CELL BIO - Chapter 6: DNA replication
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
only first part of chapter 6 since its all that's gonna be on the exam :P
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Helicase
Enzyme that unzips DNA. Uses the energy of ATP hydrolysis. Pries apart ahead of replication fork.
Polymerase
Replicates DNA from the 3’ end. Can also proofread nucleotides as they are added.
Primase
Makes primer (starting line) out of RNA so polymerase knows where to replicate. Starts from 3’ end of the original strand/5’ of the new strand. Gets removed at end of cellular replication since it’s RNA not DNA, which leaves gaps
Ligand
Reconnects replicated DNA fragments on lagging strand by filling in gaps left by primase
SSB (single stranded binding proteins)
Keeps single stranded DNA halves separate
Topoisomerase
Prevents DNA from supercoiling by making transient breaks in one strand of the DNA double helix
Sliding Clamp
Keeps polymerase attached
Clamp Loader
Locks sliding clamp onto DNA strand. Uses energy of ATP hydrolysis
Okazaki Fragments
Chunks/fragments of replicated DNA created by the lagging DNA strand being unable to create a continuous strand
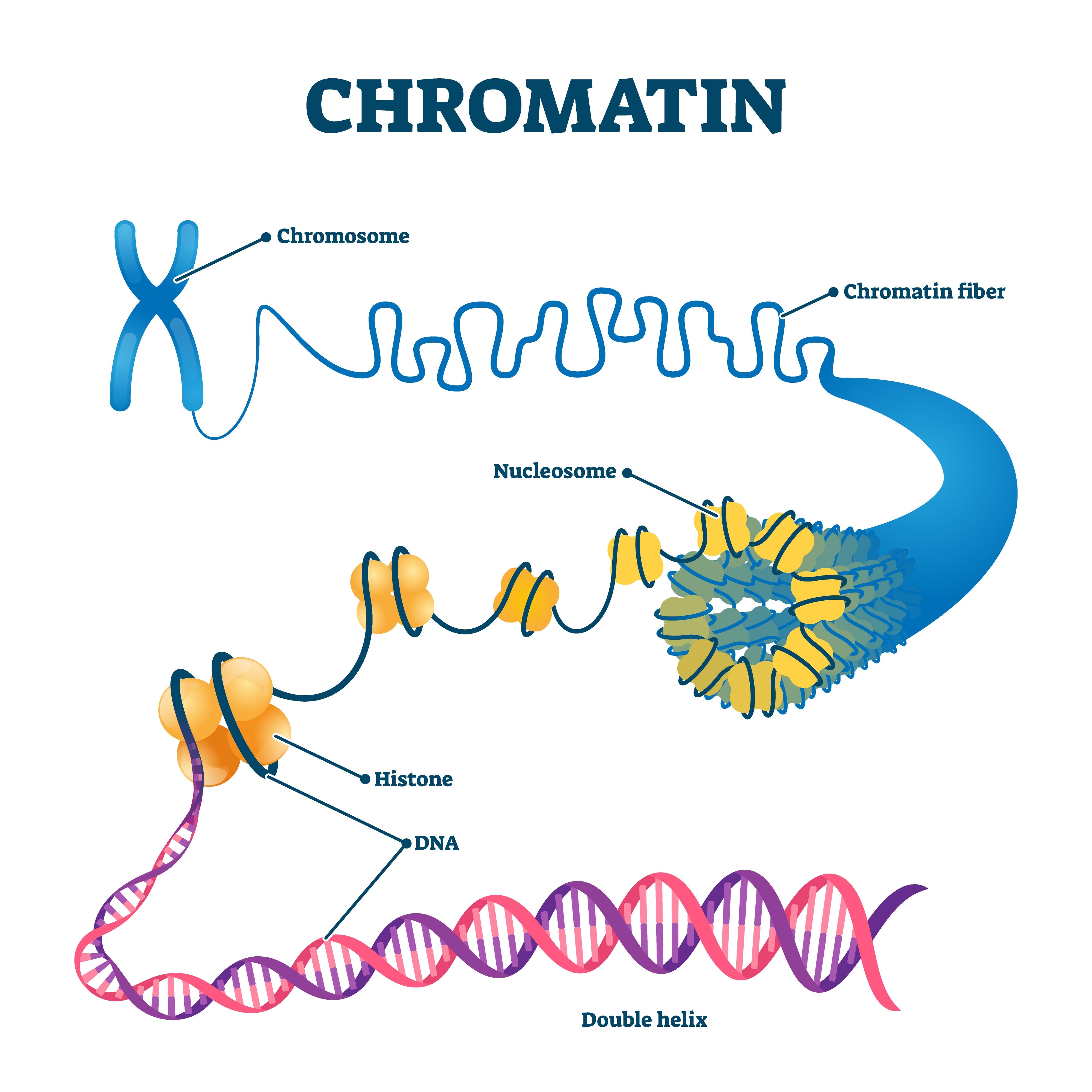
Histone
Protein “spools” that DNA winds around
Nucleosome
Structural unit created when DNA winds around (eight?) Histones
Chromatin
Condensed bundles of nucleosomes. Forms during cell division.
Chromosome
Tightly coiled structural units made of chromatin that code for genetic information. Set number within cells, exists when cells begin to divide
Structural order of DNA
DNA helix → wrapped around histones → creates nucleosomes → bundles into chromatin → compacts into chromosome
What removes RNA primers in DNA replication?
Nuclease