Alcohols
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What functional group do alcohols contain?
-OH
Alcohol
A homologous series with the functional group OH, and general formula CnH2n+1OH.
What is the suffix for alcohols? Give an example.
-ol
Ethanol
What is the general formula for alcohols?

Mnemonic for order of alcohols
Monkeys eat peeled bananas
molecular formula of methanol
CH4O

structural formula of methanol
CH3OH
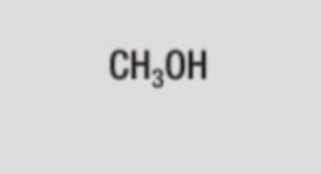
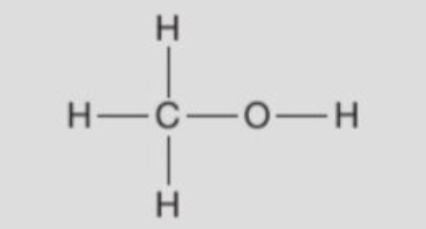
displayed formula of methanol
molecular formula of ethanol
C2H6O

structural formula of ethanol
CH3CH2OH
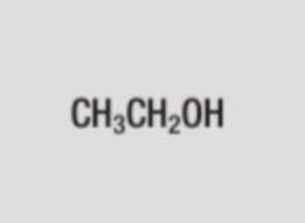
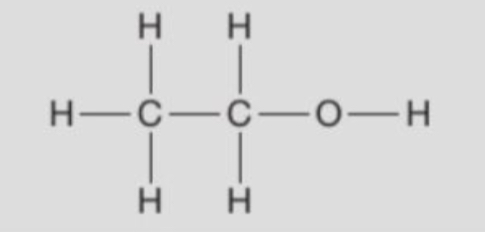
displayed formula of ethanol
molecular formula of propan-1-ol (propanol)
C3H8O
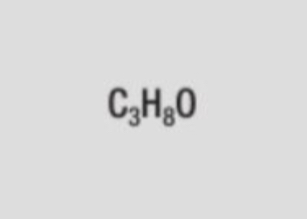
structural formula of propan-1-ol (propanol)
CH3CH2CH2OH
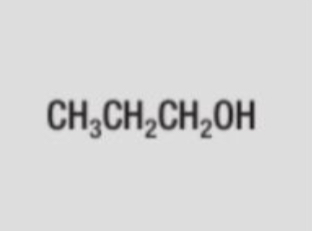
displayed formula of propan-1-ol (propanol)
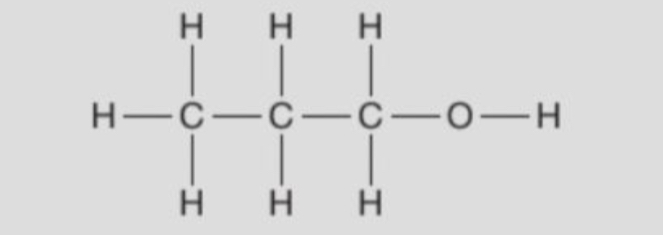
molecular formula of butan-1-ol (butanol)
C4H10O
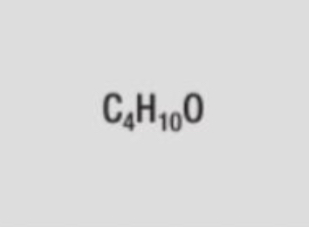
structural formula of butan-1-ol (butanol)
CH3CH2CH2CH2OH

displayed formula of butan-1-ol (butanol)

Isomer
Molecules with the same molecular formula but different structure.
Characteristics of a homologous series (alcohols)
Same general formula
Same functional group
Consecutive members differ by CH2 (alcohols structural formula)
Similar chemical properties
Physical properties vary in a predictable way
Is the functional group of an alcohol OH- or -OH
-OH
functional group is not a hydroxide
Methods of manufacturing ethanol
Fermentation of glucose
Hydration of ethene
Fermentation of glucose
in the absence of air, at an optimum temp of ~30 degrees Celsius and using the enzymes in yeast
Hydration of ethene
reacting ethene with steam in the presence of a phosphoric acid catalyst at a temperature of about 300 degrees Celsius and a pressure of about 60-70 atm
What’s the mnemonic to remember what you need to mention for each method of manufacturing ethanol?
Red monkeys Create Ethanol Perfectly Swiftly
Raw materials Conditions Equation Purification Speed
What conditions affect rate of fermentation
Yeast enzyme catalyst
25–35 degrees Celsius temperature
Glucose used in anaerobic respiration
Raw materials of Fermentation
Yeast (containing zymase enzymes, which acts as a catalyst for the reaction)
Sugar solution
Conditions for fermentation
Anaerobic conditions (otherwise ethanol c acid forms)
25-35 degrees Celsius
Equation for fermentation
Glucose —> ethanol + carbon dioxide
C6H12O6 —> 2C2H5OH (or 2C2H6O) + 2CO2
Purification for fermentation
Distillation: impure ethanol is formed
Speed of fermentation
Slow
What type of reaction is fermentation?
Exothermic because fermentation involves yeast respiration which releases energy.
Raw materials for the hydration of ethene
Crude oil (containing ethene and water)
Conditions for hydration of ethene
60 - 70 atm (atmospheric pressure)
300 degrees Celsius
Concentrated phosphoric acid (H3PO4)
Equation for the hydration of ethene
ethene + water —> ethanol
C2H4 + H2O —> C2H5OH (or C2H6O)
Purification of hydration of ethene
No need. Trick question.
Speed of hydration of ethene
Fast
Alcohols burn in oxygen to make…
Alcohol + oxygen —>
Alcohol + Oxygen —> Carbon dioxide + water