Balfe Unit 2 Summative Test
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What was the Middle Passage?
The voyage across the Atlantic, it was the second leg in the triangular trading routes that linked Europe, Africa, and America.
What was the Atlantic Slave Trade?
It was a business where European merchants, African traders, and American planters traded slaves. It used the Middle Passage to trade humans.
How did slavery differ in the Deep South compared to the Middle Colonies and New England?
Slavery in the Deep South was more brutal and plantation-based, while the Middle Colonies and New England had smaller-scale slavery and more diverse economies.
What are some cultural impacts of slavery on American society?
Music, cuisine, language, and social structures in American culture were influenced because of this.
What was the Stono Rebellion?
A significant slave uprising in 1739 in South Carolina, where enslaved people marched for freedom, killing colonists on the way.
What role did Enlightenment thinking play in American history?
It inspired ideas of natural rights, democracy, and reason, which shaped the Revolution, the Declaration of Independence, and the U.S. Constitution. It encouraged a government based on liberty, equality, and the consent of the governed.
What was the Great Awakening?
A religious revival in the 18th century that
encouraged people to have a personal connection with God rather than rely only on church authority. It led to new churches, greater religious freedom, and ideas about equality and individual rights.
What was the significance of the French and Indian War?
This war ended French power in North America and gave Britain control of more territory, but it also left Britain in heavy debt, leading to new taxes on the American colonies. These taxes and tensions eventually helped cause the American Revolution.
What was the Proclamation of 1763?
A law issued by Britain after the French and Indian War that forbade colonists from settling west of the Appalachian Mountains. Meant to avoid conflicts with Native Americans, but many colonists were angered because they wanted to expand into that land, increasing tensions with Britain.
What were the Committees of Correspondence?
Groups organized by American colonists in the 1770s to share news and coordinate responses to British policies. They helped the colonies communicate, unite, and organize resistance leading up to the American Revolution.
How did the Sons of Liberty influence the independence movement?
By organizing protests, boycotts, and acts of resistance against British taxes and laws, like the Stamp Act. Their actions, including the Boston Tea Party, helped unite the colonies and build support for independence from Britain.
What was the impact of the Boston Massacre?
Increased tension and anger between the colonists and Britain after British soldiers killed several unarmed colonists during a protest in 1770. It was used as patriot propaganda to show British cruelty and helped unite the colonies against British rule.
What was the significance of the Boston Tea Party?
It was a major act of protest against British taxes, where colonists dumped tea into Boston Harbor to oppose the Tea Act. It showed the colonists' willingness to take bold action and led Britain to pass the Intolerable Acts, which further united the colonies toward independence.
Why was 'Common Sense' successful?
Thomas Paine wrote it in clear, simple language that ordinary colonists could understand, and it powerfully argued for independence from Britain. It inspired many Americans to support breaking away from British rule and helped build momentum for the Revolutionary War.
What was the importance of the Battle of Saratoga?
The Battle of Saratoga was a turning point in the Revolutionary War, leading to French support for the American cause.
What does it mean to be a Republic?
A Republic is a form of government in which representatives are elected to make decisions on behalf of the citizens.
What was the role of religious freedom in the Revolution?
Religious freedom was a key issue that motivated many colonists to seek independence and establish a government respecting diverse beliefs.
What is Free Trade Economics?
Free Trade Economics advocates for minimal government intervention in trade, promoting open markets and competition.
What is 'Republican Motherhood'?
Republican Motherhood is the idea that women have a role in shaping the morals and values of future citizens.
Who was James Oglethorpe?
James Oglethorpe was the founder of the Georgia colony and an advocate for social reform and the humane treatment of prisoners.
What did the Stamp Act do?
The Stamp Act made it so that colonists had to buy specific paper (stamped) for things like legal documents, playing cards, newspapers, etc. It made colonists upset because they thought Parliament shouldn’t tax them and it should be their own assemblies. There were protests against this fighting for the ability to have independence in their taxes and government.
What were the Townshend Acts?
The Townshend Acts were a series of laws that taxed goods imported to the American colonies, escalating tensions with Britain.
The Townshend Acts added taxes to important goods like glass, tea, paper, etc. The taxes paid the British officials. There were protests and it made people want independence in their government even more.
What were the Coercive (Intolerable) Acts?
The Coercive Acts were a sort of punishment to Massachusetts. The Boston Harbor was closed, town meetings were limited, and officials that were accused of something were able to go to Britain to be tried. It seemed like colonists freedom was being attacked. After this, the First Continental Congress was united and the colonies collectively turned against the British.
Who was James Oglethorpe?
A British general and founder of the colony of Georgia.
What is John Locke known for?
His philosophy on natural rights and government, influencing Enlightenment thought.
Who was John Peter Zenger?
A printer and journalist whose trial established the principle of freedom of the press.
What contributions did Benjamin Franklin make?
He was a Founding Father, inventor, and diplomat, known for his role in the American Enlightenment.
Who was Jonathan Edwards?
A preacher known for his role in the First Great Awakening and his sermon 'Sinners in the Hands of an Angry God.'
What role did Pontiac play in American history?
He was an Ottawa chief who led a rebellion against British rule in 1763.
What is Thomas Paine famous for?
His pamphlet 'Common Sense,' which advocated for American independence from Britain.
Who was George Washington?
The first President of the United States and a key leader during the American Revolutionary War.
What was Marquis de Lafayette's contribution?
A French general who played a significant role in the American Revolutionary War, supporting the colonists.
Who was Abigail Adams?
John Adams wife, wrote him a famous letter saying to "remember the ladies" when creating new laws for the United States. She asked him to consider women's rights and protect them from unfair treatment as the country gained independence.
Stamp Act
A 1765 law that imposed a direct tax on printed materials in the American colonies, requiring them to use specially stamped paper.
Townshend Acts
A series of laws passed in 1767 that imposed duties on imported goods such as tea, glass, and paper, leading to widespread protest in the colonies.
Coercive Acts
A series of punitive measures enacted in 1774 in response to the Boston Tea Party, aimed at suppressing colonial resistance and enforcing British authority.
Boston Tea Party
A 1773 protest against British taxation where colonists dumped tea into Boston Harbor as a demonstration against the Tea Act.
Sons of Liberty
A secret organization formed in the colonies to oppose British policies and taxes, known for organizing protests and acts of civil disobedience.
Declaratory Act
The Declaratory Act (1766) declared that Parliament could, in any case, make laws such as the ability to tax them. It made it clear that Britain still had control over the colonies, they thought they had no voice in the government. Came after the Stamp Act.
Tea Act
A 1773 act that granted the British East India Company the right to sell tea directly to the colonies, undermining local merchants and leading to the Boston Tea Party.
First Continental Congress
A gathering of colonial delegates in 1774 to organize resistance against the Coercive Acts and to assert colonial rights.
Boston Massacre
A confrontation in 1770 where British soldiers killed five colonists, escalating tensions between Britain and the American colonies.
Quartering Act
A law requiring colonial governments to provide housing and supplies to British troops stationed in America, contributing to colonial resentment.
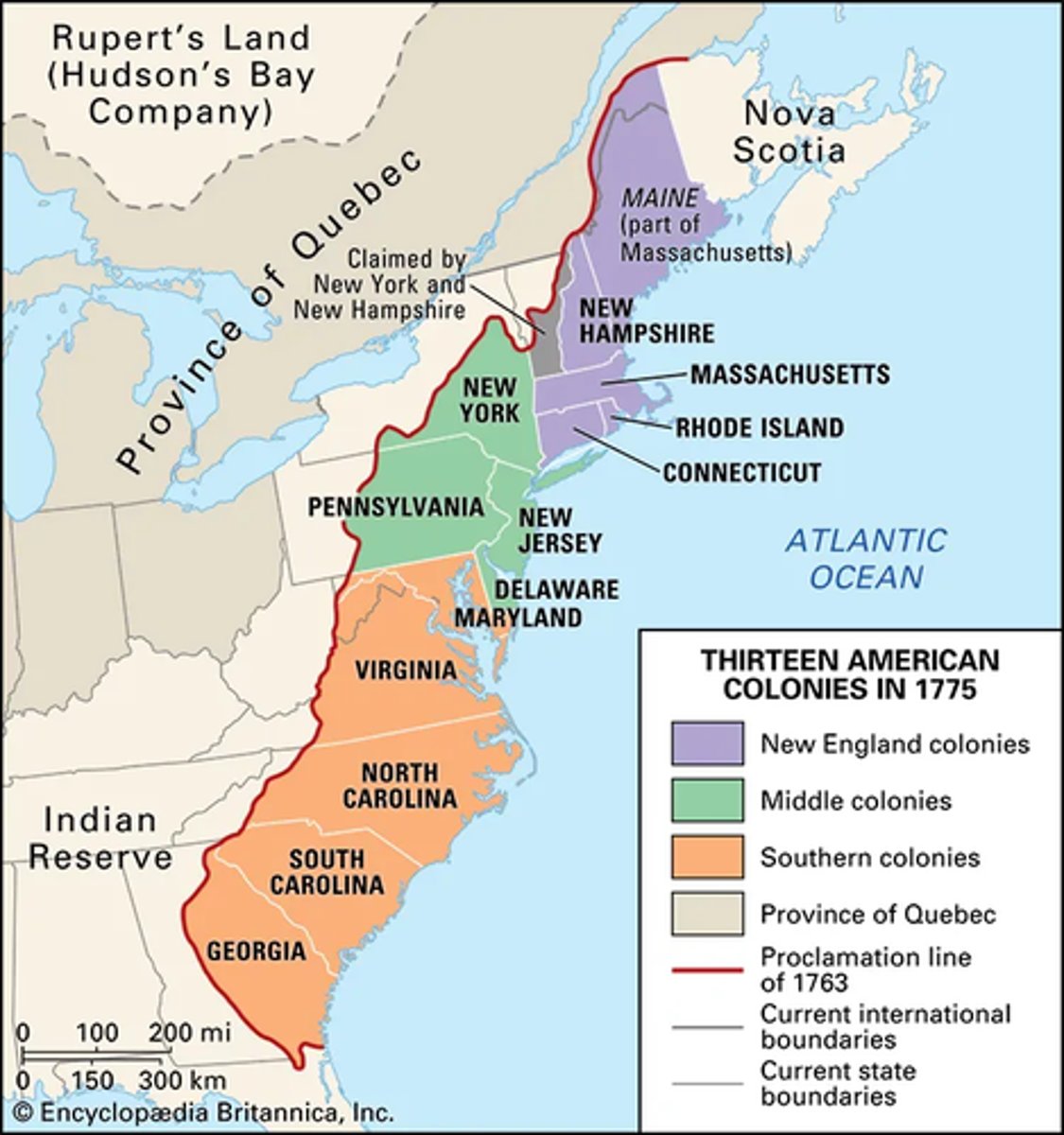
List the states from the bottom to top
Georgia, South Carolina, North Carolina, Virginia, Maryland, Delaware, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Connecticut, Rhode Island, New York, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Maine (GSNVMDnjPCrinyMnhM)
Be able to talk about some of the big ideas from your "Three Simple Rules for Winning a Revolution" assignment. Be able to explain a bit about how America won the Revolution.
....
Be able to talk about groups that either gained or lost liberty following the Revolution (Women, African Americans, Loyalists, The Poor, Religious Groups)
.....
Republicanism
"your needs aren't as important as the needs of the entire group"
Liberalism
Focused on individual needs