week 6 DNA damage
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
what biological molecules can undergo repair upon damage
DNA only
what happens to other biologial molecules upon damage
simply degraded and recycled
difference between DNA damage and DNA mutation
DNA damage is the initial alteration of normal DNA structure
If the cell systems fail to repair DNA damage prior to DNA replication, the damage will become a DNA mutation
can cells recognize dna damage
yes
The cell can recognize DNA damage as potentially lethal and will attempt to repair it immediately
can the cell recognize dna mutation
no
remains as a permanent change in the DNA sequence
are dna mutations or dna damage hertiable
dna mutations
table for differences between dna damage and dna mutations
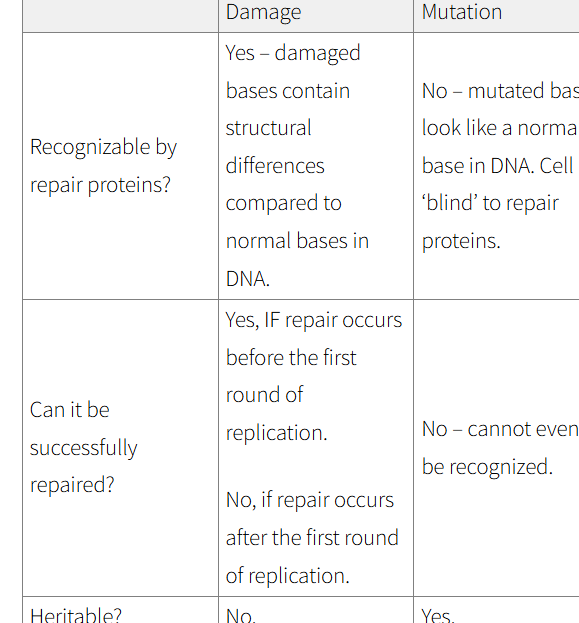
After DNA damage occurs, there are three possible outcomes
successfull dna Repair
unsuccessful dna repair
no dna repair
when does successful dna repair occur?
repair proteins correct the DNA damage before DNA replication
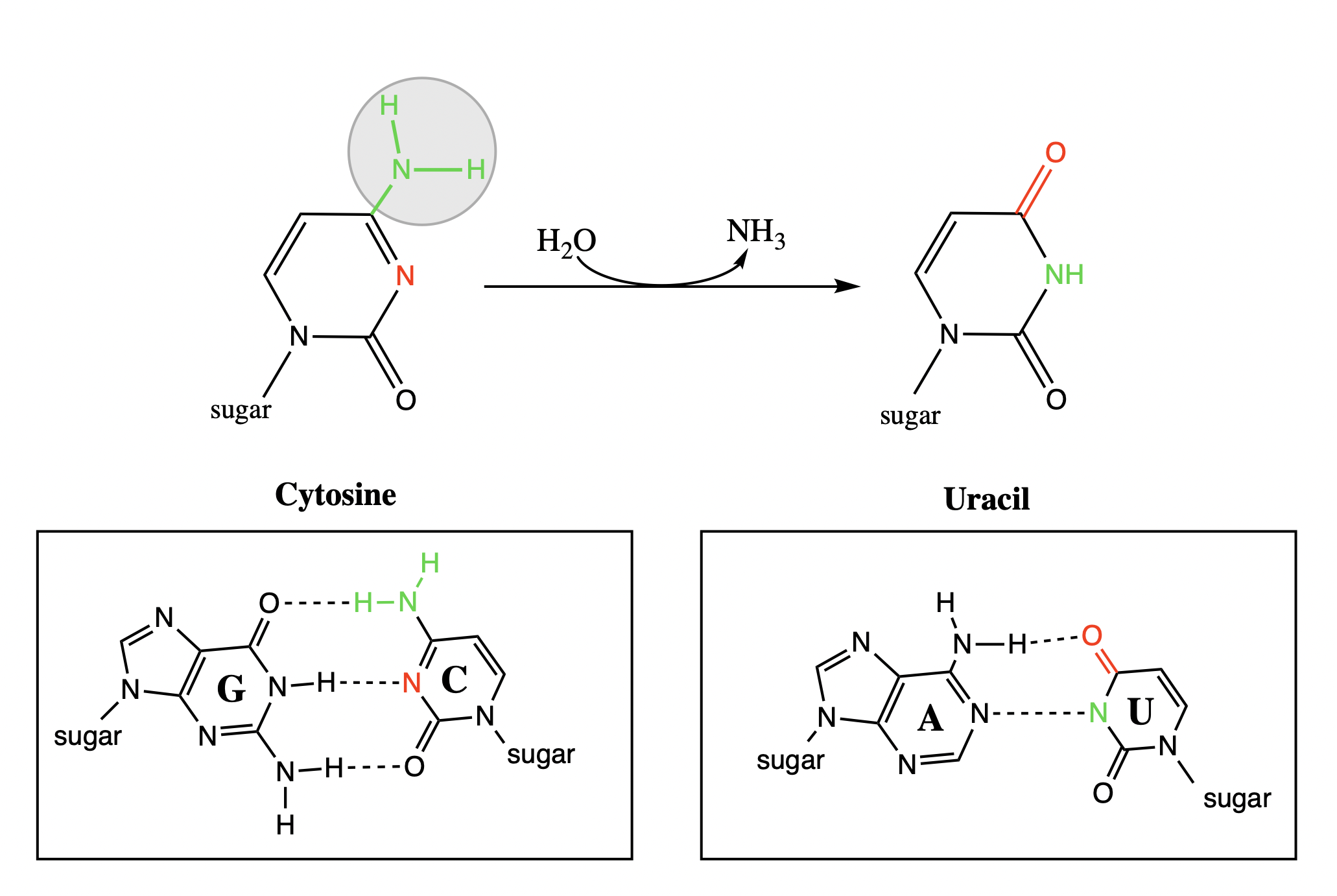
when does unsuccessful dna repair occur? (use the example of cytosine → uracil)
If the damaged DNA molecule undergoes a round of replication
2 non identical DNA molecules produced (1 that uses damaged strand as template and 1 that uses normal strand as template)
uracil in damaged one pairs with adenine
cytosine in normal one pairs with guanine
result = adenine mutation!
repair proteins remove the uracil because they can recognise it and replace it with T (thymine) because of the incorrect A
when does No dna repair occur
after incorporttion of the mutation
Spontaneous, or endogenous, DNA damage encompasses
any DNA damage that arises due to the nature of the cellular environment
three key sources of endogenous DNA damage
depurination/depyrimidation, deamination and reactive oxygen species
Depurination and deamination occur because
DNA is not chemically inert, leading to occasional spontaneous chemical modifications of its components
reactive oxygen species can inadvertently be generated during
energy metabolism, causing damage to DNA.
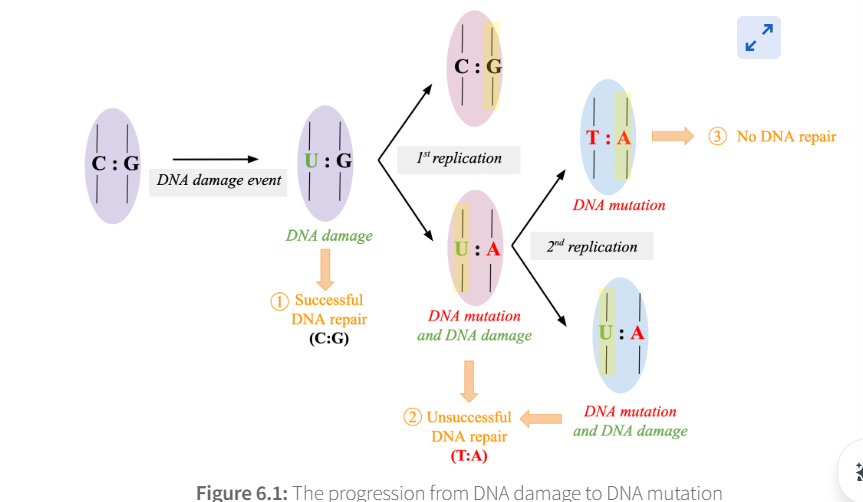
Depurination or depyrimidination is the spontaneous hydrolysis of a nucleotide's ______________ bond
N-glycosidic
Cleavage of this bond therefore releases the base from the nucleotide, forming an
apurinic site or apyrimidinic site (AP site), more generally referred to as an abasic site
most common form of DNA damage in humans
formation of abasic sites via depurination or depyrimidination
depurination is more common than losing a pyrimidine base (depyrimidination).
During DNA replication, if DNA polymerase alpha, epsilon, or delta encounters an abasic site
replication will stop
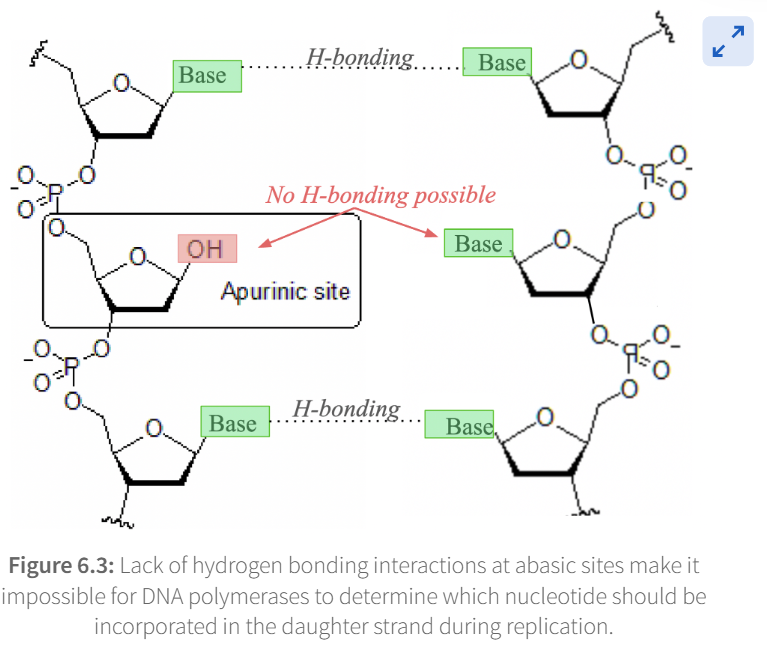
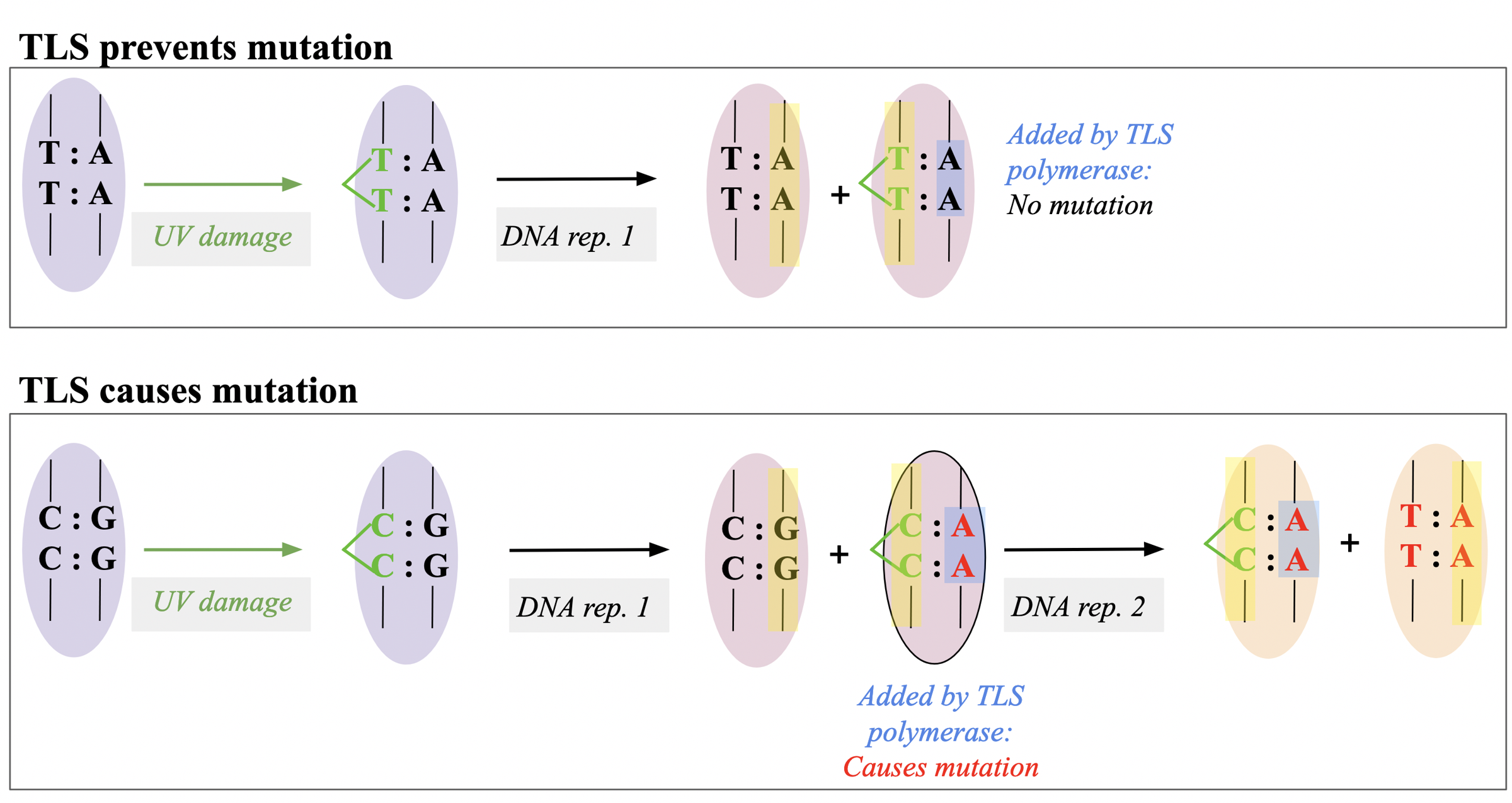
To bypass the abasic site and complete DNA replication, a specialized ___________________________) must be used.
trans-lesion synthesis polymerase (TLS
When an abasic site is encountered, TLS does what
incorporates a random nucleotide in the daughter strand which then allows DNA polymerase to continue replicating DNA. This process is highly mutagenic
consequence due to abasic sites
cleavage of the DNA backbone
minor relatively: TLS error rate
cleavage of the DNA backbone occurs in two steps
cyclic form → linear form
b elimination
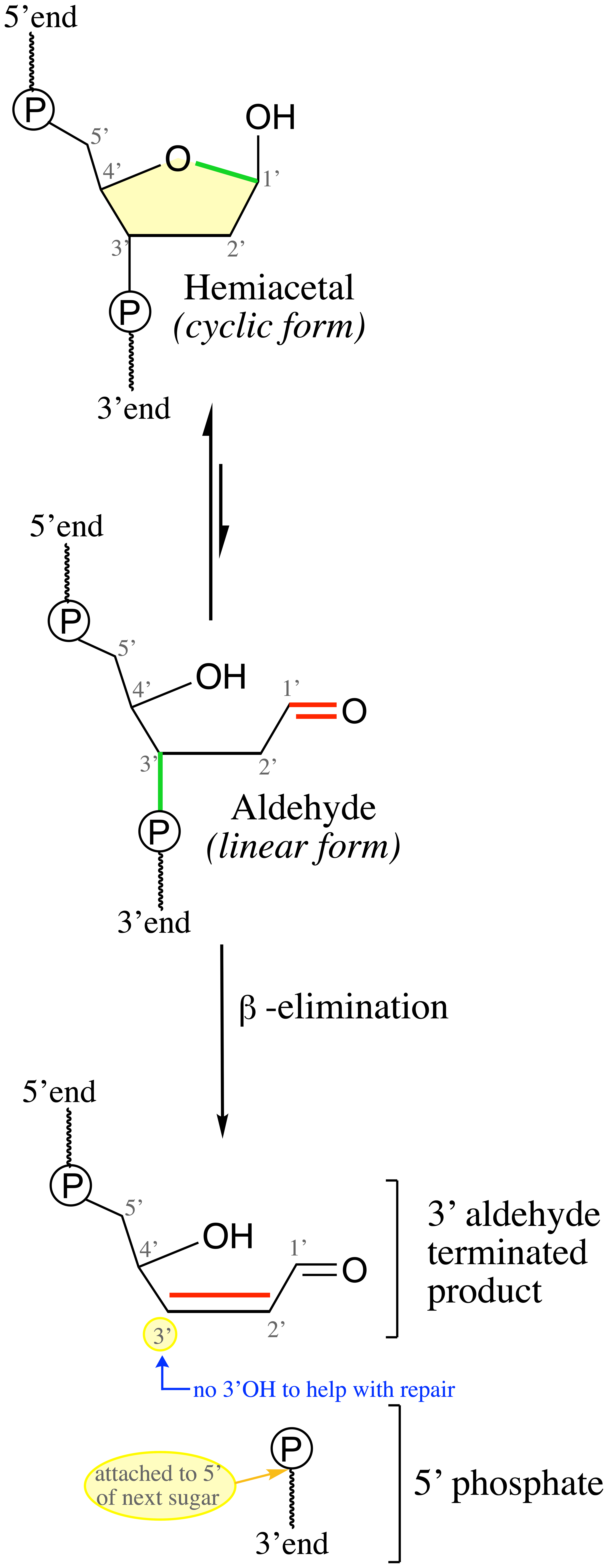
beta-elimination breaks
breaking the 3’ phosphodiester bond of the abasic site.
products:
3’ aldehyde-terminated product (comprising the sugar and the non- cleaved phosphate) and a
5’ phosphate attached to its adjacent sugar
which bases have an exocyclic amine groups prone to spontaneous deamination
Adenine, guanine, and cytosine
what does the amine group become in deamination
a carbonyl group
amine: hydrogen bond donor
carbonyl: hydrogen bond acceptor
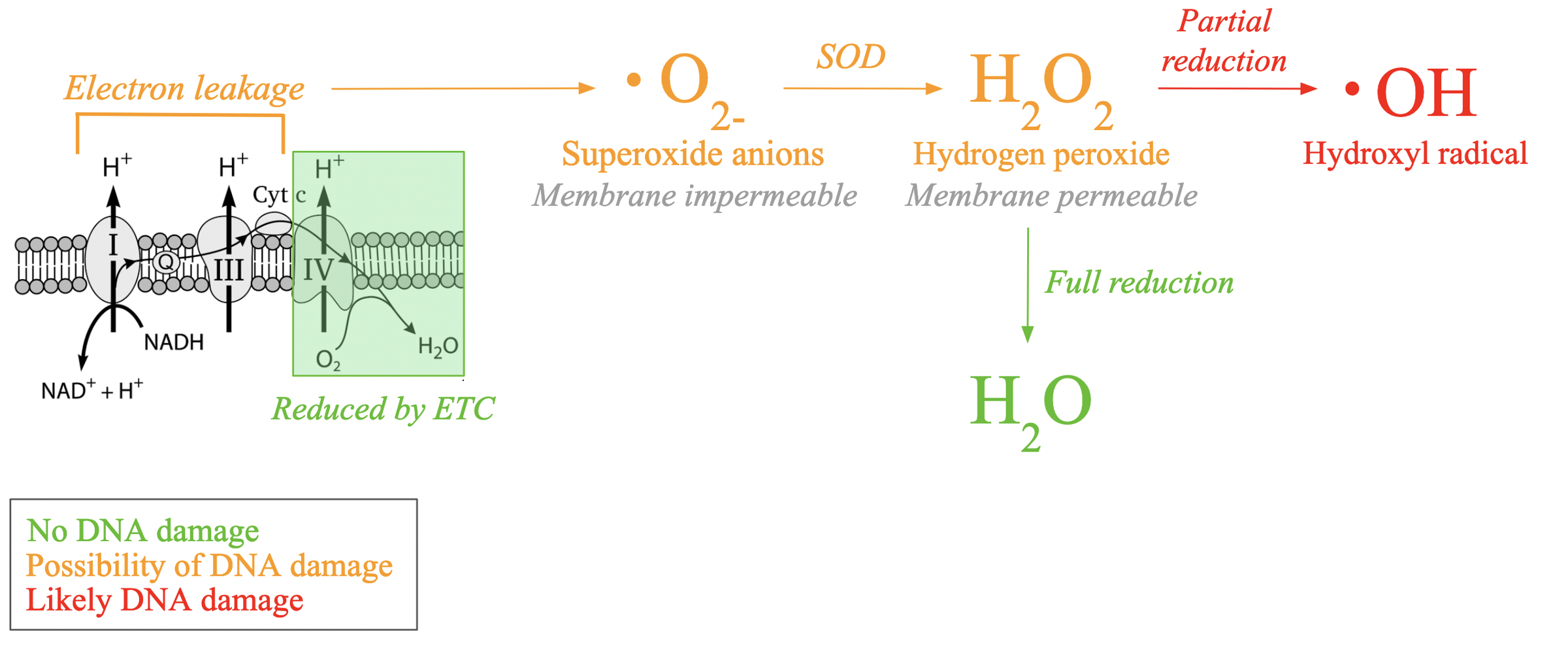
How are reactive oxygen species generated?
produced within the mitochondria during oxidative phosphorylation
The final complex (IV) in the ETC normally uses electrons to reduce oxygen to water.
But 0.2-2% of electrons leak out of the ETC before reaching this final step, and they bind to oxygen and form superoxide anions
Superoxide anions are ______________ to the mitochondrial membrane
impermeable
therefore restricted to the mitochondria
what convert superoxide anions into hydrogen peroxide
Superoxide dismutase (SOD)
hydrogen peroxide is _______ to the mitochondrial membrane
permeable
If hydrogen peroxide is fully reduced, it will form
water molecule
partial reduction of hydrogen peroxide will lead to the formation of
hydroxyl radical that has the potential to cause DNA damage
Generation of hydroxyl radicals.
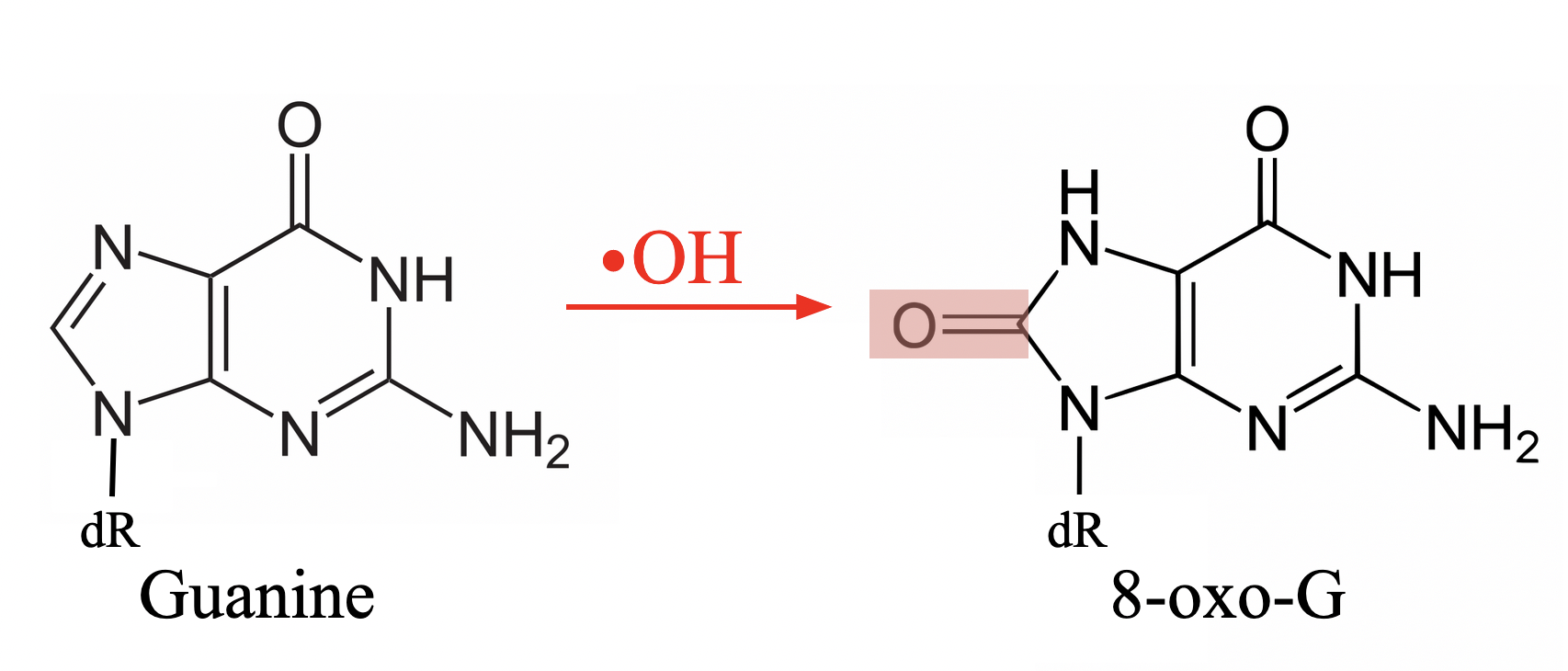
oxidized form of guanine
8-oxo-guanine ( addition of carbonyl group at position 8 of guanine)
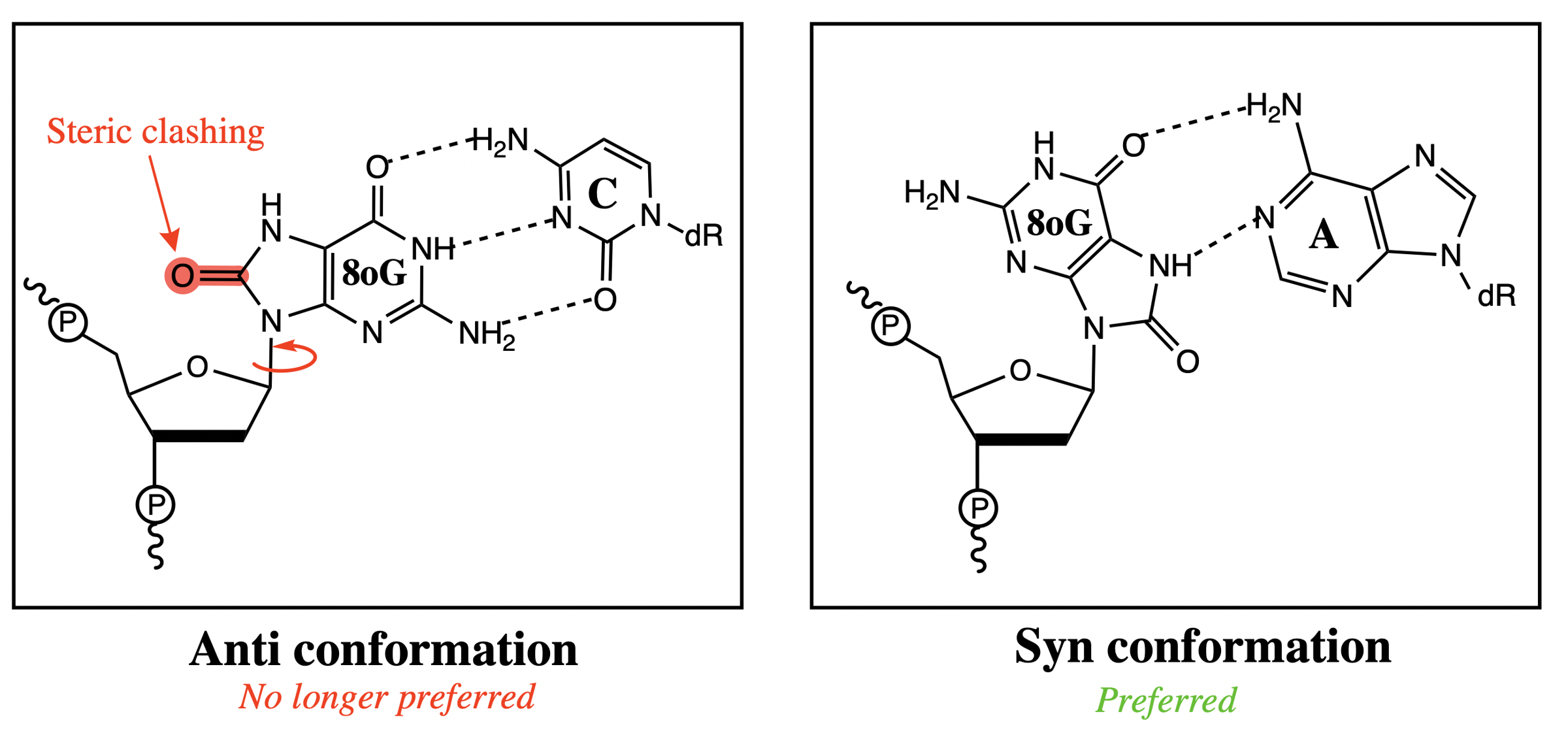
what conformation does 8-oxo-guanine favour and why
syn (whereas normally it would be anti since guanine is a purine)
bulky carbonyl group in 8-oxo-G causes significant steric clashing with the ribose sugar
Watson-Crick base pairing occurs when nitrogenous bases adopt ___________ conformation
anti
base pairing syn vs anti 8oG
Hoogsteen base pairs with adenine, instead of the typical Watson-Crick pairs with cytsoine
Environmental, or exogenous, DNA damage encompasses
DNA damage that occurs due to interaction with physical agents outside the cell
two key sources responsible for exogenous DNA damage;
UV light and alkylating agents
UV damage occurs when ____________ bases absorb UV light
pyrimidine
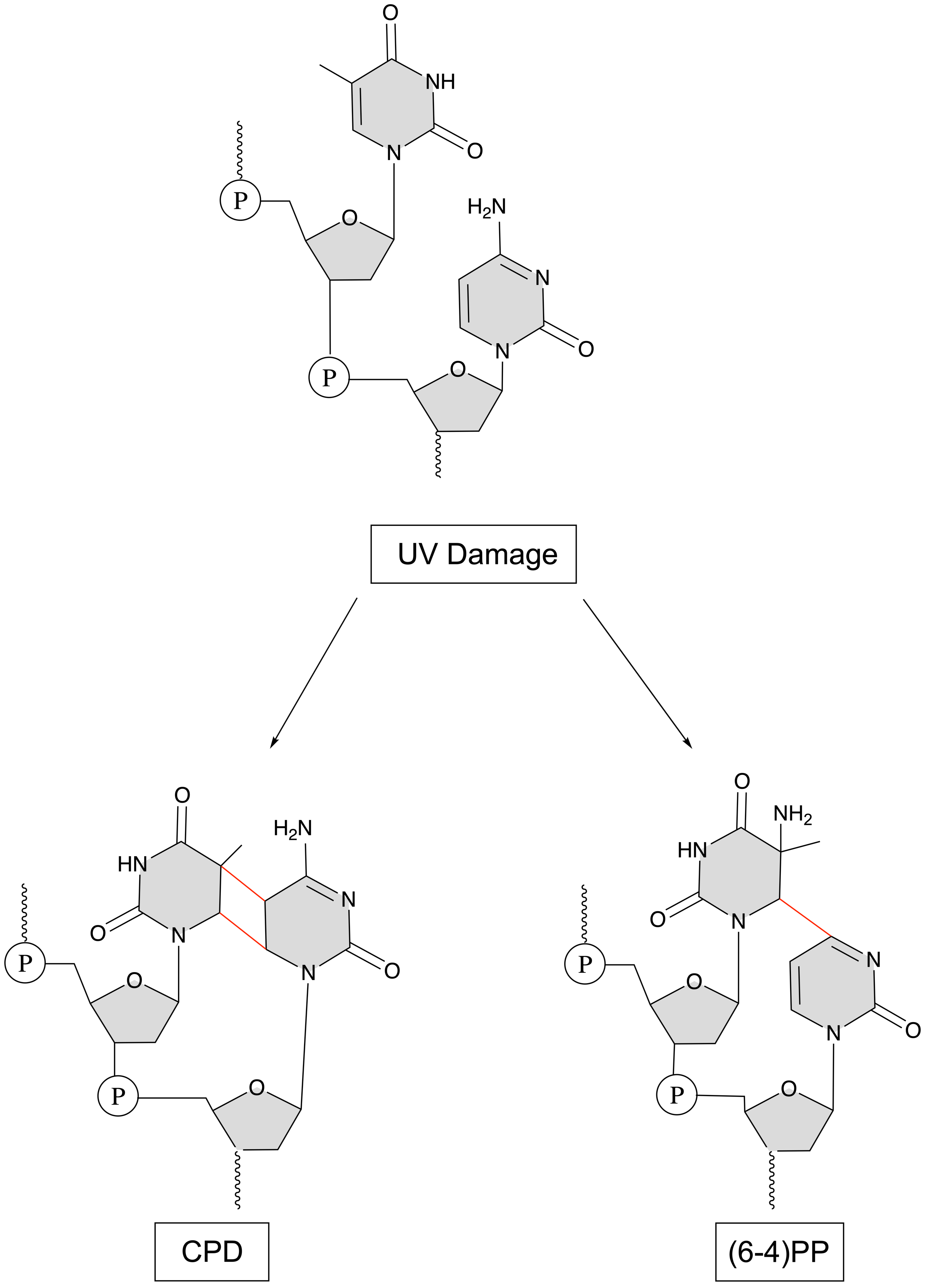
2 possibilities of uv light damage
2 bonds between adjacent pyrimidines => a cyclobutene pyrimidine dimer (CPD)
1 bond between adjacent pyrimidines => a 6-4 photoproduct (6-4) PP
distance between normal stacked/adjacent nucleotides in a DNA strand is
3.4 Å.
pyrimidine dimer distance
1.5 Å, equivalent to the length of the C-C bond that links them together
Structural changes to the double helix due to the presence of a pyrimidine dimer
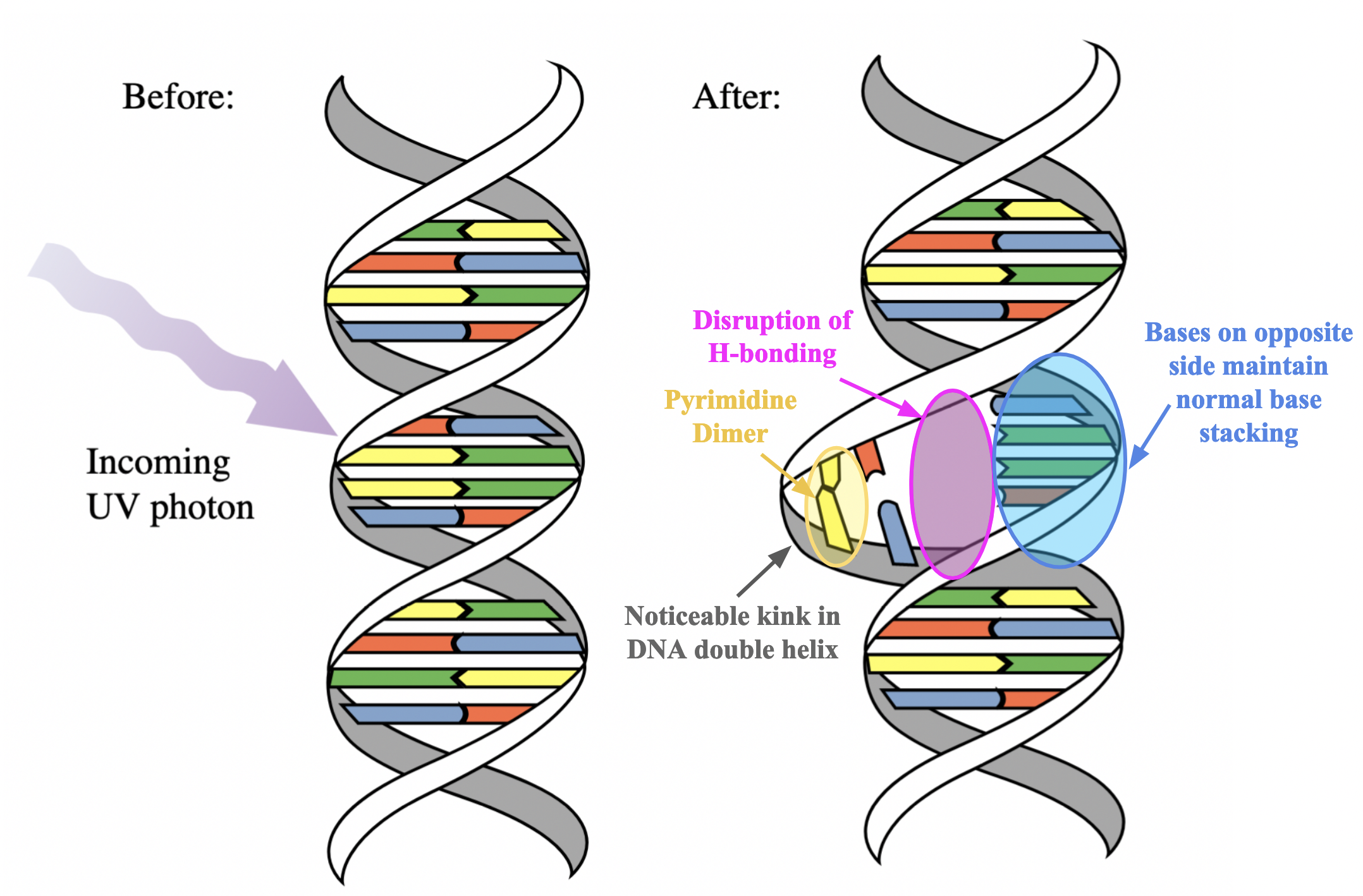
replicative enzymes reach the pyrimidine dimer, they will stall, and their enzymatic activities will come to a halt. To resume their synthetic processes, they require the action of
a unique trans-lesion synthesis (TLS) polymerase. This TLS prefers to insert AA opposite to any pyrimidine dimer
this corrective mechanism fails if the dimer
involves any other pyrimidine combination (CC, TC, CT).
Alkylating damage occurs when alkyl groups are transferred to the ____________ of a nitrogenous base
nitrogen or oxygen atoms
One common type of alkylating damage is
the methylation of O6 in guanine, forming O6-methyl-guanine
Methylation of guanine at the O6 position causes two key alterations in the nucleotide’s base pairing
O6 loses ability to participate in bond
N1 becomes a h bond acceptor
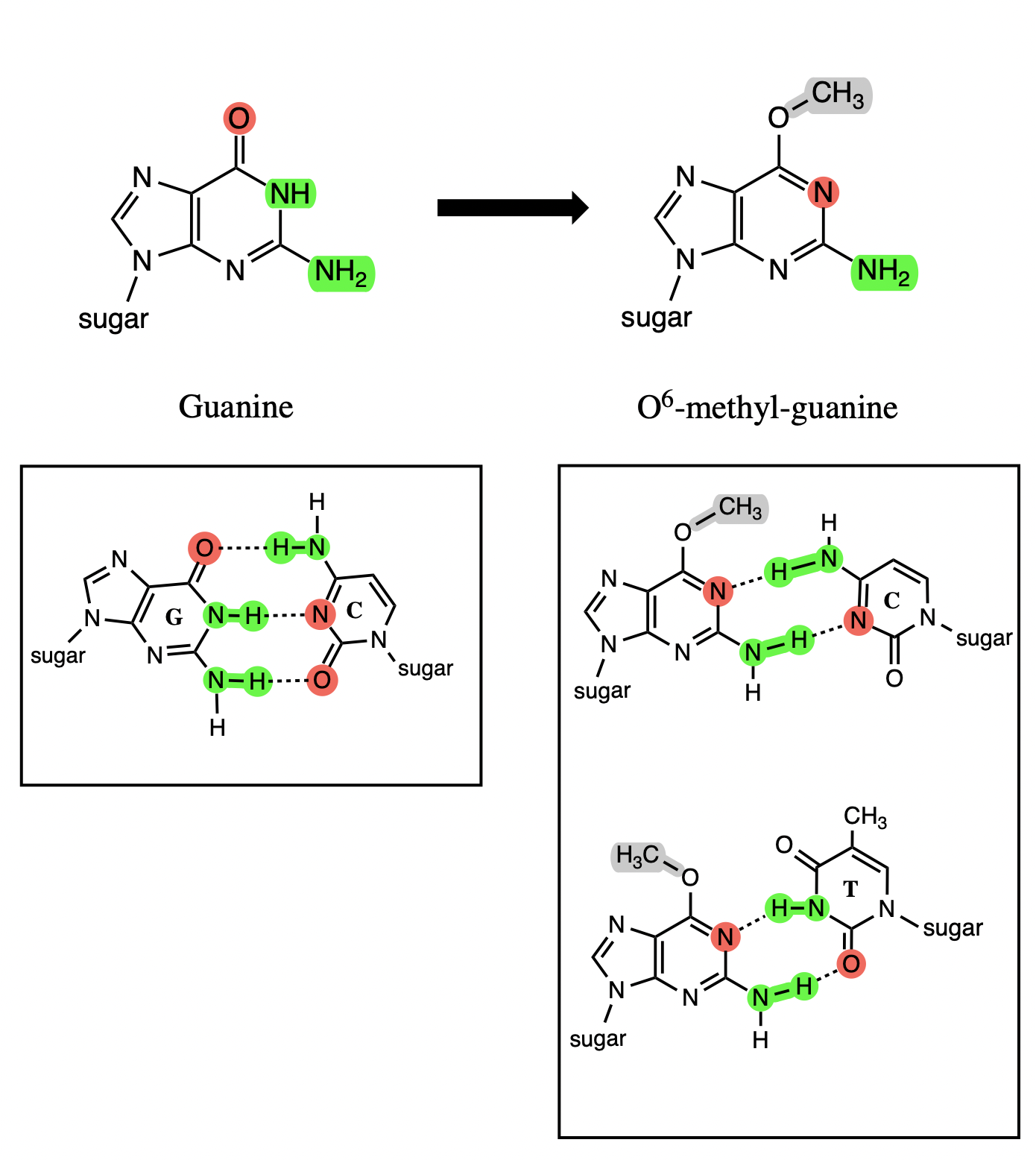
O6-methyl-guanine forms __________ hydrogen bonds with ______________
two hydrogen bonds with either cytosine or thymine via Hoogsteen base pairing
during DNA replication, there is no preference as to which pyrimidine will be chosen so 50% chance of mutation
three key repair pathways
direct repair, base excision repair, and nucleotide excision repair
the damaged base O6- methylguanine is repaired by the enzyme
MGMT
enzymatic process associated with MGMT occurs in three phases
Accessing the damaged base through interdigitation.
Repairing the damaged base through a single-step chemical reaction.
MGMT is degraded after repairing DNA damage.
interdigitation
O6-methyl-guanine is flipped out of the DNA helix
cytosine it formerly based paired with in the opposite strand becomes an ‘orphan nucleotide’.
MGMT’s key arginine residue extends into the DNA helix through the minor groove
arginine residue is able to form hydrogen bonds with the ‘orphan nucleotide’
which stabilizes the DNA double helix while the O6-methyl-guanine undergoes repair in the MGMT active site
In the active site of MGMT, the _______ atom of a key ________ residue binds to the methyl group of the O6-methyl-guanine
sulfur
cysteine
what type of bond is formed in the repair enzymes active site
irreversible S-methyl bond
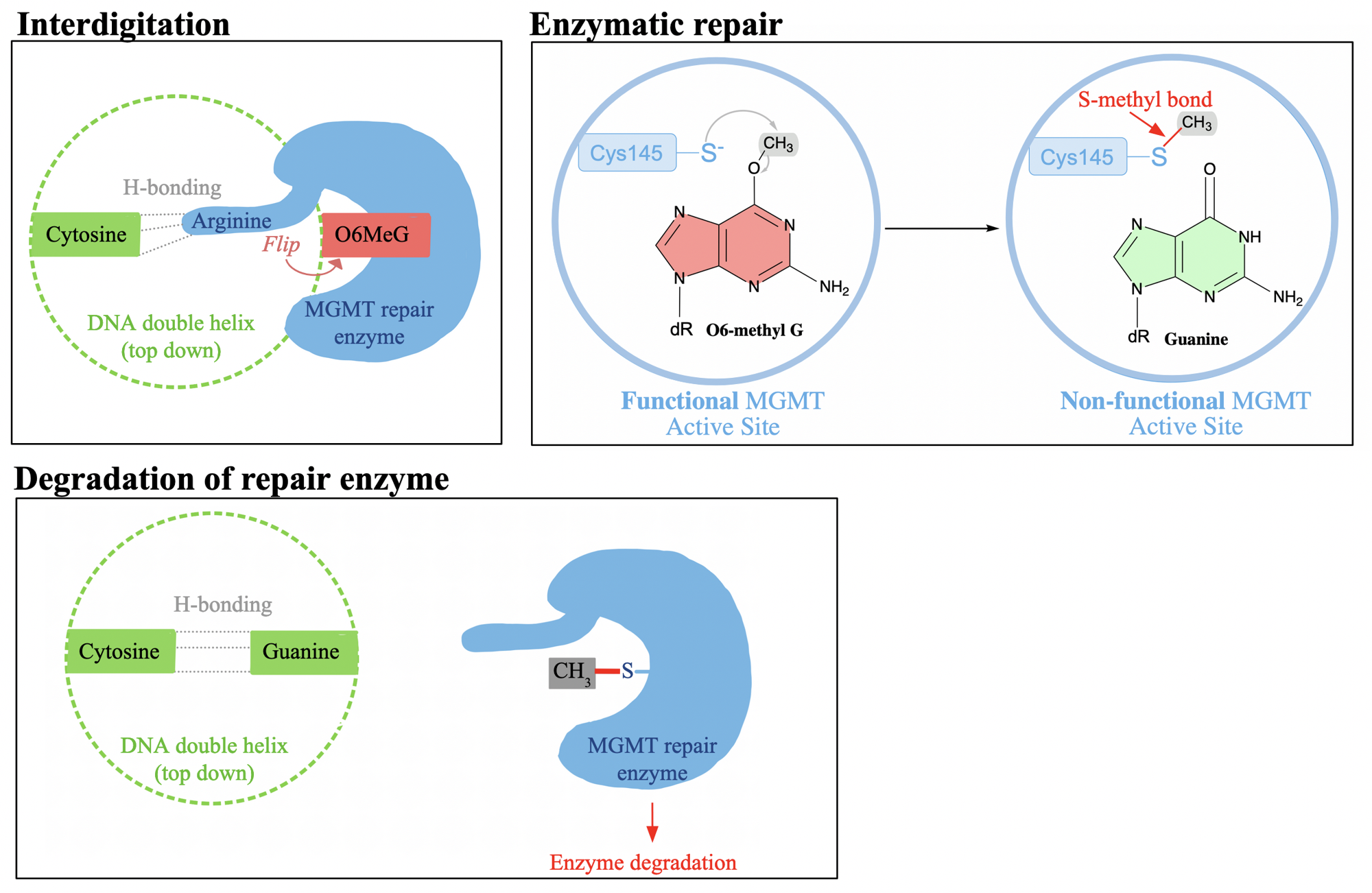
proteins like MGMT are referred to as
suicide enzymes
the enzyme loses its functionality and must be degraded
The cell's ability to repair alkylation damage is directly linked to
the quantity of repair enzymes it produces
In BER, these damaged bases are removed from the DNA strand and replaced with a new nucleotide using _________ enzymes
multiple different enzymes
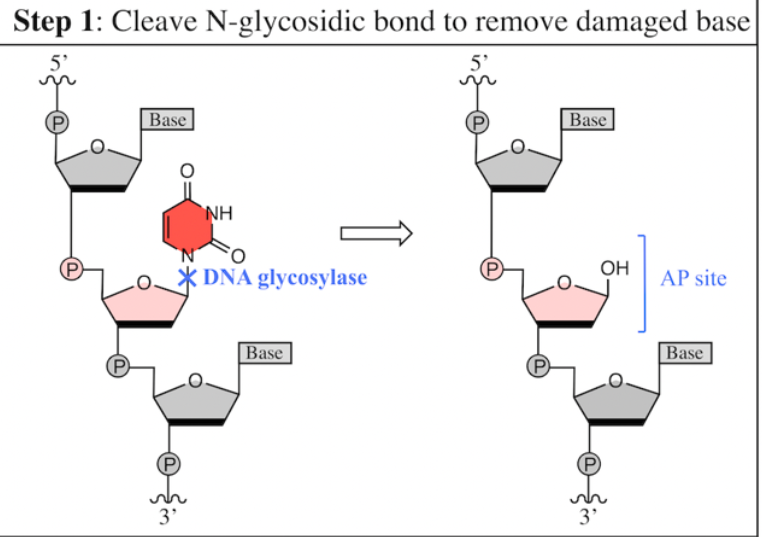
four key steps of BER
Cleave N-glycosidic bond to remove the damaged base
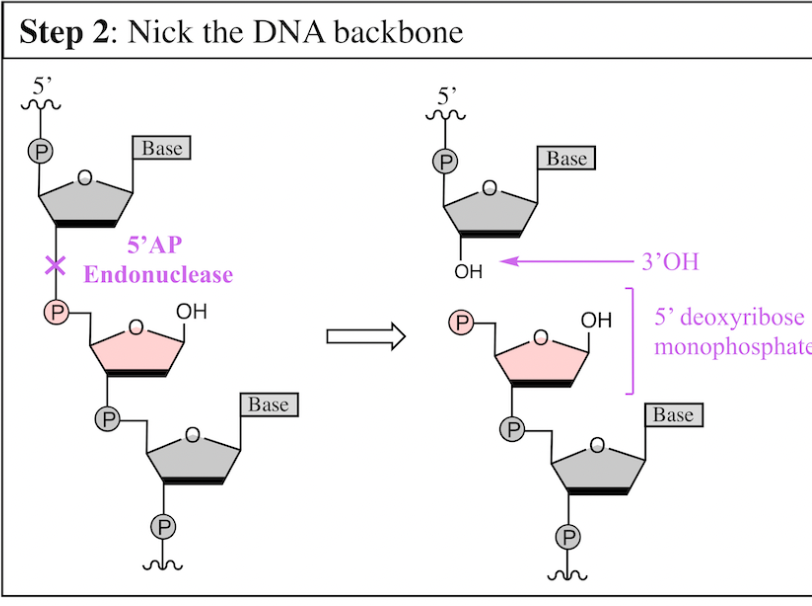
Nick the DNA backbone
Removal of deoxyribose monophosphate
Fill the gap with a new nucleotide
A specific ________ identifies the damaged base and cleaves its __________ bond
DNA glycosylase
cleaves its N-glycosidic bond to generate an AP site
Each DNA glycosylase can only recognize one specific type of damaged base
how does DNA glycosylase specificity enhance DNA repair capacity
allows the cell to increase the production of DNA glycosylases specific for frequently occurring forms of damage
how does DNA glycosylase specificity reduces the types of damage that can be repaired by BER
DNA glycosylases are unable to identify novel forms of DNA damage
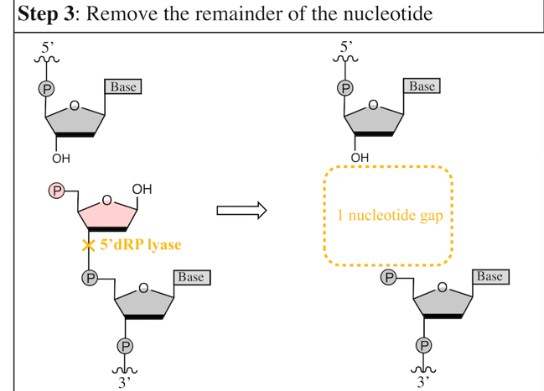
Once the damaged base has been removed, a_______ makes a nick in the DNA backbone
generates:
5’AP endonuclease
generates a 3’OH and 5’deoxyribose monophosphate
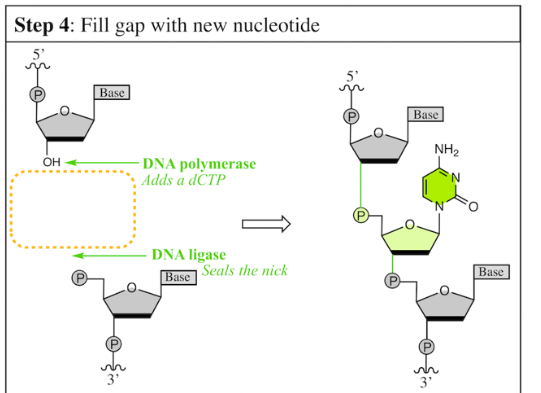
__________ removes the deoxyribose monophosphate to produce a one nucleotide gap
dRP lyase
what 2 enzymes are used to Fill the gap with a new nucleotide
what does NER recognize
general distortions in the DNA helix structure, which are caused by larger base-modifications during DNA damage
does not specifically recognize minor modifications of damaged bases, such as depurination or deamination
The enzymatic process of NER occurs in four key steps
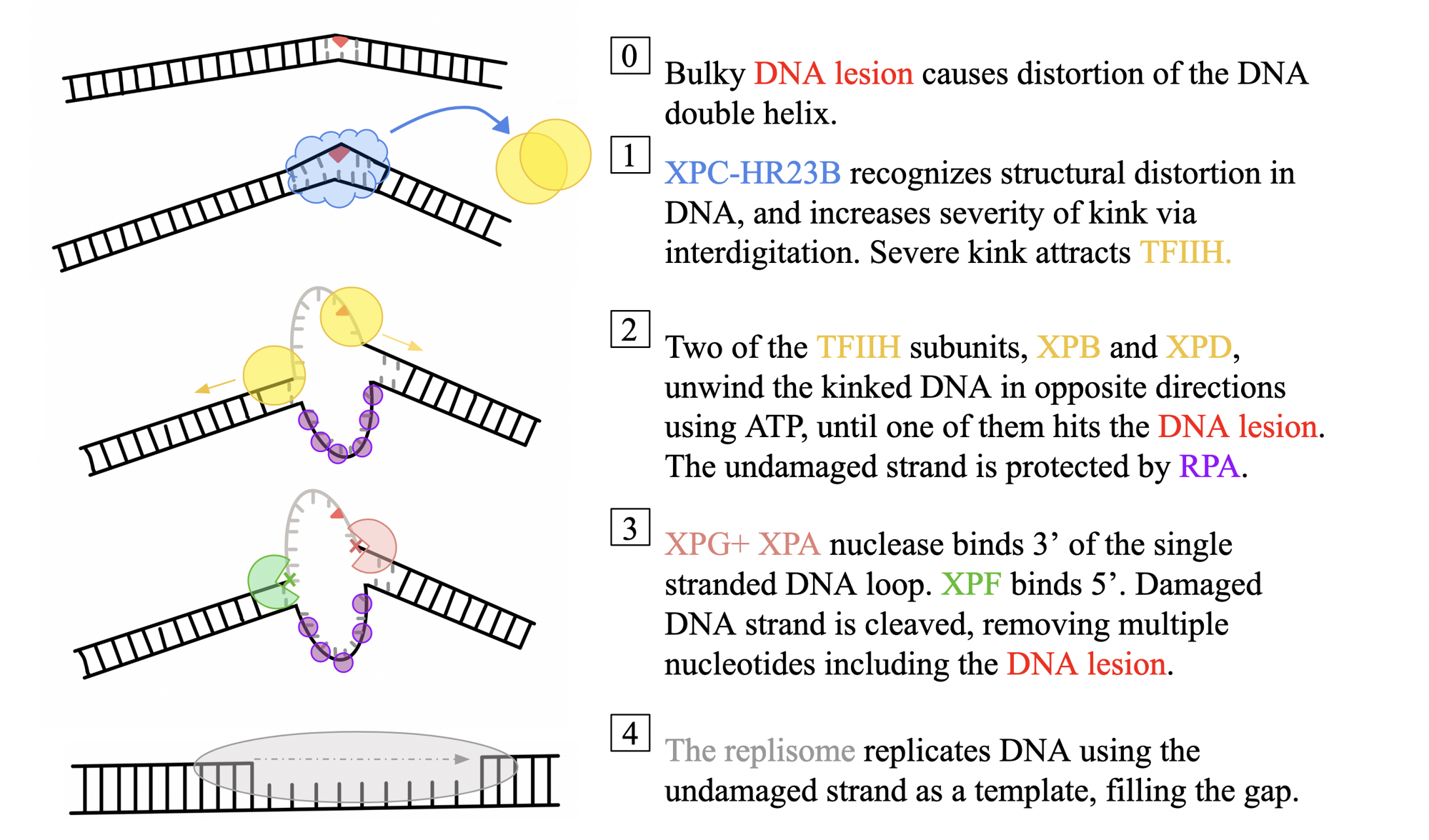
The protein complex _______ recognizes and binds to the DNA double helix at sites of structural distortion
XPC-HR23B
TFIIH is composed of two subunits
XPB and XPD
the undamaged strand will be protected by the single stranded binding protein
RPA
_______________nuclease binds 3’ of the loop and _____________binds 5’ of the loop
XPG + XPA
XPF
Since multiple nucleotides are excised, the _______ is used to fill in the gap.
entire replisome
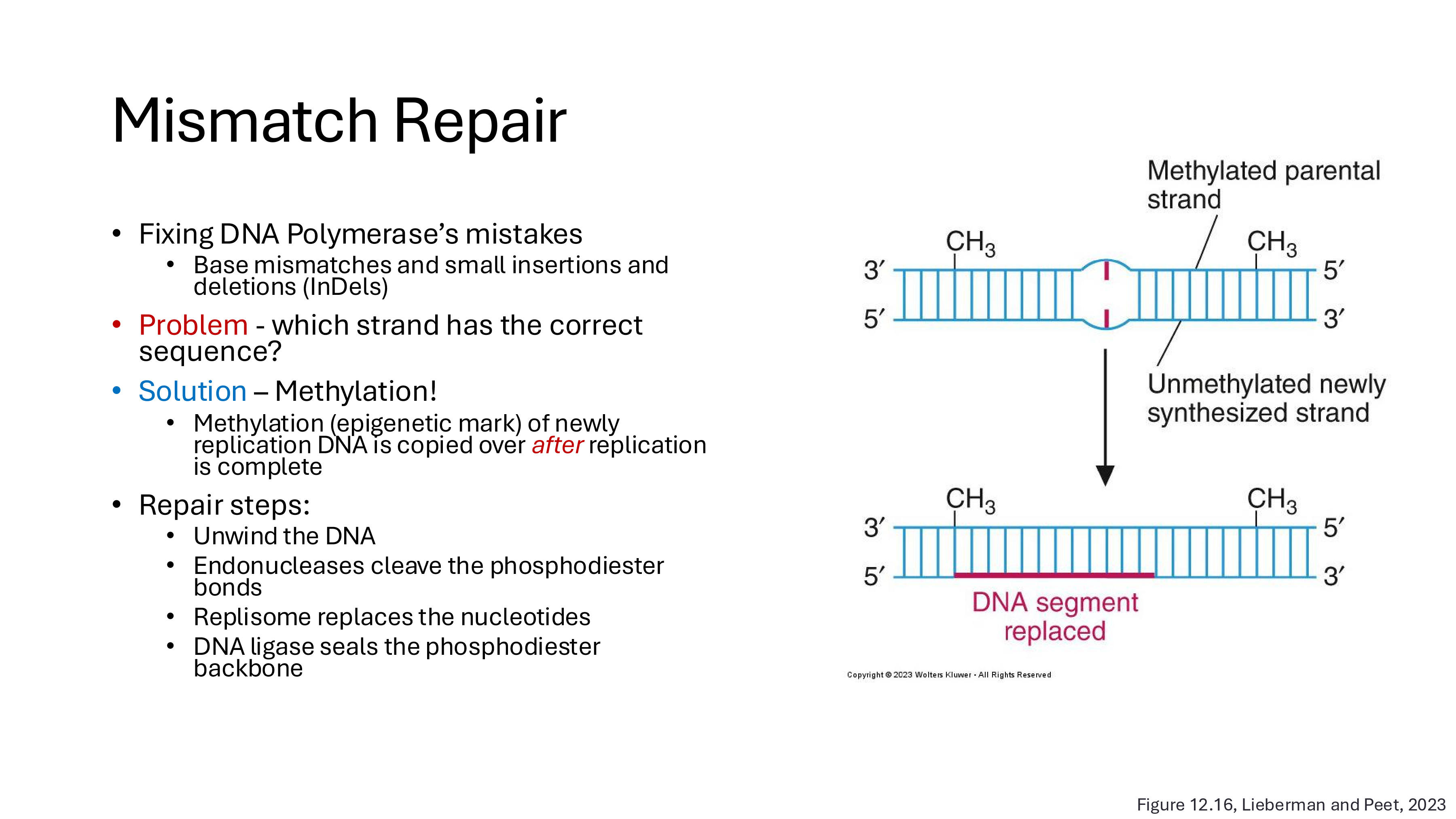
mismatch repair