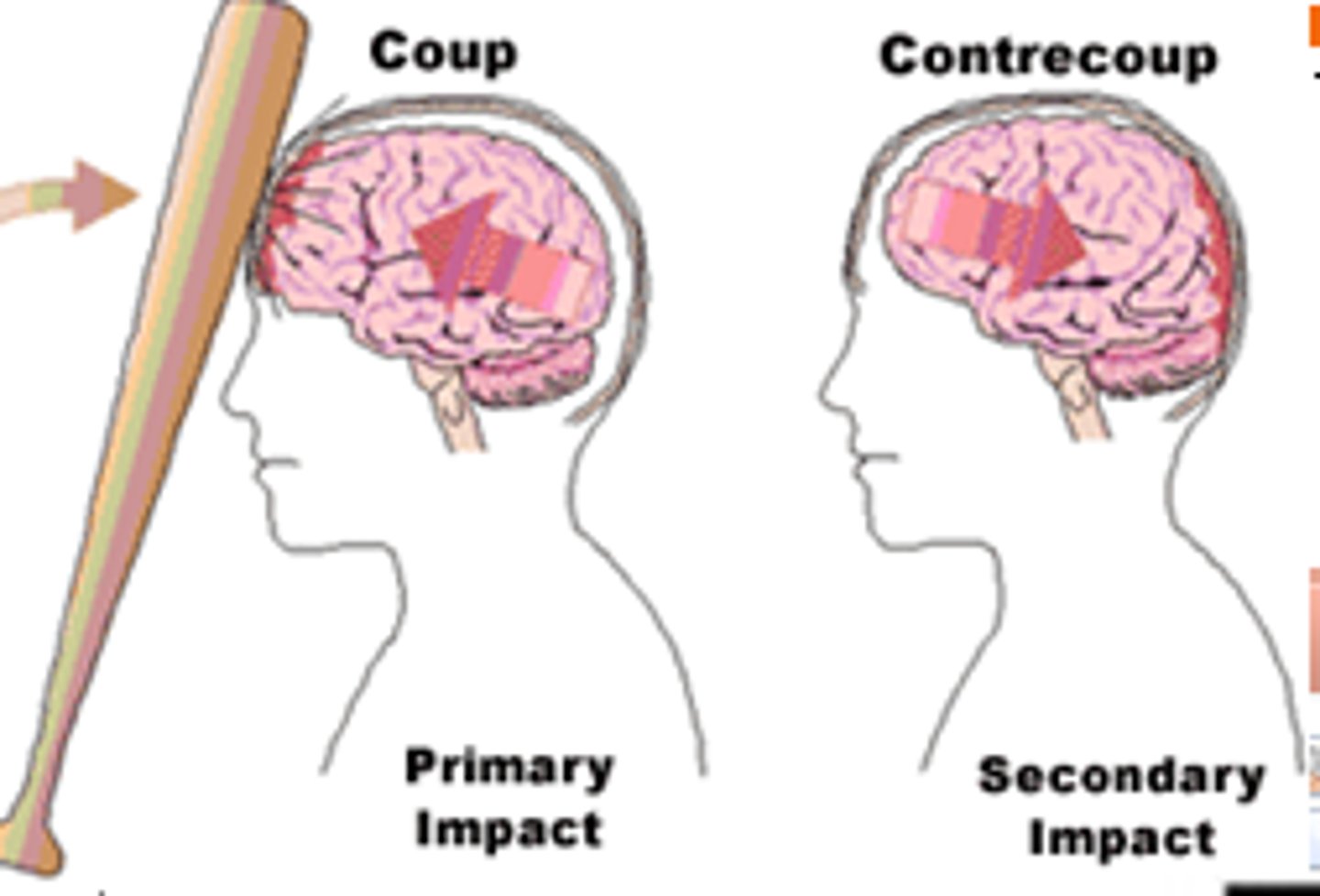
coup tbi
brain damage at site of blow
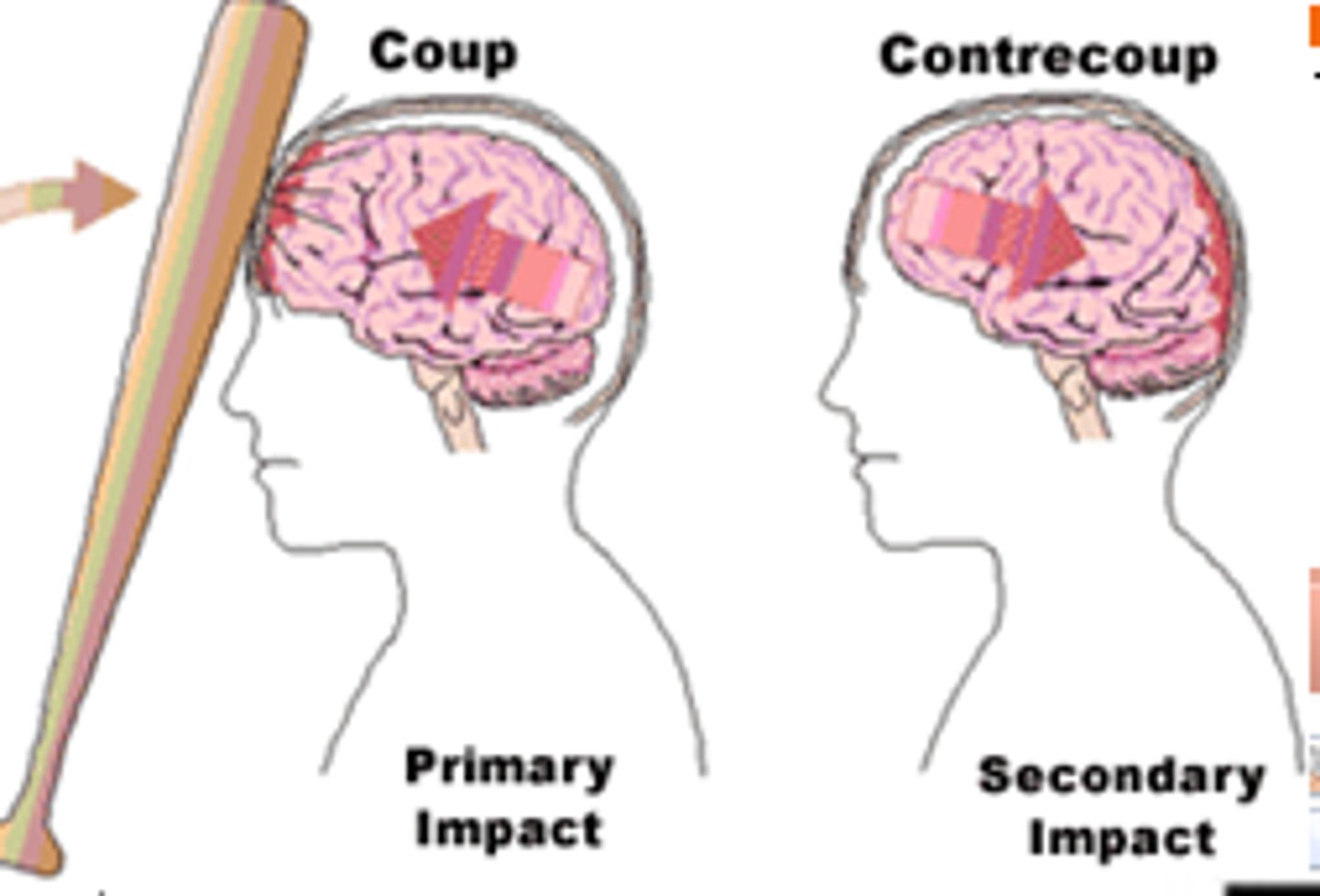
countercoup tbi
Rapid acceleration/deceleration
-The brain is damaged on the opposite side
- car accidents
indirect injury
force applied to another body part with a rebound effect to the brain

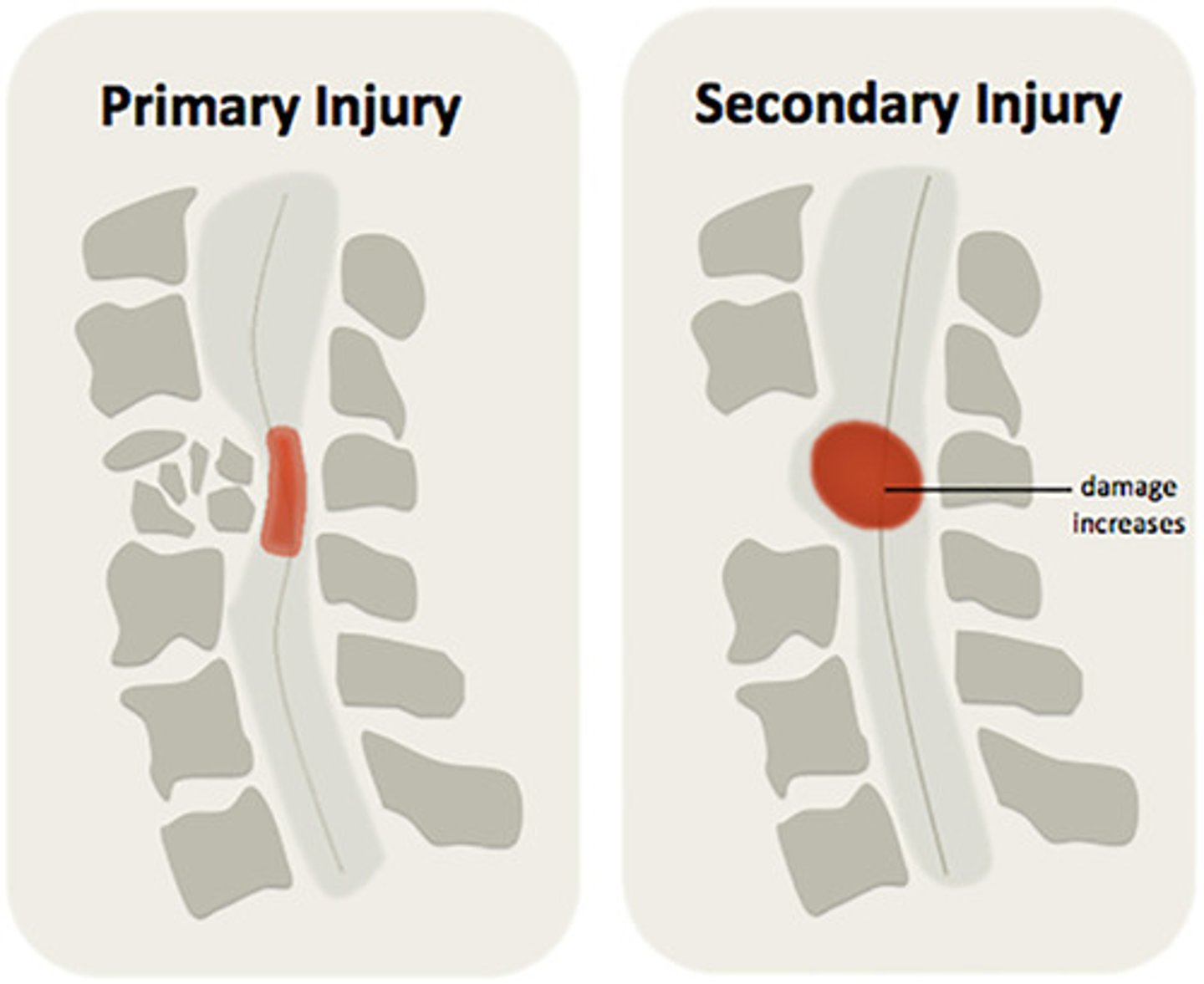
secondary injury
brain damage that occurs as a response to the initial injury. ex: hematoma, hypoxia, ischemia, increased intracranial pressure, and post-traumatic epilepsy
TBI treatment (contusions)
need to relieve intercranial pressure
- shunt
- remove hematomas
brain contusions can cause
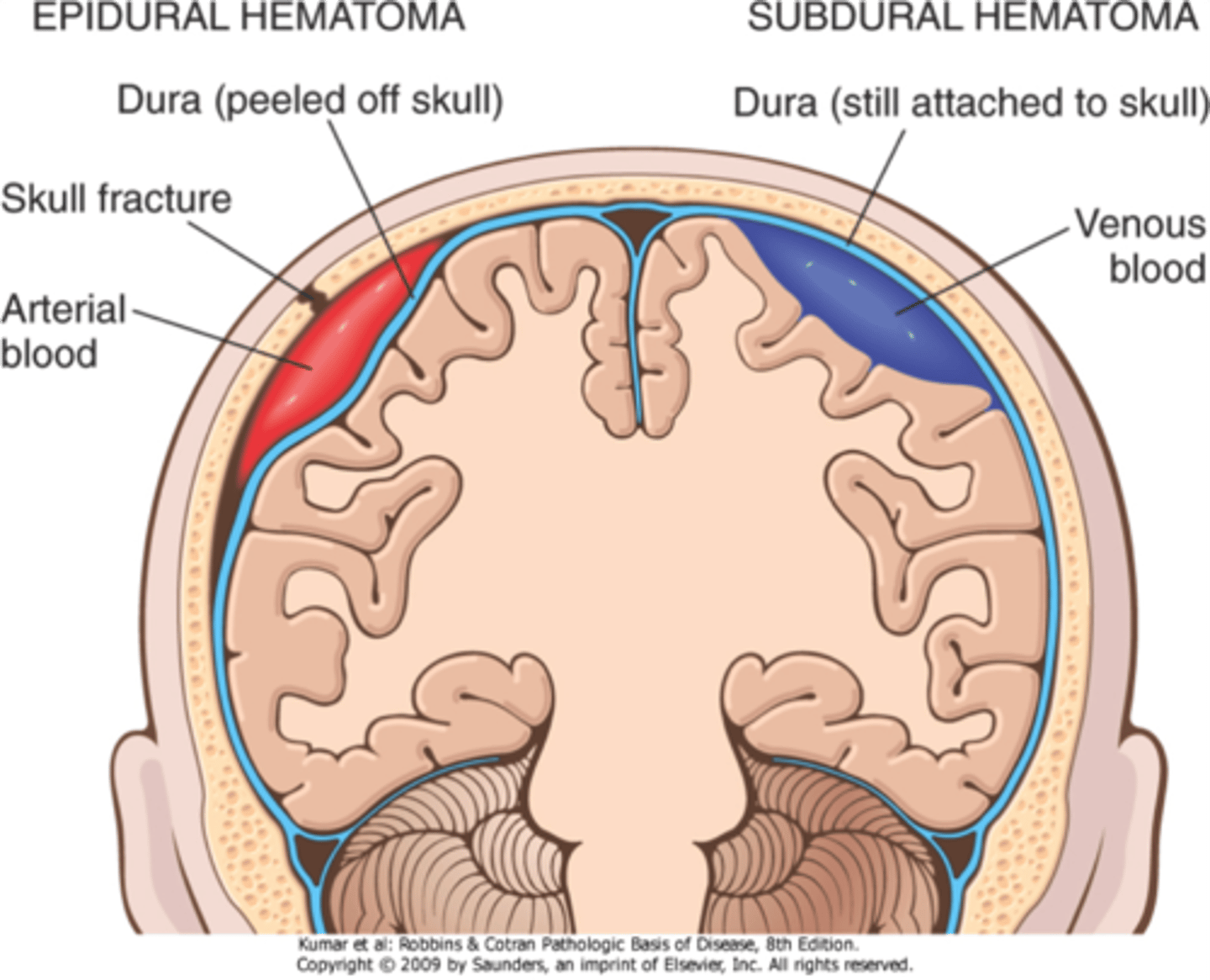
Epidural (extradural) hematoma
Subdural hematoma
Intracerebral hematoma
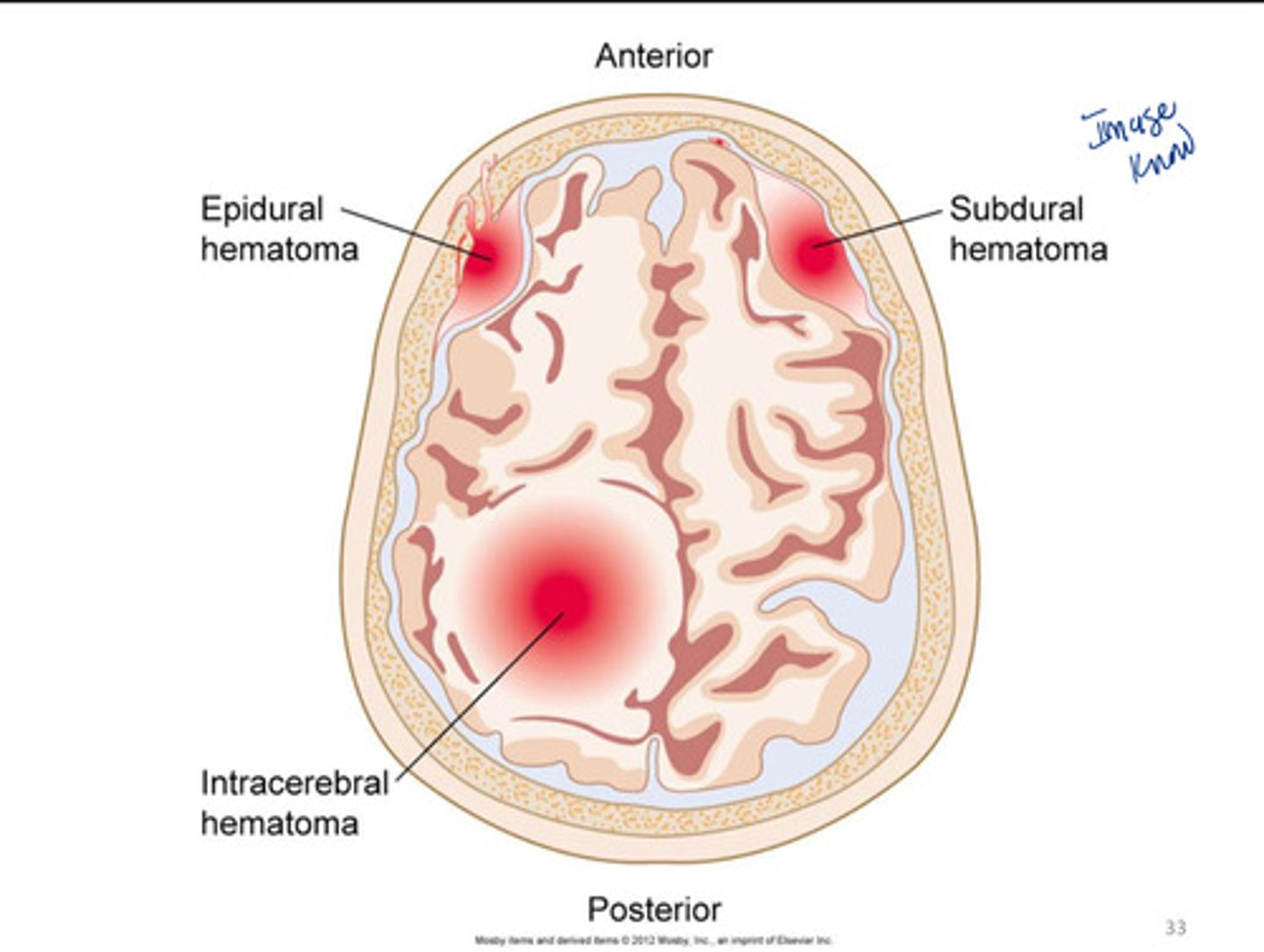
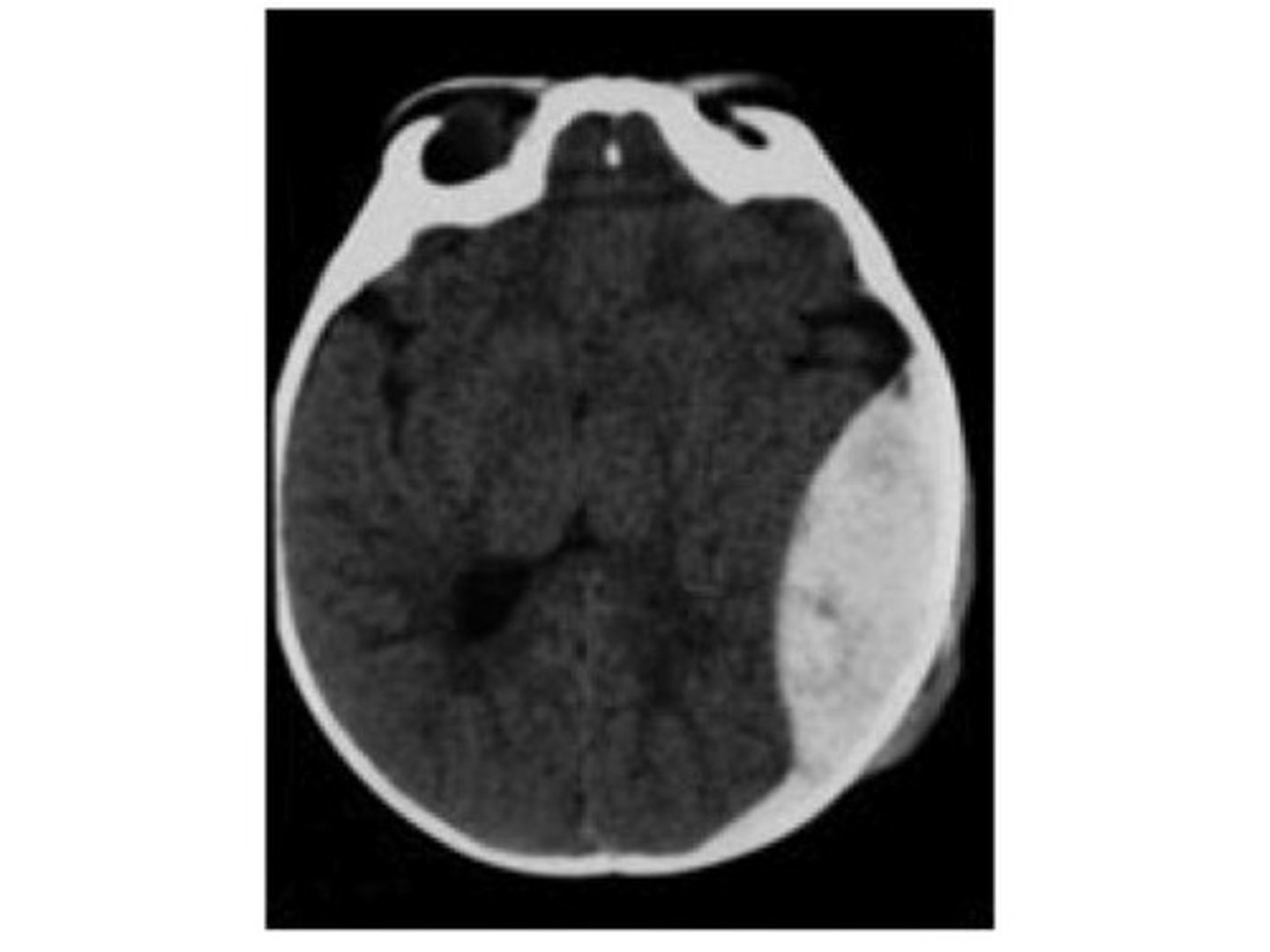
epidural (extradural) hematoma
a hematoma located on top of the dura
can occur in spinal cord
- loss of consciousness at time of injury followed by lucid period
- due to bleeding vein
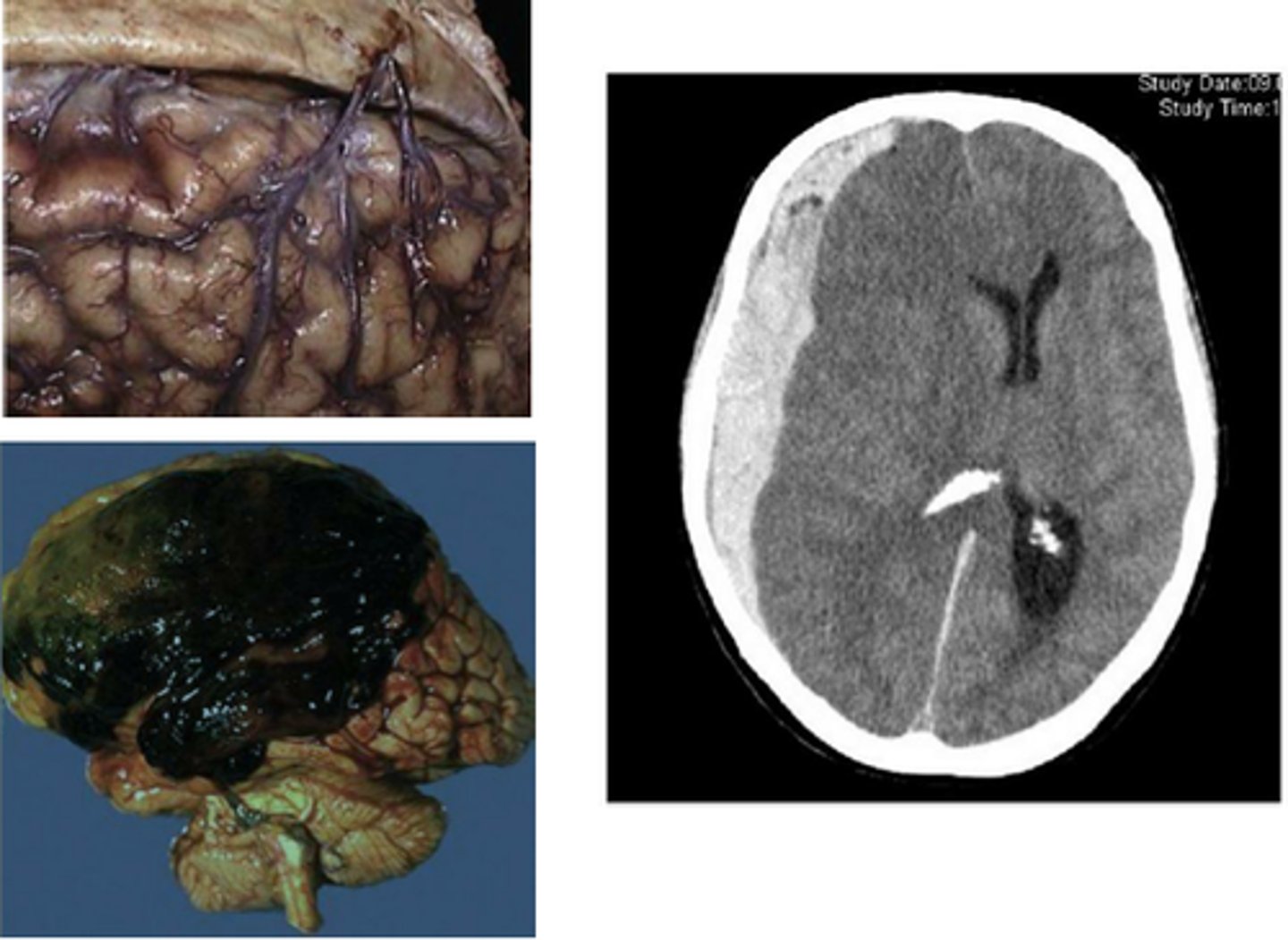
subdural hematoma
a hematoma located beneath the dura
- subarachnoid space
- can resolve
- develop within 48 hrs. of skull fracture
intracerebral hematoma
a hematoma located inside the brain tissue
- ventricles
- can be chronic
- craniotomy can remove
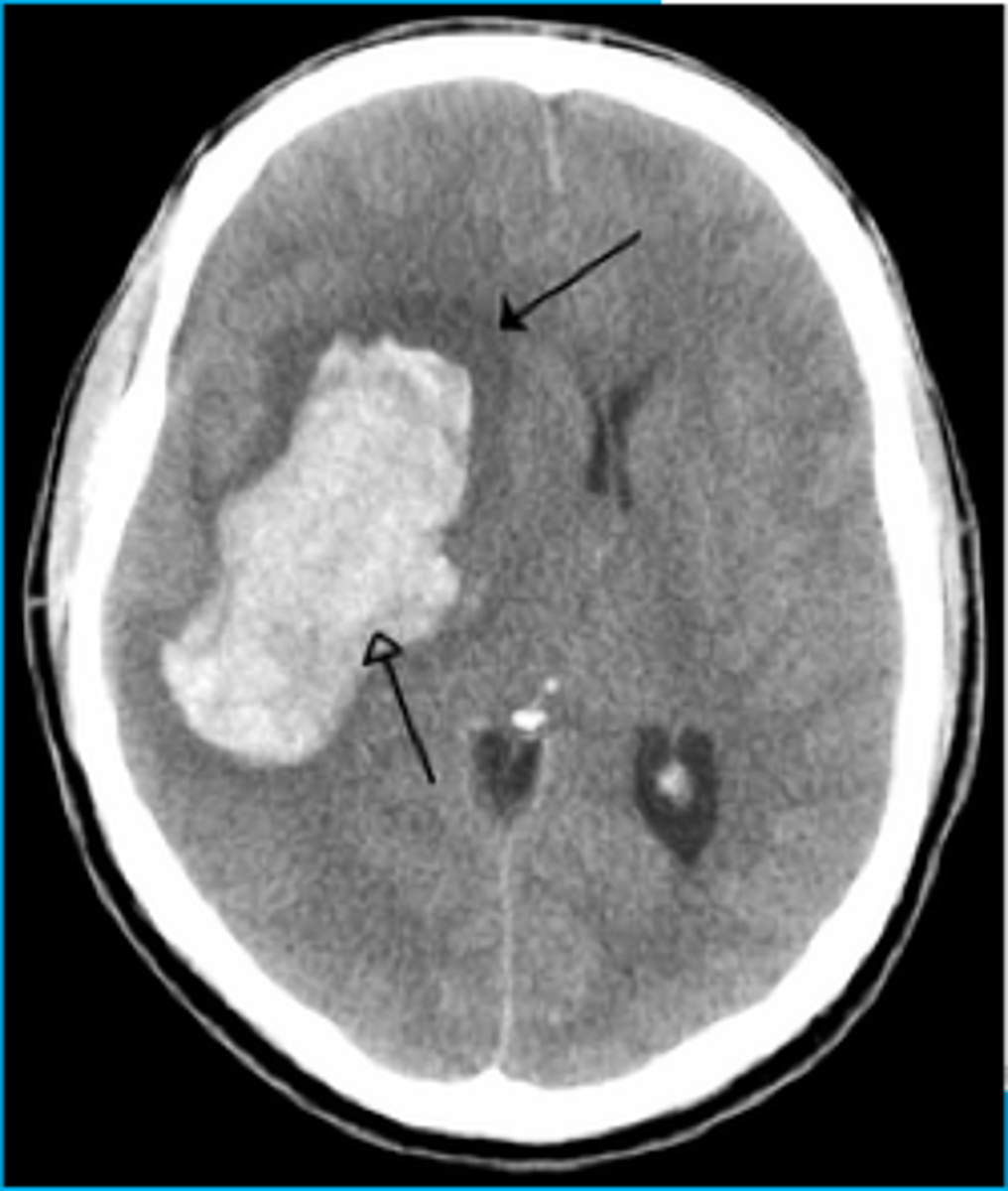
An unconscious person is admitted to the hospital after a motorcycle accident. The person experienced a brief loss of consciousness at the scene followed by an awake, lucid period of 1 hours. You suspect this individual has a(n)
extradural hematoma
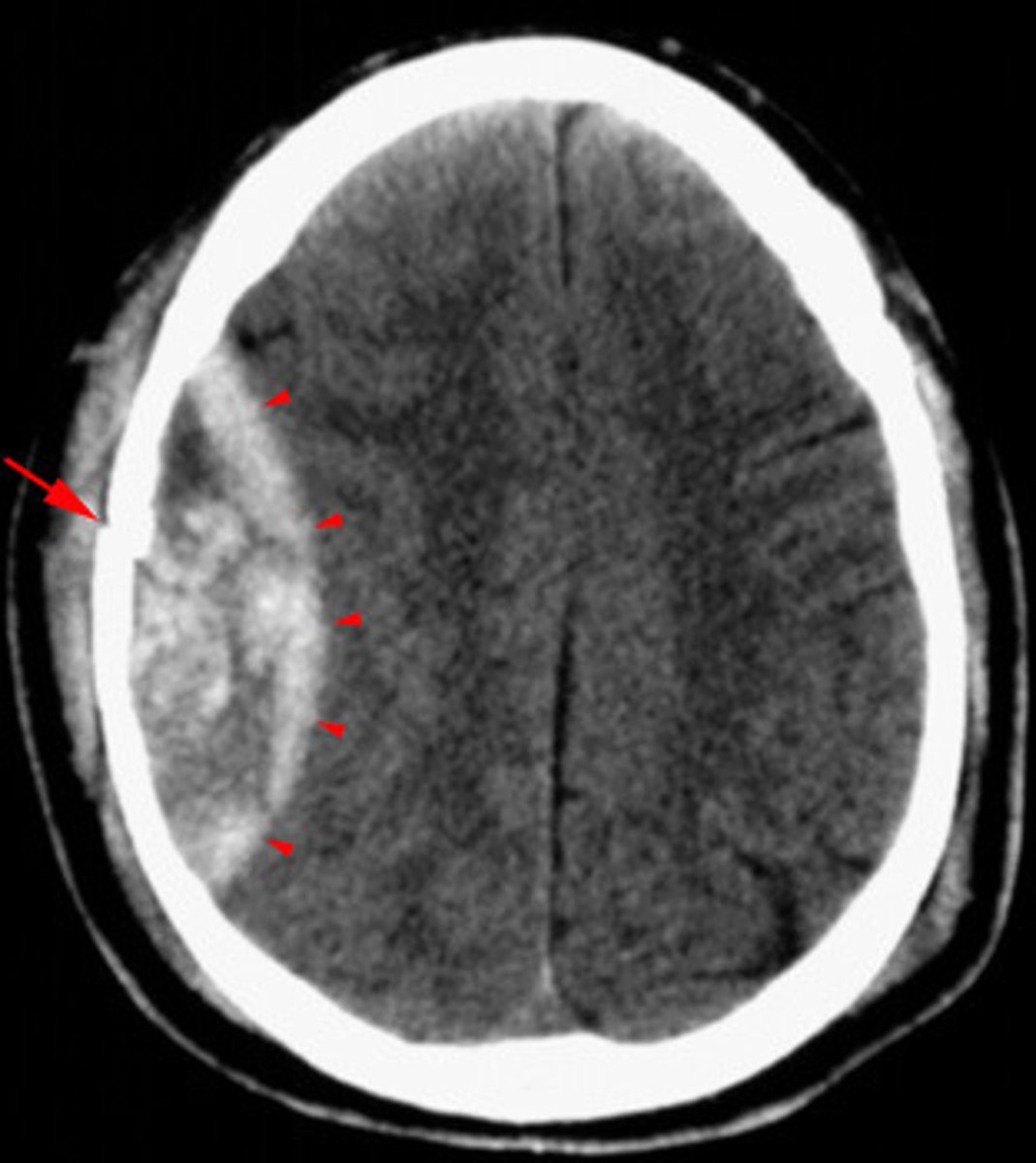
concussion
violent shaking up or jarring of the brain
- bruising of brain
- damage to axonal fibers + white matter tracts
- blunt damage to gray matter
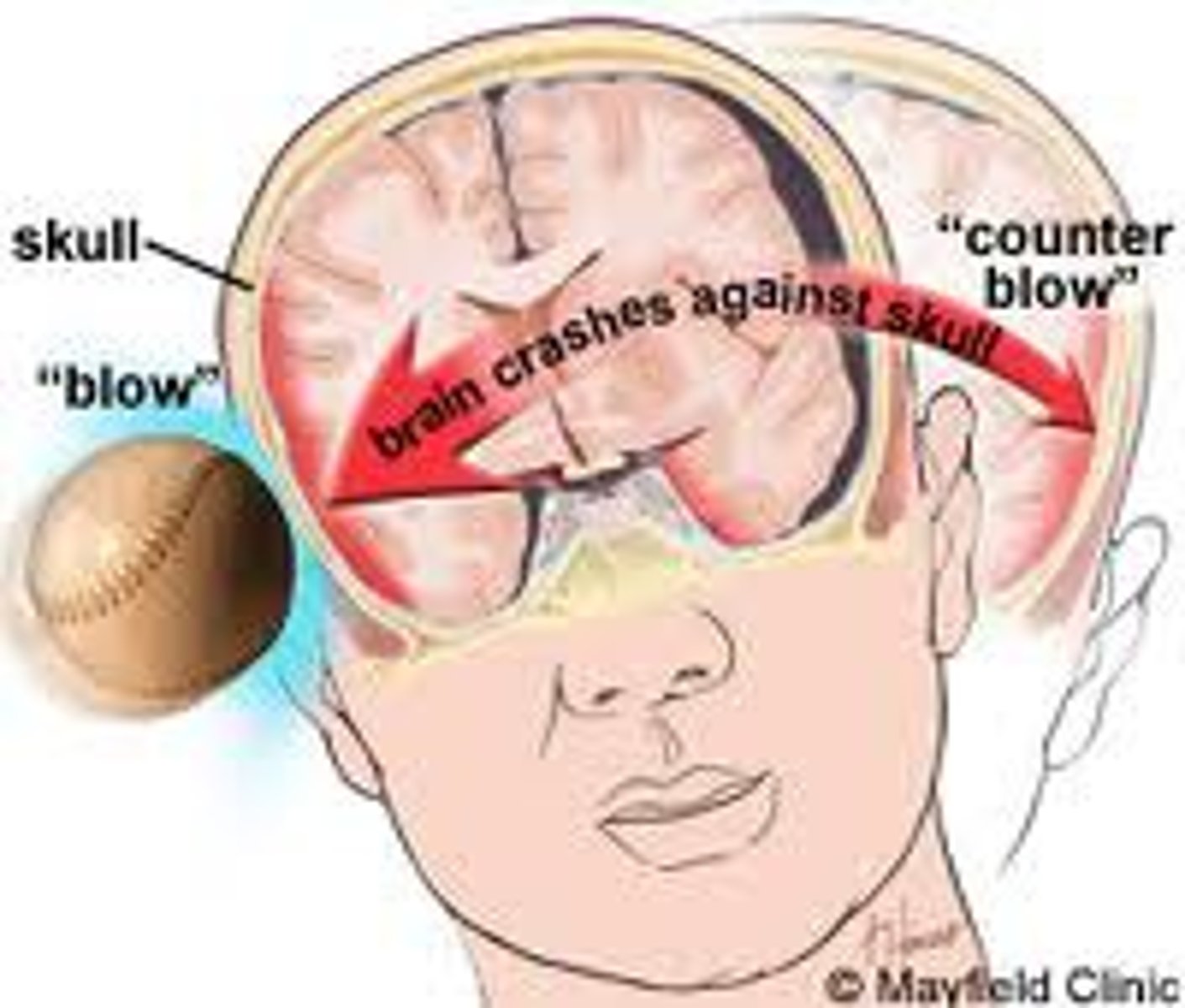
concussion complications
post concussion syndrome
post traumatic seizures
chronic traumatic encephalopathy
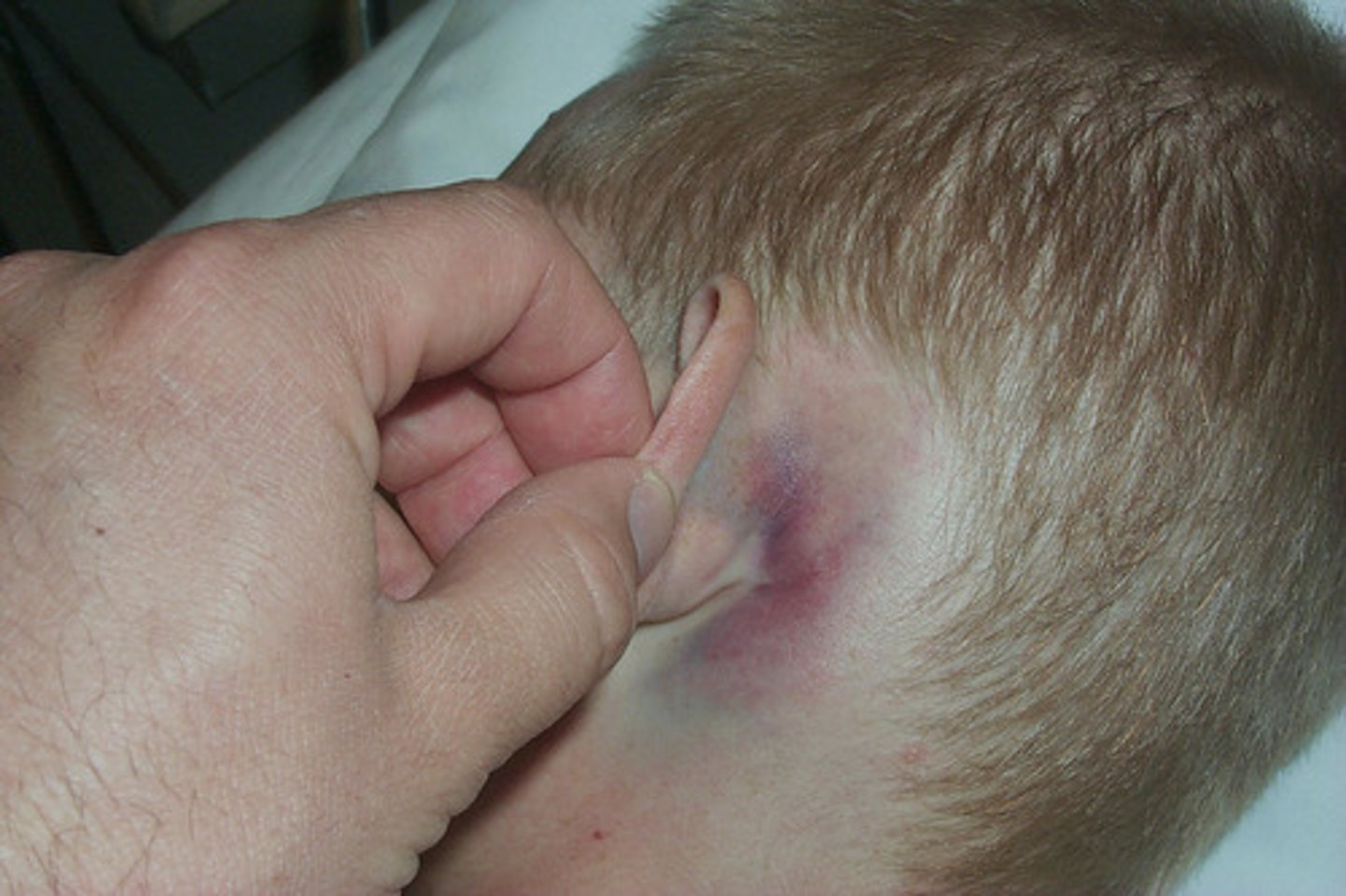
post concussion syndrome
lingering symptoms from a concussion that last for an extended period of time

post concussive syndrome symptoms
- Light headedness
- Vertigo
- Headache
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Photophobia
- Cognitive and memory dysfunction
- Tinnitus
- Blurred vision
- Difficulty concentrating
- Amnesia
- Fatigue
- Personality change
- Balance disturbance
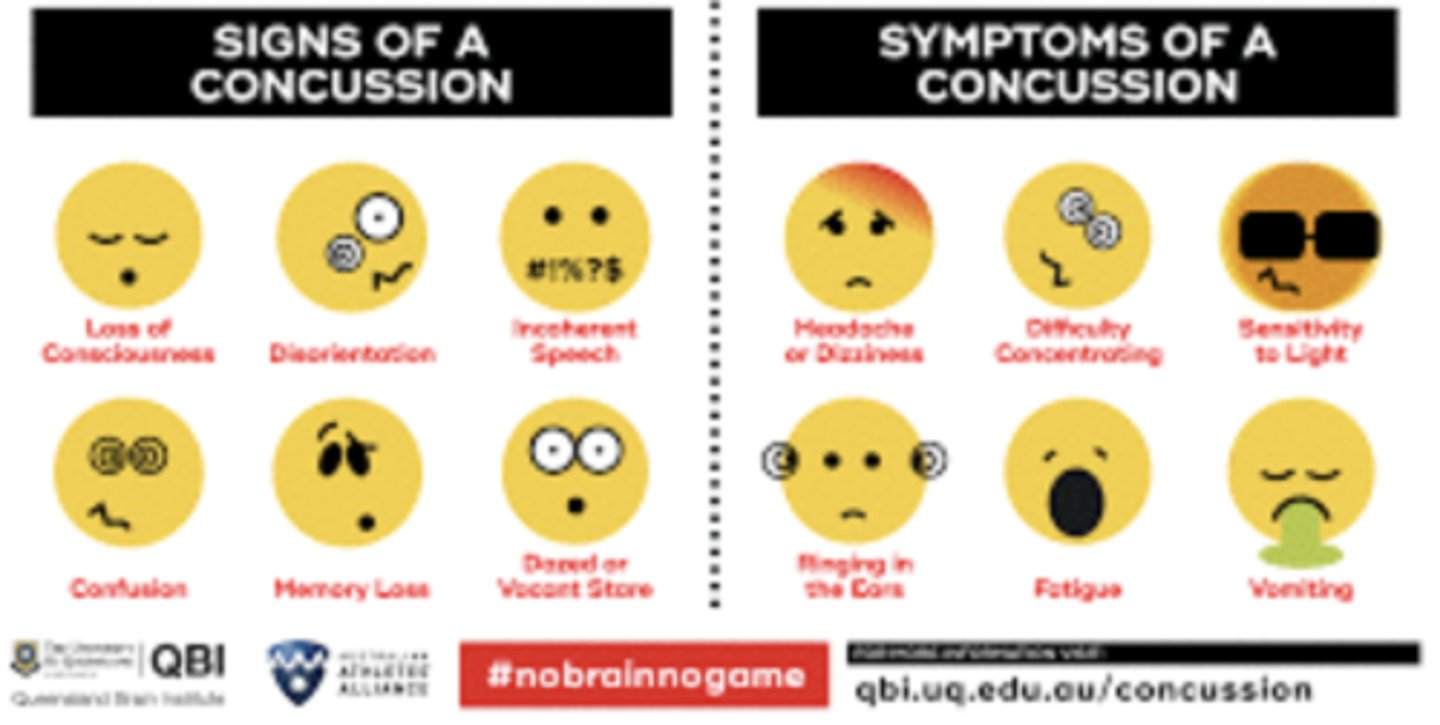
post concussive syndrome treatment
-supportive (managed by PCP)
-close observation for 24 hours for immediate intervention due to a slow bleed

post traumatic seizures
Seizures occurring after a traumatic brain injury.
- epilepsy
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE)
a progressive, degenerative condition involving brain damage resulting from MULTIPLE episodes of head trauma
- football + boxing
- only diagnosed after death

mild concussion
Temporary axonal disturbance causing attention and memory deficits but no loss of consciousness
- symptoms usually resolve in 15 mins

moderate concussion
LOC of 30 min to 6 hrs. GCS-9-12
No brainstem injury, usually some permanent deficiencies
- skull fractures

severe concussion
- LOC more than 6 hours
- GCS 3-8
- signs of brainstem injury, permanent deficiencies, vegetative state or even death from TBI or complications
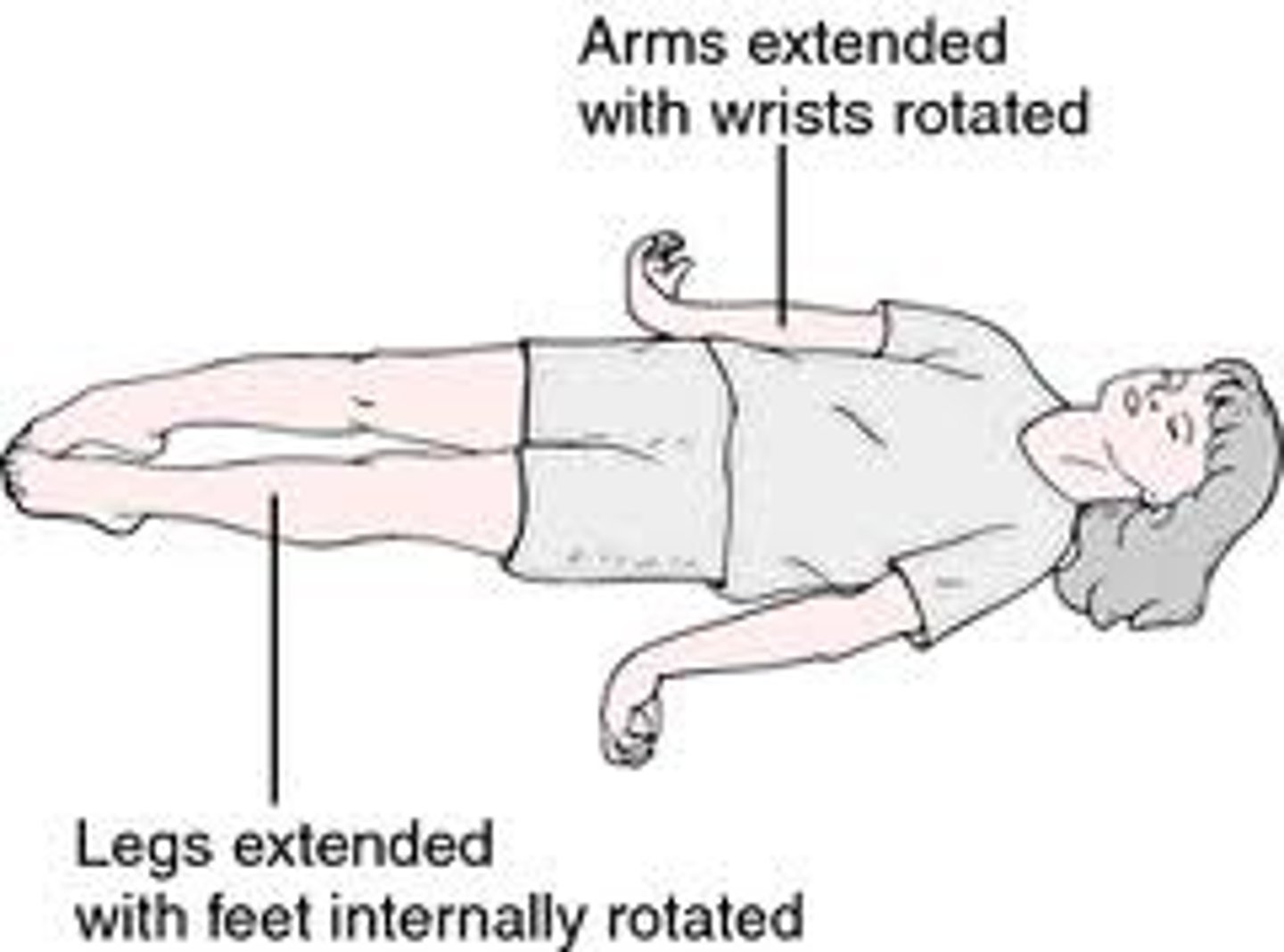
decerebration
condition of loss of mental functions caused by damage to the midbrain
- dysfunction of white matter
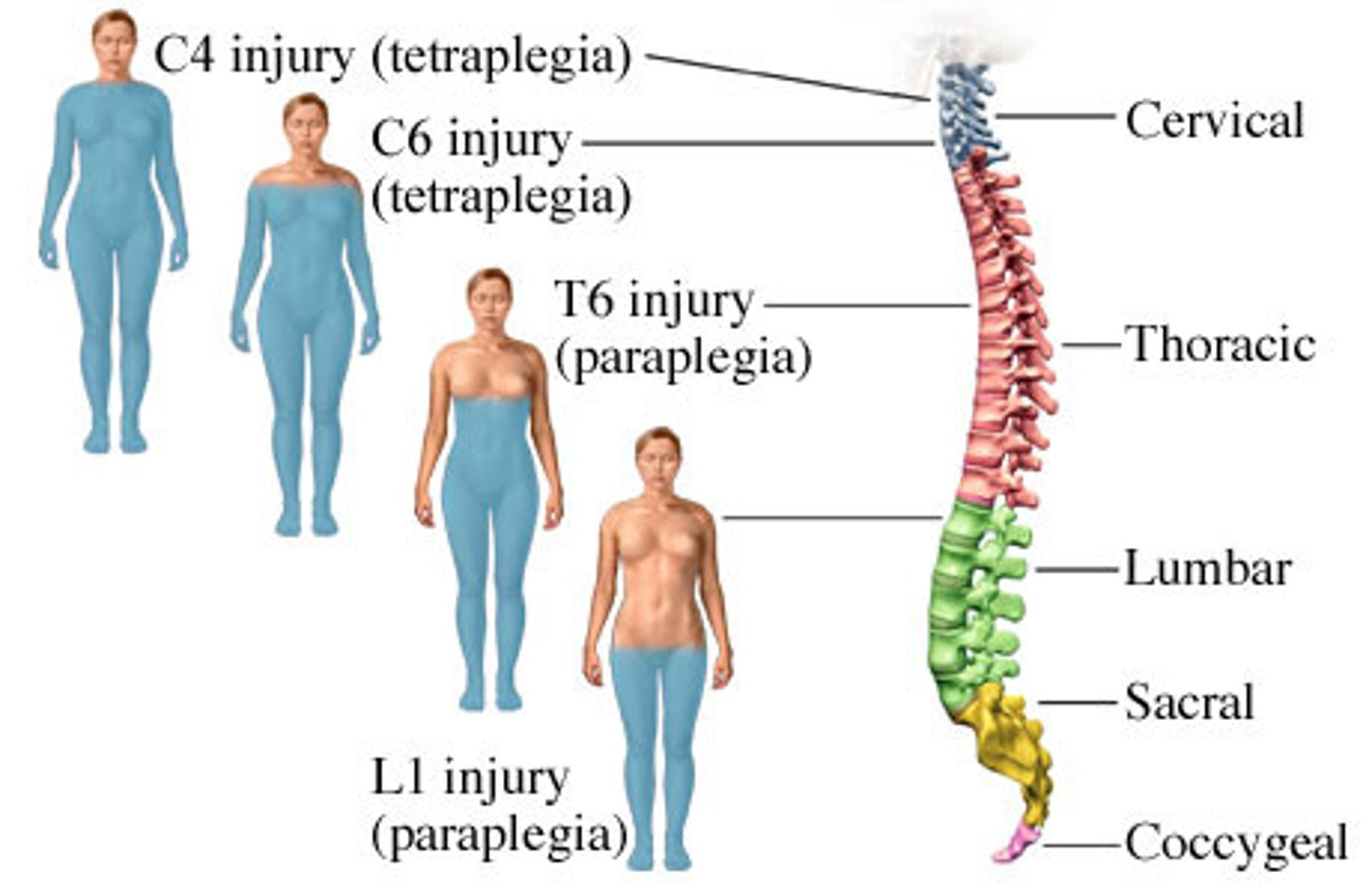
spinal cord injury
the type of paralysis is determined by the level of the vertebra closest to the injury
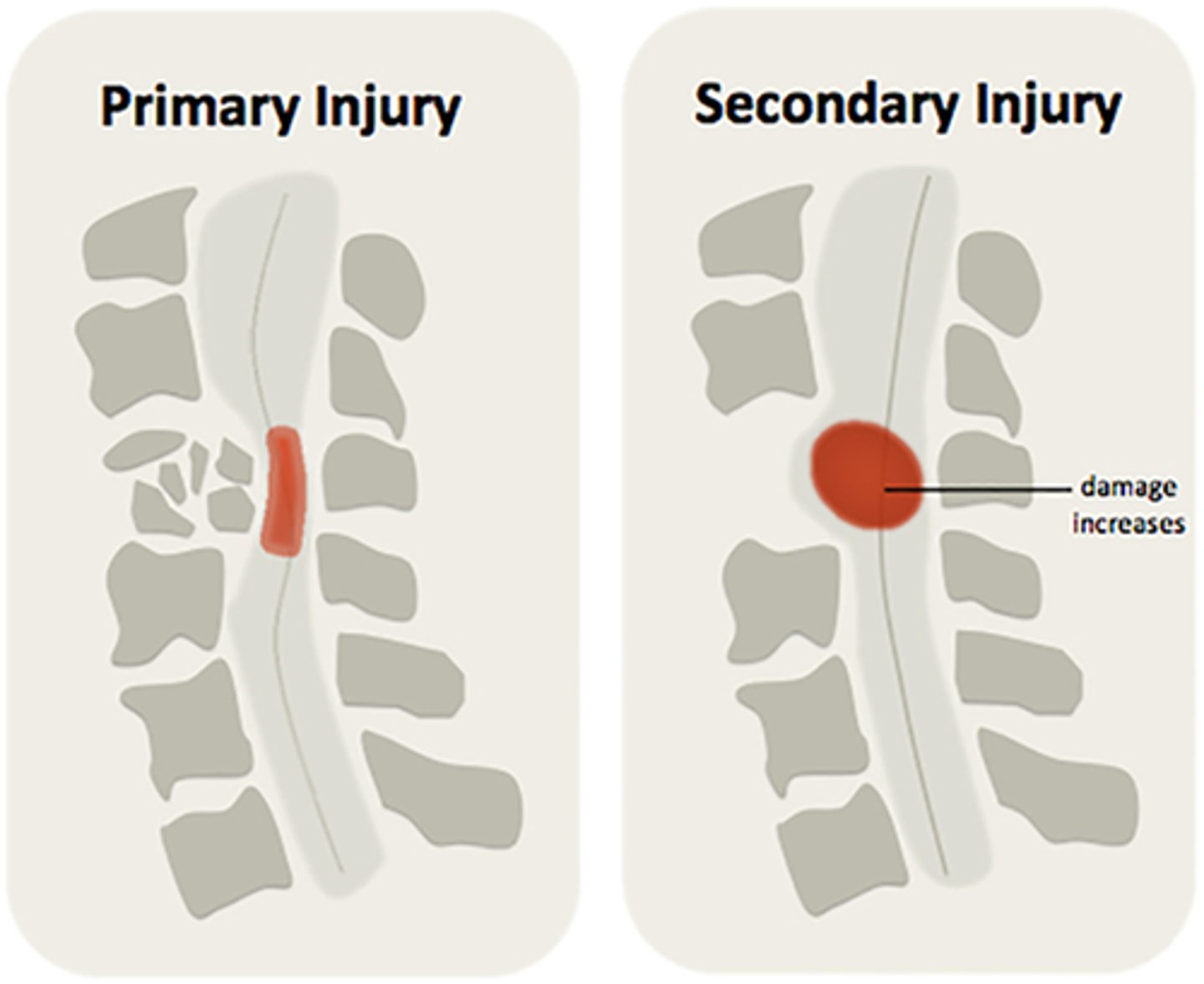
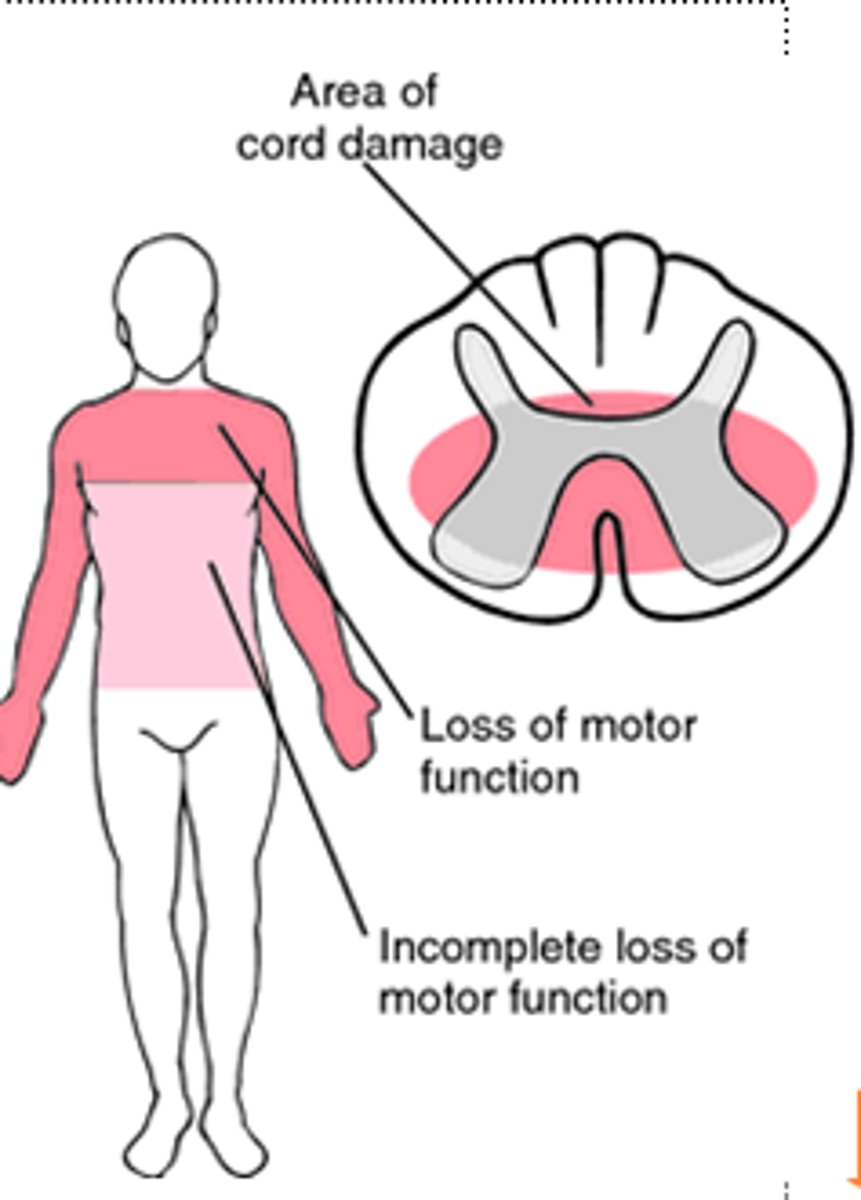
primary spinal cord injury
segmental paralysis at level of lesion or below
- dysfunction in lower motor neurons
- mechanical damage to white matter tracts or gray matter in spinal cord
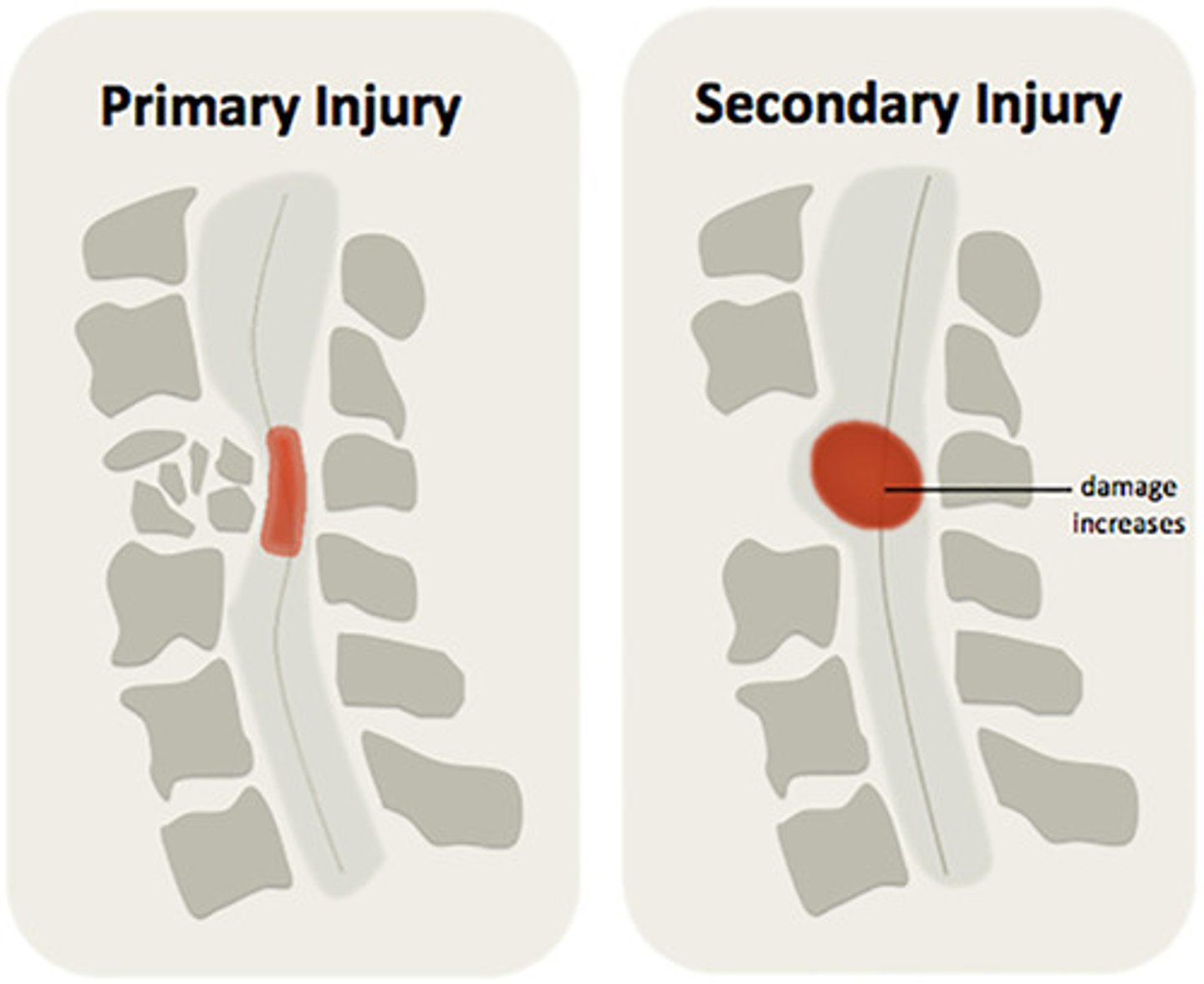
secondary spinal cord injury
Result of vascular, chemical, and inflammatory process that follows primary injury
clinical manifestations of spinal cord injury
spinal shock
neurogenic shock
autonomic dysreflexia

who do spinal cord injuries affect most?
young men
- most common in car accidents
- falls
- violence

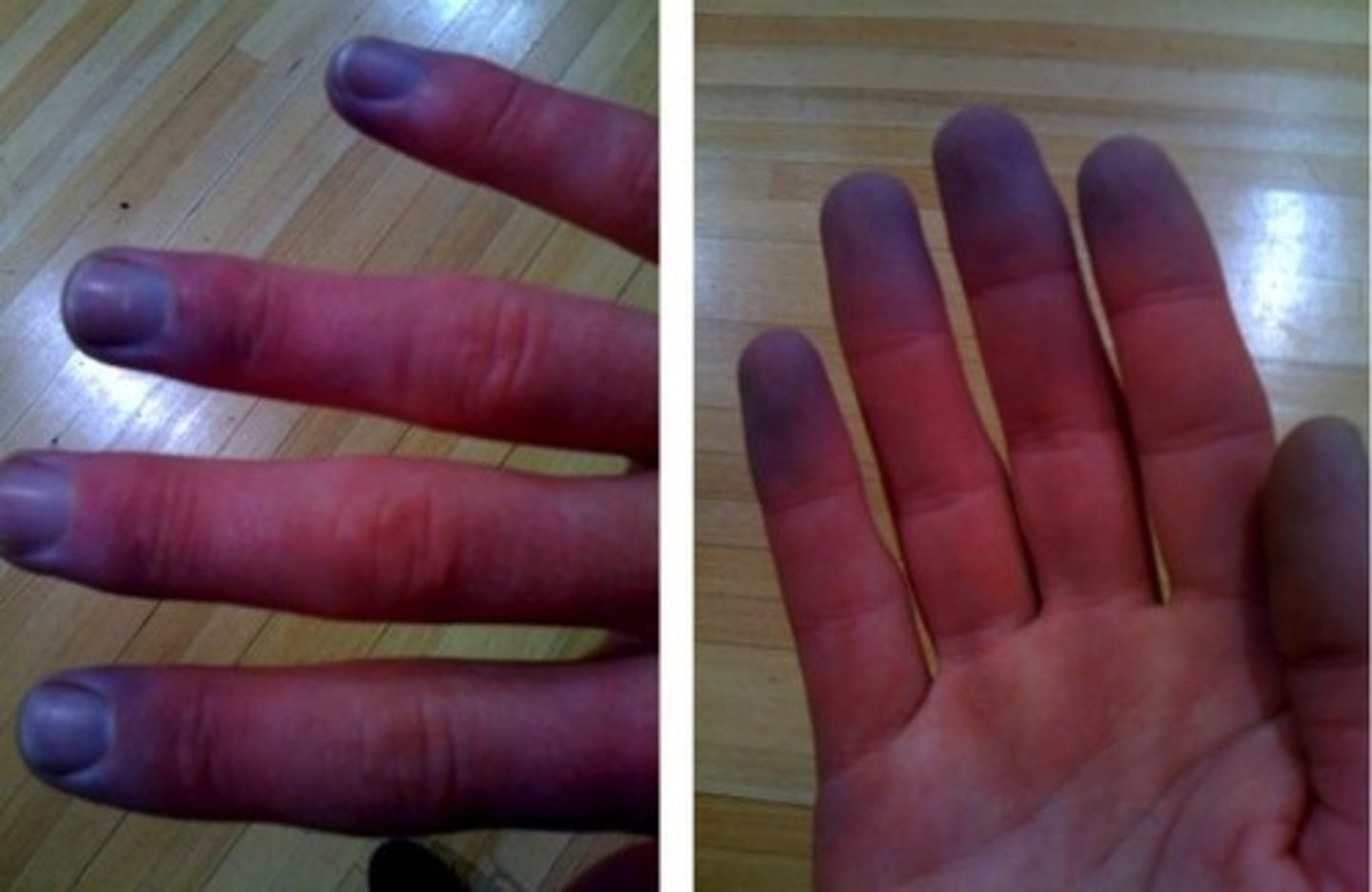
spinal shock
total loss of reflexes below level of lesion
- flaccid paralysis, sensory deficit, loss of bladder + rectal control, drop in BP, disturbed temperature
- days up to 3 months
- results in poor venous circulation
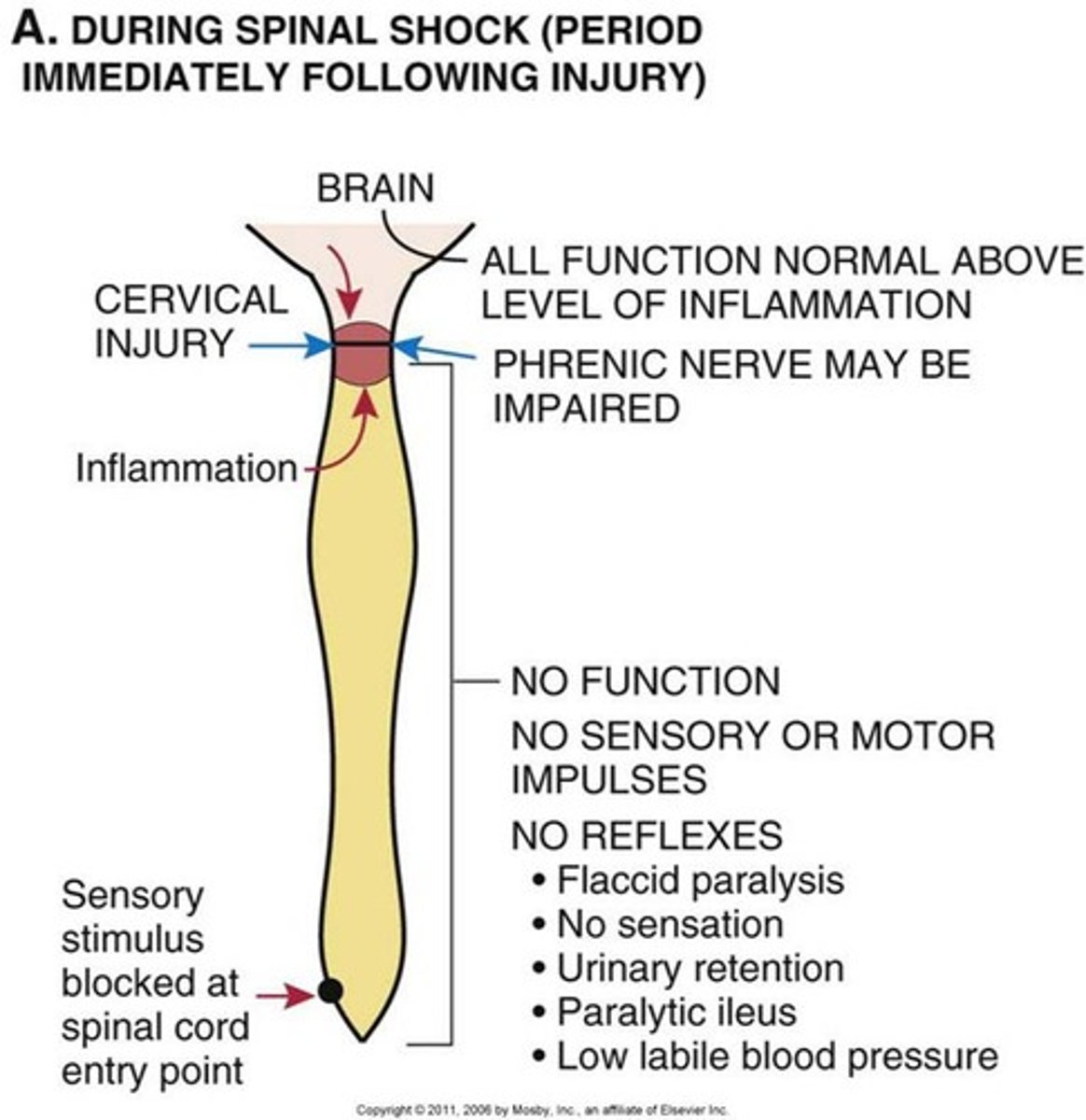
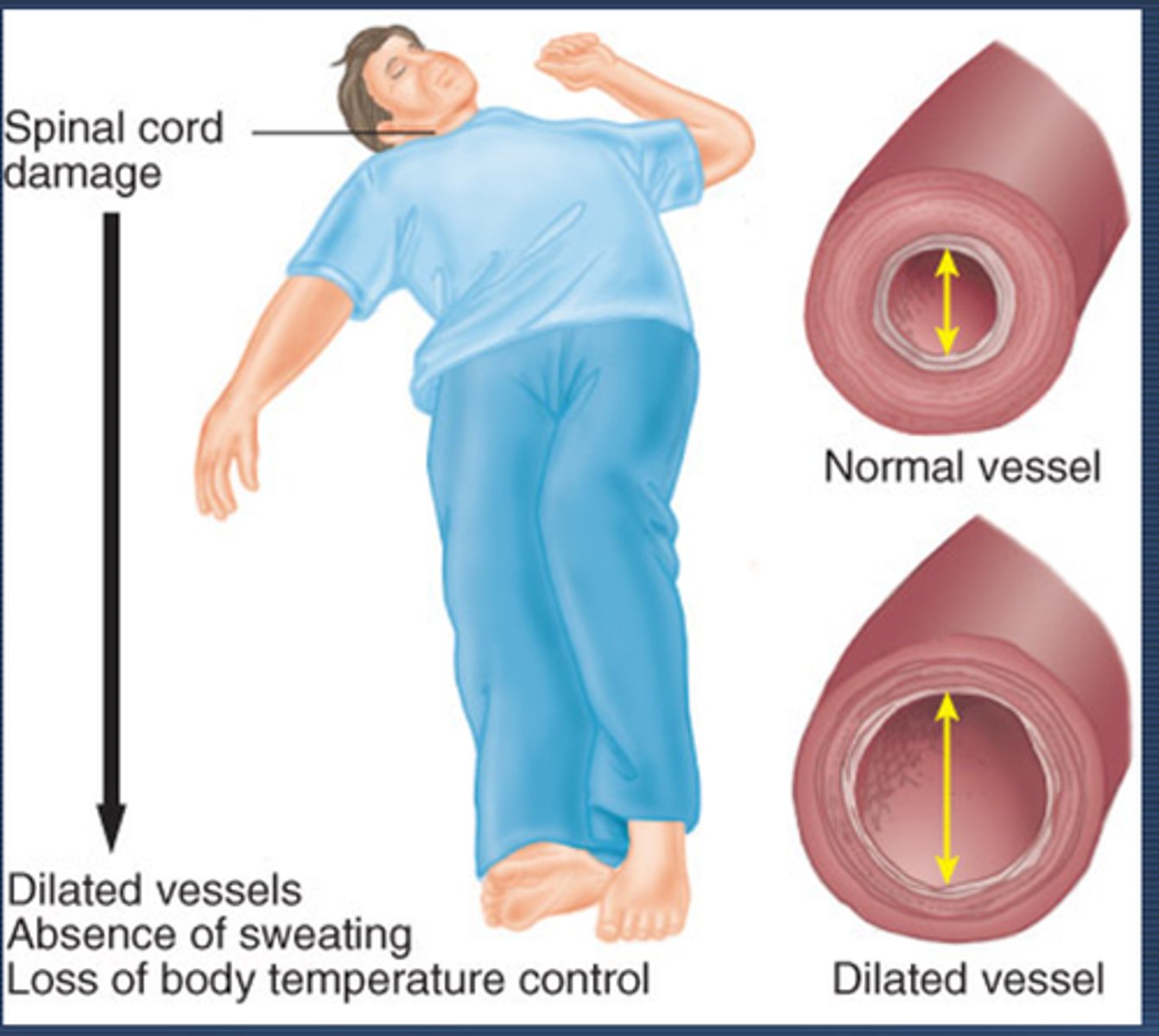
neurogenic shock
cervical or upper thoracic injuries
- In addition to spinal shock.
- caused by absence of sympathetic activity and unopposed parasympathetic tone mediated by an intact vagus nerve
- vasodilation
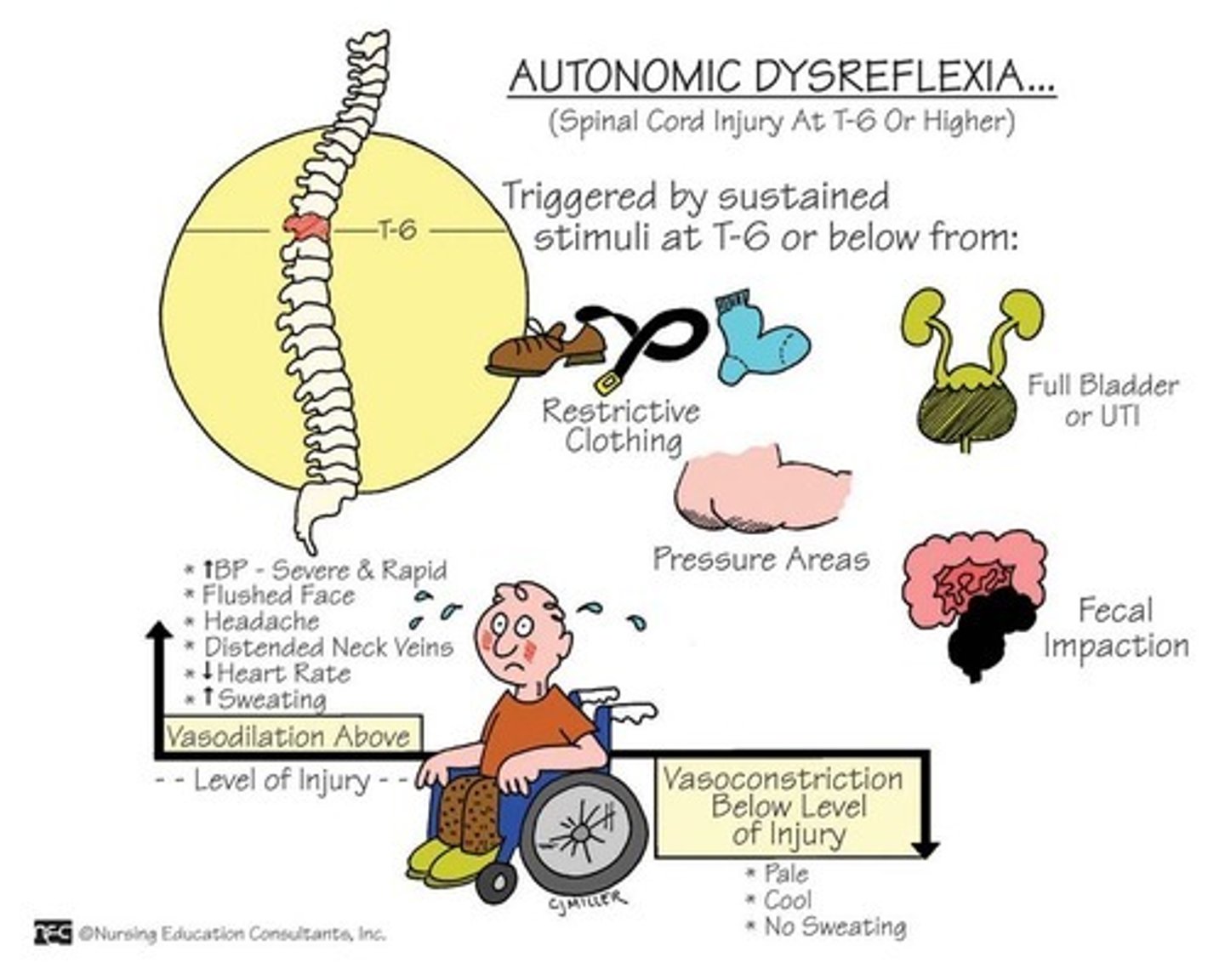
Autonomic Dysreflexia
life-threatening condition that occurs in individuals with spinal cord injuries at or above T6.
- results from exaggerated autonomic response to a noxious stimulus below the level of the injury
- leads to severe hypertension, bradycardia, and other autonomic disturbances.
most common spinal cord injury
contusions
- caused by bending of vertebral column
- COMPRESSION ON CORD
You know that spinal shock results in
poor venous circulation

Degenerative Disc Disease
gradual breakdown of spinal discs due to aging, wear and tear, or injury.
- Discs lose water, shrink, and become less flexible, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
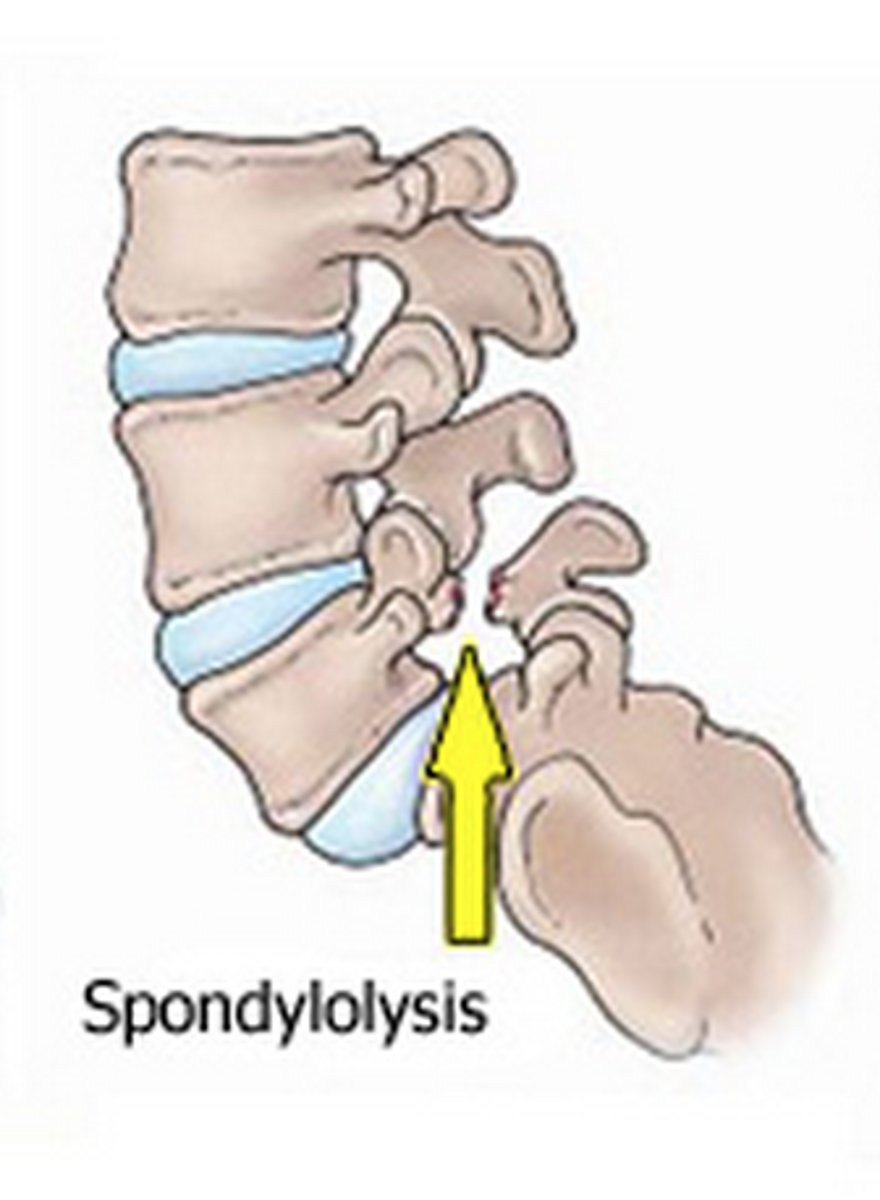
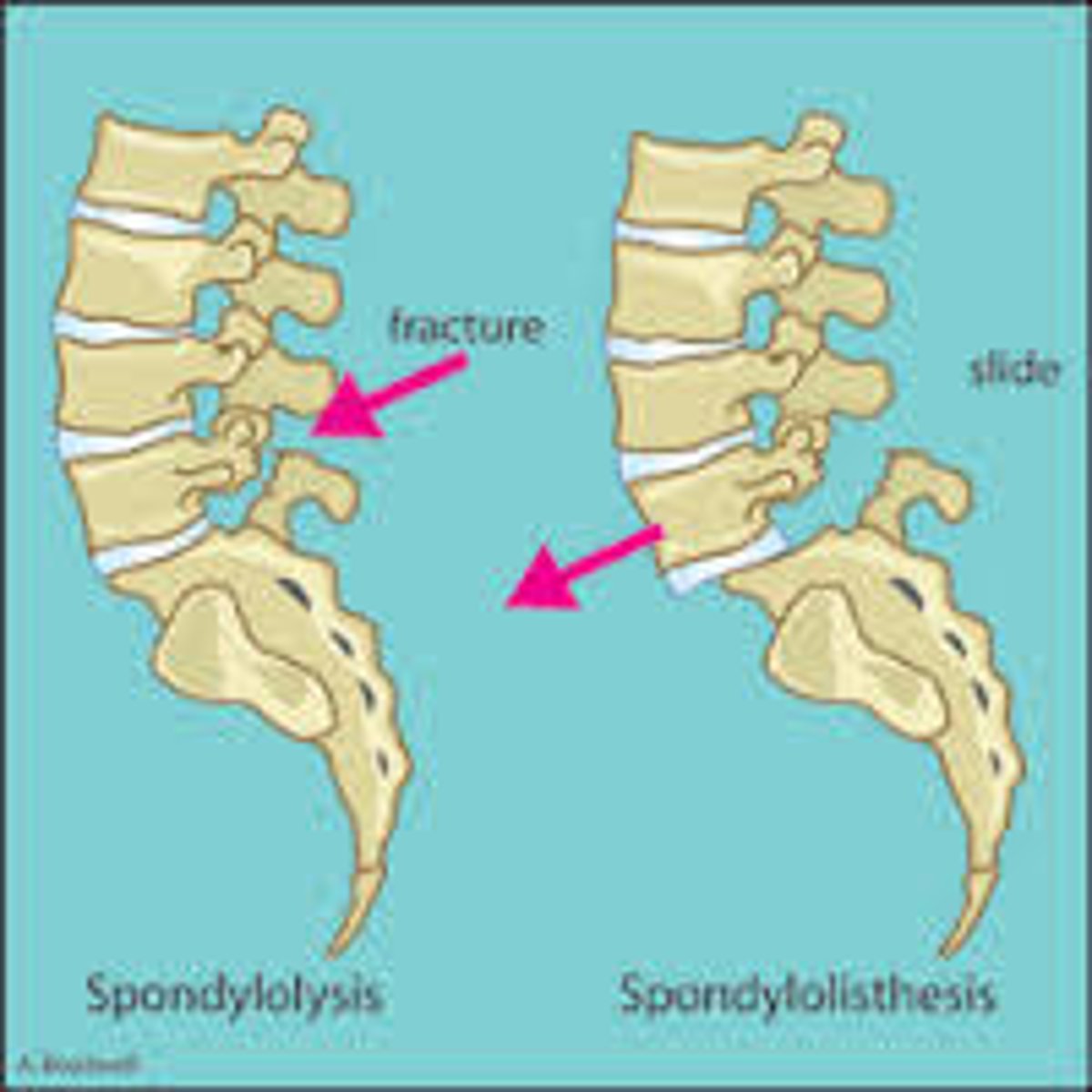
spondylolysis
the breaking down of the vertebral structure
- hereditary
- soft tissue damage
spondylolisthesis
forward slipping of one vertebra over another
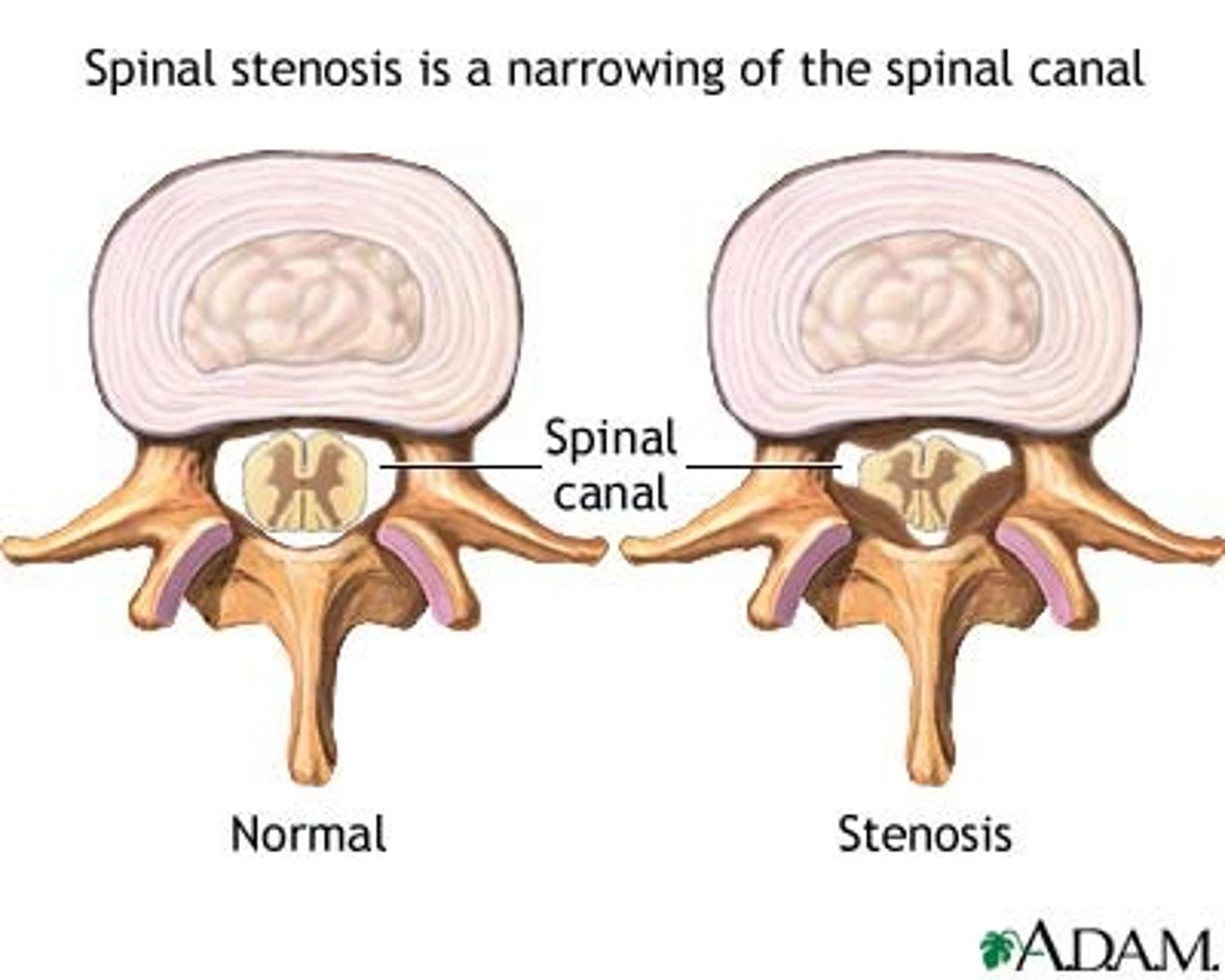
spinal stenosis
narrowing of the spinal canal
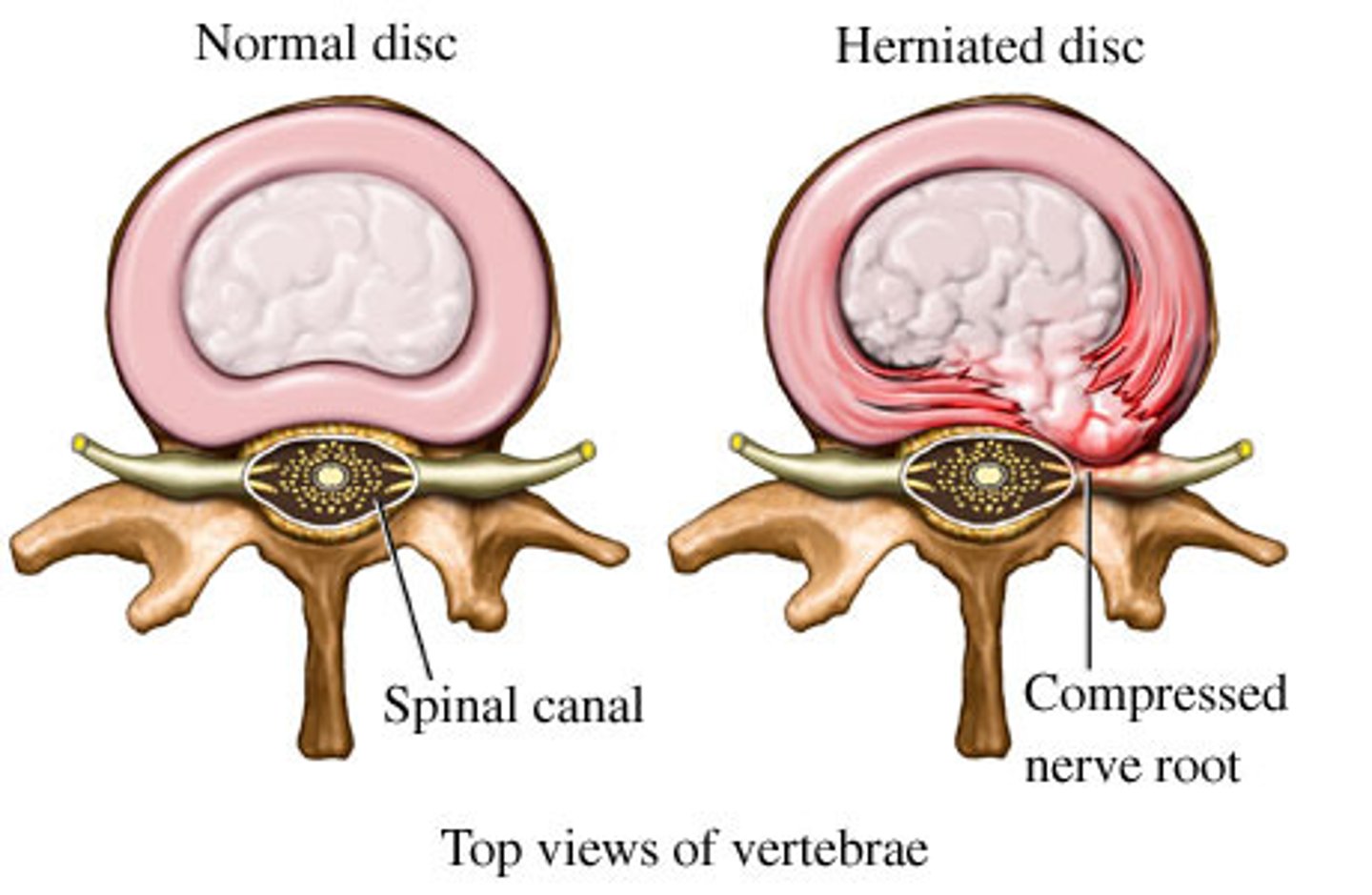
herniated disc
soft inner core of an intervertebral disc pushes through a tear in the outer layer, potentially pressing on nearby nerves
- pain
- can be repaired
- sciatica
- hip pain
most common neurologic disorders
- CVA's (strokes)
- transient ischemic attacks
- aneurysms/ malformations

cerebrovascular accidents (CVAs)
strokes
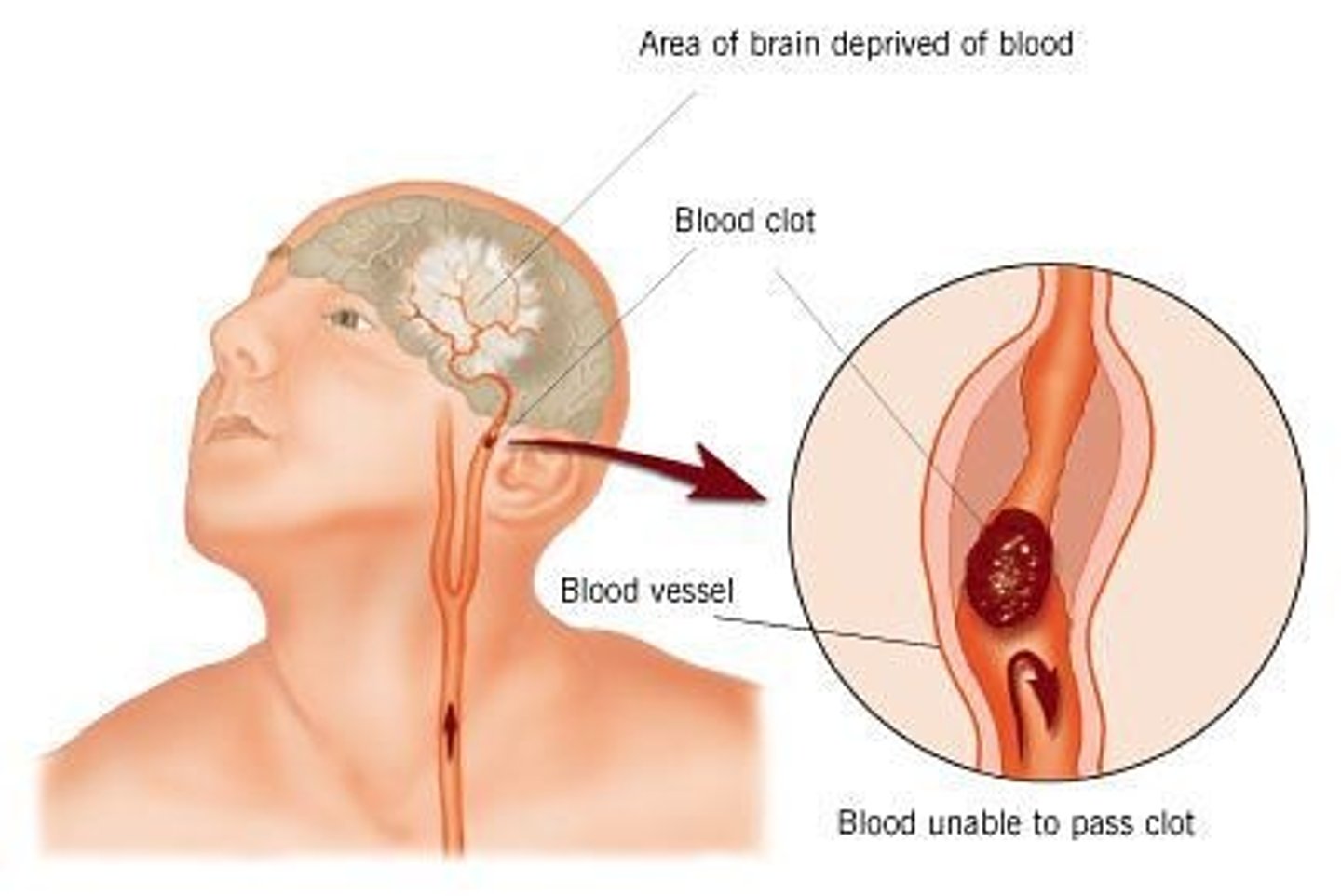
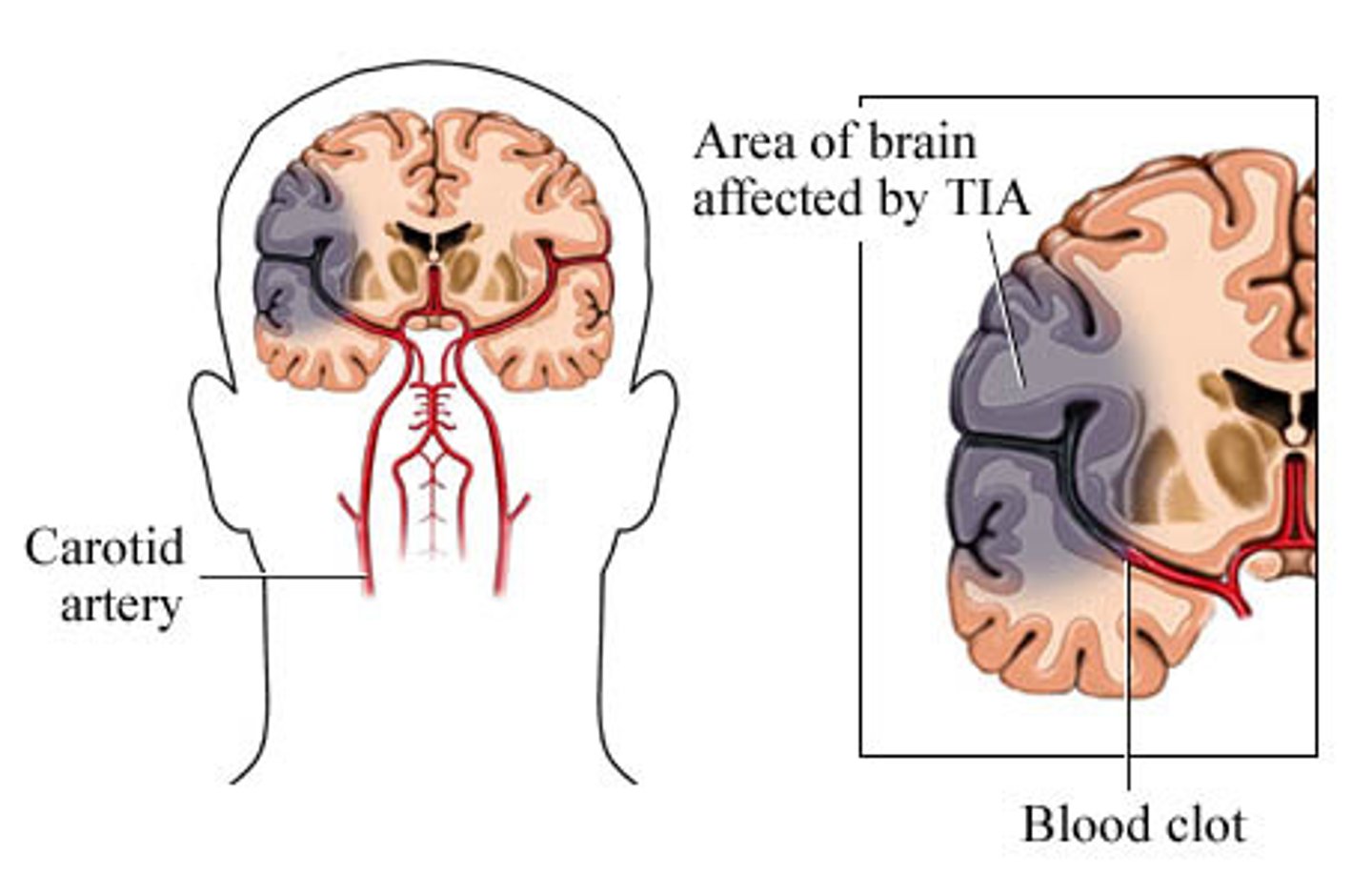
Transient ischemic attacks
mini strokes
- twitching
- usually not permanent
CVA (stroke)
5th leading cause of death
- minimal or life threatening
- greatest risk factor: hypertension

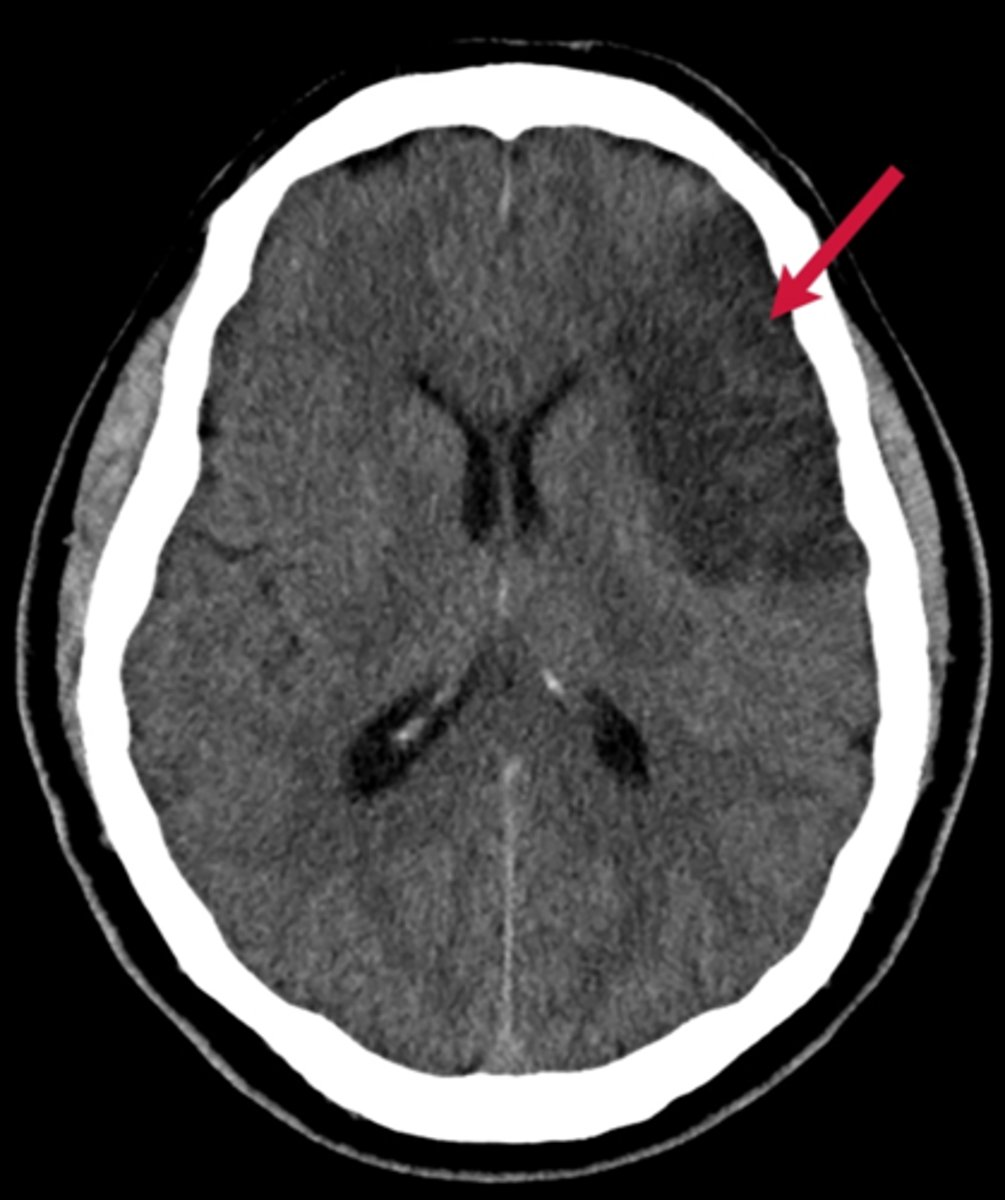
ischemic stroke
stroke that occurs when the flow of blood to the brain is BLOCKED
- aspirin can help
- blockage can be from thrombocytes, embolisms
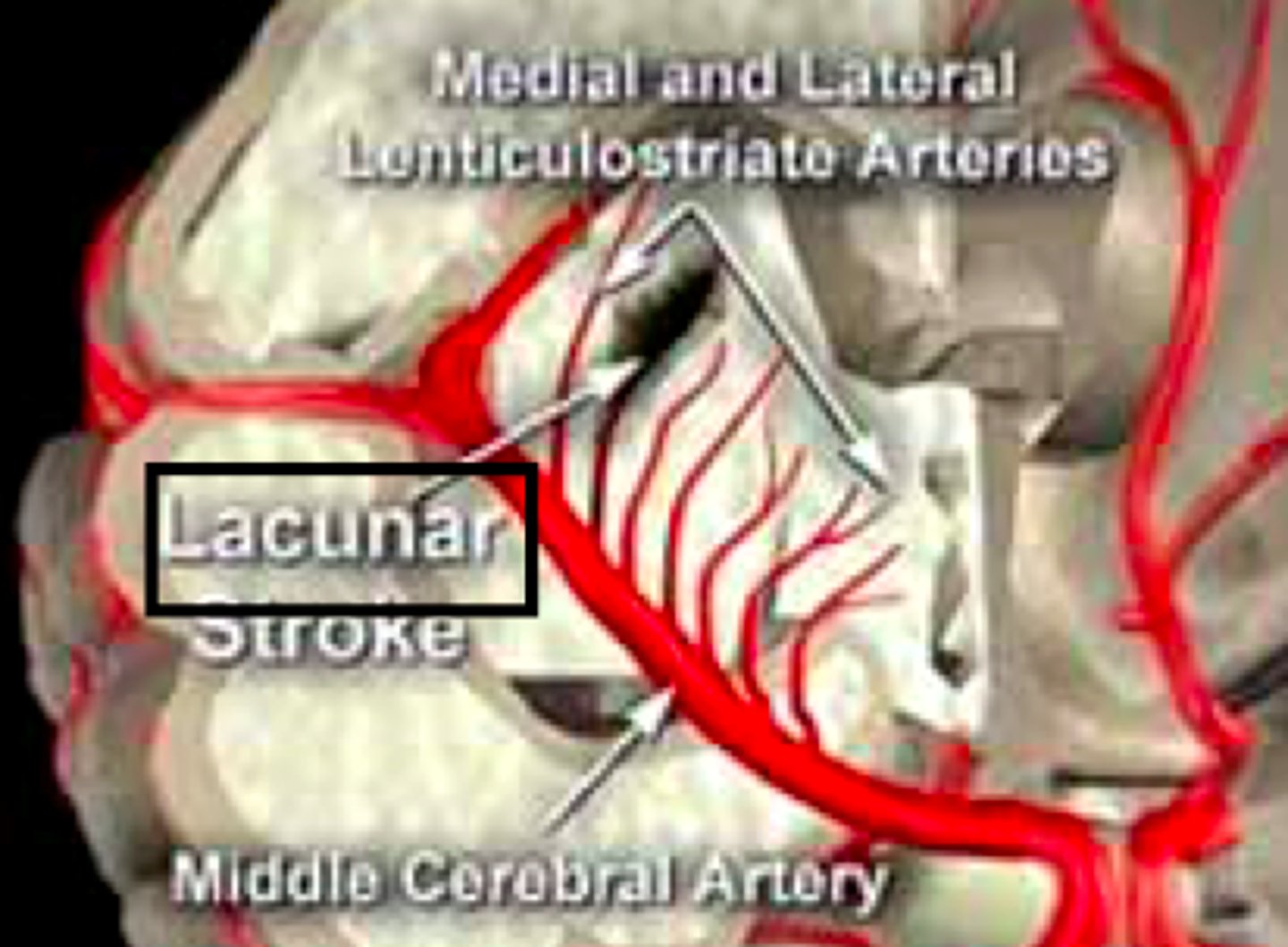
lacunar stroke
a stroke resulting from occlusion of a small penetrating artery with development of a cavity in the place of the infarcted brain tissue
- less dysfunction
- smaller areas
hemorrhagic stroke
occurs when a blood vessel in the brain leaks or ruptures; also known as a bleed
- lower fat intake
- can cause epilepsy
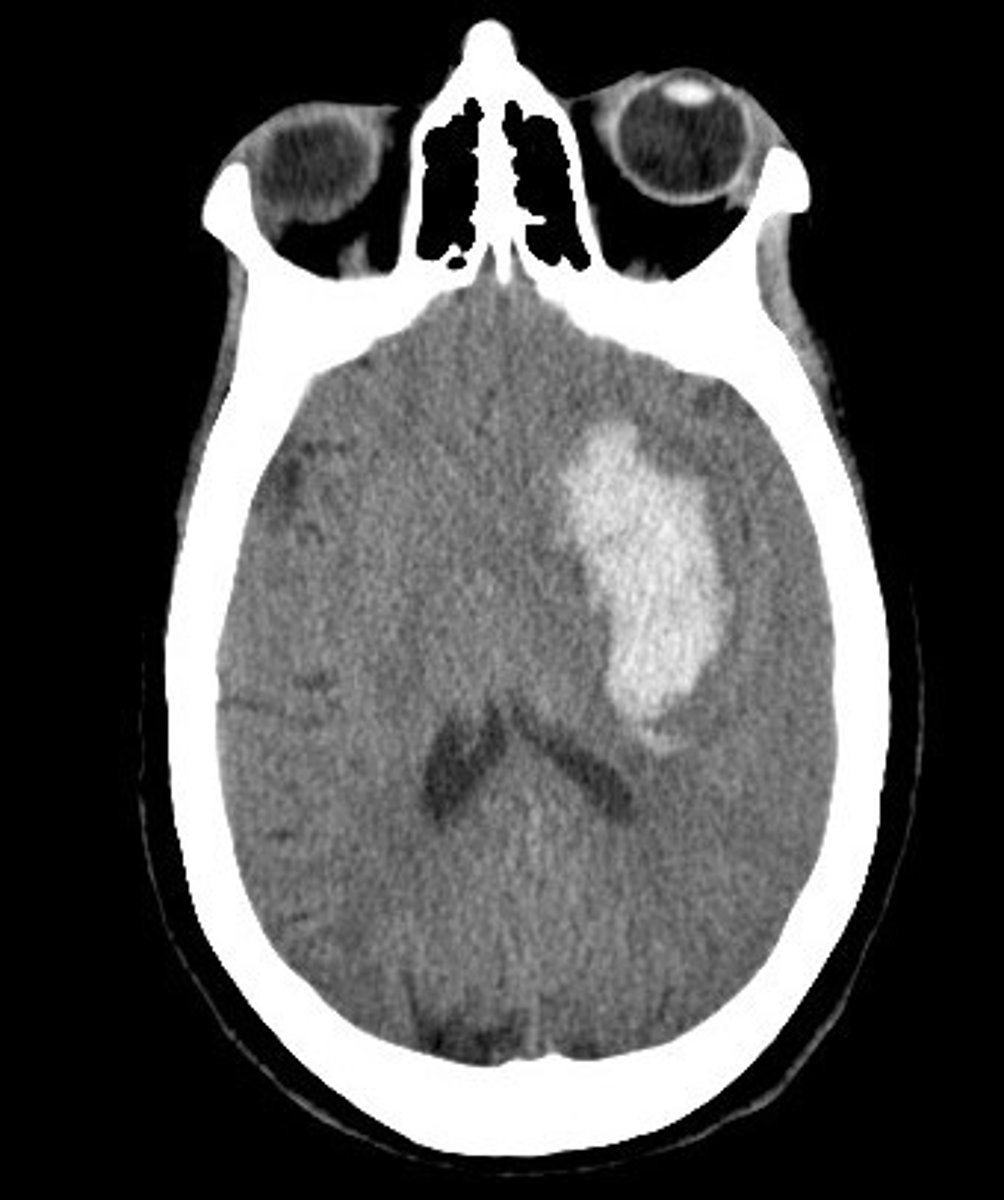
CVA (stroke) artery
usually the middle cerebral artery
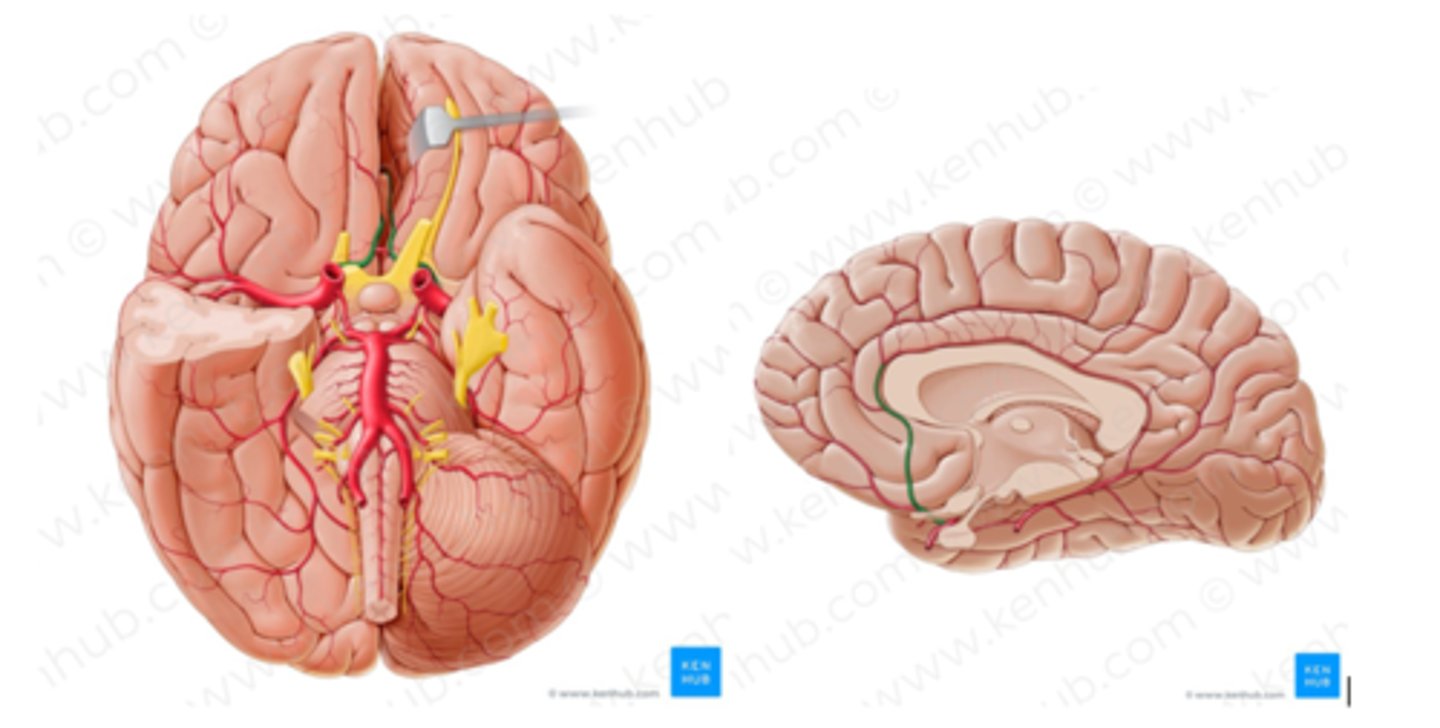
intracranial aneurysm
bulging artery caused by a weakening in the arterial wall
- usually from atherosclerotic disease
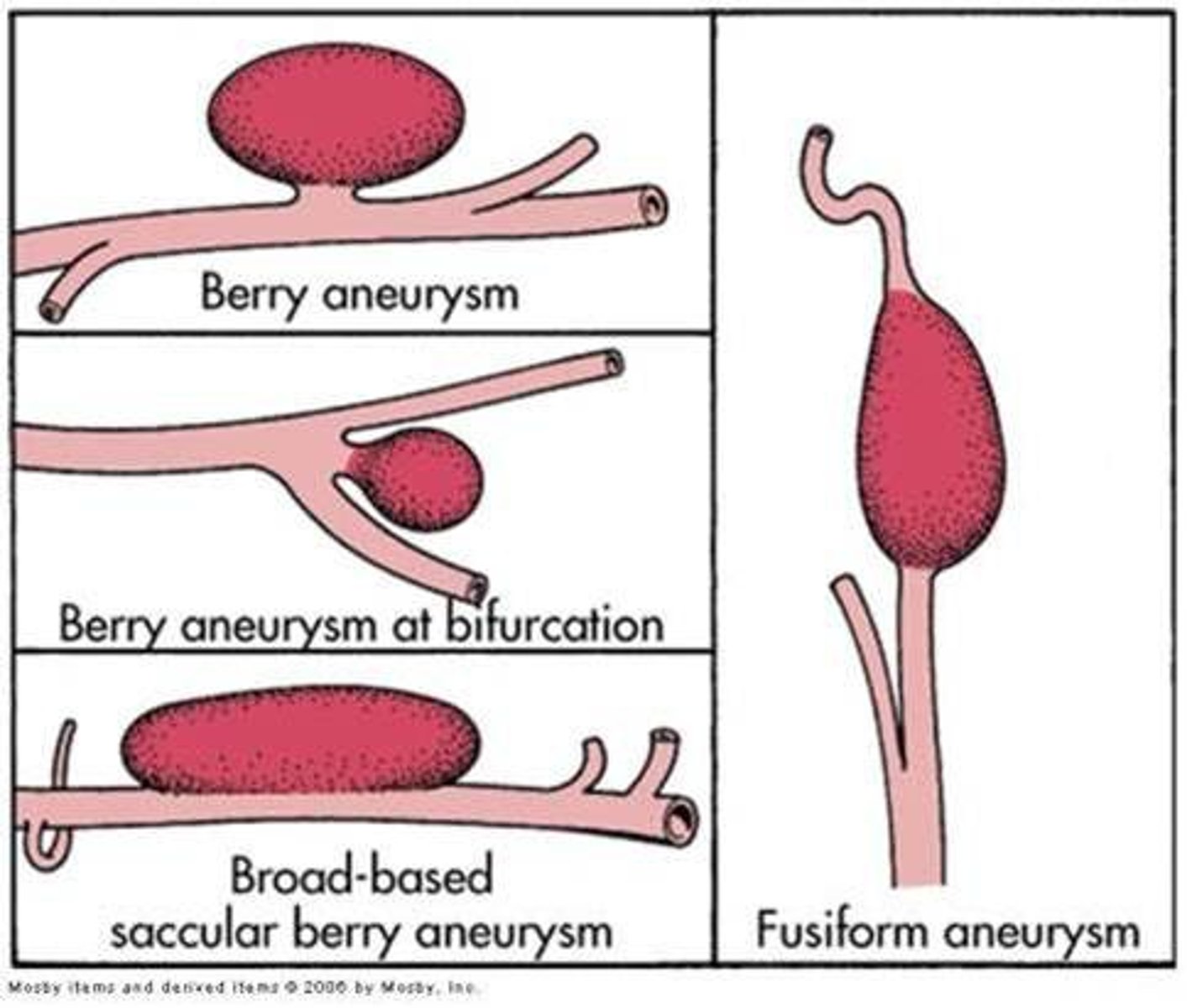
Saccular (berry) aneurysm
Most common cause of subarachnoid hemorrhage
- congenital (present at birth)
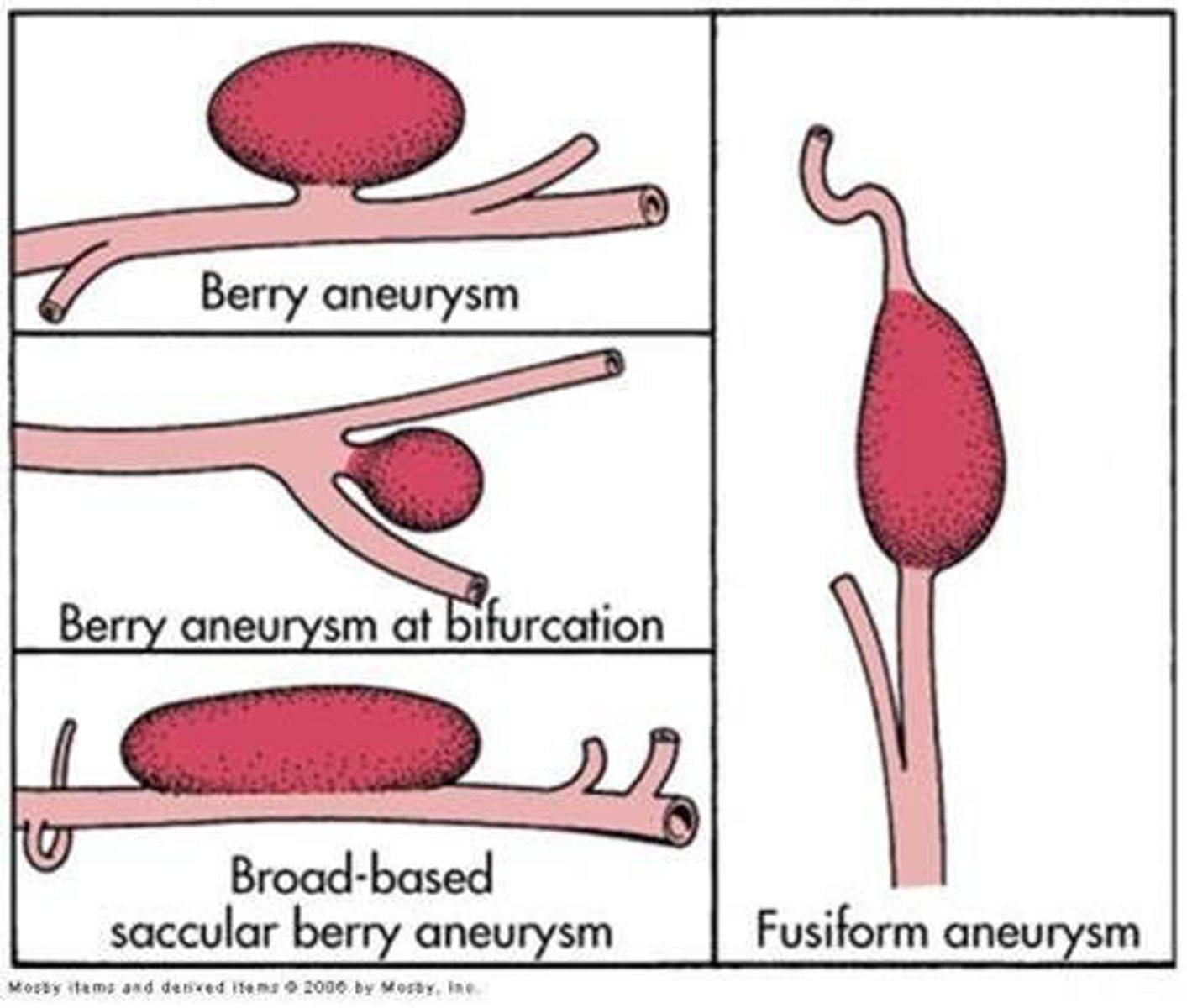
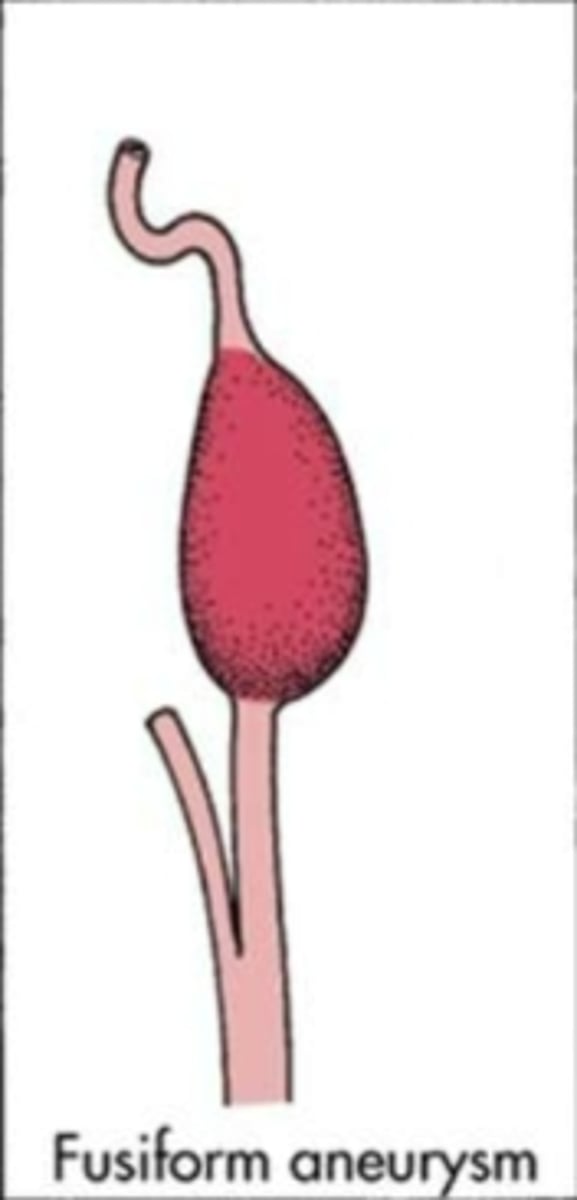
Fusiform (giant) aneurysms
entire artery swells
- from arteriosclerotic changes

Mycotic aneurysm
aneurysm caused by infection
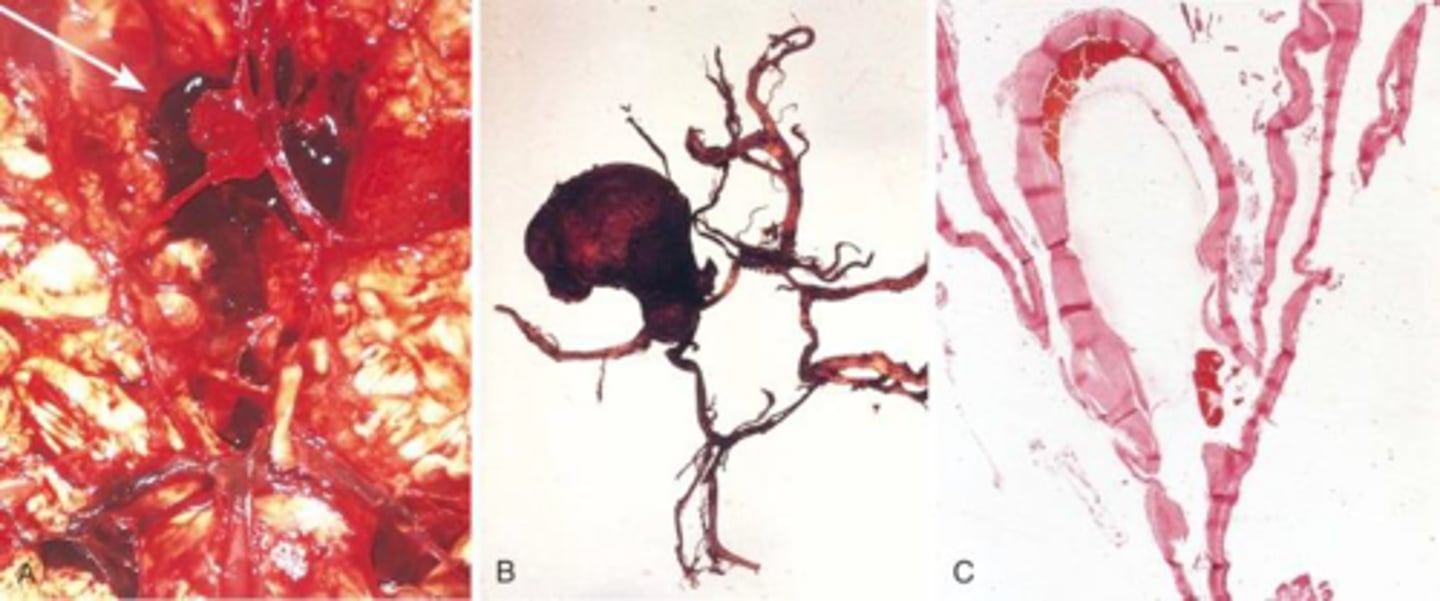
Traumatic (dissecting) aneurysm
show up when they burst
- usually you don't know
- headache
- vomiting
You recall that fusiform aneurysms are
due to arteriosclerotic changes
arteriosclerotic
Narrowing of the lumen of arteries resulting in decreased blood supply to the extremities

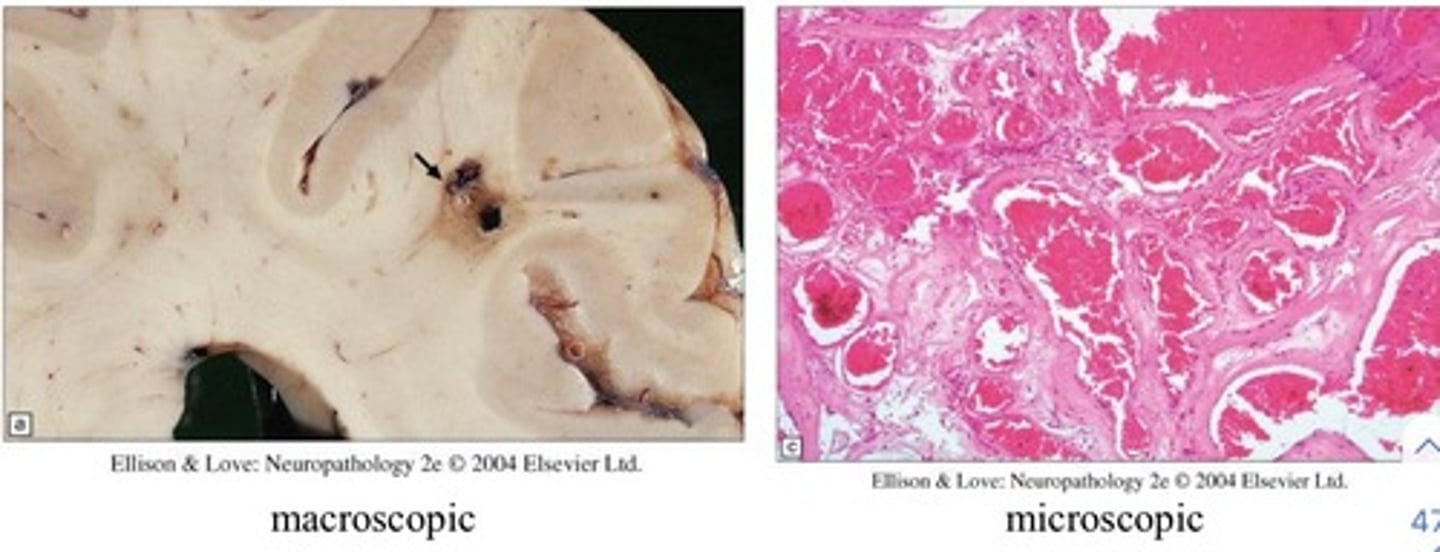
cavernous angiomas
Sinusoidal collections of blood vessels without interspersed brain tissue
capillary telangiectasias
dilated capillaries in brain tissue
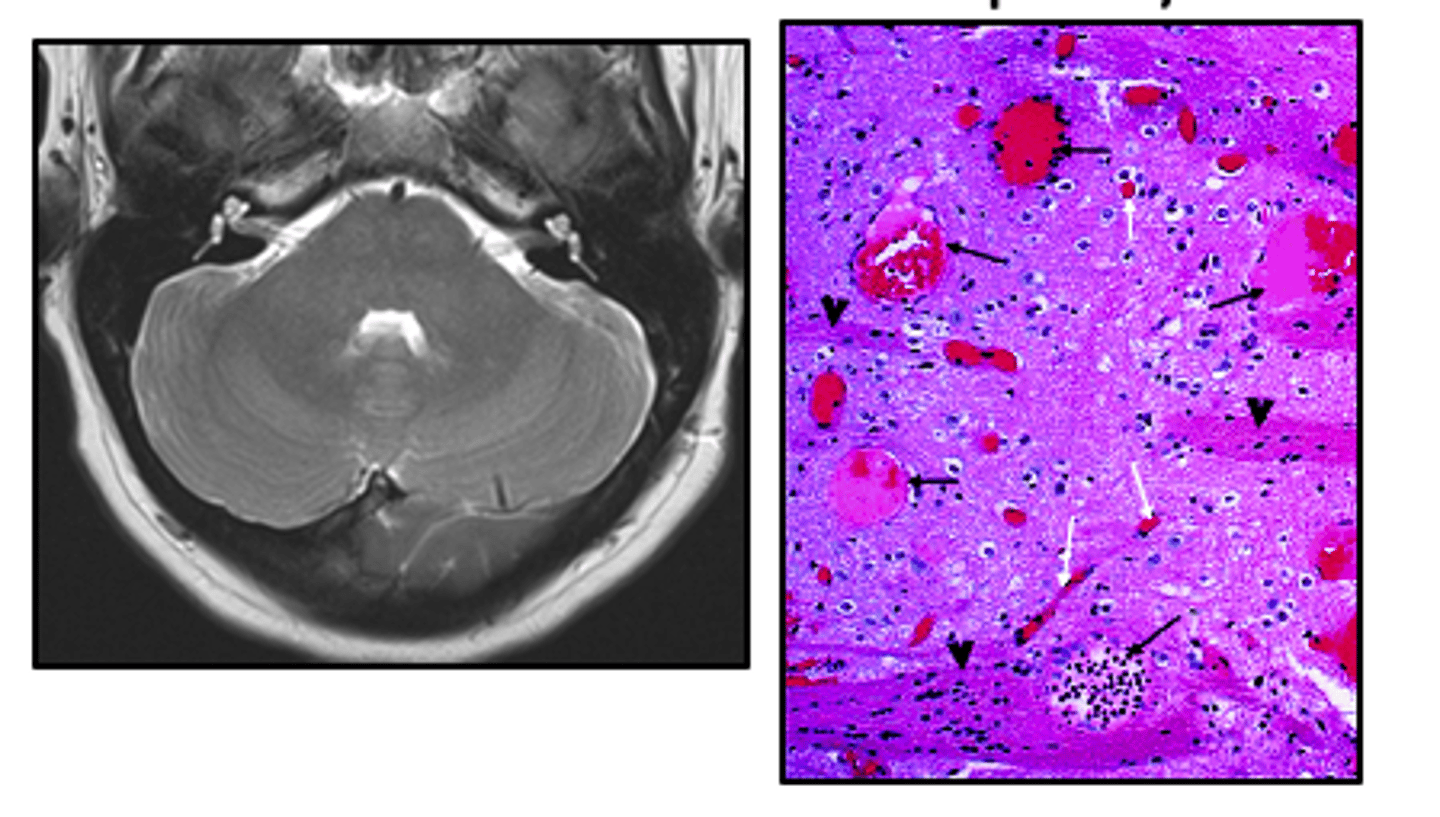
venous angioma
most common
primitive embryologic veins in a radial pattern feeding a central vein
arteriovenous malformation (AVM)
a vascular malformation that is a tangle of abnormal blood vessels connecting arteries and veins in the brain
- can lead to hemorrhage
- surgical treatment
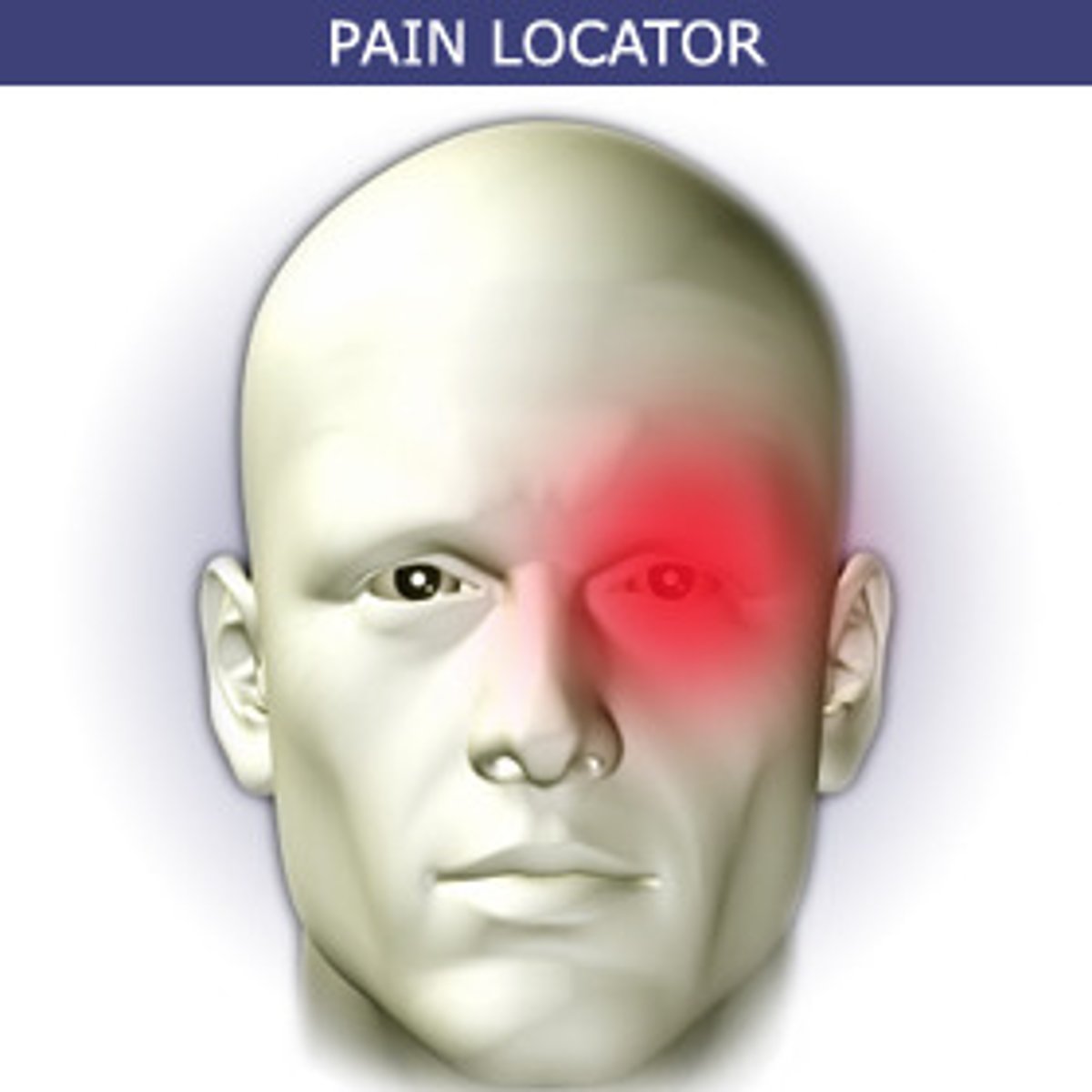
migraine
severe, recurring, unilateral, vascular headache
- light sensitive

cluster headache
Unilateral, severe periorbital headache with tearing and conjunctival erythema.
- several attacks at once
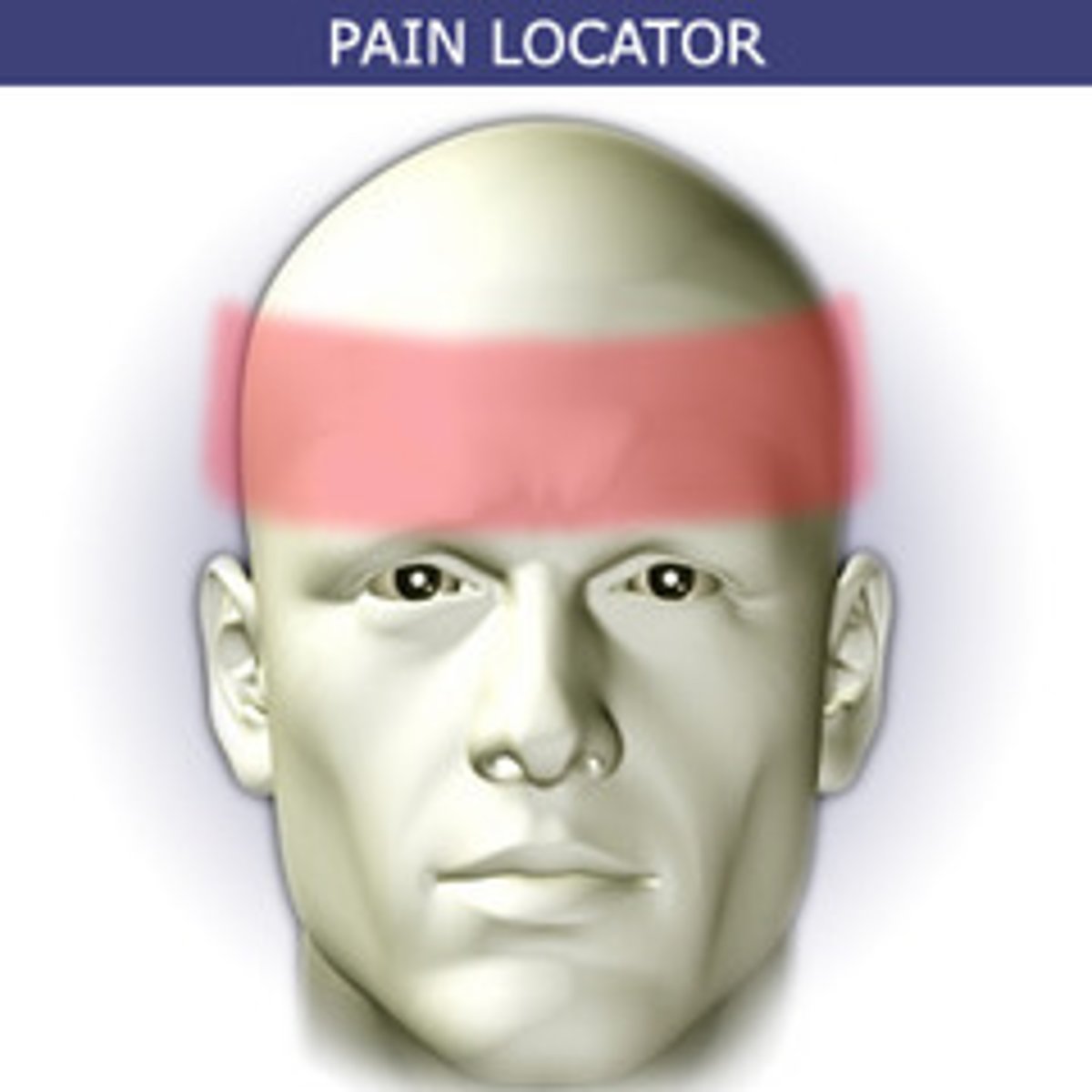
tension headache
most common
- tight band of squeezing pressure
- from muscle tension
headaches are caused by
change in intercranial pressure or pressure in the head muscles
- changes in vasculature

A person arrives at the clinic and reports a unilateral headache for 2days that worsens with movement and light. No trauma has occurred. You suspect
migraine

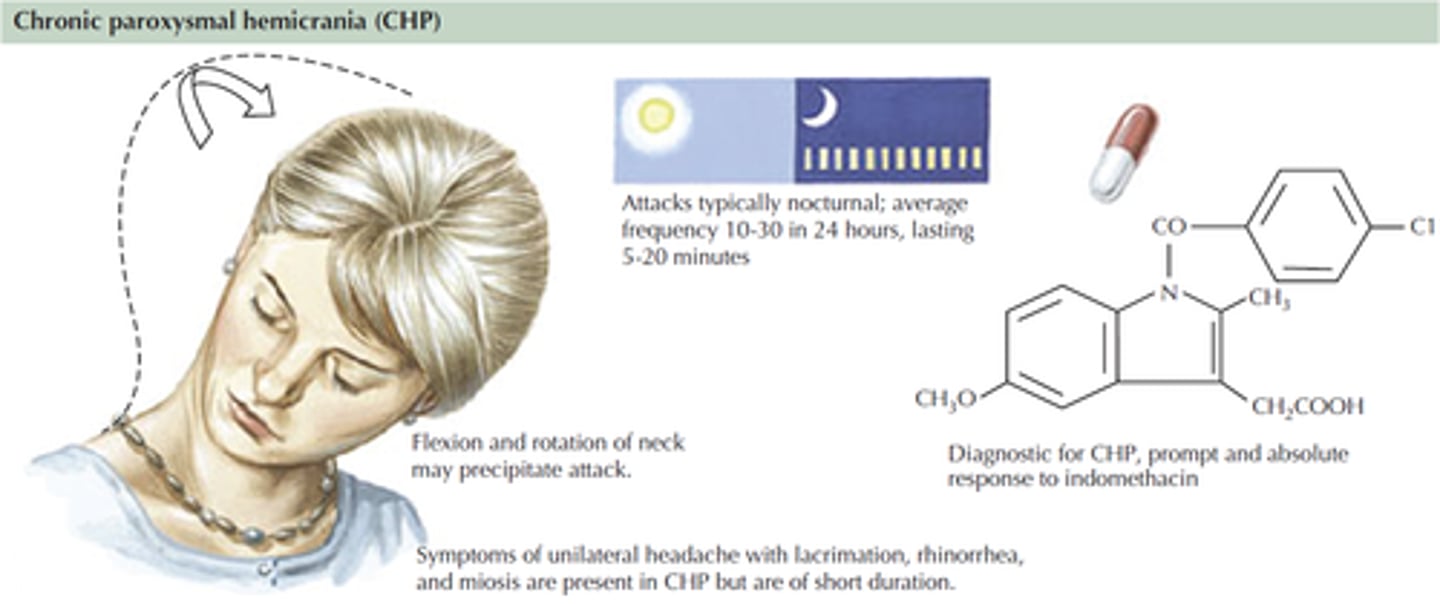
Chronic paroxysmal hemicrania
Cluster-type headache that occurs with more daily frequency (4 to 12/day) but with shorter duration (20-120 minutes)
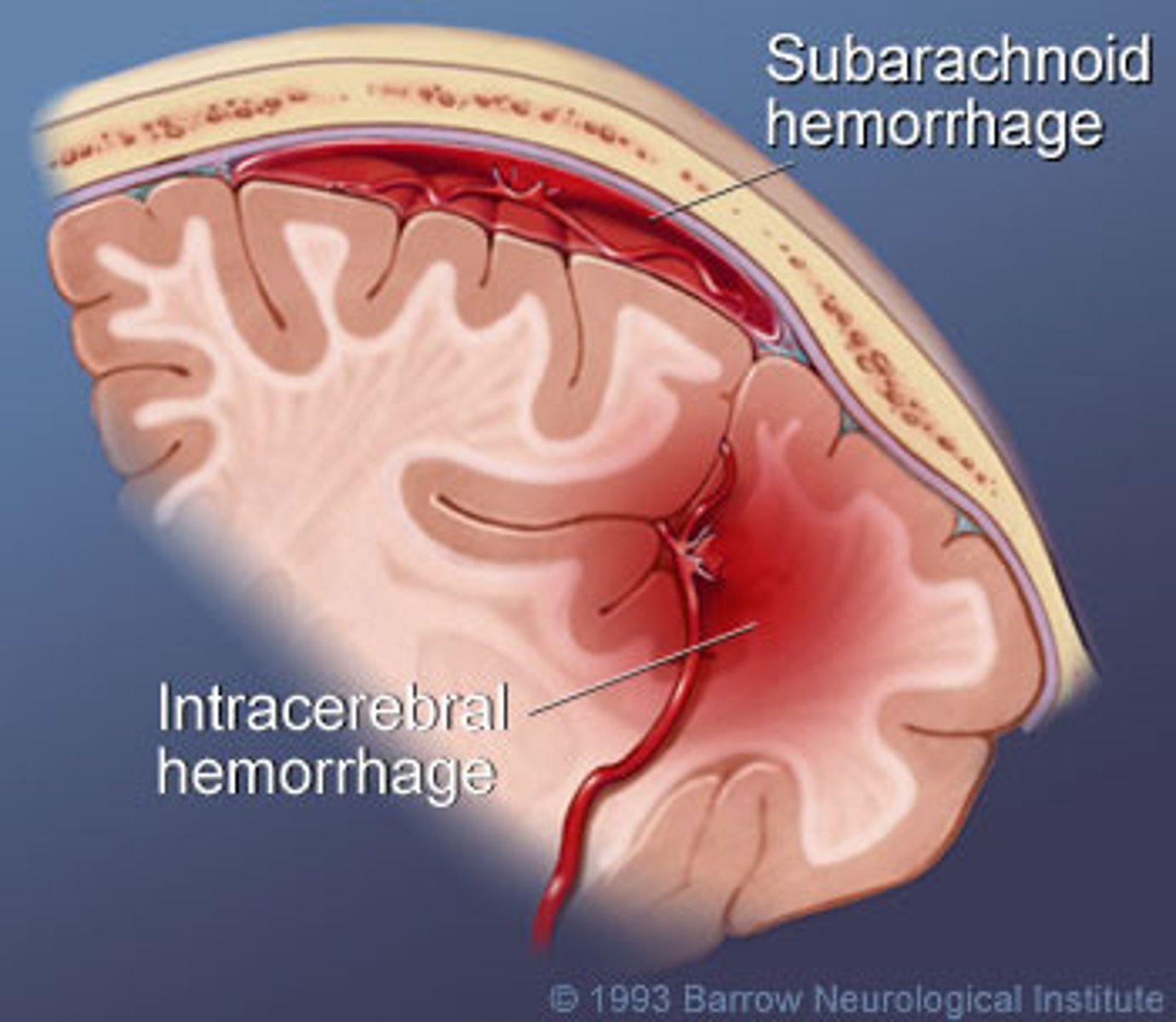
subarachnoid hemorrhage
Bleeding into the subarachnoid space, where the cerebrospinal fluid circulates.
infections of the CNS
Meningitis
Encephalitis
Brain Abscess
NeuroAIDS
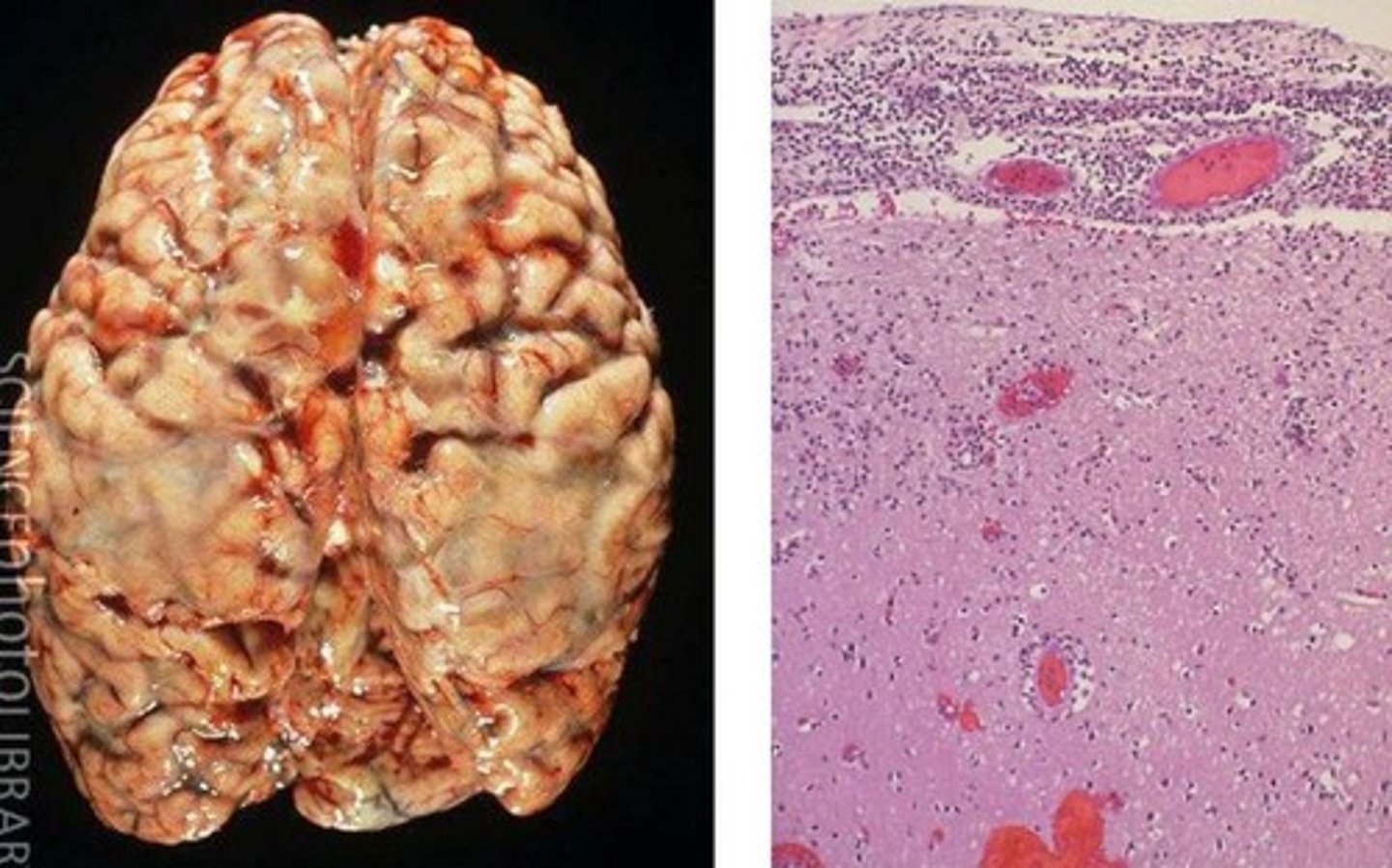
Meningitis
inflammation of the meninges of the brain and spinal cord
- viral or bacterial
- pus on brain (bacterial)
brain abscess
collection of pus anywhere within the brain
- bacteria
- can cause neck stiffness, fever, headache
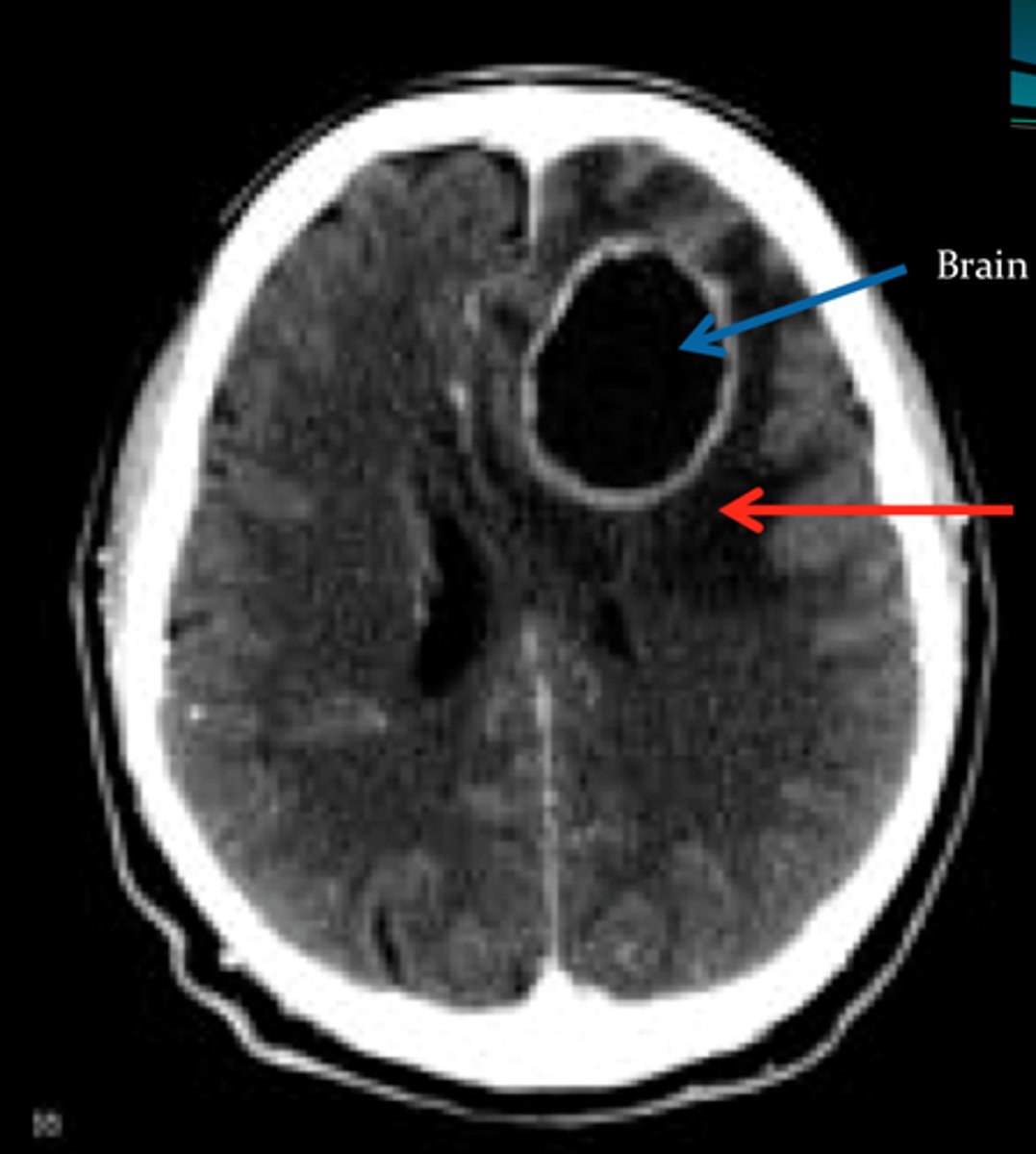
extradural abscess
Abscess located outside the dura mater
- can cause local pain
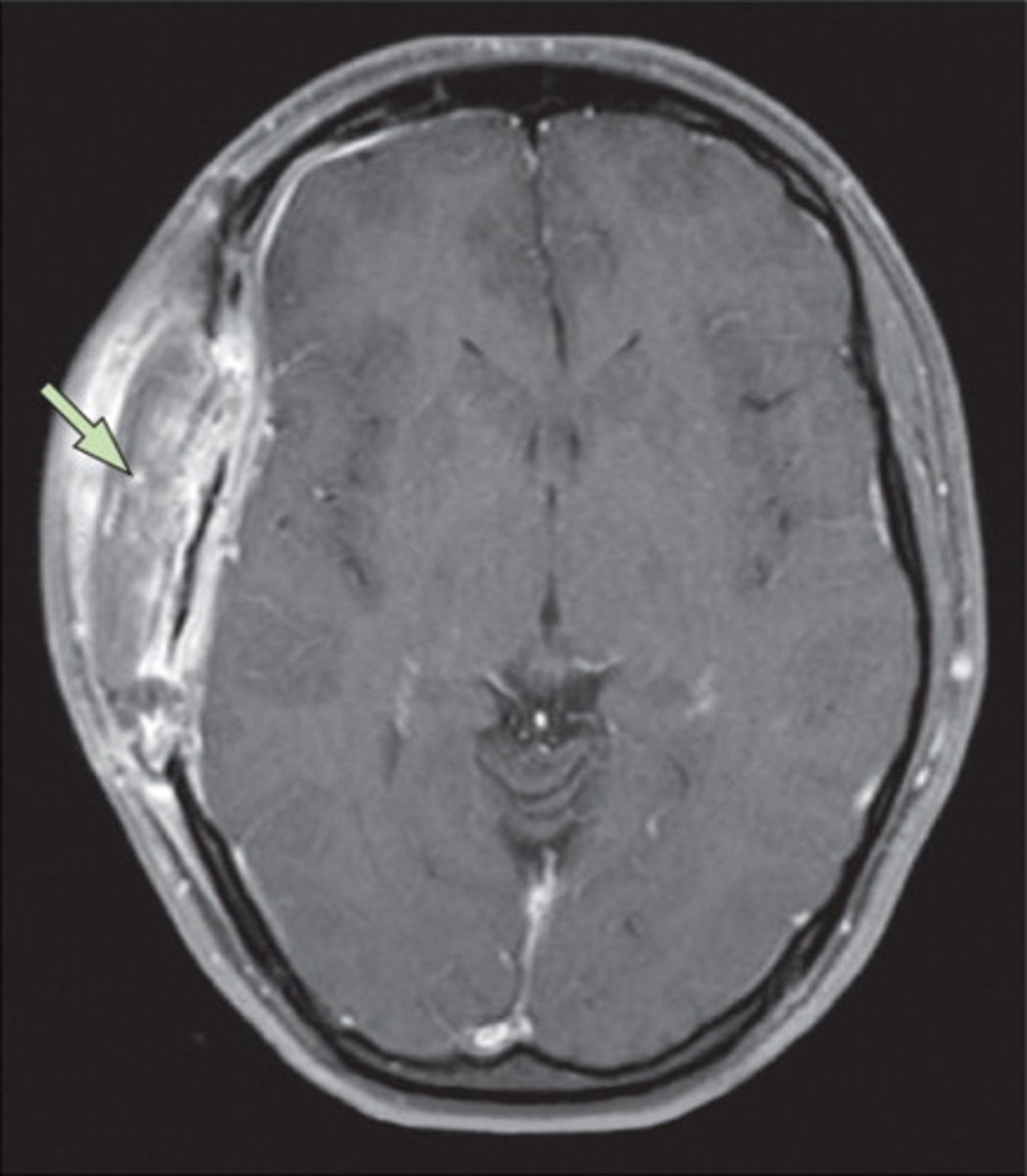
subdural abscess
collection of pus between dura mater and arachnoid mater
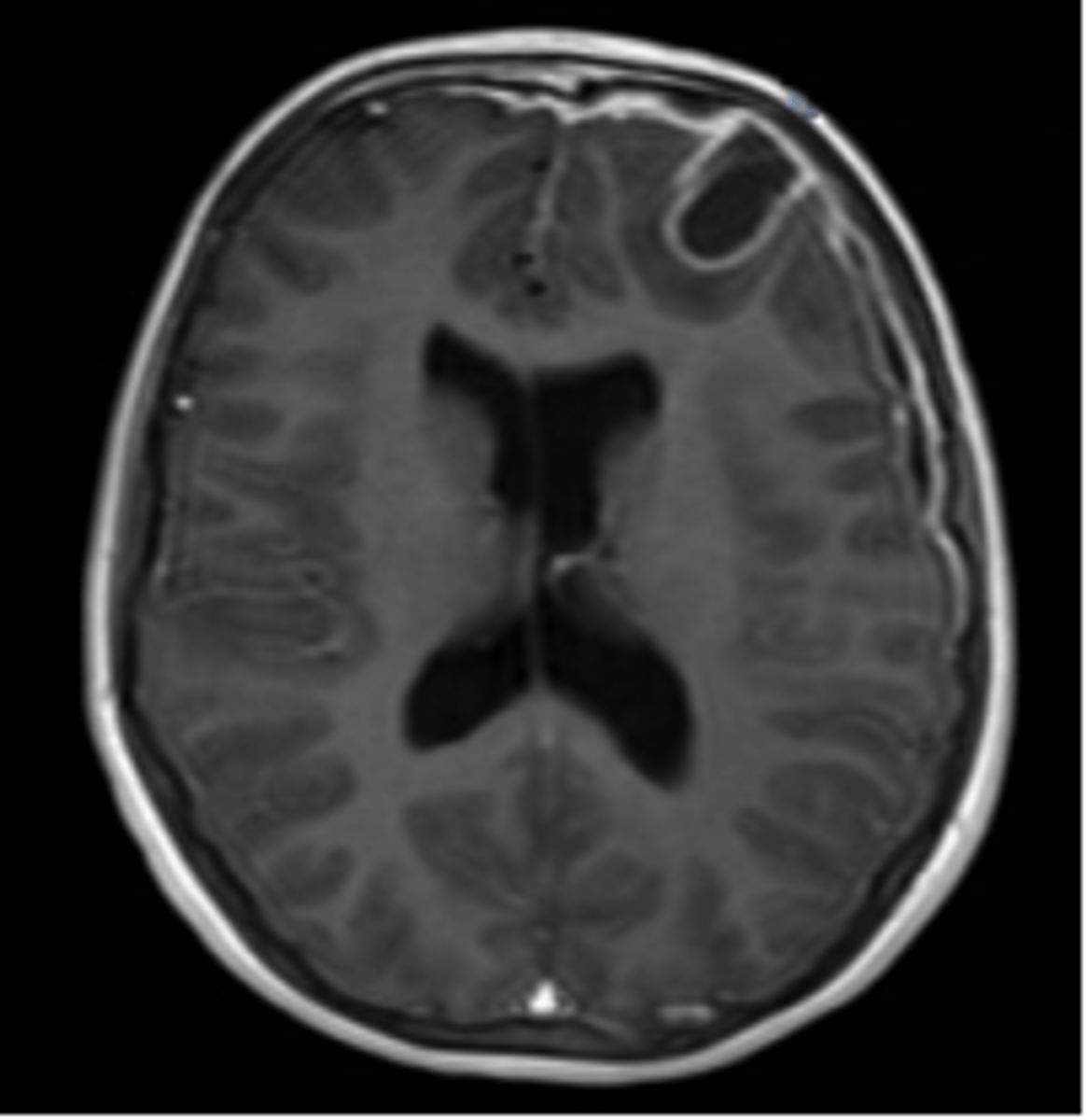
encephalitis
inflammation of the brain usually caused by a virus
- acute febrile illness
- usually arthropod or herpes
- high ICP
- in brain tissue
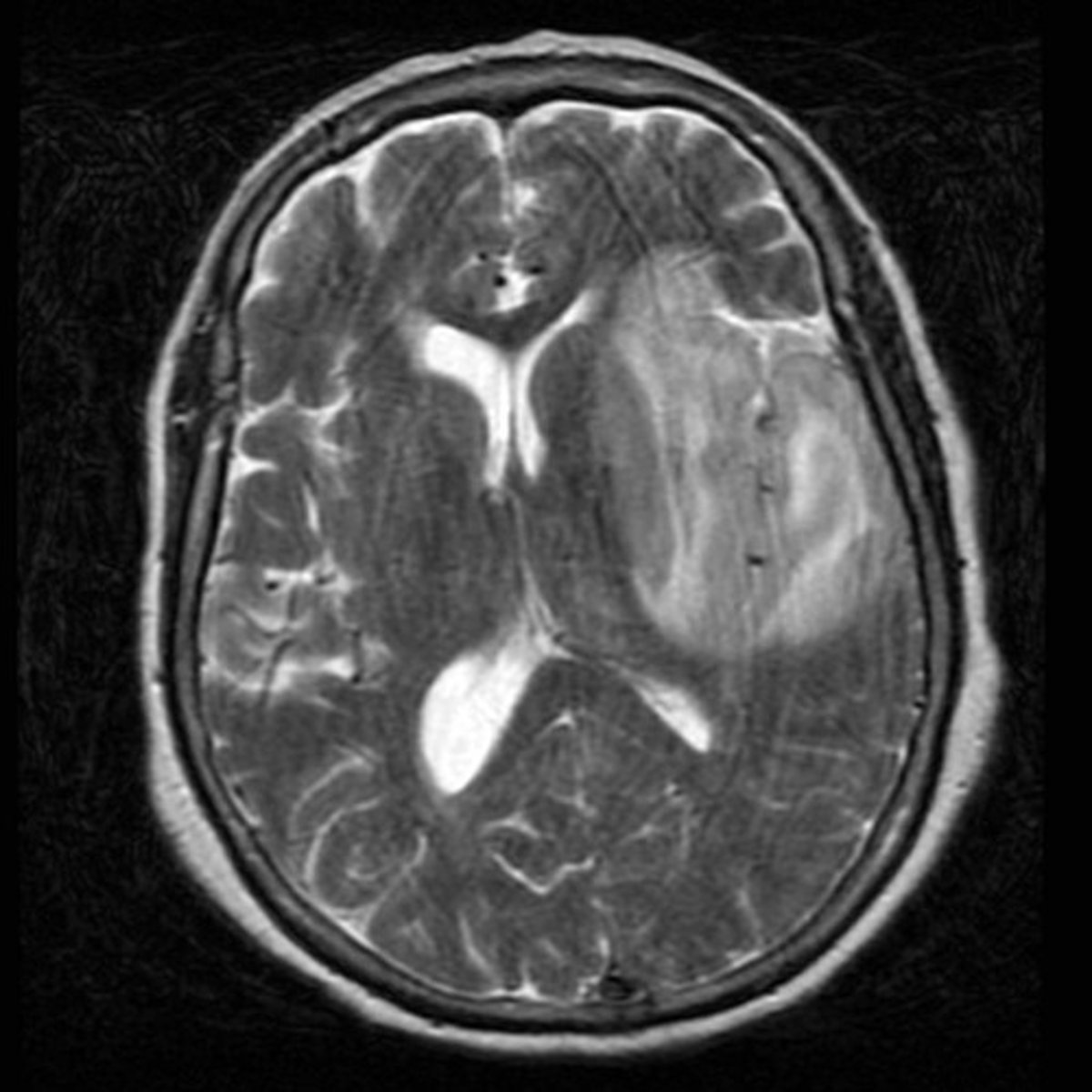
neuroAIDS
Neurological changes as a result of HIV/AIDS that create cognitive deficits and dementia.
- ca infect microglia + perivascular macrophages in CNS
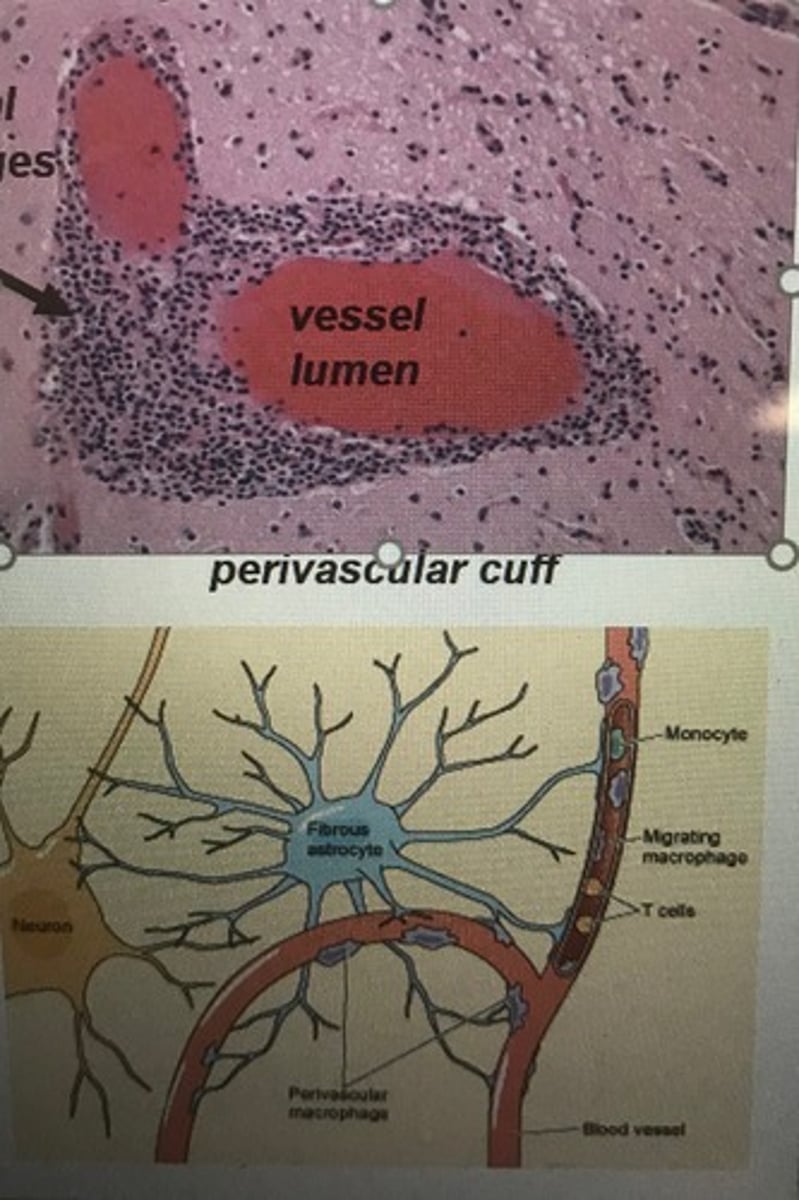
multiple sclerosis
CNS
- demyelination
- autoimmune
- chronic inflammation
- more often in women
- lesions more common in white matter
- steroids can help, vit D and b cell therapy
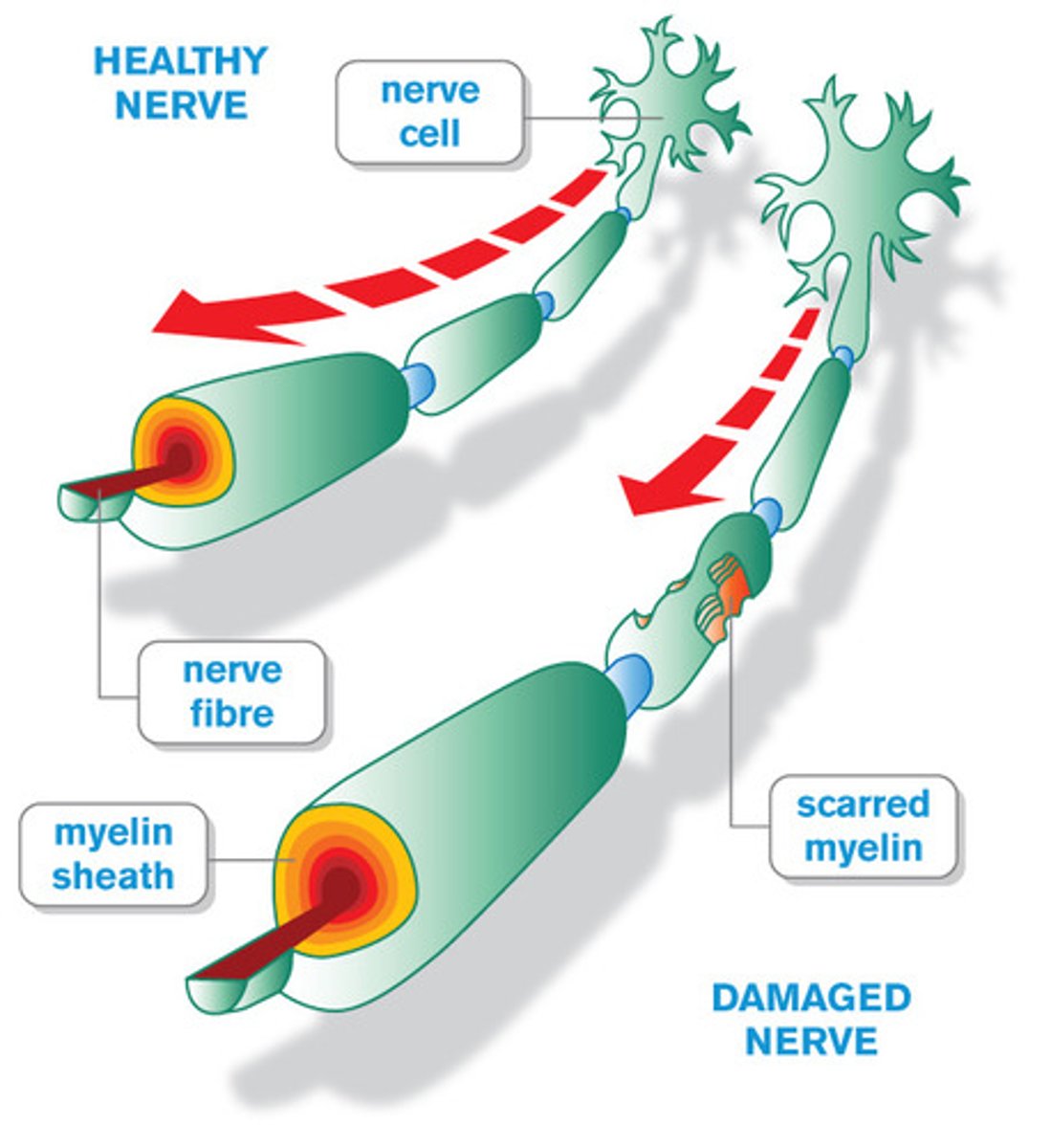
Guillain Barre Syndrome
PNS
inflammation of the peripheral nerves where myelin sheaths on axons are destroyed, resulting in decreased nerve impulses, loss of reflex response, and sudden muscle weakness
- attacks schwann cells
- occurs after viral infection
- acute
- autoimmune
neuropathy
dysfunction in peripheral nerves
Generalized symmetric polyneuropathies
type of neuropathy characterized by symmetrical involvement of sensory, motor, or autonomic fibers
- diabetic neuropathy
- guillain barre

generalized neuropathies
sensory or motor
what is usually affected by neuropathy?
usually the feet/ lower limbs
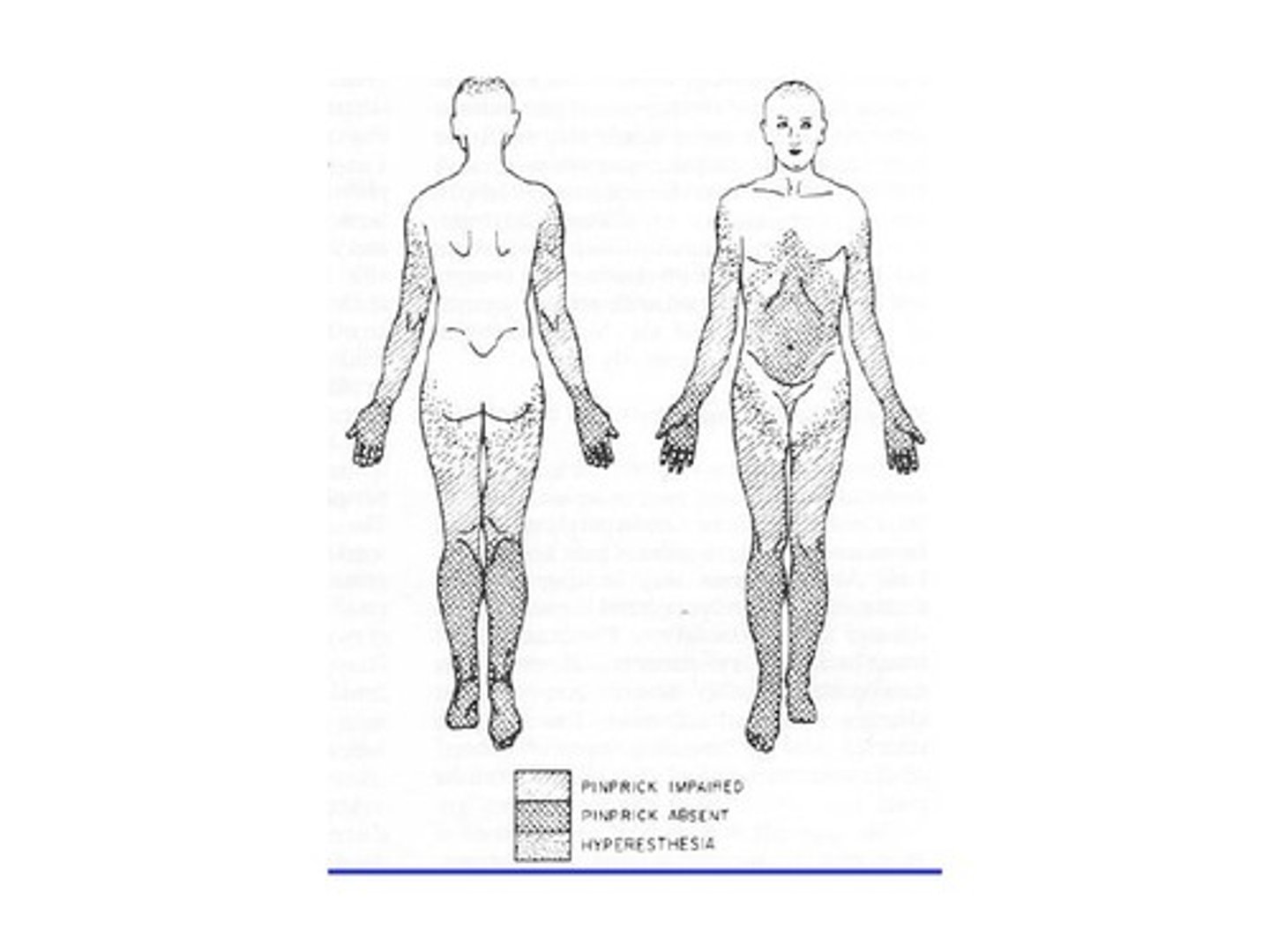
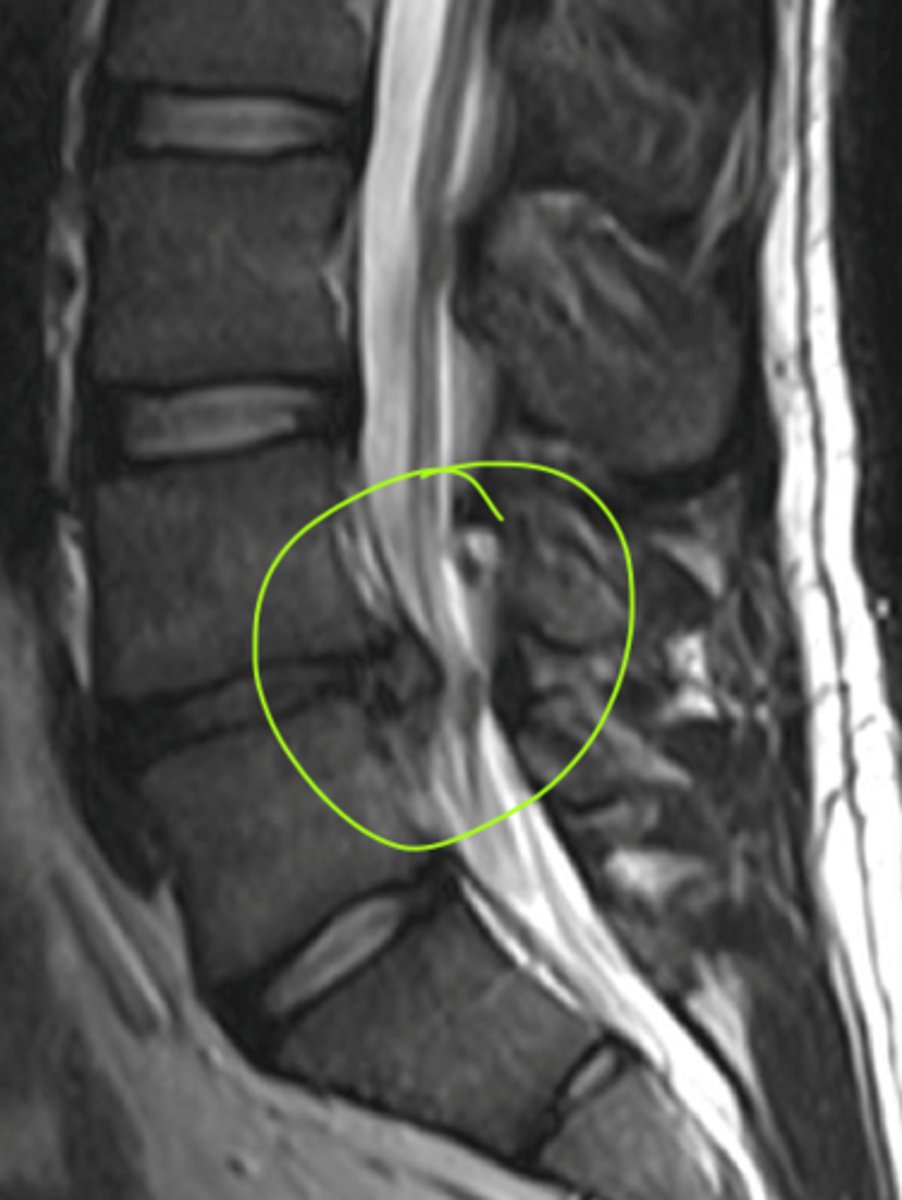
radiculopathies
Disorders of spinal nerve roots
- Caused by compression, infection, inflammation, ischemia, or direct trauma
- action potential prevented
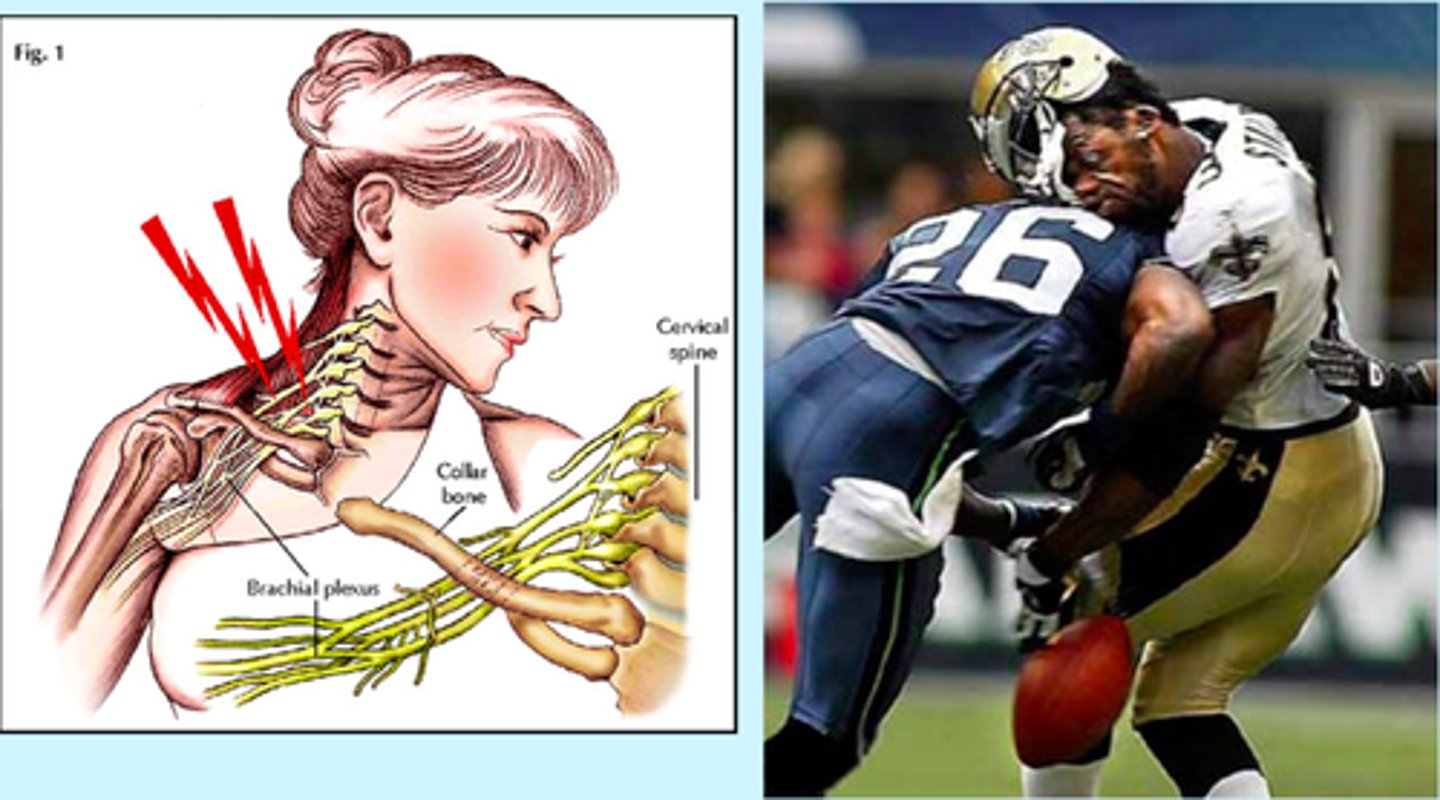
plexus injuries
occurs when the nerve networks (brachial or lumbosacral plexus) are damaged due to trauma, stretching, or compression, leading to weakness, numbness, or paralysis in the affected limb
- rehab
- amino acids
- repair tissues
neuromuscular junction disorders
Myasthenia gravis, Lambert-Eaton syndrome
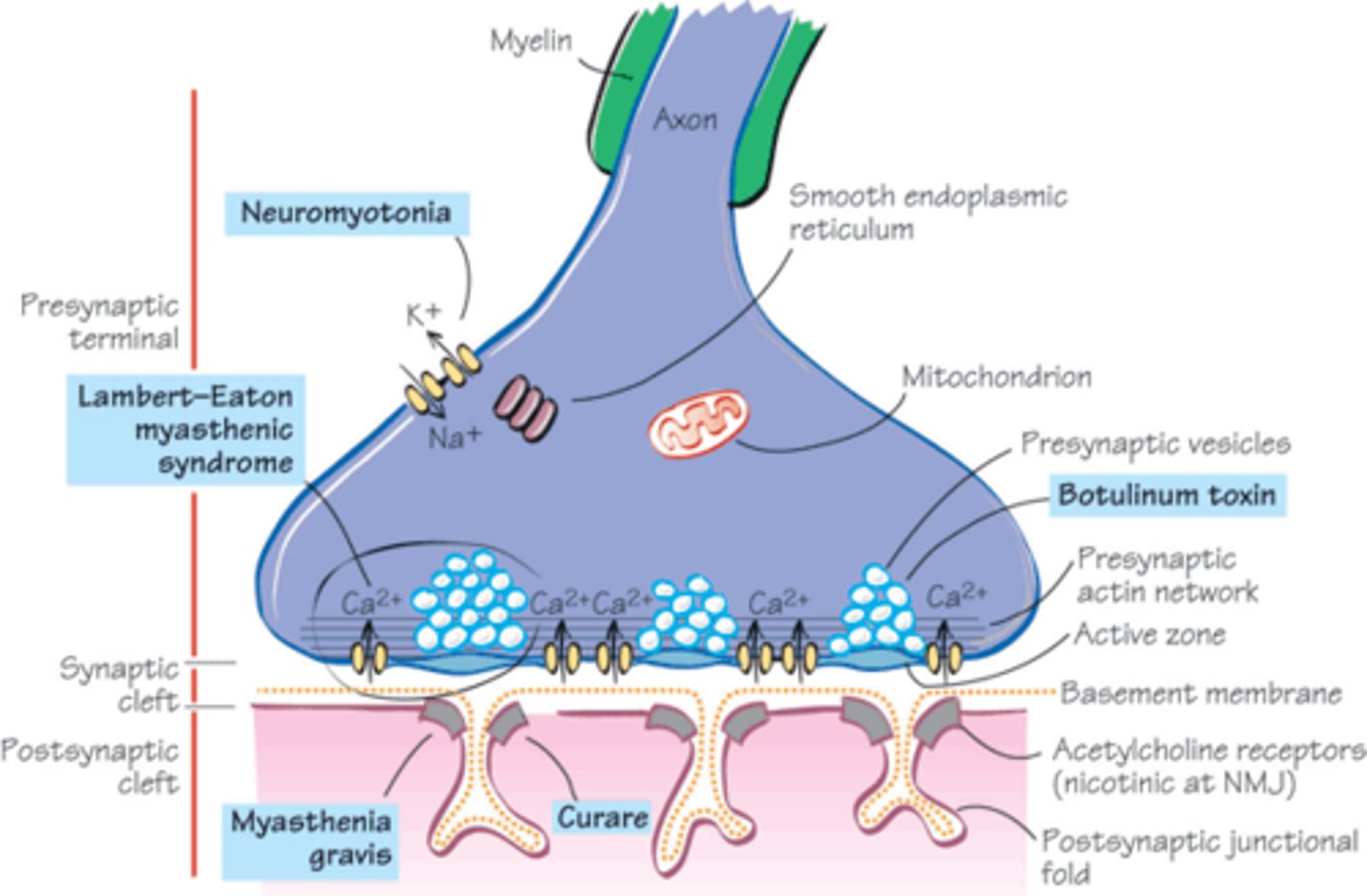
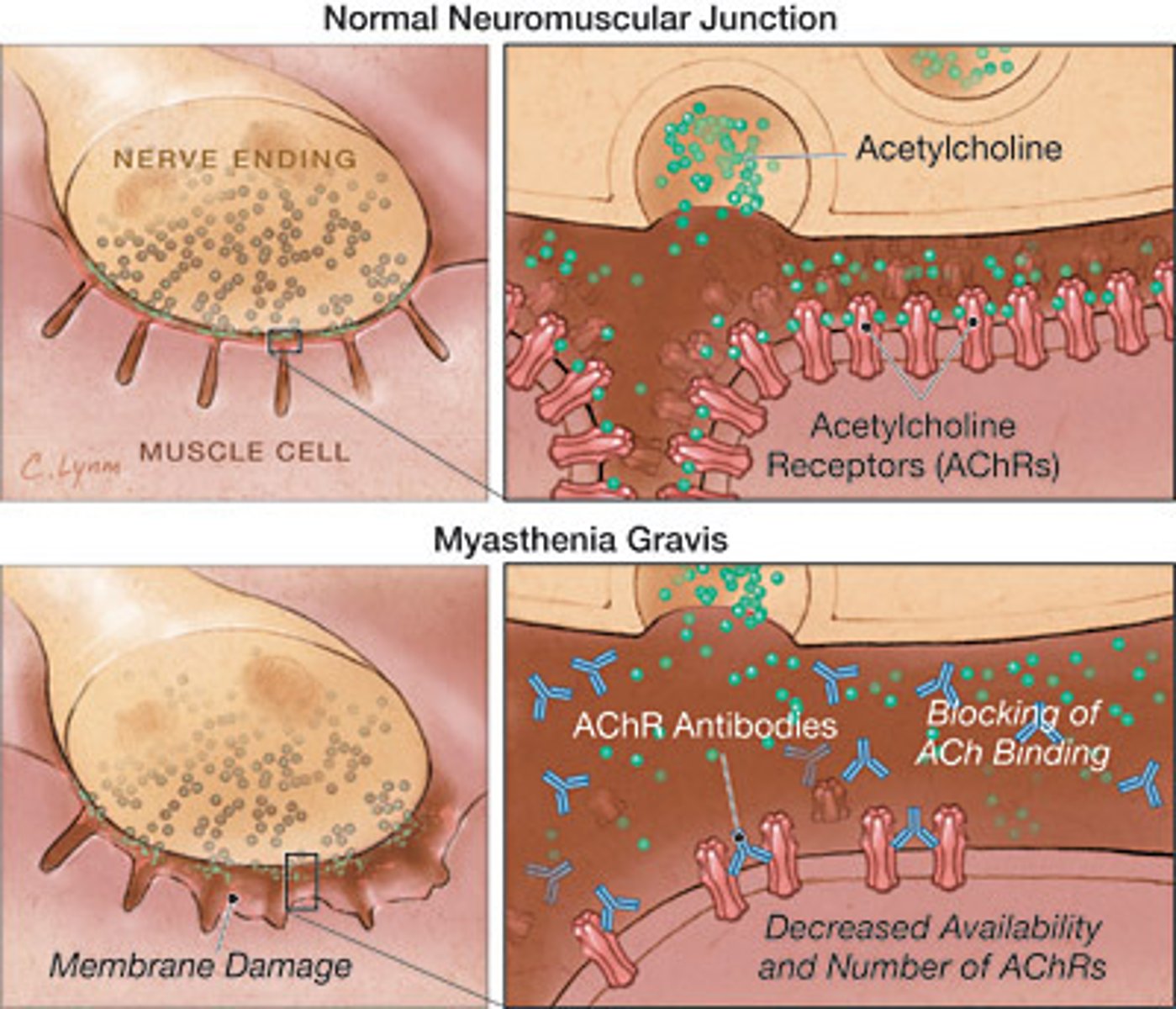
myasthenia gravis
a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the neuromuscular junction by producing antibodies (IgG) against acetylcholine receptors
- can paralyze diaphragm
- immunotherapy best cure
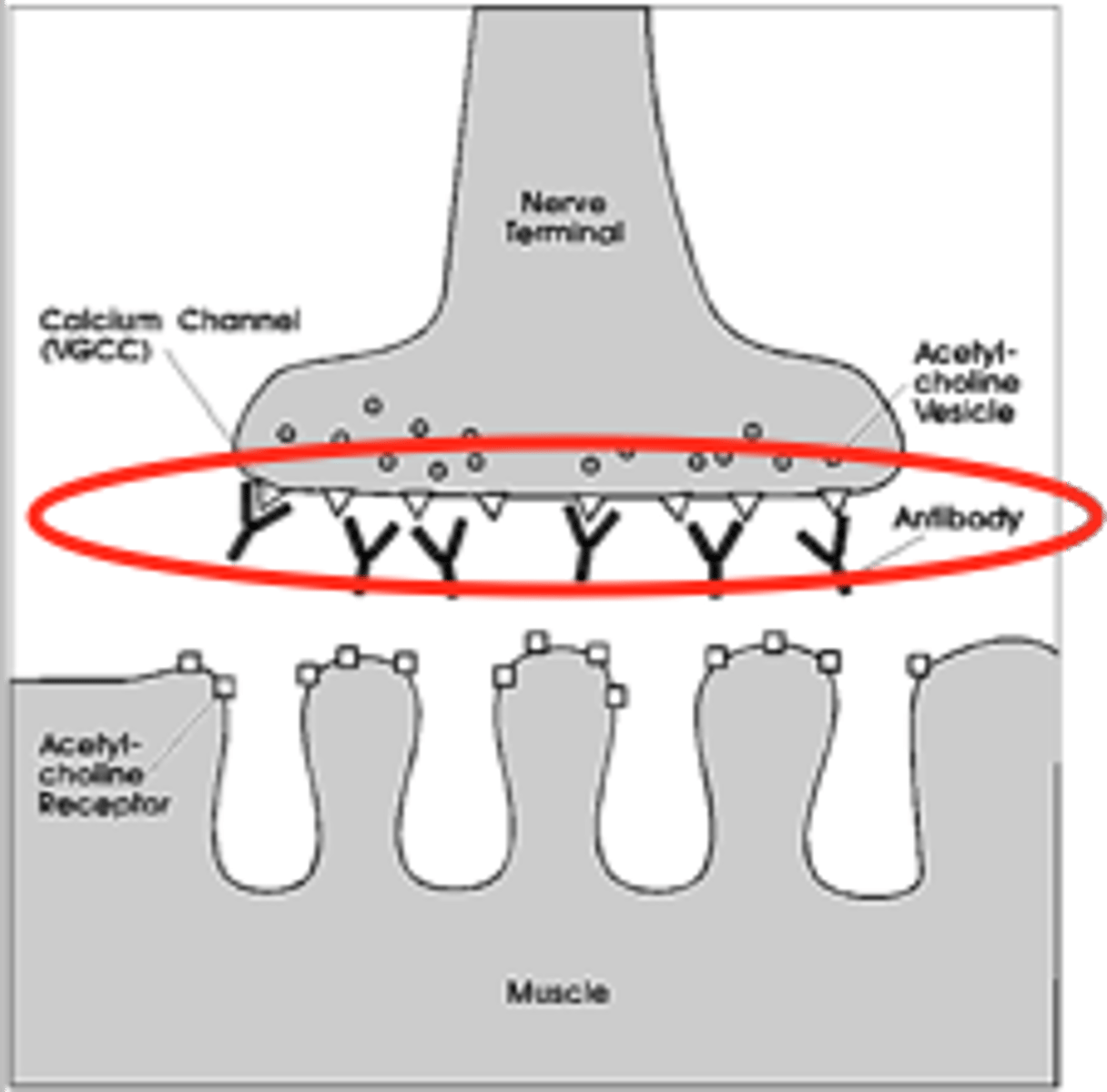
Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome
body's immune system attacks calcium channels at the nerve endings, reducing neurotransmitter release and causing muscle weakness.
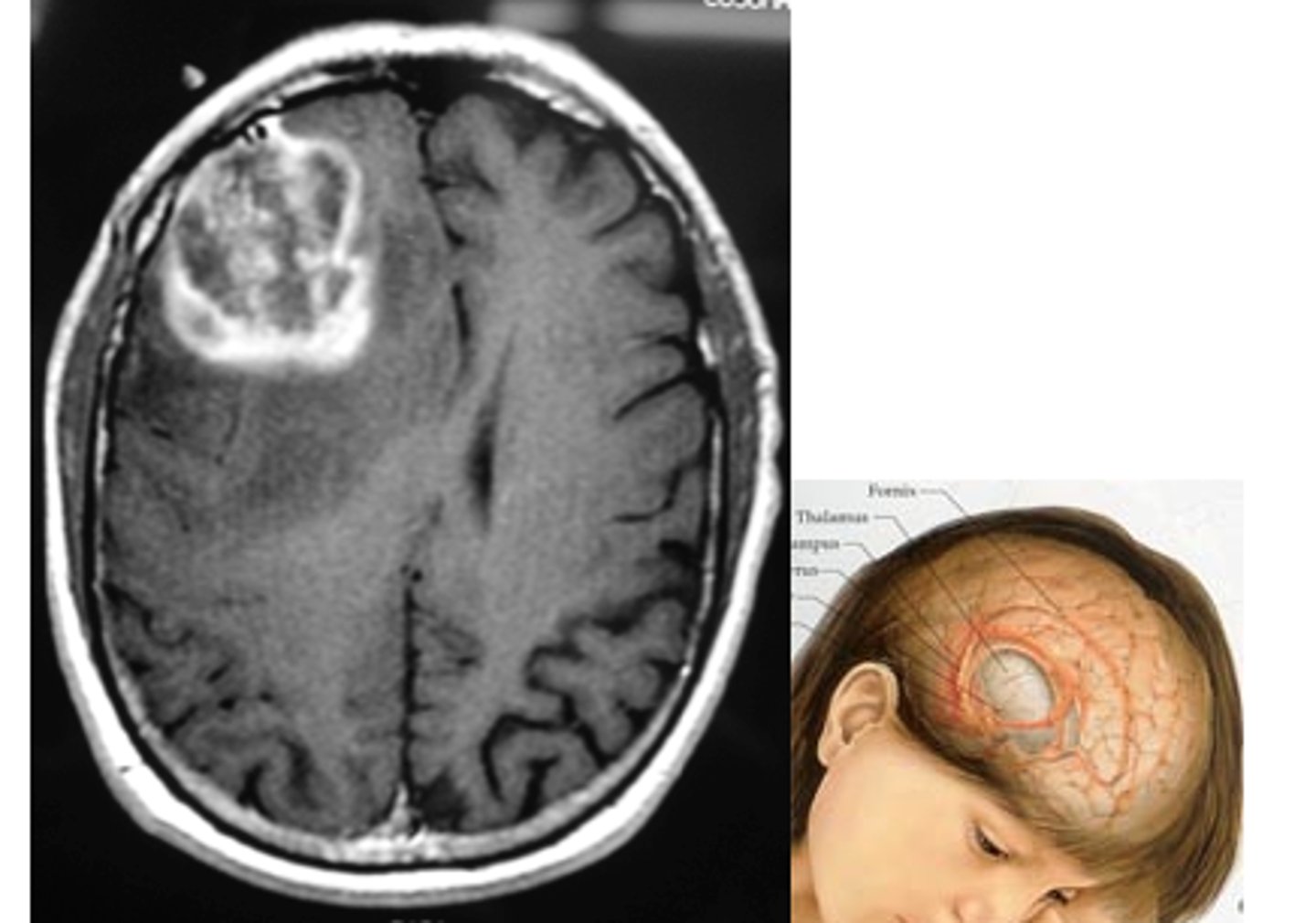
primary brain tumor (gliomas)
brain tumor that originates in the brain
- radiotherapy most affective, chemo cat get through BBB
- compression causes the issues
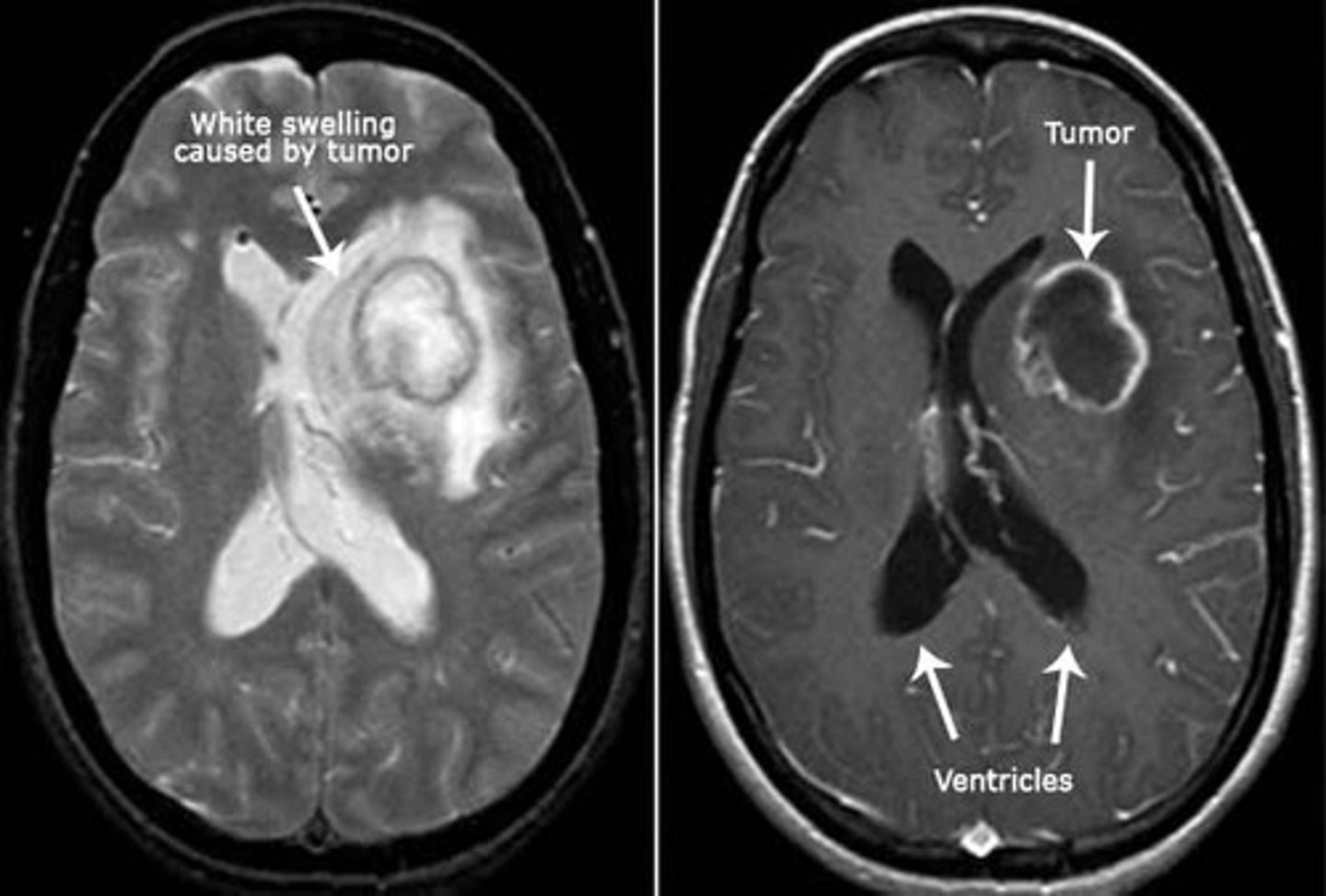
glioblastoma
malignant brain tumor arising from glial cells
- worst form
- stage 4 astrocytoma
oligodendroglioma
Malignant tumor of oligodendrocytes
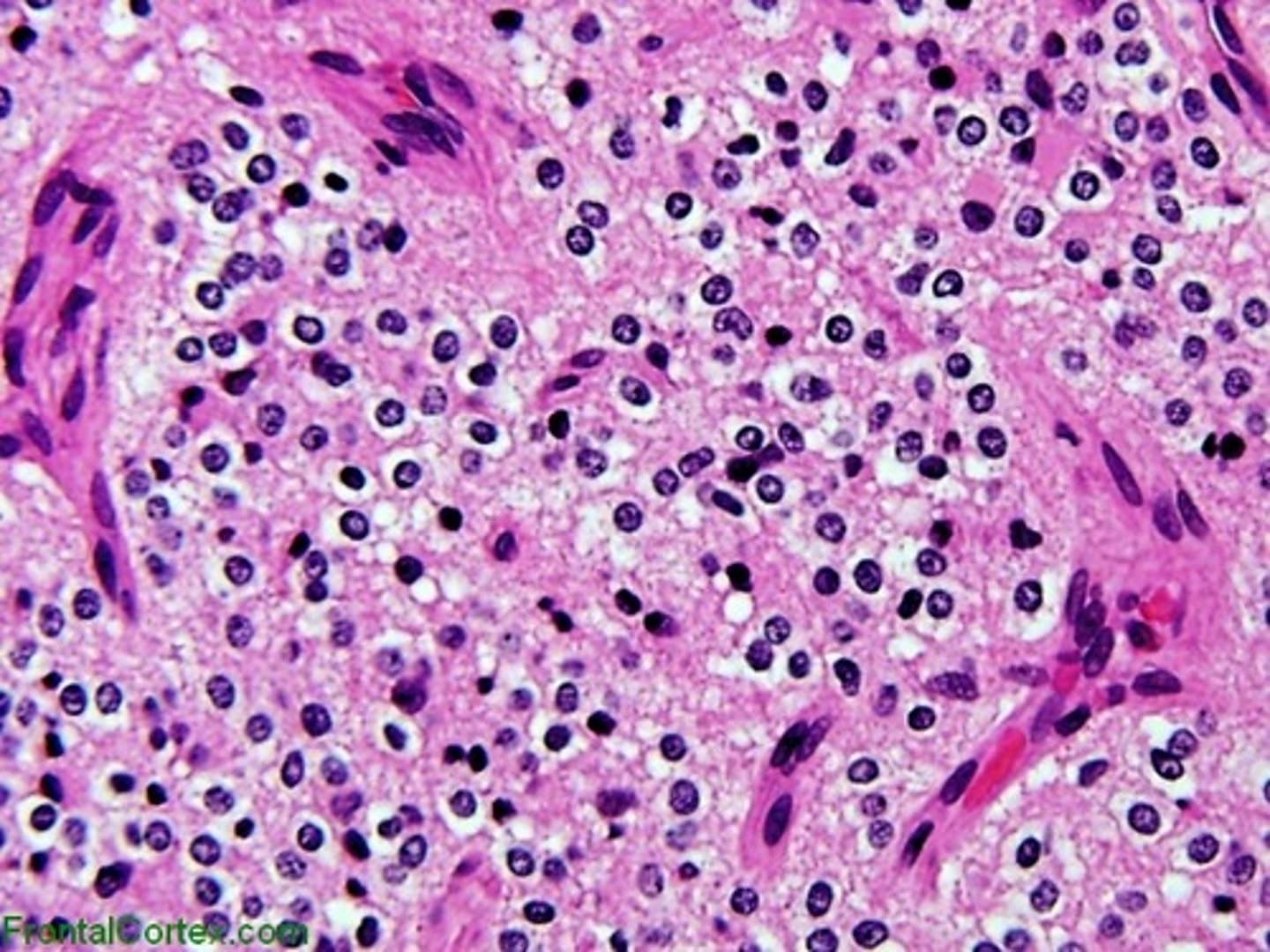
astrocytoma
tumor deriving from Astrocytes; basically benign, slowgrowing tumor.
- surgery, radiation
- most common
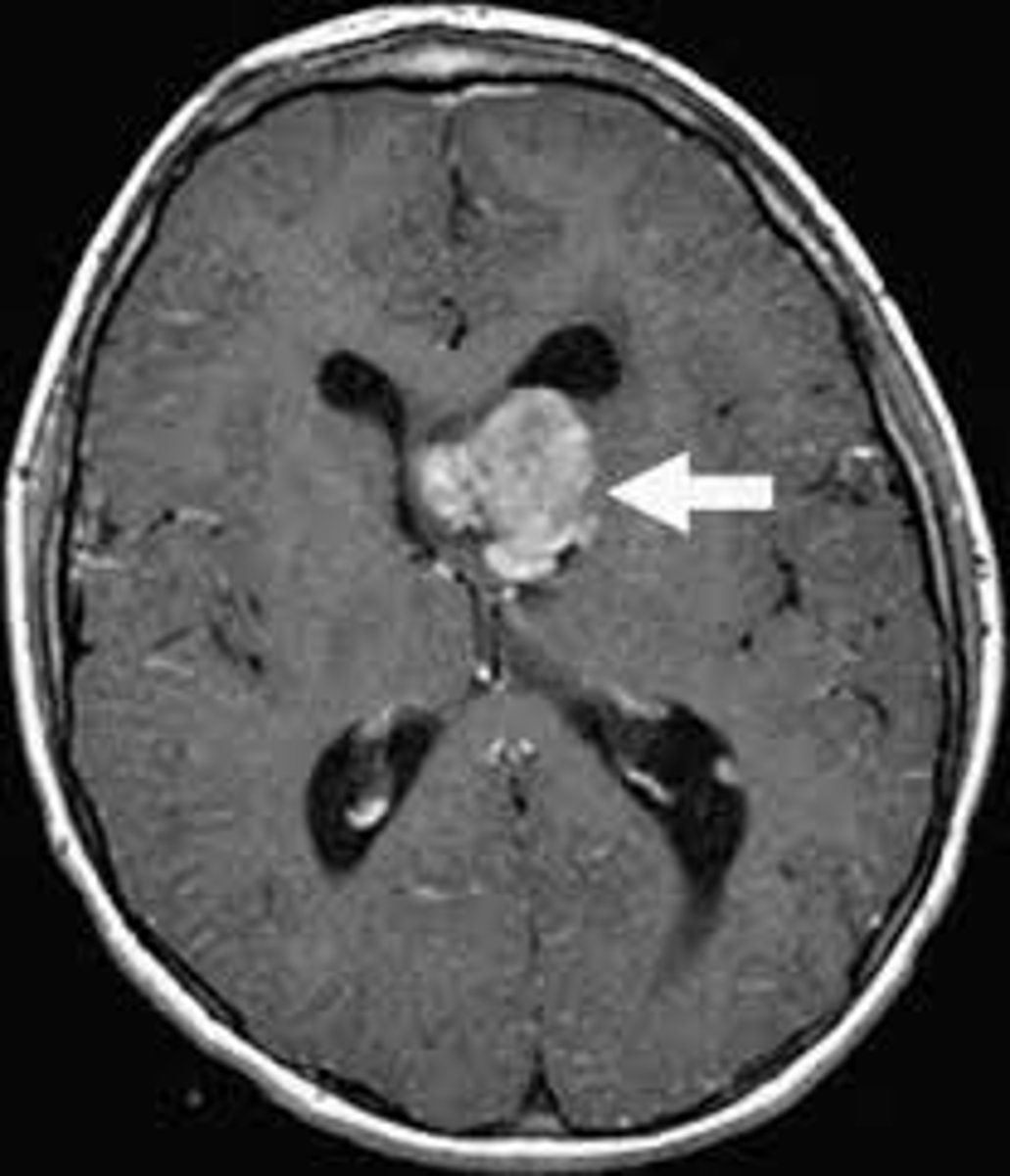
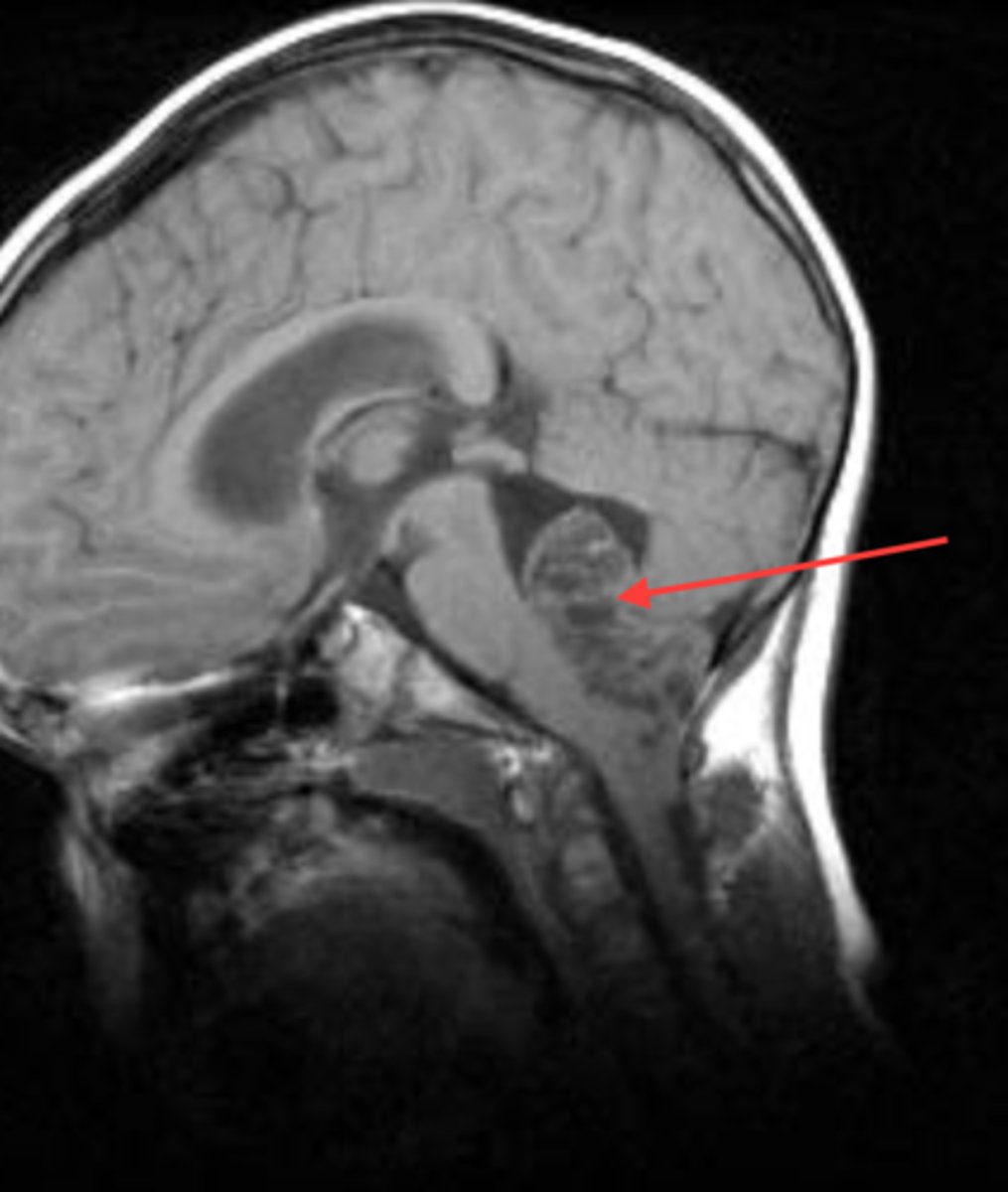
ependymomas
Tumor arising from the wall of the fourth ventricle, especially in children, and the lateral ventricles in adults
- non capsulated makes surgery hard
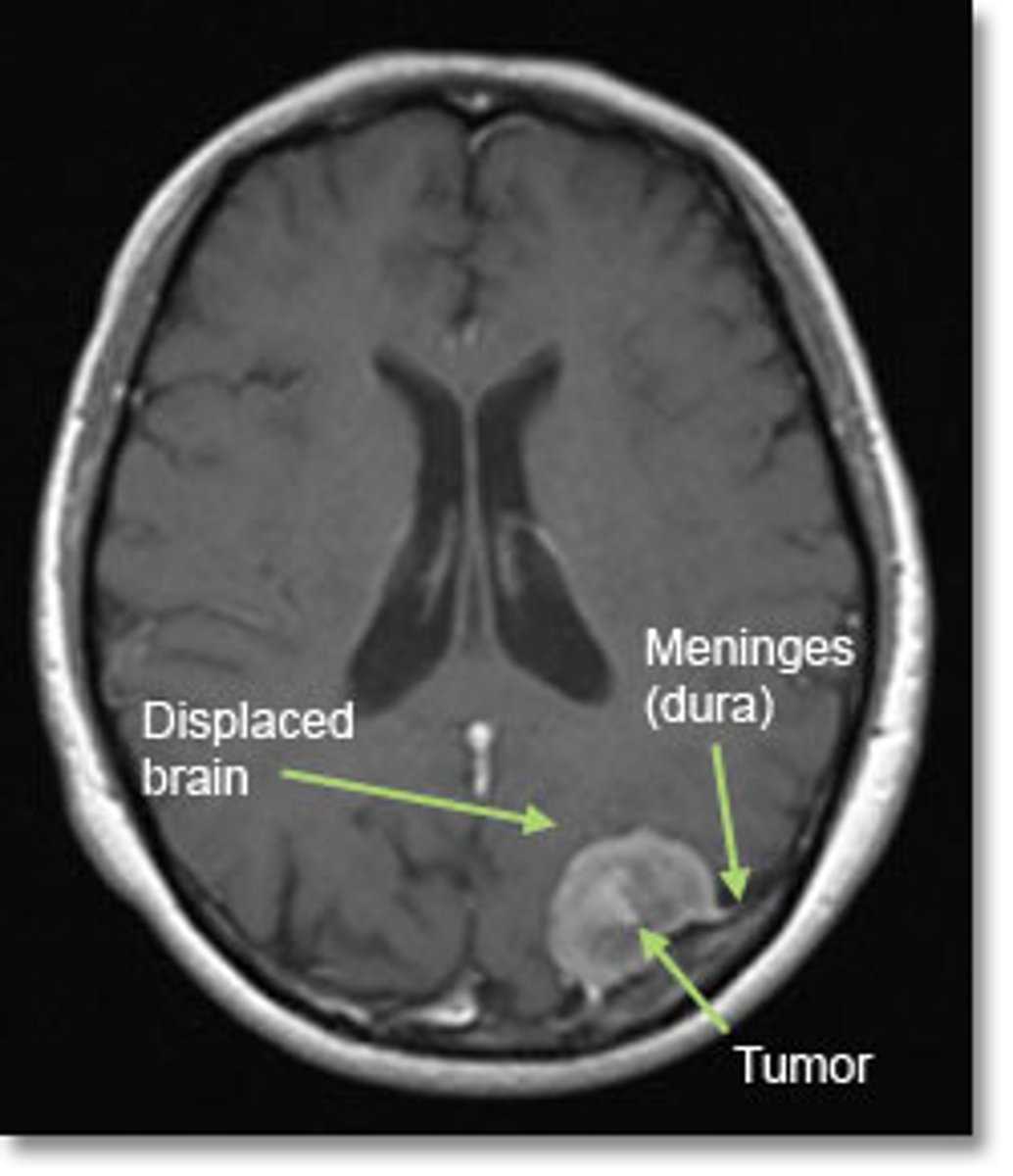
meningiomas
tumors that grow between the meninges
- slow growing
- capsules
- pressure causes seizures
- surgery + drugs to reduce tumor
brain tumor symptoms
compression causes cerebral edema
- headache
- vomiting
- seizure
-behavioral issues
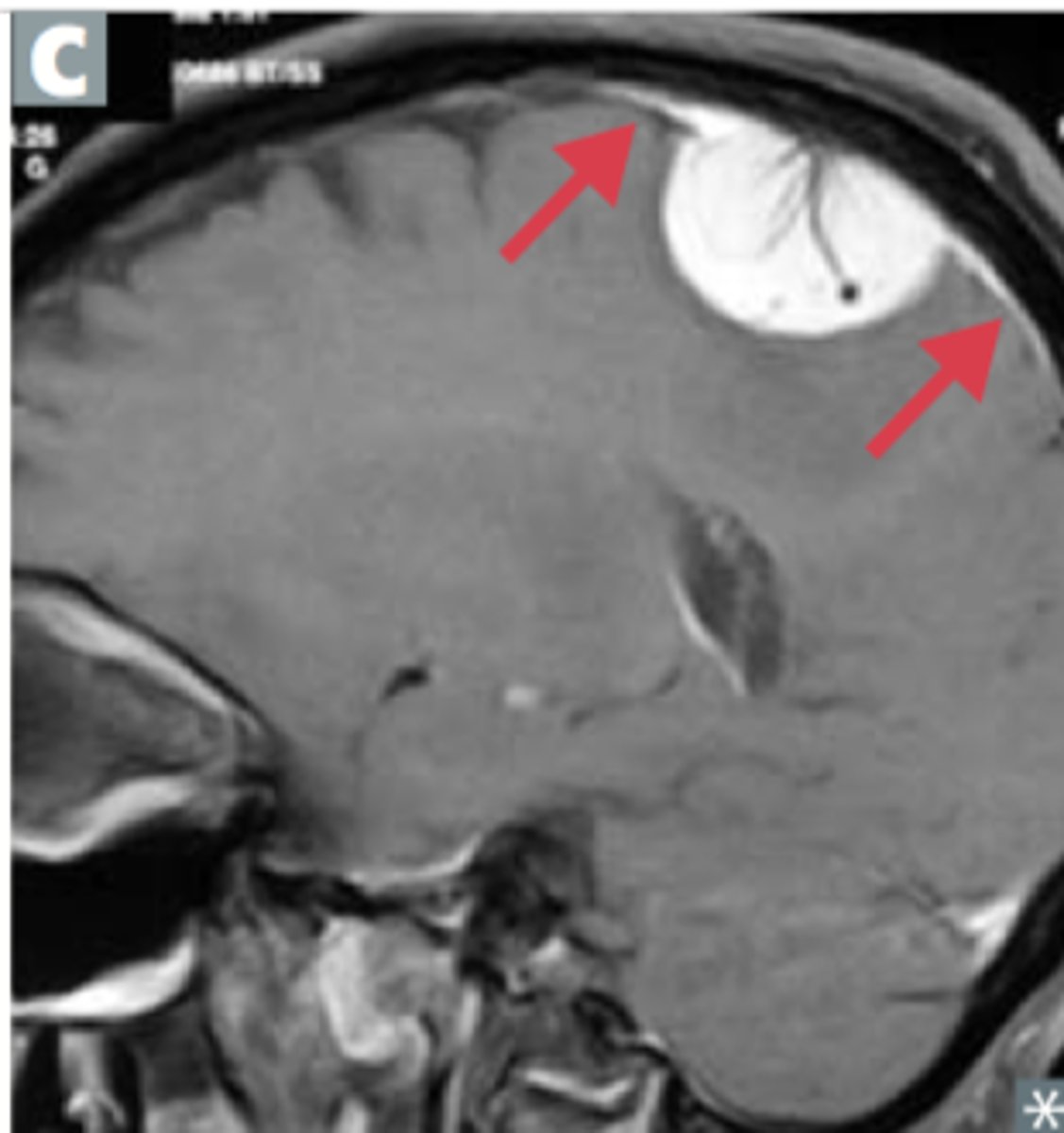
brain metastases
The spreading of a primary tumor to the brain.
- usually from Lung, breast, kidney cancers
- common place of metastases