1.9 Chemical Analysis ⚗️
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GCSE CCEA Specification GCSE Chemistry Double Award Science, Triple Award Science Unit 1: Structures, Trends, Chemical Reactions, Quantitative Chemistry and Analysis
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
Pure substance
single element or compound not mixed with any other substance
Examples of pure substances
Diamond, only element carbon
Water, only the compound water
Table salt, only the compound sodium chloride
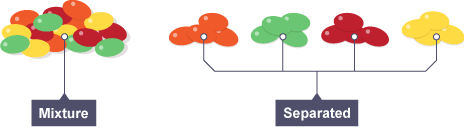
Mixture (impure)
two or more substances mixed together, usually easy to separate

Examples of mixtures
Air, mixture of oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen and other trace gases
Mineral water, mixture of water and dissolved salts
Milk, mixture of water, lactose, fat and minerals
Melting point
temperature at which solid changes into liquid
Boiling point
temperature at which liquid changes into gas
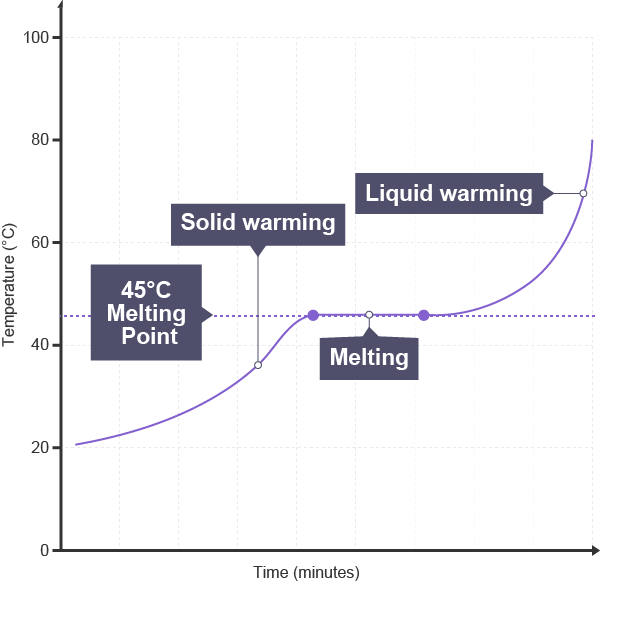
Melting and boiling points of pure substances
specific points/ temperatures
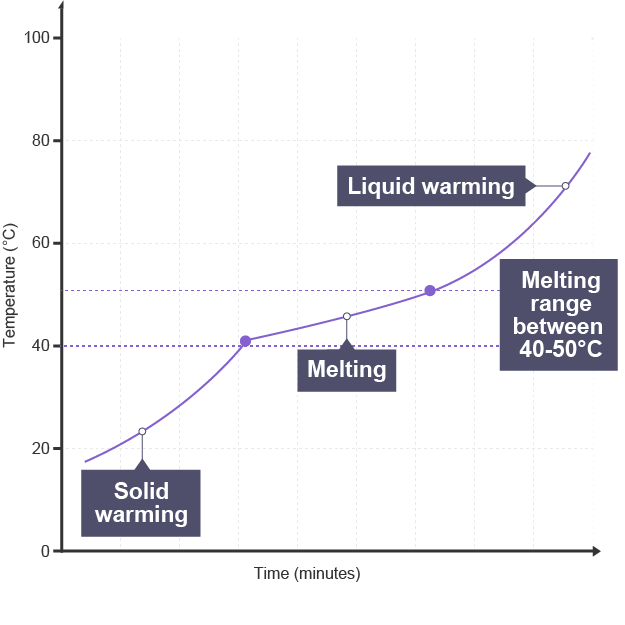
Melting and boiling points of impure substances
will melt/ boil over range of temperatures, gradually
melts at lower temperature than expected
boils at higher temperature than expected
Why impure substances has lower melting point
impurities disrupt regular lattice arrangement so bonds between particles are weaker
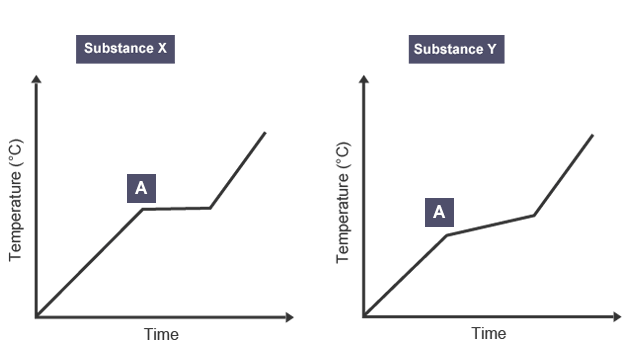
Differences in melting and boiling points
allow us to distinguish between pure substances and mixtures e.g X is pure
Formulation
mixture designed as useful product (+ how formed)
How are formulations made
mixing different substances in carefully measured quantities to ensure it has required properties
Alloys as formulations
mixture of two or more metals, usually through melting, mixing and cooling
Examples of alloy formulations
stainless steel, made from iron, chromium and other elements e.g carbon or nickel
Medicines as formulations
contain ingredients other than active drug, usually to prevent complication e.g timed release
Examples of medicine formulations
Calpol, made from paracetamol and liquid flavourings
Fertilisers as formulations
contain multiple compounds depending on plants used for
Examples of fertiliser formulations
NPK fertilisers, made from nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium
Separating mixtures
relatively easy (no chemical reactions needed) because they are not chemically joined to each other
Soluble
dissolves in water
Insoluble
does not dissolve in water
Solute
substance which dissolves
Solvent
liquid which dissolves the solute
Solution
mixture of solute dissolved in solvent
Miscible
liquids mix e.g water and ethanol
Immiscible
liquids do not mix e.g oil and water
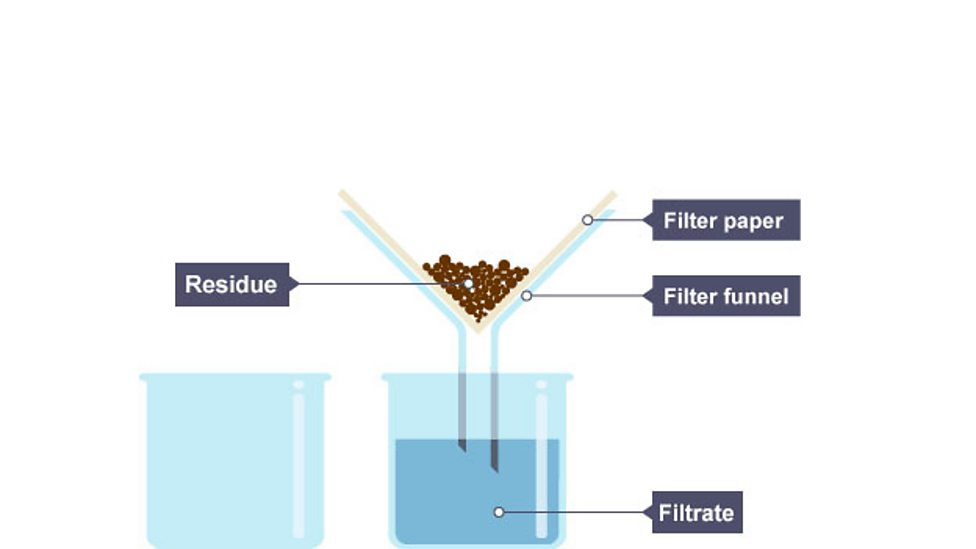
Filtrate
filtered solution
Residue
solid which remains on filter paper
Distillate
liquid produced by distillation
Evaporation
when liquid is heated and changes state into gas
Condensation
when gas cools and changes state into liquid
Filtration
separating insoluble solid from liquid e.g sand from water
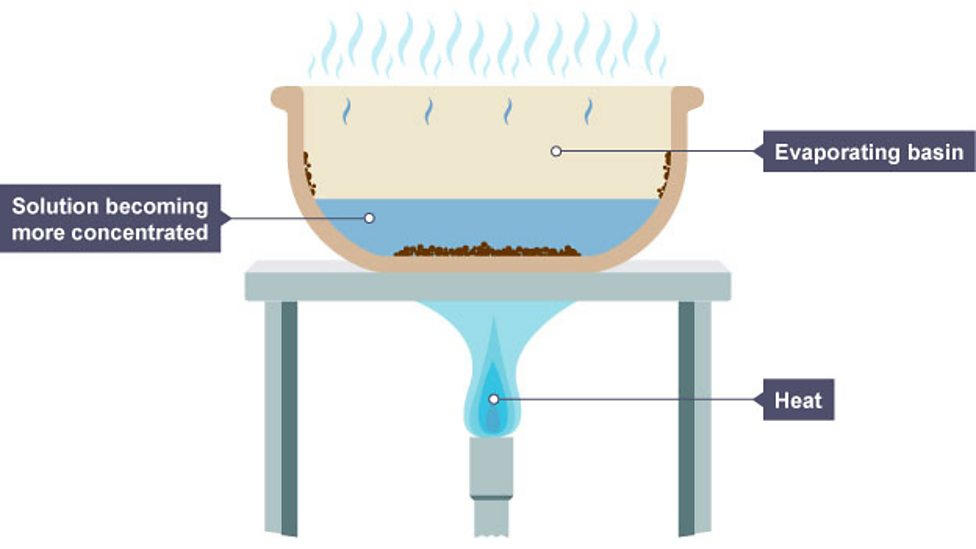
Crystallisation
separating soluble solid from solvent through evaporation, leaves behind saturated solution and cools to form crystals e.g obtaining pure soluble salts
Paper chromatography
separating of mixtures of soluble substances by running solvent through mixture on paper, causing different substances to move through at different rates
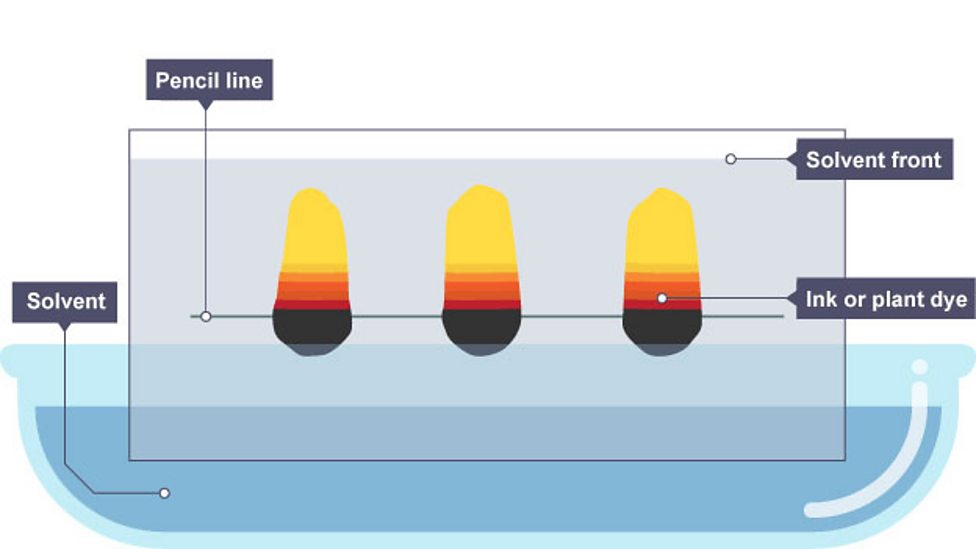
Why substances move at different speeds
strength of attraction to each phase
Phases of chromatography
two phases with different properties
paper is stationary phase
solvent is mobile phase
Substances with strong attraction to paper
move slowly and only travel short distance
Substances with strong attraction to solvent
move quickly and travel further
Extracting chemicals from chromatography
spot can be cut out and solvent dissolved
Colourless spots
can be viewed under UV light or spraying chemical developing agent and drawn round in pencil
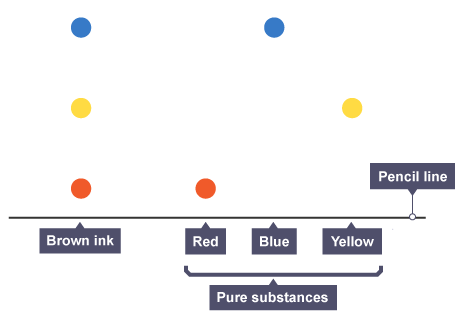
Interpreting a chromatogram
pure substance has single spot whereas impure substances have two or more spots
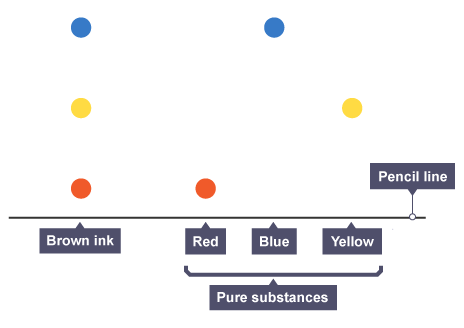
Identifying same substances
produce same number of spots
spots travel at same distance and have same Rf value
e.g brown contains all three colours
Rf value
measure of distance substance travels relative to the solvent
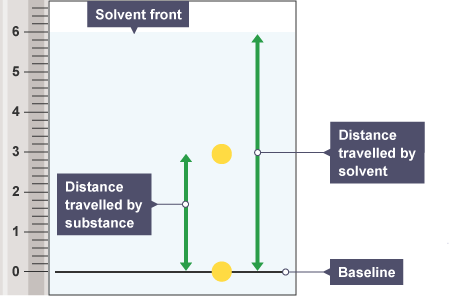
Rf value equation
distance moved by spot/ distance moved by solvent
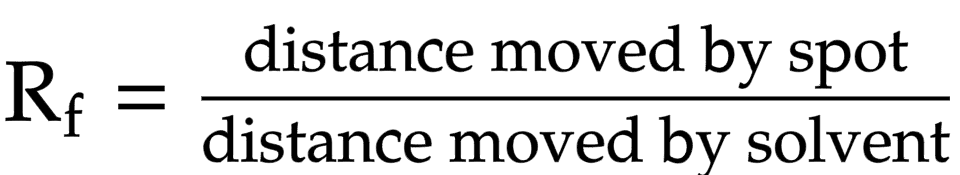
Interpreting Rf value
value of 0 is not attracted to solvent, value of 1 if not attracted to paper
Separating funnel
separating immiscible liquids based on densities e.g oil and water
How does a separating funnel work
mixture is placed in funnel and clamped
liquids do not mix so float on top of each other
tap is opened until first liquid is drained into beaker
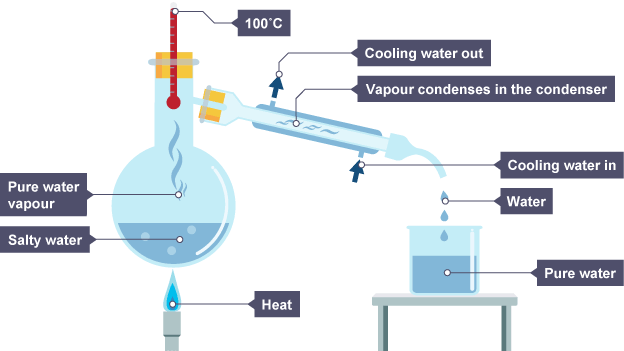
Simple distillation
separating solvent from solution or two miscible liquids with different boiling points using evaporation and condensation e.g salt and water
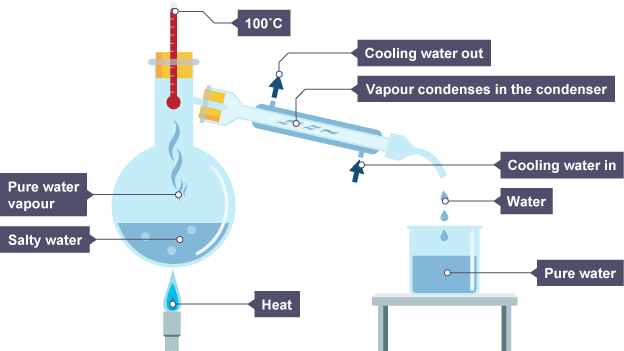
How simple distillation works
solution is heated
dissolved solute has much higher boiling point that solvent so only it evaporates
gas moves away and cools in condenser
it then drips into beaker
remaining solution becomes more concentrated as amount of solvent decreases
Fractional distillation
separating mixture of liquids with boiling points that are close together e.g water and ethanol
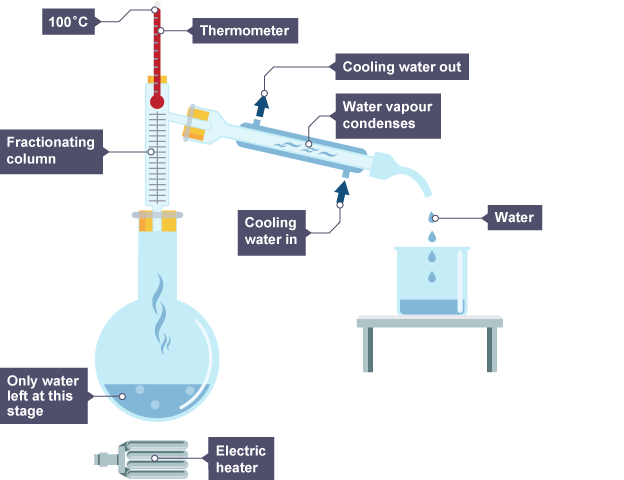
How fractional distillation works
has fractionating column (hot at bottom and cooler at top)
vapor condenses when reaching part of column below their boiling point going back into flask
gas that makes it to top of column enters condenser to be changed into liquid
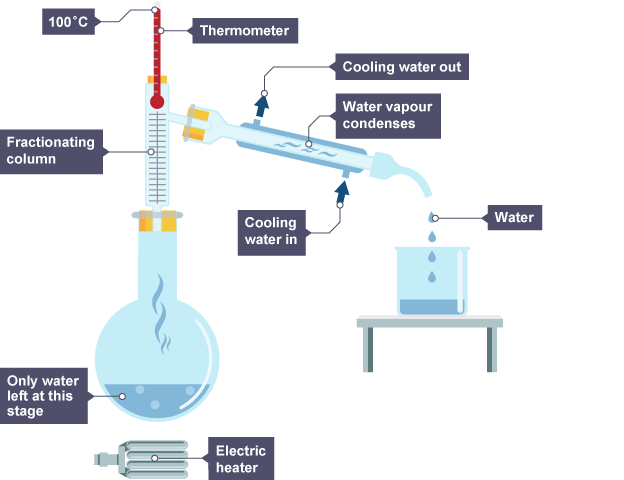
Fractionating column
gradually changes the temperature so liquid with lowest boiling point will evaporate first
Fractions
different components of the mixture
Boiling point of water and ethanol
100° C, 78° C
Where is fractional distillation mostly used
refining of crude oil as is complex mixture of many different compounds
Potable water
water that is safe to drink, must be treated first
How to make potable water from fresh water
Filtration - to remove insoluble solids like stones and leaves, water is passed through layers of sand and gravel called filter beds
Sedimentation - Aluminium sulfate is added to help tiny particles clump together so they settle to bottom and clean water can be drawn off the top
Chlorination - Chlorine gas is bubbled through water to kill any harmful microorganisms, such as bacteria
Desalination
removal of salt from seawater
How to make potable water from seawater (desalination)
salt water is heated so water is allowed to evaporate
water vapour is collected rather than being lost
it’s condensed to form pure water/ fresh water
salt is left behind and can be used for other purposes
Potable water from fresh water vs sea water
desalination uses lots more energy and is more expensive
Uses of desalination of seawater
useful in countries that have coastlines but no readily available fresh water sources however mostly those that are quite wealthy
Pure/ anhydrous copper (II) sulfate
when water is added changes colour from white to blue
Precipitate (ptt)
insoluble solid formed when two solutions are mixed
Equation for testing water
anhydrous copper(II) sulfate + water ⇌ hydrated copper(II) sulfate
CuSO4 + 5H2O ⇌ CuSO4.5H2O
Testing for cations
flame tests
precipitate tests
Flame tests
metal ions produce strong colour in blue bunsen flame, can be used to identify it
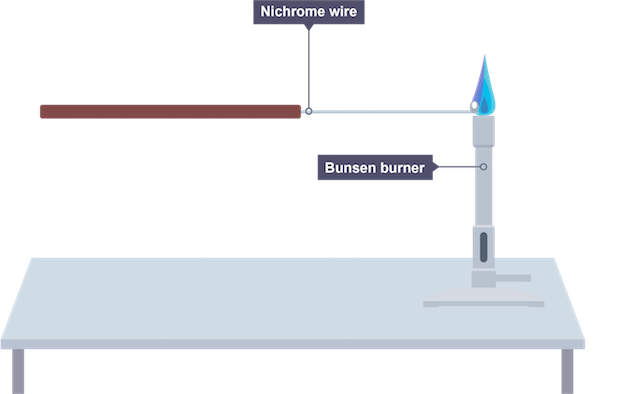
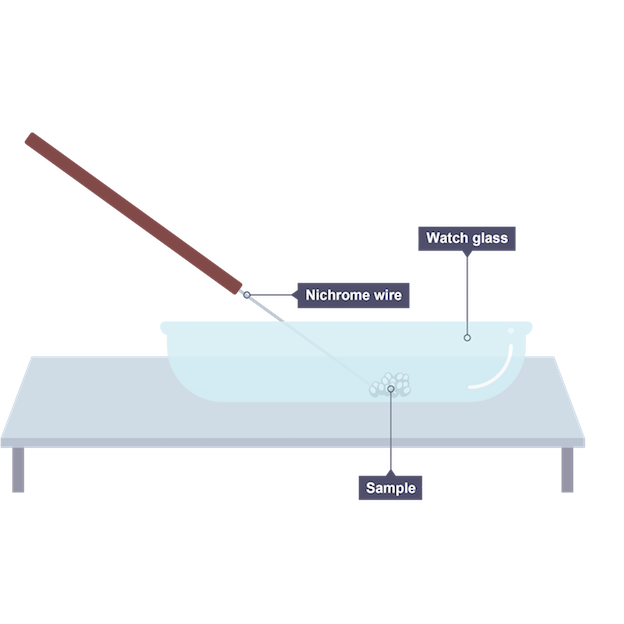
Carrying out flame tests
use nichrome wire which is cleaned using concentrated hydrochloric acid
Flame colour of lithium ion (Li+)
crimson
Flame colour of sodium ion (Na+)
yellow/ orange
Flame colour of potassium ion (K+)
lilac
Flame colour of calcium ion (Ca2+)
brick red
Flame colour of copper ion (Cu2+)
blue-green
Precipitate tests
when metal ions combine with hydroxide ions they form precipitates with characteristic colours
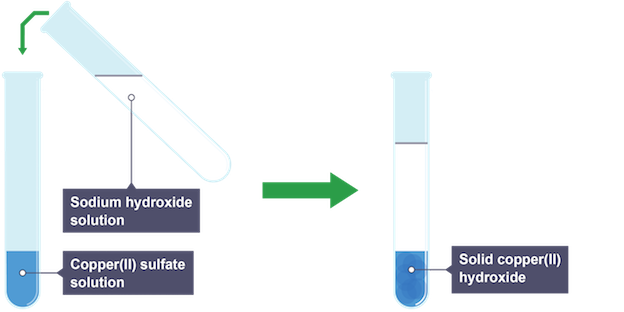
Percipiate colour of copper(II) ion (Cu2+)
blue perciptate, remains in excess sodium hydroxide but dissolves to form deep blue solution in ammonia solution
Percipitate colour of iron(II) ion (Fe2+)
Green precipitate, remains in excess
Percipitate colour of iron(III) ion (Fe3+)
brown percipitate, remains in excess
Percipitate colour of magnesium ion (Mg2+)
white percipitate, remains in excess
Percipitate colour of aluminium ion (Al3+)
white percipitate, dissolves to form colourless solution in excess sodium hydroxide solution but remains in ammonia solution
Percipitate colour of zinc ion (Zn2+)
white precipitate, remains in excess ammonia solution but dissolves to form colourless solution in sodium hydroxide solution
Ionic equations for testing for anions
Ba2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → BaSO4(s)
Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq) → AgCl(s)
CaCO3 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + CO2 + H2O
Colour of chloride ion precipitate (Cl-)
white
Colour of bromine ion precipitate (Br-)
cream
Colour of iodide ion precipitate (I-)
yellow
Colour of sulfate ion precipitate (SO4-2)
white