Unit 2 - Bonding and phases
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
Ionic bonds are usually formed between
Metals and non-metals
Electrons in Ionic Compounds are…
Localized around the anion as the cation gives up its electrons
Properties of Ionic substances are…
Poor conductors of electricity
Due to lattice structures and localized electrons
Ionic Liquids can conduct electricity as the ionic molecules themselves move
High melting points
Higher coulombic attraction = Higher melting point (vice versa)
High Boiling points
Metallic bonds are formed between…
the same metallic element
Properties of metallic bonds…
good conductors of electricity
the positive core (nucleus and core electrons) are stationary while the valence electrons move around
Alloy
combination of 2 different metals
Interstitial alloy
formed between metals of 2 different radii (smaller atom occupies the crevices “interstices” formed by the bigger element

Substitutional Alloy
Formed between atoms of similar radii (some atoms are substituted for atoms of the other)

Covalent bonds
the sharing of electrons by atoms
sigma (σ) bond
the first bond formed in a covalent bond
pi (π) bond
the second and third bonds formed in a covalent bond ( one pi bond, double pi bond)
Covalent bonds form at _________ because…
“minimum potential energy”
Too close = the repulsive forces push away the atoms and no bond can form
Too far = The nucleus of one atom cannot attract the electron of another
Network Covalent bonds
Elements that form lattice like structures with localized electrons
Most common network covalent are either C or Si as they have 4 valence electrons
Doping
The process of increasing conductivity by adding an impurity
P-doping
some of the atoms in the structure is replaced with an atom with fewer valence electrons which leaves a hole in the bonding (positive) so it draws outside electrons that create a chain reaction to increase the overall conductivity
N-doping
some of the atoms in the structure is replaced with an atom with more valence electrons which have nowhere to bond so they roam around increasing the conductivity
The central element in a Lewis dot structure is…
the least electronegative
have atleast 8 to a max of 12 valence electrons
Resonance forms/ structures
used to show that electrons are delocalized and can be shared with multiple atoms in an molecule
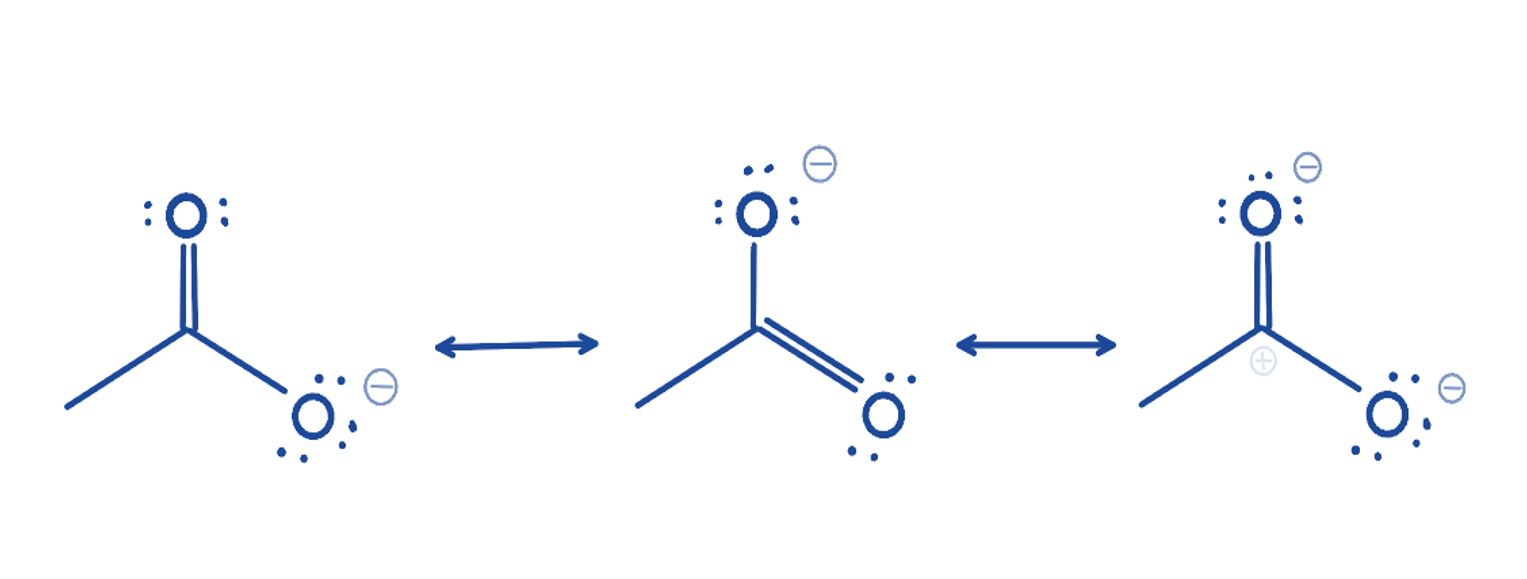
In a resonance form all the bonds…
have the same length and strength (somewhere between a double bond and a single bond)
Bond order
The way to determine the strength and length of bonds
single bonds have a bond order of 1
double bonds have a bond order of 2
triple bonds have a bond order of 3
You can calculate the bond order for resonance structures by…
Add the total bonds
Divide by the number of possible resonance forms
Ex: \frac{\left(1+2+1\right)}{3}=1.33
Only these 3 elements do not need 8 valence electrons to be stable…
H (Hydrogen) only needs 2
He (Helium) only needs 2
B (Boron) only needs 6
Formal Charge
as Lewis dot structures can be drawn in multiple ways this is the way to find the correct way to draw them
Rules of Formal Charge
Neutral molecule has a formal charge of 0
Polyatomic Ion has a formal charge = to the overall charge of the ion
How to calculate formal charge…
Formula: Valence electrons - lone pairs - ½ bonding electrons
VESPR Theory (valence electron shell pair repulsion)
electron pairs repel each other so they position themselves to minimize repulsion
Electron groups
lone pairs, bonds, single upaired electron, etc
this has 2 electron groups
linear
this has 3 electron groups
trigonal-planar
this has 4 electron groups
tetrahedral
this has 5 electron groups
trigonal-bipyramidal
this has 6 electron groups
octahedral
terminal electrons
the outermost electrons in a molecule
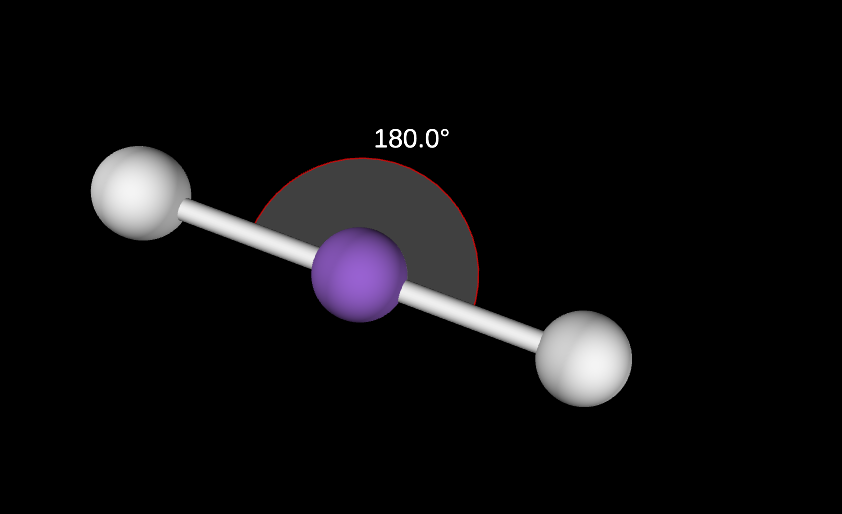
0 lone pairs
180 degree angle
Linear
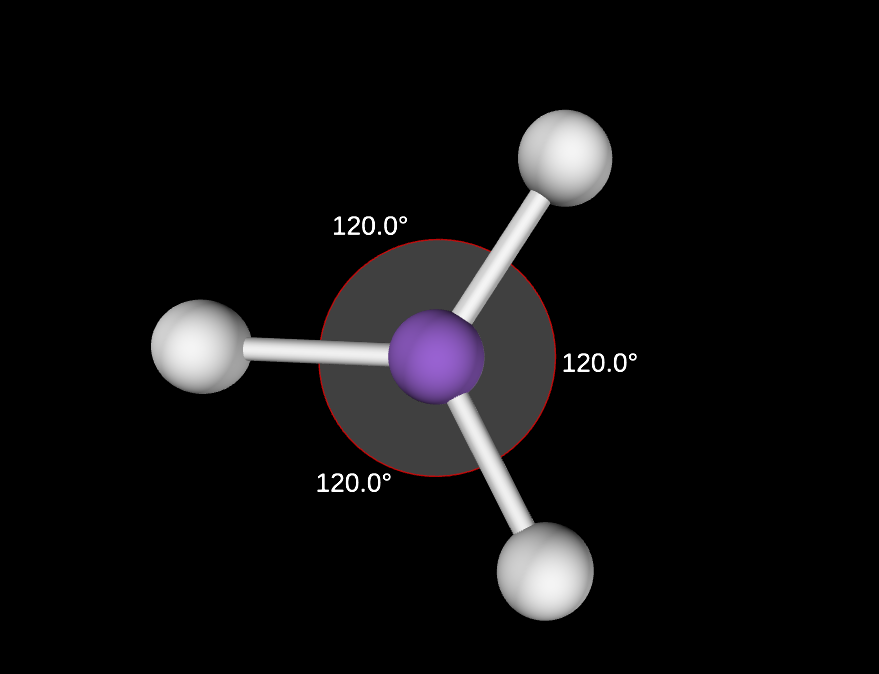
0 lone pairs
120 degree angle
Trigonal Planar
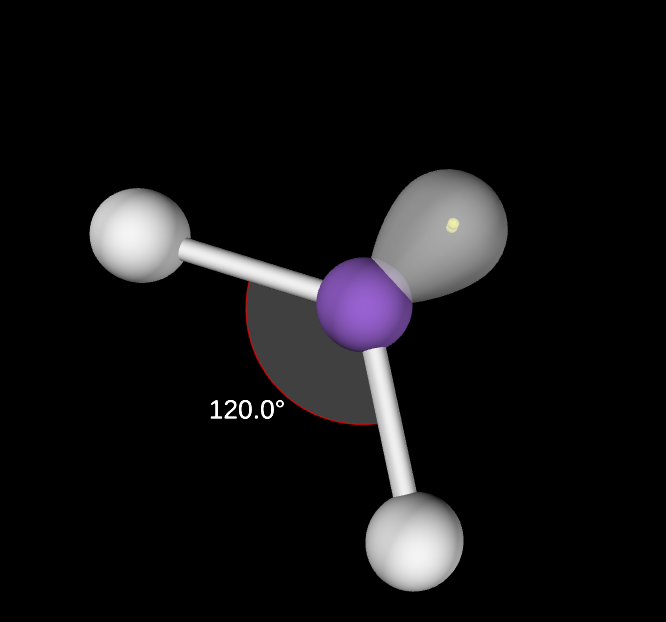
1 lone pair
120 degree angle
Bent trigonal planar
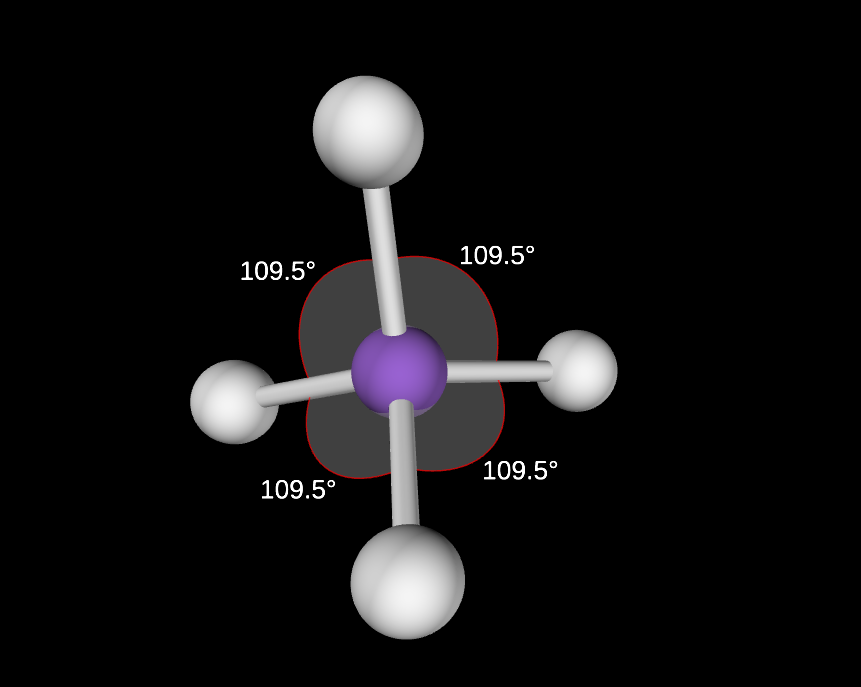
0 lone pairs
109.5 degree angle
tetrahedral
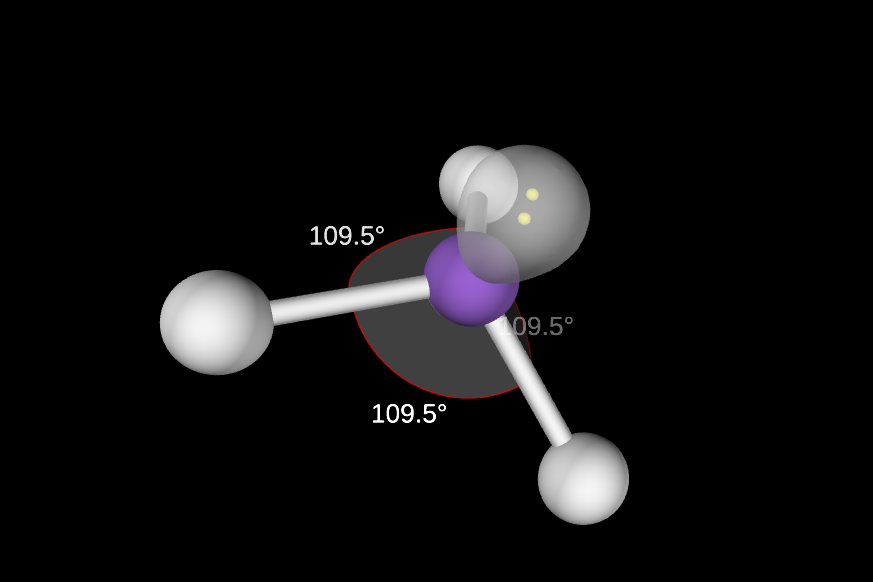
1 lone pair
slightly less than 109.5 degrees
Trigonal Pyramidal
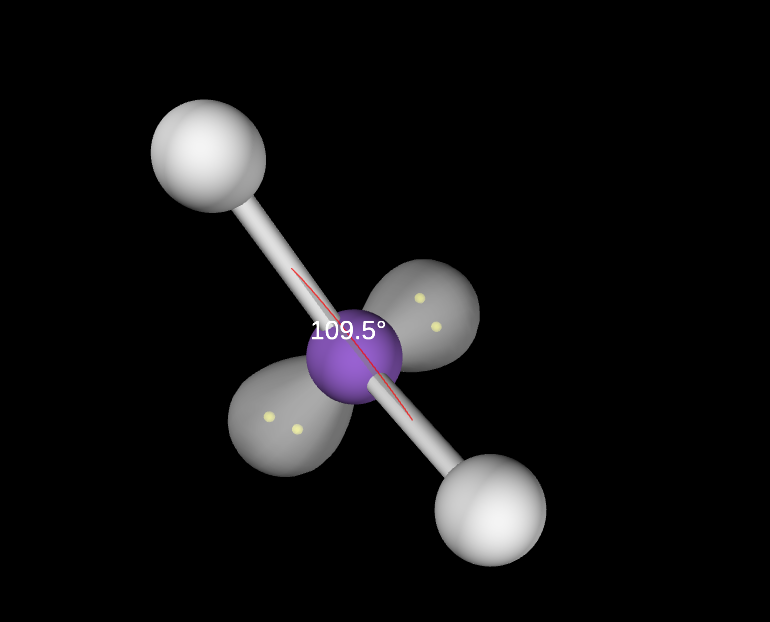
2 lone pairs
slightly less than 109.5
Tetrahedral Bent
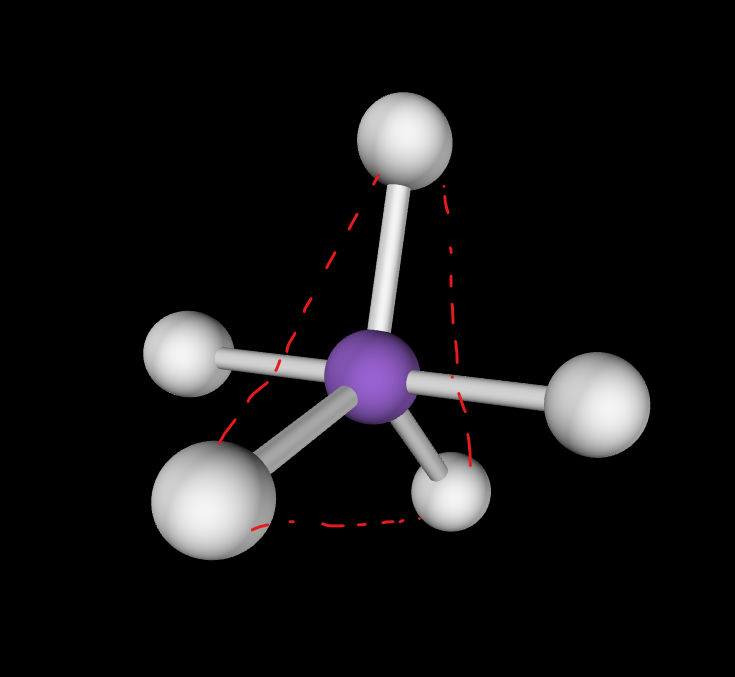
0 lone pairs
Trigonal Bi-pyramidal

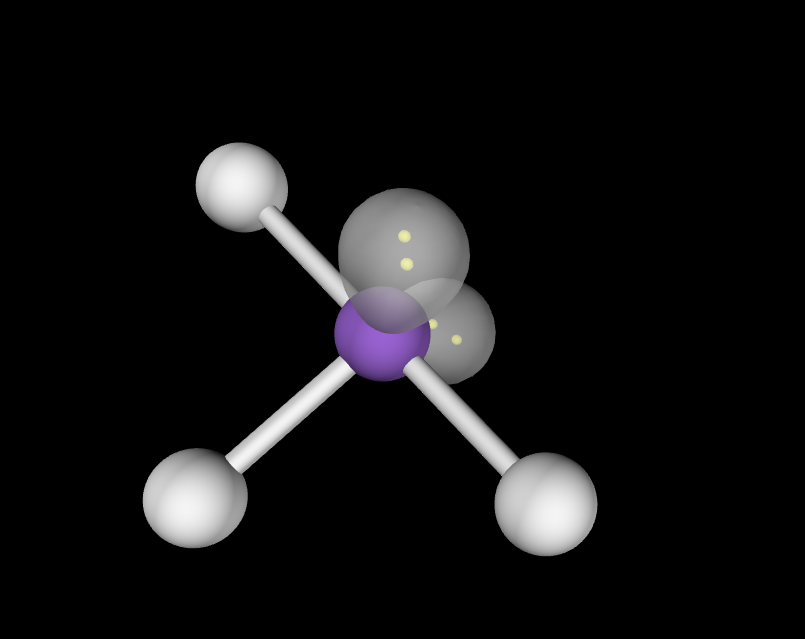
1 lone pair
Trigonal Bi-pyramidal seesaw
2 lone pairs
Trigonal bi-pyramidal t-shaped
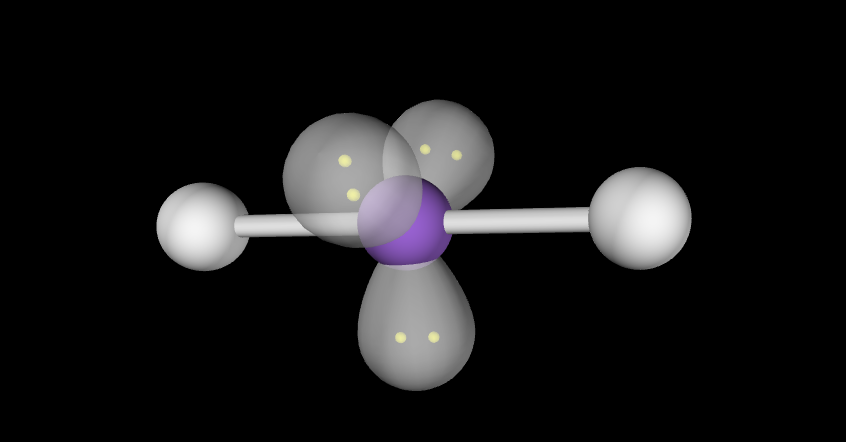
3 lone pairs
Trigonal bi-pyramidal linear
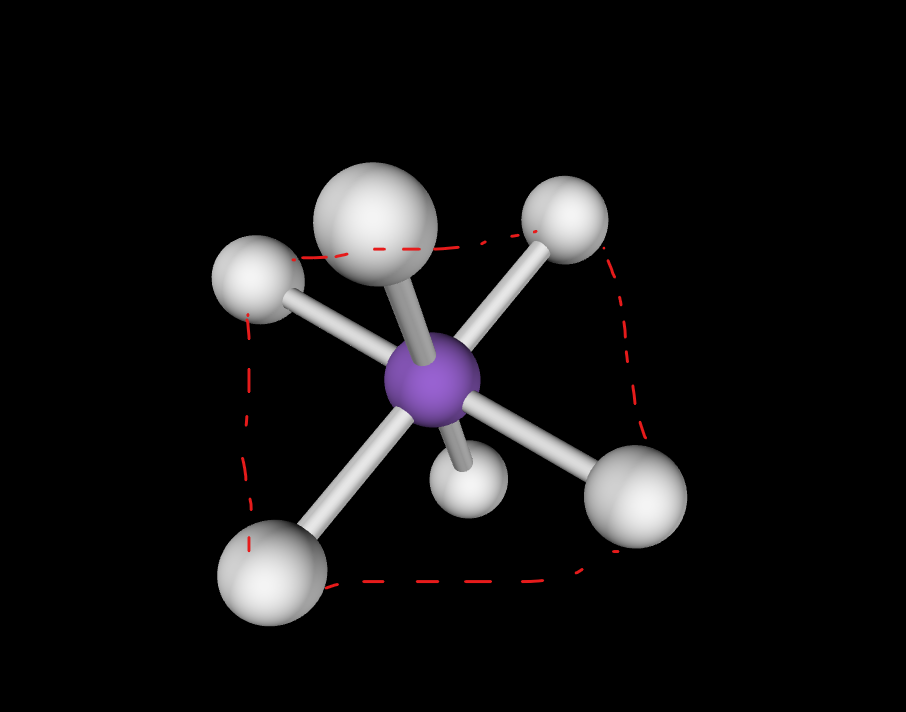
0 lone pairs
Octahedral
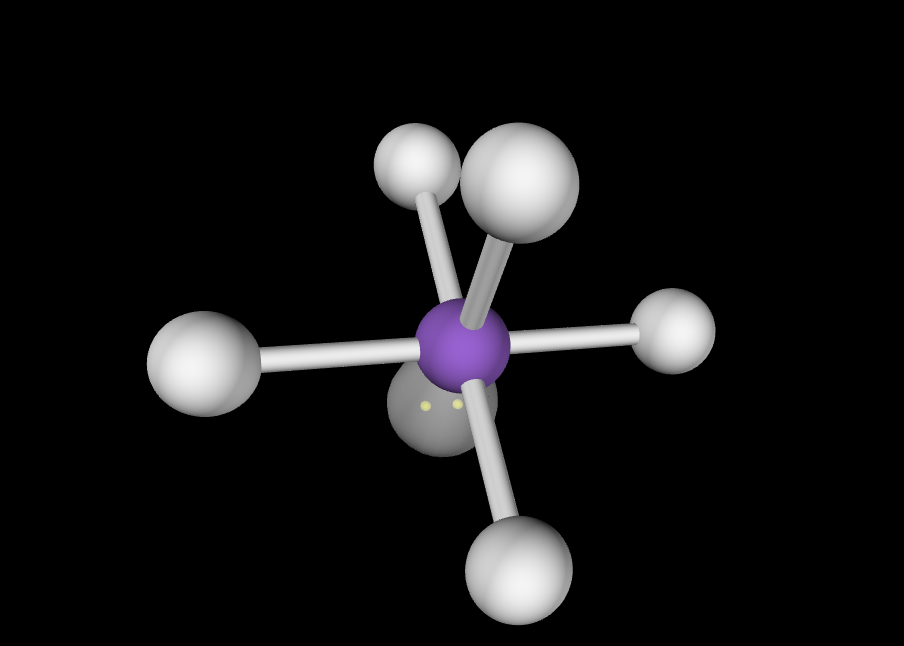
1 lone pair
square- pyramidal

2 lone pairs
square-planar
Polarity
In a covalent bond electrons aren’t shared equally as higher electronegative elements have the electrons crowding around them
Polar covalent bonds
In a covalent bond between 2 different electronegative elements and one will pull more atoms
Non-polar covalent bonds
A covalent bond between 2 of the same elements so electrons are shared equally
Dipoles
in polar covalent bonds the electrons crowding in one region creates a negative pole and a positive pole
Rule of thumb for molecular polarity
a molecule is non polar if it’s central atom has no lone pairs which means the molecule is symmetrical
Exceptions to the rule of thumb for molecular polarity
Hydrogen will always be a positive dipole as its electronegativity is low
molecules in a square planar shape are usually nonpolar as the terminal atoms are in the same plane despite central atom having lone pairs
Intermolecular Forces (IMFs)
forces between covalently bonded molecules that have to be broken fot phase change
Dipole-Dipole Forces
The positive dipole is attracted to negative dipoles
substances with only dipole dipole forces are usually liquid or gases at stp
Hydrogen bonds
A type of dipole-dipole force, when the positive dipole of a hydrogen atom in one molecule is attracted to a very electronegative atom of another molecule
strong as Hydrogen has no electrons to shield due to the bonding
London Dispersion Forces
random movements of electrons create temporary dipoles and occurs in all molecules
can be stronger than H bonds in rare occasions
more electrons = more LDF
more molar mass = more electrons
more molar mass = more LDF
IMFs ranked by strength
Hydrogen bonds
Dipole-dipole forces
LDF
Vapor pressure
when molecules in a liquid which are always in random motion hit the surface of the liquid with enough KE to turn into a gas
temp ∝ vapor pressure
strong IMF = weaker vapor pressure
Solutes
the thing to be dissolved
Solvents
the thing that its to be dissolved in
polar solutes dissolve best in…
polar solvents
non-polar solutes dissolve best in…
non-polar solvents
Electrolytes
the ions in a solvent that dissolved an ionic solute (conductivity increases)
Chromatography
the process of passing a mixture through a medium to separate it
paper chromatography
a paper is suspended above a (polar or nonpolar) solvent and mixture is blotted on paper as the solvent climbs the substances at mixtures climb to different rates depending on polarity, polar solutes climb the furthest for polar solvents
Rf
used to calculate the attraction between solute and solvent
higher Rf = more attraction
(distance traveled by solute/ distance traveled by solvent)
Column chromatography
a column is filled with a stationary substance then its injected with analyte which is at the stationary phase then its injected with eulent which as it exits the column the more attracted the analyte molecules are the faster they exit the column as well
Analyte
the solution to be seperated
Eulent
another solution
Distillation
Takes advantage of substances having different boiling points
boils mixture at x degrees C and only the substance with x degrees C evaporates and is collected
Kinetic Molecular Theory
KE=\frac12mv^2
m = mass (kg)
v = velocity (m/s)
Assumptions of Kinetic molecular theory
temp ∝ Avg. KE
there is no attractions between the molecules in the gas
if the sample is a mixture of gasses they will all have the same Avg. KE
Gas molecules are in constant elastic motion
volume of the ideal gas is insignificant compared to the volume of the container
Maxwell-Boltzman diagrams
used to model the velocities of different gases at different temps, or same gas at dif temps
Effusion
the rate of which a gas will escape through microscopic holes in a container
higher temp = higher rate of effusion
same temp, lower molecular mass = higher rate of effusion
Ideal Gas Law
PV=nRT
P = Pressure (atm)
V = Volume (L)
n = moles
R = Gas constant
T = Temp (K)
Boyles Law
as pressure increases, volume decreases
Charles Law
as temp increases, volume increases
Daltons Law
the total pressure of a gas is the sum of all the partial pressures, the partial pressure of a gas ∝ to the percent of moles of that gas in the mixture
Gases deviate from ideal state when…
the temp or pressure gets too high or too low
This Happens when gasses deviate from ideal state
molecules stick
the volume of the gas is significant
Density
D=m/v or molar mass = DRT/P