Biological molecules - carbs, lipids, proteins
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
define a monomer
smaller units from which larger molecules are made
define polymer
large molecule that is made up of many smaller repeating units
condensation reaction - dehydration synthesis
when monomers are combined to form polymers by removing water (hydrolysis opposite)
monosaccharides
monomer of carbohydrates, sweet tasting, soluble
maltose
two glucose monomers
lactose
glucose + galactose
sucrose
glucose + fructose
alpha glucose structure
beta glucose structure
(switched on carbon 1)
define isomers
compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures and properties
whys galactose a different sugar
the H and hydroxyl on carbon 4 are switched from glucose
what does a condensation reaction create
glycosidic bond
starch
made of alpha glucose in the forms of amylose (1,4) and amylopectin (1,4 +1,6)
starch structure - amylose
an unbranched helix
starch structure - amylopectin
long, branched
starch function
energy storage in plants
starch - how structure fits function
insoluble so doesn't affect water potential and is osmotically inactive
too large to pass through membranes, so good for storage
compact so can be stored in small place
branched structure increases SA for rapid hydrolysis back to glucose
when hydrolysed forms a-glucose which is easily transported and readily used for respiration
glycogen structure
alpha glucose, branched structure even more than starch with 1,4 linkage bonds and 1,6 branches
glycogen function
storage of glucose in animals
glycogen - how structure fits function
stored mainly in liver and muscle cells important for regulating blood glucose levels
branched structure increases SA for rapid conversion back to glucose when energy is needed, more important for animals as more active
insoluble so won't affect water potential, no water draws into cell
compact
cellulose structure
beta glucose, straight chains (1,4) with H-bonds linking adjacent chains forming microfibrils
cellulose function
structure in plants - provide support and rigidity
cellulose - how structure fits function
-long straight chains, and cross-linked hydrogen bonds add strength
-grouped to form microfibrils which then forms fibres to add strength
-cell walls need to be strong so that leaves are held in a position to absorb max sunlight and stems need to withstand wind etc
chitin
A structural polysaccharide, beta (1,4) with straight chains and H-bonds found in many fungal cell walls and in the exoskeletons of all arthropods.
test for reducing sugars
add 2cm³ of food sample to a test tube
add an equal volume of Benedict's Reagent
heat the mixture in a gently boiling test tube for 5 mins
brick red is a positive result - insoluble red precipitate of copper(1) oxide
test for non-reducing sugars
heat with Benedict's
if negative (stays blue), hydrolyse substance with HCl into constituent monosaccharides and neutralise with sodium hydrogencarbonate
repeat original test with same outcome if positive
test for starch
2cm^3 of iodine solution
shake or stir
blue black colouration
structure of triglycerides
3 fatty acids and one glycerol molecule
structure of phospholipids
2 fatty acids, one glycerol molecule and a phosphate group
reaction to form triglycerides
condensation reaction, where carboxyl group of fatty acid reacts
what bond is formed in triglycerides
an ester bond and 3 water molecule is removed
what is saturated
no double bonds, usually solid at room temp, animals
what is unsaturated
at least one double bond, usually liquid at room temp, found in plants
what do fatty acids contain
hydrocarbon with a methyl group and carboxyl group
are fatty acids hydrophobic
yes, they’re the ‘tail’ and are uncharged so don’t interact with water
are phosphate groups hydrophobic
no, they’re hydrophilic because they have a negative charge and so form hydrogen bonds with water
emulsion test
-sample should be ground and in liquid form
-add 2cm³ of ethanol and shake
-add 2cm³ of deionised water
-gives a milky white emulsion
are lipids soluble in water
no
triglycerides have a higher ratio of energy storing C-H bonds to C atoms so
good source of energy
triglycerides have a low mass to energy ratio so
good storage molecule
triglycerides are large and nonpolar meaning they’re insoluble in water so
storage doesn’t affect osmosis of water potential in cells
triglycerides have a high ratio of H to O so
release water when oxidised so important source of water
phospholipids are polar molecules so
form a bilayer within membranes,which is hydrophobic as
what do phospholipid heads help
hold well at surface of cell membranes
phospholipid structure allows formation of glycolipids by combinging with carbs at cell membrane which is
important for cell recognition
what are the monomers of proteins
amino acids
structure of amino acid
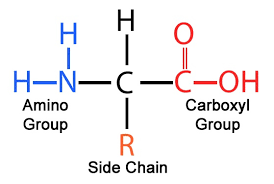
what replaces the r group
one of the 20 amino acids that differ
what does a condensation reaction of amino acid form
a dipeptide or polypeptide with peptide bond(s)
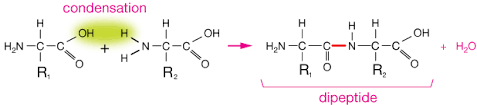
what type of compound are proteins
amphoteric
buiret test
add a little sodium hydroxide to clear solution and make alkaline
add some copper (II) sulfate solution
turns purple if present (stays blue if not)
primary structure for proteins
the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
secondary structure for proteins
3 dimensional folding arrangement of primary into coils or pleats held by H bonds
structure of alpha helix and beta pleaated sheet
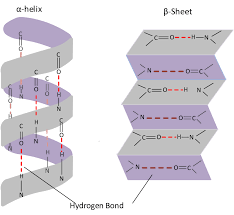
what do groups in amino acids posess and why easy to H bond
NH has a positive charge and C=0 has a negative charge, readily forms weak H bonds which causes twists
tertiary structure for proteins
supercoiling of a helix to give 3D shape or ‘conformation’of protein due to bonding between R groups on chain
different types of bonds on tertiary structure
disulphide bridges - strong and form between sulhur atoms in cysteine amino acids
hydrogen bonds - numerous but easily broken
ionic bonds - formed between carboxyl + amino not involved in forming peptide bonds, weaker than D, easily broken by changes in pH
quaternary structure for proteins
the way polypeptide chains are assembled together
example of protein with quaternary structure
haemoglobin - has 4 polypeptide chains, each containing an iron containing HAEM group that binds to molecules of oxygen
fibrous protein
structural, insoluble, eg keratin, collagen - 3 polypeptide chains twisted like a rope
globular proteins
specific 3D shape, soluble, eg enzymes
why are globular proteins soluble
at tertiary structure level hydrophobic amino acids are bound in the interior of molecule and hydrophilic amino acids are bound towards exterior