The Vertebral Column
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering the anatomy and function of the vertebral column.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Vertebral Column Function
Supports body weight & thorax, transmits forces, provides flexibility & support for head & upper limbs, protects nervous system.
The Vertebral Column consists of a series of ___ vertebrae
which includes ___ separate vertebrae and ___ fused vertebrae
33 vertebrae
24 – separate vertebrae = are mobile
7 cervical
12 thoracic
5 lumbar
9 — fused vertebrae
5 sacral = fused together to form wedge-shaped sacrum
4 coccygeal = fused together to form coccyx
There are ____ separate vertebrae AND includes?
24 – separate vertebrae = are mobile
7 cervical
12 thoracic
5 lumbar
there are ___ Fused Vertebrae which includes?
9 fused vertebrae:
5 sacral = fused together tp form wedge-shaped sacrum
4 coccygeal = fused together to form coccyx
The three main regions of the vertebral column (spine) are the ___
cervical, thoracic, and lumbar regions.
Function & Characteristic — Vertebra Body
Characteristic:
Block shaped structure
Forms anterior part of the vertebra
Get progressively larger and thicker from cervical region down to the lumbar region
Function:
Main weight bearing part
Posterior Vertebral Arch — Function & Characteristic
Characteristic:
ring shaped structure
Forms the posterior part of the vertebra
Function:
Protects the spinal cord and cauda equina, attachment for ligaments and muscles.
Attachment for ligaments and muscles
Vertebral Arch consists of?
Pedicles (short bony struts, sticks out from posterior part of vertebral body)
Lamina (sheets/ plates project medially from the right and left pedicles, each meet in the midline to complete the bony arch
together forms a bony opening called Vertebral Foramen
Vertebral Foramen is formed by ___ , articulated to form _____
Bony opening formed by the vertebral arch, articulates to form vertebral canal.
Contains spinal cord, chord aquina and spinal meninges
Projection out from Vertebral Arch has number of Processes: (3)
R & L Superior and Inferior Articular Processes
R & L Transverse Processes
Single Spinous Process
R & L Superior and Inferior Articular Processes — Explain
Projects upwards and downwards from junction of the pedicle and lamina
Has an oval-shaped articular surface in their ends that forms the zygoporphisal joints
R & L Transverse Processes — Explain
Projects laterally outwards from the junction of the laminate and the pedicles
Serves as the attachment point for both ligaments and muscles of the spine
Thoracic region also contains small articular surface which forms parts of the joints with the ribs
Spinous Process — Explain; projection
projects backwards from the midline
Cheify for the attachment of ligaments and muscles
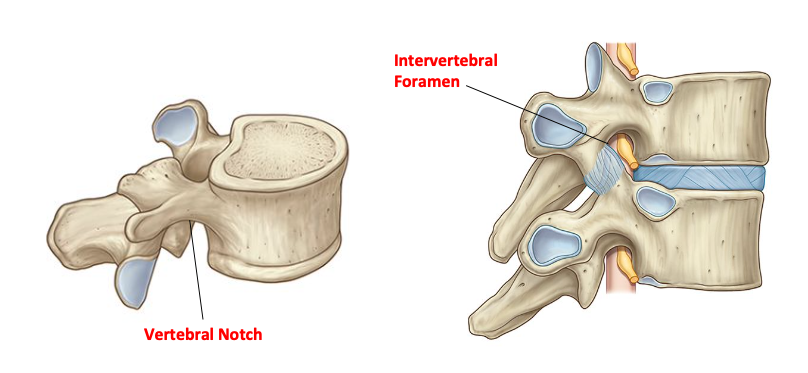
Vertebral Notch — location, articulation forms?
Location:
From side viewe there is a notch below the area where pedicles come off the upper part of vertical body
when articulated with the vertebral below the notch becomes a hole = intervertebral foramen
Cervical Vertebrae (C1-C6) has an opening in the Transverse Process called ___?
called: Transverse Foramen
only found in cervical vertebrae
contains the vertebral artery
what are the Upper two cervical vertebrae that is highly specialized, to accommodate movement of the head
Atlas (C1)
Axis (C2)
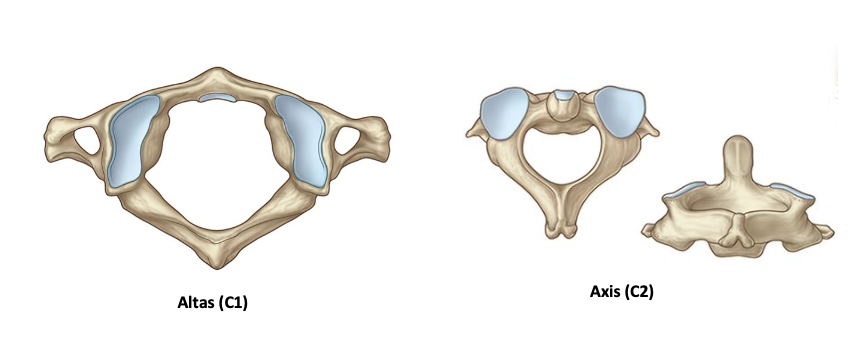
Atlas (C1)
Ring-shaped
has 2 lateral masses connected by an anterior and posterior arch
No vertebral body articulates with occipital condyles.
Axis (C2)
Has a peg/tooth-like projection that extends superiorly from vertical body called Odontoid (DENS) process
Each side has a large oval-shaped L& R superior articular surface, articulation with atlas above
Sacrum
Single wedge-shaped, five fused sacral vertebrae.
Cervical Vertebrae Characteristics
Short square-shaped vertebral body, bifid spinous process, transverse foramen.
Thoracic Vertebrae Characteristics
Characterized by superior and inferior articulations on posterior vertebral bodies for the ribs
Articular surface on the transverse process for the tubecel of the rib
Has spinous process thats long, slender and downwards
Smaller circular-shaped vertebral foramen
Lumbar Vertebrae Characteristics
Large thick vertebral bodies = due to increased weight bearing requirements in lumbar spine
thick pedicles and lamina = for added strength
triangular vertebral foramen.
Long thick transverse processes (except for L5) = (larger than thoracic region) = to accommodate lumbar enlargement of the spinal cord
Spinal processes are more square and projects straight backwards
Sacrum and Coccyx bones location
Located at the inferior end of the vertebral column
Sacrum — explain
shape
formed by?
articulations
shape: Triangular wedge shaped, narrower apex pointed downwards formed from first 4 Fused Sacral Vertebrae
formed by 5 fused vertebrae (S1-S5) and connects the spine to the hip bones, providing stability and support.
S1 articulates with the L5 vertebra above Sacral Promontory
Sacrum — Sacral Foramina
4 openings
allows the passage of the ventral and dorsal rami of S1-S4 spinal nerves
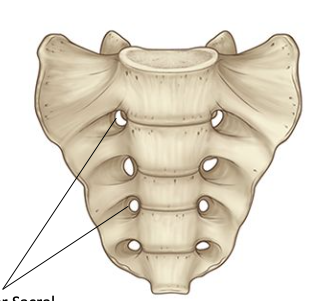
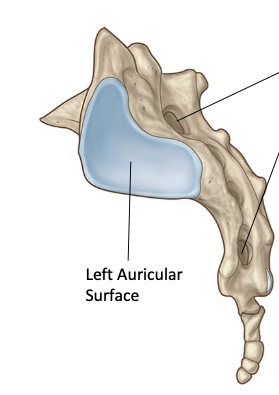
Sacrum — Auricular Surface
two L & R L-shaped articular surfaces
articulate w/ adjacent hip bone from L & R sacroiliac joints
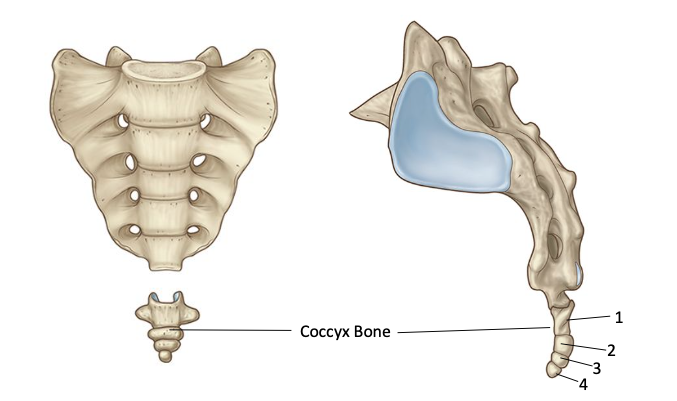
Coccyx bone — explain
articulated by?
fused by
characterized by?!
articulated by fibrocartilaginous disc
4 fused Coccygeal Vertebrae
characterized by Vertebral Foramen absense