Science Section 2 Academic Decathlon 25-26
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
James Joule
Connection between heat & work
William Thomson
"Lord Kelvin"
Laws of Thermodynamics
1st Law of Thermodynamics
Conservation of energy
2nd Law of Thermodynamics
Kinetic energy exchange
Always goes high to low
3rd Law of Thermodynamics
No system can reach absolute zero
Kinetic Energy
Moving energy
Flow of kinetic energy
Nuclear reactions in suns core -> sunlight -> food chain -> energy in muscles -> throwing ball -> sound; vibrations; air compression
Heat
Energy in transit between objects at different temperatures
Can only emit or absorb heat, not contain it
Phlogiston
Formerly thought to be the heat being exchanges (own substance)
Now understood that heat is a property inherent in materials
Temperatures
Average kinetic energy of the atoms in a substance
Fast moving transfers energy into slow moivng
Zero temperature
Atoms in a substance are not moving at all
Nothing lower than zero, so no way to cool it off more
Gravitational potential energy
Energy that an object possesses due to its position in a gravitational field
Electric potential energy
No gravity and a negatively charged floor with a positive pendulum
Pos pendulum is pulled towards negative floor
Same as gravity
Proportional to charge
Voltage
Differences in electric potential
Electric Potential
Electric Potential Energy/Charge
Measured in volts or joules per coulomb
Environment around object
Describes how the electric field changes across some distance
Cannot be directly measured (Instead, voltage across 2 points)
Equipotential line
Indicates steepness (strength) of electric field
ΔE=q*V
Alessandro Volta
Invented a modern battery
Volts named after him
"Battery"
Formerly a military term for a coordinated group of artillery weapons
Inspired Ben Franklin's name for connected Leyden Jars
"Piles"
Lucia and Luigi Galvani
1780s, during a dissection of a frog (later, any dead body) the body jumped when touched with two different metals
Conclusion: Movement of dead frog was due to electricity within it, activated by metals
Actual: Acids in frogs skin dissolved metals, electrons transferred
Galvanism
Electricity = life force?
Volta and Galvansism
Electricity came from the metals, not the corpse
Tested with silver and zinc sheets with saltwater soaked cardboard -> 30 volts created
Giovani Aldini
Nephew of Lucia and Luigi Galvani
Left hemisphere controls the right side of the body, vise versa
Electroshock can cure depression
Modern battery
Device that maintains a constant voltage by keeping two collections of positive ad negative charge separate from each other
Carbon Electrode (+), Zinc Electrode (-), Sulfuric Acid
Acid dissolves zinc, gains + charge while Zinc is -
+ Acid polarizes carbon rod so it's - in Acid and + outside
Wire connect terminals, positive charge flows to neutralize negative
Acid-> allows terminals to recharge and maintain imbalance
Zinc will eventually corrode
Primary cell batteries
Disposable, one-use batteries
Secondary cell batteries
Can be recharged
Lithium Ion Battery
Move lithium ions through a conducting chemical fluid
When charging, the terminals switch, so the ions flow to the other side
Heat is generated through friction, transferred to surroundings (takes energy) - fire
Phones, cars
Electric Circuit
Closed loop in which energy continuously flows
Positive energy tries to neutralize negative energy in battery, connected by wire - but battery maintains charge separation
Direct Current (DC), no changes in direction
Battery keeps charge from gathering at an area of low potential
Voltage
Electromotive force (EMF)
Tells how powerful the circuit will be
Flow of electricity
the ELECTRONS are moving
when we say that a charge is flowing (positive), the electrons are moving in the opposite direction
Electric current
measuring the amount of charge that flows past a point per second
measured in Amperes
André-Marie Ampére
Namesake for Amperes (amps)
Amperes
Measure of electric current
1 amp = 1 coulomb / sec
Effect of Amps
0.001 = Shock
0.005 = Painful Shock
0.015 = Loss of Muscle Control
0.070= Fatal
Why are Amps dangerous
They disrupt the electric signals in your body
Electrocardiogram (EKG)
Measured voltage across parts of the body to measure heartbeat
When heart is beating too fast, doctors stop it so that the body starts it again (pacemaker)
Electrophysiology
Study of electricity in the human body
Frankenstein by Mary Kelly
Inspired by demonstrations of electric shocks & corpses
Ohm's Law
Measure current in a circuit

Ohm's Law Equation
V= Battery Voltage; I= Current; R= Resistance
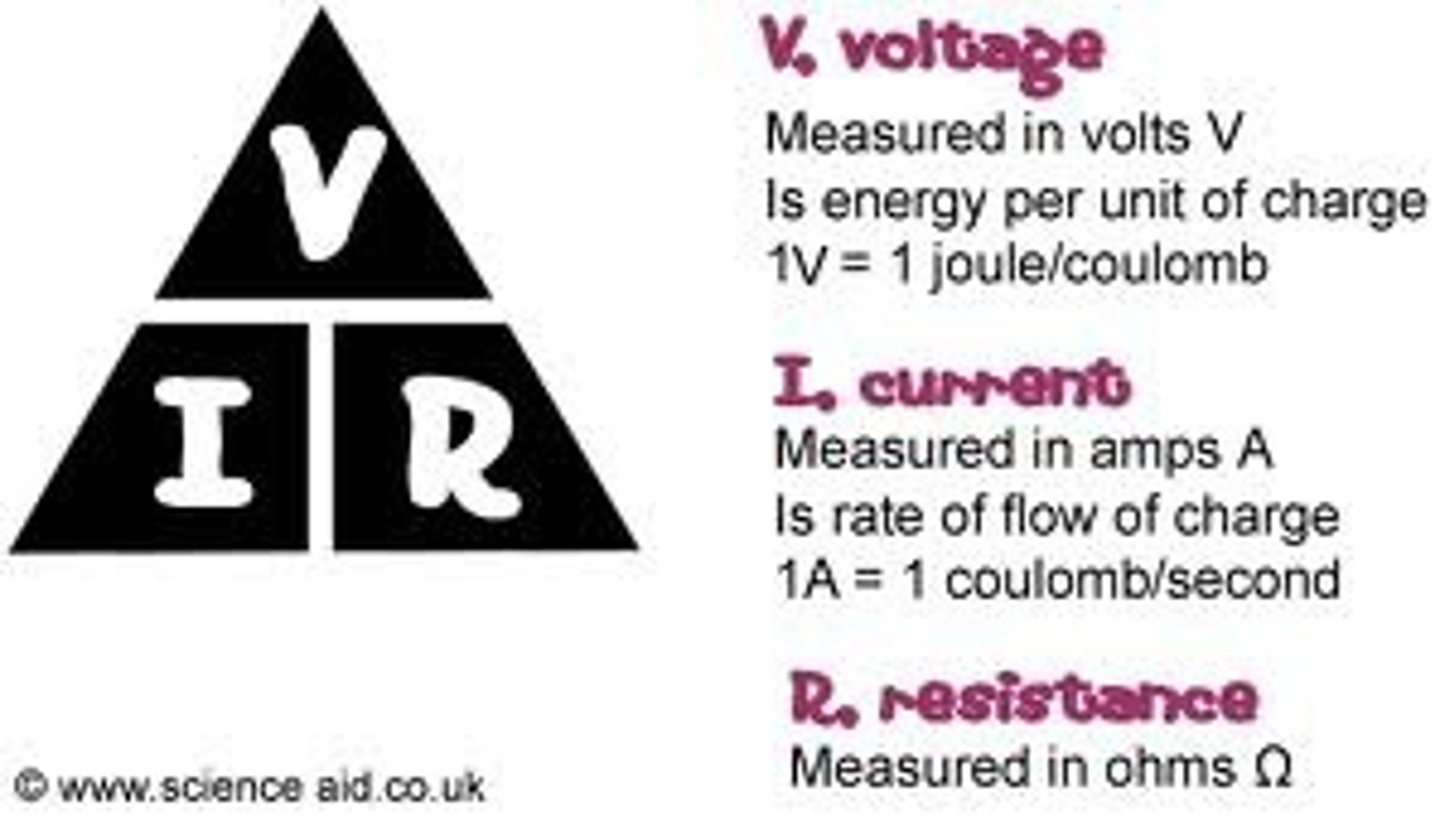
Resistance (R)
Resists the flow of the current
Measured in ohms (Ω)
Conductive=low, insulation=high
Long wire>short wire
High voltage
Rubbing a balloon
"Height" that the charges in a circuit "fall" down from high potential (+) to low potential (-)
Any charge that flows will be building up energy BUT it depends on the amount of charged particles
Creates the conditions for the current
POTENTIAL difference
High current
What affects you
120 V in wall outlet
Power
Rate of energy change over time
Measured in watts
Watts
Measures power
1 watt=1 joule/second
Lightbulb
Wire that has a current will heat up enough to glow
Tungsten filament in an incandescent lightbulb
2000 Celsius, glows Yellow
Kilowatt Hour
3,600,000 joules
Resistance & Temperature
Increasing in current causes an increase in temperature, which leads to an increase in resistance
Superconductors
Resistance is zero
Resistor
Resists current by taking energy away from the flow of charge into another form of energy