AP: Unit 3
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Renaissance [Time]
1300s-1600s
Renaissance
Rebirth of art and literature

Humanism
A belief that emphasizes faith and optimism in human potential and creativity

Secular
Non-religious; wordly

Vernacular
Everyday language of ordinary people

Patron
a person who provides financial support for the arts
Skepticism
An attitude of doubt; question everything

Printing Press
15th century invention which revolutionized the ability to print information.

Printing Press Social Impact
More people could read and write, new ideas spread quickly

Renaissance [Location]
Italy
Theocentric
having God as a central focus

Literacy
the ability to read and write
Reform
change

Protestant Reformation
A religious movement that resulted in the creation of Protestant churches.
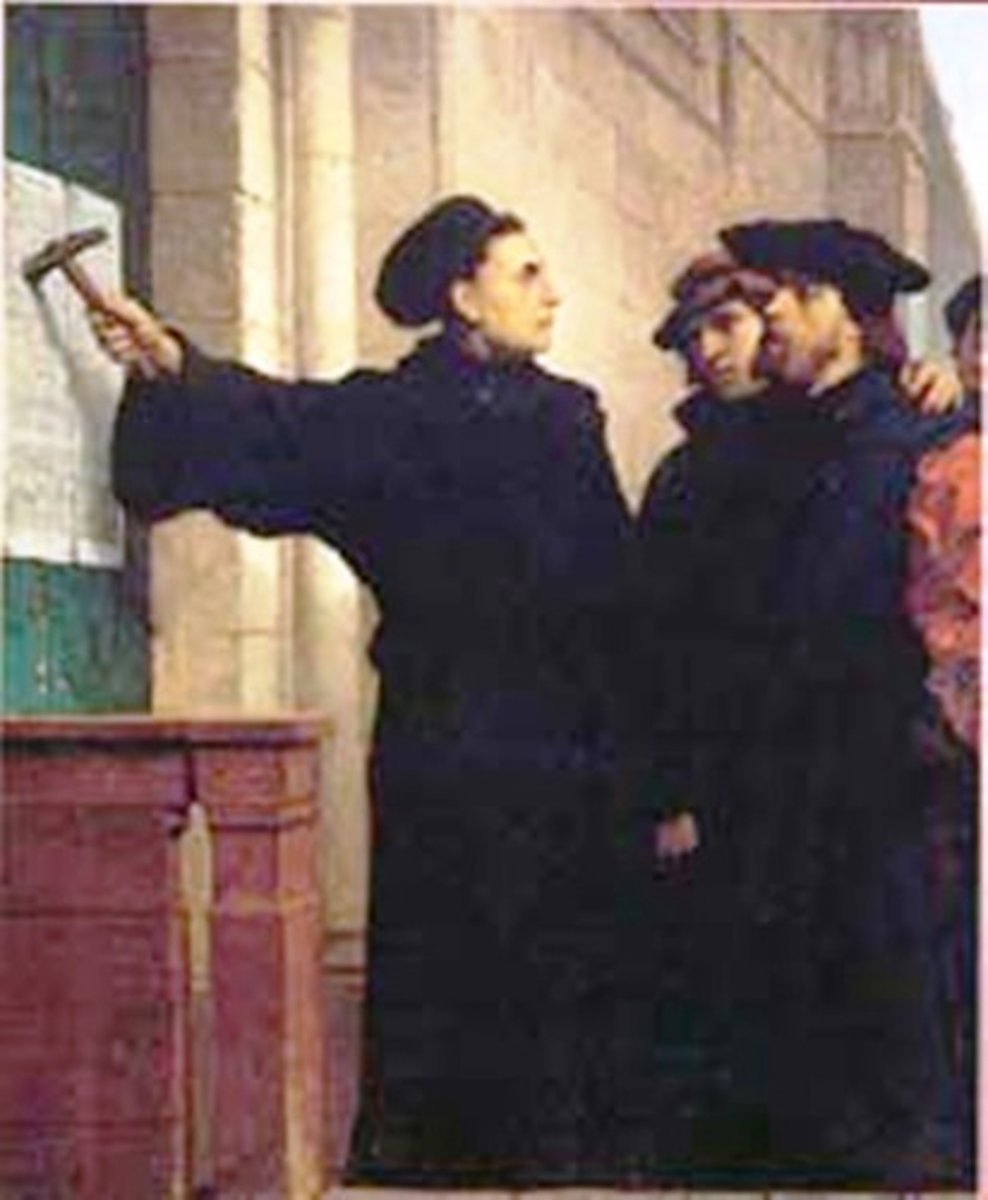

Martin Luther
German priest who led the Reformation

Indulgences
Selling of forgiveness by the Catholic Church.
95 Theses
Arguments written by Martin Luther against the Catholic church in 1517.

John Calvin
Religious reformer who believed in predestination and a strict sense of morality for society

Predestination
The belief that what happens in human life has already been determined by some higher power.

Henry VIII of England
Launched the English Reformation. Allowed the Bible to be printed in English legally for the first time.

Anglican Church
Church of England created by Henry VIII when the Pope would not let him divorce his wife.

Church of England
Anglican Church created by Henry VIII when the Pope would not let him divorce his wife.

Turmoil
Great commotion and confusion

Gunpowder Empires [Names]
The Ottoman Empire, Safavid Empire, and Mughal Empire
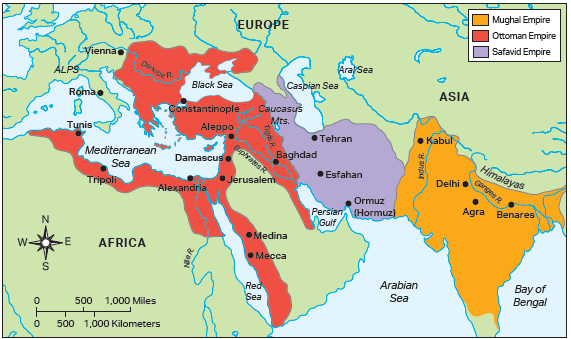
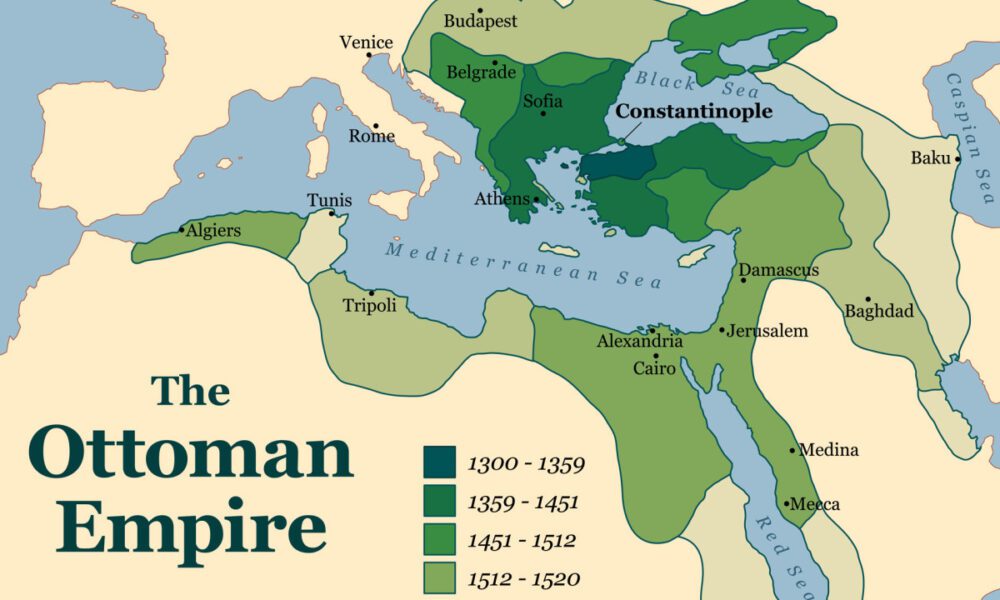
Ottoman Empire Location
Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and North Africa
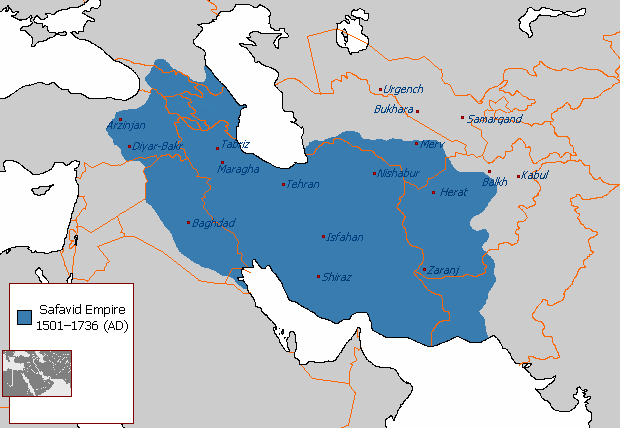
Safavid Empire Location
Modern-day Iran and parts of surrounding countries.
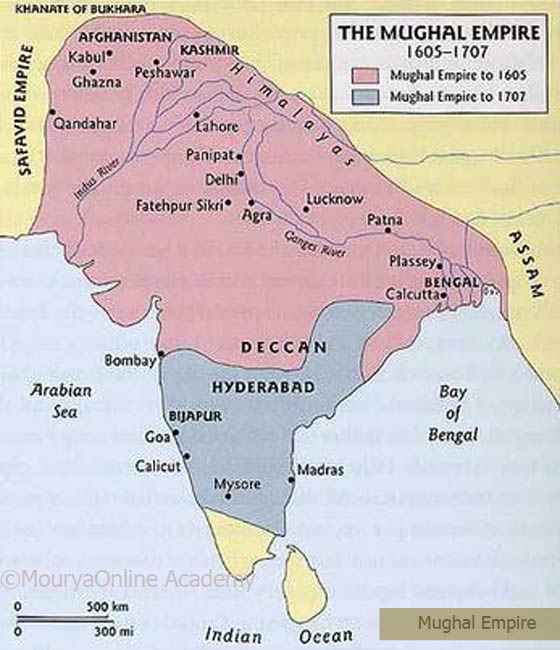
Mughal Empire Location
Present-day India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh, e
Gunpowder Empire [Definition]
an empire formed by outside conquerors who unified the regions that they conquered through their mastery of firearms
Akbar the Great
The most famous Muslim ruler of India during the period of Mughal rule. Famous for his religious tolerance.
Sikhism
Monotheistic religion founded in northern India that combines elements of Hinduism and Islam
Shogun
Japanese military leader who held power during the feudal period.
Tokugawa Shogunate
The last feudal Japanese military government characterized by a strict social order and isolationist foreign policies.
Russian Empire
Vast territory expansion in Russia
Spanish Inquistion
Purpose was to root our the heretics in Spain.
Heritics
Non believers of Catholicism
Council of Trent
A council of the Catholic Church held between 1545 and 1563 to address issues of reform and clarify Catholic doctrine in response to the Protestant Reformation.
Jesuits
A religious order founded to spread Catholicism and combat the Protestant Reformation through education and missionary work.
Ignatius of Loyola
Founder of the Jesuits, he emphasized education and spiritual discipline.
Simony
The buying or selling of ecclesiastical offices or privileges, considered a sin in the Catholic Church.
Inquisition
Questioning of people’s beliefs that often involved torture and punishments.
Gunpowder Empires
A term referring to three powerful empires in the early modern period—Ottoman, Safavid, and Mughal—that utilized gunpowder technology to expand their territories and consolidate power.
Bureaucracy
A system of government characterized by hierarchical organization and a set of rules and procedures.
Decentralized Government
government where power is distributed among various regional or local authorities rather than concentrated in a central authority.
Centralized Government
a system where power is concentrated in a central authority, allowing for uniform decision-making and administration.