Hearing and Balance and Olfactions
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Pina
outside of ear
Ear inside tell me how to get in
external ear, inner ear, middle ear
Hearing workflow
sound goes into the internal ear, tap on the tympanic membrane, vibrations cause vibration of ossicles, then the inner ear vibrates sending signals to VIII (vestibulocochlear)
nasopharynx is connected to middle ear via pharyngotyympanic tube.
External ear made up of what?
2/3 cartilage 1/3 skin attacahed to bone
3 Ossicles
Malleus attached to incus attached to stapes
Ear infections
more horizontal pharygotympanic tube causing infected ear and reduced hearing and buldging tympanic membrane
Oval window
transition from middle ear to inner ear
Cochlea
3 fluid filled chambers: Scala media, scala vestibuli, scala tympani (vestibuli and typani continous with eachother).
coclear duct has endolymph in it with perilymph in the sacala vestibuli and scala tympani surrounding it
Sounds
Treble closest to oval window, mid, bass furthest.
Walk me through how sound is heard from oval window
Vibrations from oval window cause perilymph in the scala vestibuli to shake, this causes the cochlear duct to shake as well. which then in turn leads to the tectorial membrane shaking. Bending of the hair cells in cilia cause sound. then it is released through round window.
Conductive vs Sensorineural hearing loss
conductive is mechanical disruption (unilateral), bilateral neural
Balance 3 main organs and which cranial nerve
Utricle (horizontal) and Saccule (vertical)
Semi-circular canals (rotational acceleration)-anterior posterior lateral
CN VIII
Othalithic Organs
Linear acceleration (utricle and saccule)
using othalithic membrane bending the hair cells
Different membranes
Tectorial - cochlea
Othalithic- Othalithic organs (utricle and saccule)
Cupula- semicircular canals
Semicircular canals
Lateral, anterior, posterior
crista has hair cells that are bent by the cupula
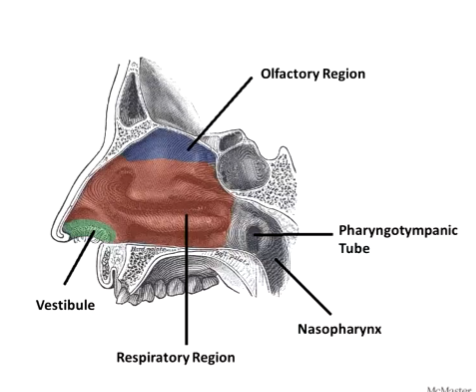
Nasal Cavity regions
Olfactory region and respiratory region
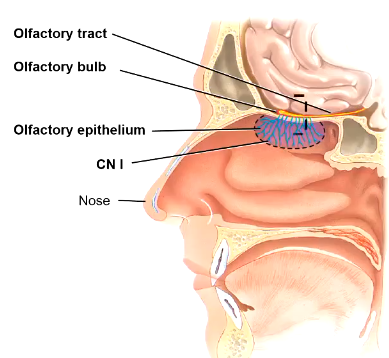
You only smell in the top portion of your nose (where CN I comes in)
Olfaction
chemoreceptors, olfactory epithelium (part of nerve) synapse at olfactory bulb, then go to olfactory tract to the cortex
Extends through the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone innervates mucosa and doesn’t go through the thalamus.