Lecture 4: Models
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
model
-simplified or idealised representation of a more complex thing
statistical models
-description of mathematical relationship between variables, that hold under specific assumptions
-doesn’t attempt to explain anything → just describing relationship
theoretical models
-description of the relationship between different mental processes
-makes assumptions about the nature of these processes
-attempts to explain and provide further predictions
behaviourism
-suggested mind is like a black box → don’t know what is happening inside and we shouldn’t investigate it
-only care about how input changes output behaviour
cognitive psychology
-mind is like a black box
-if change inputs in a certain way and record outputs in a certain way can maybe make conclusions about processes inside black box
-enough experiments can understand what is happening in black box
box-and-arrow models
-models that describe the relationship between different mental processes, under the assumption that the mind operates like multi-staged information-processing machine
-not saying this is how cognitive processes works → just a simplified version that captures key elements the researcher wants to emphasise
-can add more boxes and arrows developing on previous models
cognitive models
-manipulating the input and observing the output can provide a glimpse to the machination of the mind and allow us to test our models
-can expand and change models based on results
formal cognitive models
-a mathematical description of the relationship between two variables
-usually expressed through computer code
-black box seen as working in same way as computers
simplification
-making something simpler
-don’t need to capture every small detail of a cognitive process
-only capturing parts we deem critical of what we are trying to represent
abstraction
-generating general rules and concepts from specific information
-depends on question you are asking and what you are trying to convey
-making the model useful for goals
prediction and/or explanation
-models in science must produce some predictions
-predictions can be directional or numerical
-non-scientific theories explain after the fact but cannot provide falsifiable predictions
directional predictions
-give direction of what you think will happen
-no quantifiable amount specified - just direction
numerical predictions
-giving specific value with specific prediction
-can be more or less accurate
using models to predict and explain
data
hypothesis
model
theory
framework
data (using models to predict and explain)
-collected observations, often as part of an experiment
hypothesis (using models to predict and explain)
-narrow testable statement
model (using models to predict and explain)
-schematic representation of a theory
-more limited in scope
theory (using models to predict and explain)
-scientific proposition that provides relations between phenomena
framework (using models to predict and explain)
-conceptual system that defines terms and provides context
explanation without prediction
-models of schizophrenia can indicate causes but cannot predict individual cases
-model predicts group differences but not individual cases
-consistent with theoretical models
prediction without explanation
prediction error model
-some models can predict whether an individual will develop AD, even though we don’t understand the factors that explain AD
-may predict average directional differences between conditions
-prediction ignorant to components - do not know what variables mean and just observe correlation → consistent with statistical models
informal cognitive models
-verbal description of the relationship between different cognitive procedure
assumptions are implicit
provides directional predictions
formal/computational models
-mathematical description of the relationship between different cognitive procedure, often instantiated via computer program/simulation
assumptions are explicit
provides numerical predictions
using formal models to explain
data point
hypothesis
implementation → specific instantiation of a specification → computer program able to simulate and predict numerical outputs from input
specification → formal description of the relations described by a theory → formal model comprised of symbolic representations
theory
framework
more accurate predictions (strengths of formal models)
-having a numerical simulation allows us to see if the model provides unreasonable predictions
-help us select which experiments to perform
-numerical predictions provide a more subtle form of hypothesis testing → can see how close a model is to predicting an actual result
counter-intuitive predictions (strengths of formal models)
-model can clearly describe which predictions follow from a model
-with informal models, it’s hard to notice when they make counter-intuitive predictions → formal models clearly produce such predictions
-numbers do not always match intuition (informal models) and intuition can go awry → formal models can show intuitions don’t match theory in an objective way due to theory being counter-intuitive
benefits of explicit assumptions (strengths of formal models)
-by making assumptions explicit, can reveal unanswered questions, flaws in our reasoning, contradictory or unreasonable assumptions
-can make assumptions transparent for others to see
limits of formal models
-require substantial expertise
-only transparent for experts who can understand them
-only comparable against other computational models
-sometimes numerical predictions are premature
-changing the model is costly time-wise and can limit progress
-making a model simulate a cognitive task does not necessarily teach us much about cognition
hype timeline
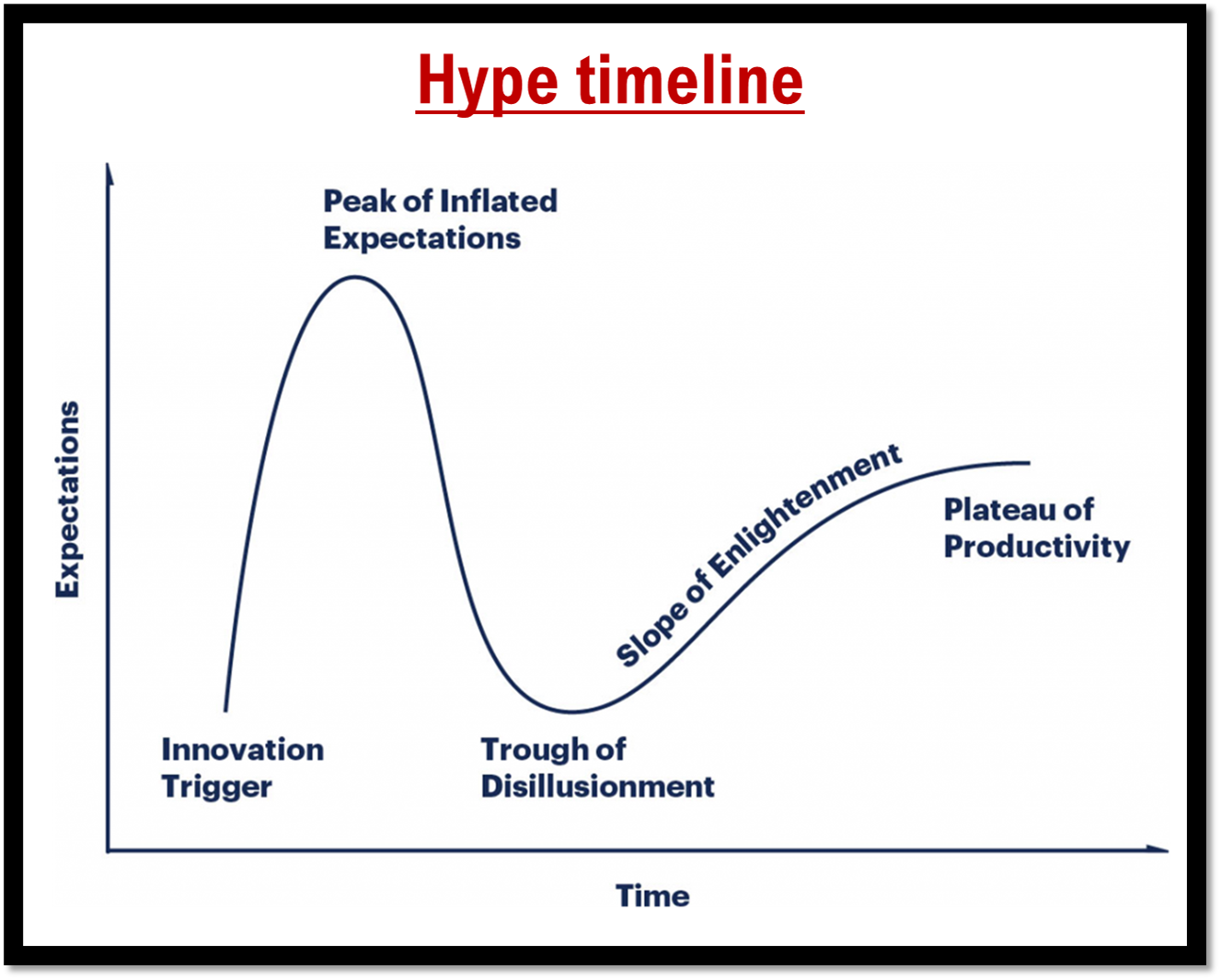
-lot of hype surrounding new tools
-but once they are understood better they reach a plateau of productivity
David Marr
-suggested we can understand and model a system at a number of levels
-pointed to three levels of understanding:
computation → problem being solved
algorithm → steps/rules to solve it
implementation → actual machinery
-suggested that something is more easily understood from its function rather than a single data point or the mechanisms (hardware) in which a function is embodied (top-down approach)
bottom-up approach (neuroscience & Marr)
implementation → machinery of neural circuits
rules → what representations and algorithms can we generate, given specific neural circuits?
problem → what problems are solved by these algorithms?
top-down approach (neuroscience & Marr)
problem → what is the problem we’re trying to solve
rules → what representations and algorithms can solve this problem?
implementation → how can these representations and algorithms be implemented in neural circuits?
-much easier to disqualify bad explanations
-but not practical so bottom-up approach is more common
theory and implementation
-researchers can:
focus on implementation without theory
focus on theory without implementation
approach problem assuming all levels (problem, rules and implementation) inform one another