glial cells
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
microglia (4)
resident macrophages/immune cell of brain
tile whole brain + spinal cord
of myeloid origin → migrate to CNS from yoke sac at embryonic day 10
can extend processes + phagocytose w/o moving their processes
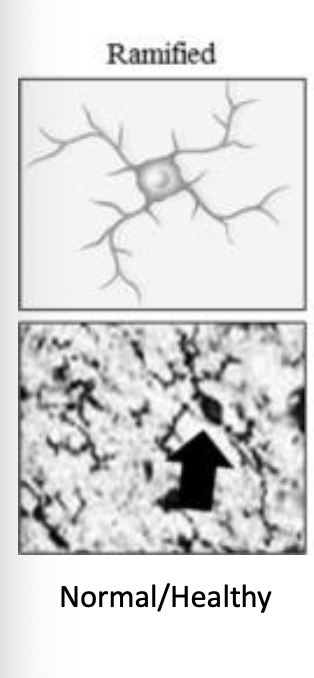
ramified, “resting state of microglia (2)
constantly surveying tissue for damaged cells, plaques, infectious agents
used for sensing tissue + they do not move their somata/migrate
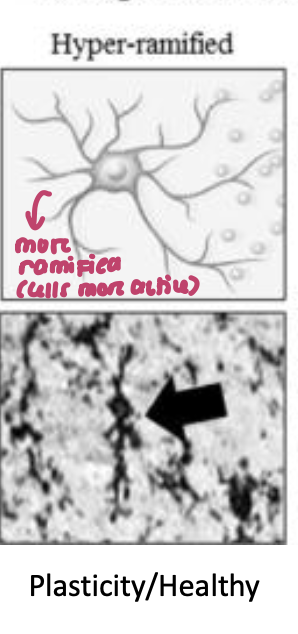
microglia motility ____ in response to neural activity
increases
can become more permanently hyper-ramified after plasticity (more active)
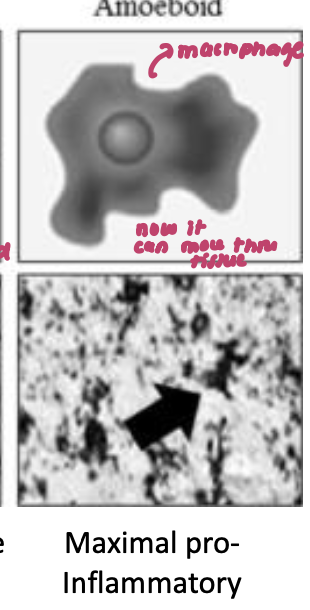
microglia amoeboid state
microglia retreat when need to move large distances of persistent problems in tissue (max pro-inflammatory)
microglia are activated by (5)
glutamate
K+
ATP
pro-inflammatory cytokines
LPS → cell wall component of gram-negative bacteria
microglia secrete pro-inflammatory signals once activated like: (3)
IL1-alpha
IL1-beta
TNF-alpha
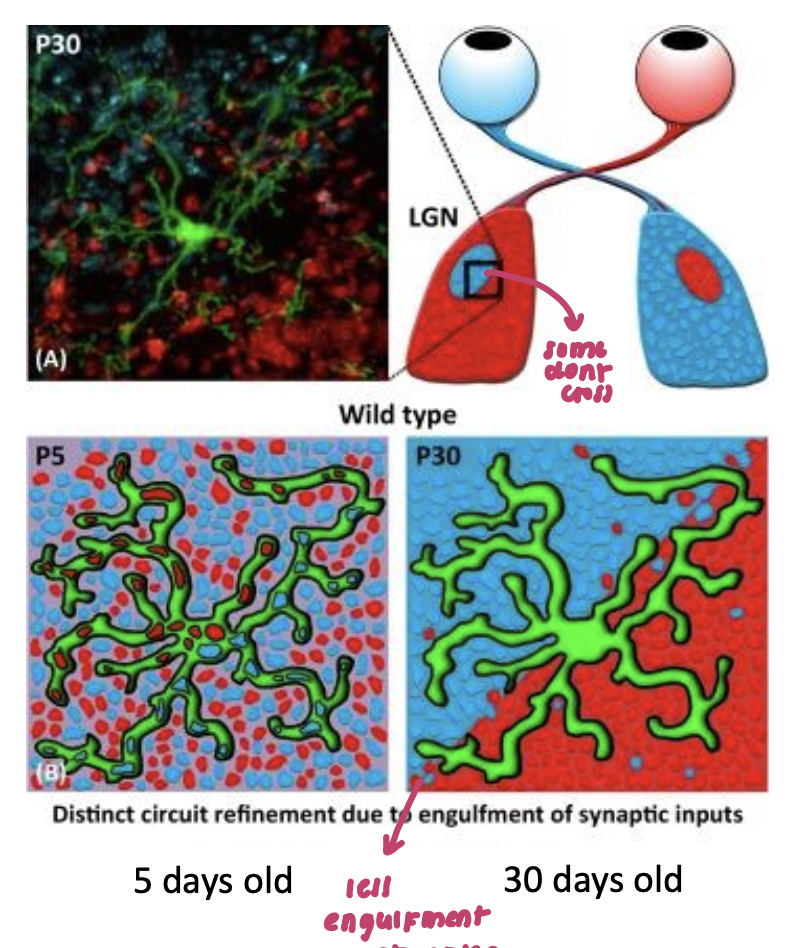
synapse elimination experiment (2)
Evidence that microglia are involved in synaptic pruning/elimination, as one can find both blue and red neural projections inside the microglia
Blue and red are retinal ganglion cells projecting to the thalamus (LGN)
the complement cascade (2)
series of proteins that are part of the innate immune system that attack a cell’s membrane
helps antibodies + phagocytes eliminate damaged cells/microbes
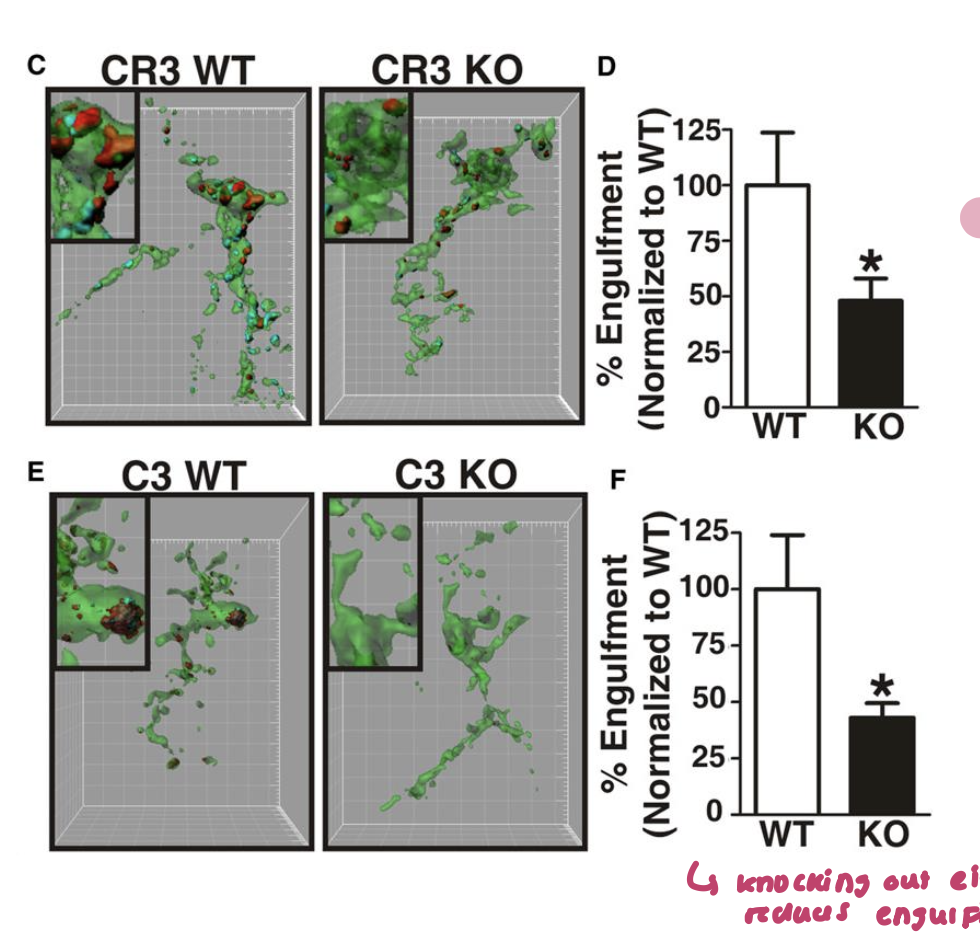
what complement cascade do synapses express (3)
complement 3 (C3)
Microglia express the C3 receptor (C3R)
knocking either out impairs synapse engulfment
oligodendrocytes (3)
provides myelin, metabolic + trophic support (GDNF + BDNF) for neurons/axons
processes form myelin segment that wraps around an axon
single cell provides myelination for multiple axons
helps speed action potential propagation by focusing event on Nodes of Ranvier
150m/s vs 0.5-10m/s unmyelinated
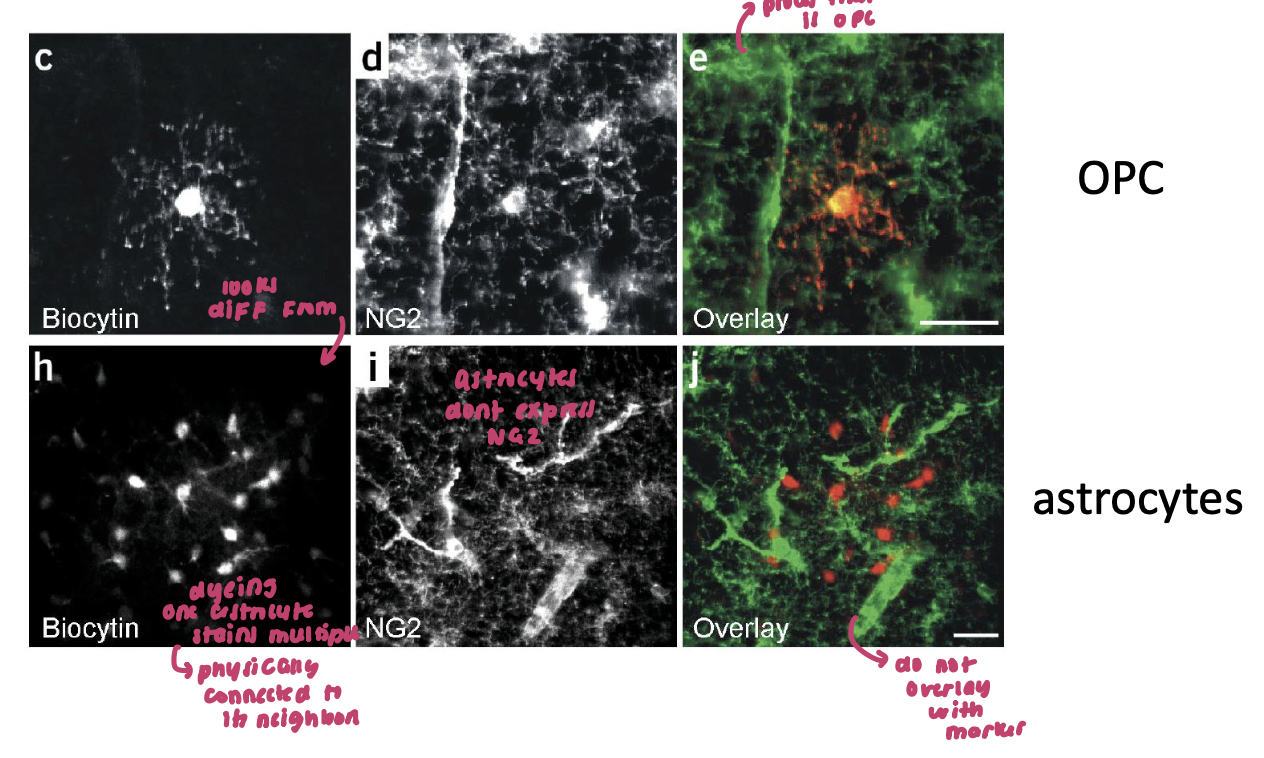
oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (3)
~4 % of the cells in the gray matter
express the proteoglycan NG2 marker → way to differentiate
precursor cell that can differentiate into mature, myelinating oligodendrocyte
don’t HAVE to differentiate
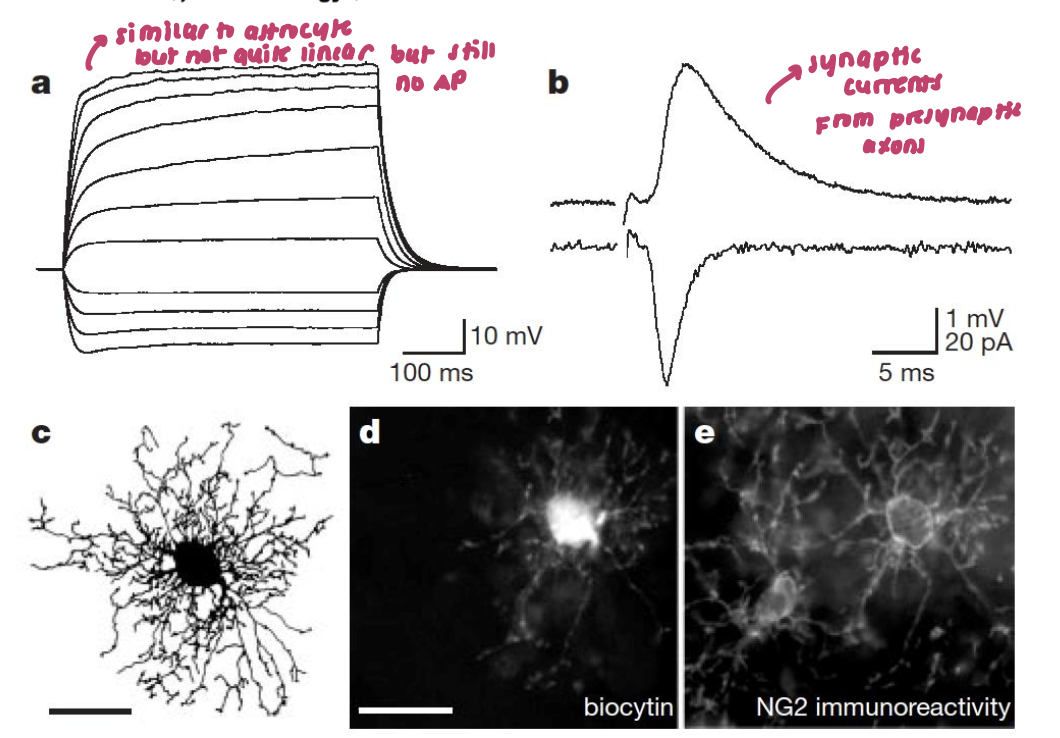
only glia to receive direct synaptic contact from neurons
oligodendrocytes:
do not fire APs but receive inhibitory/excitatory synaptic transmission
what happens if an OPC develops into mature oligodendrocyte
a neighbouring OPC will divide + replace it → keeping their numbers constant
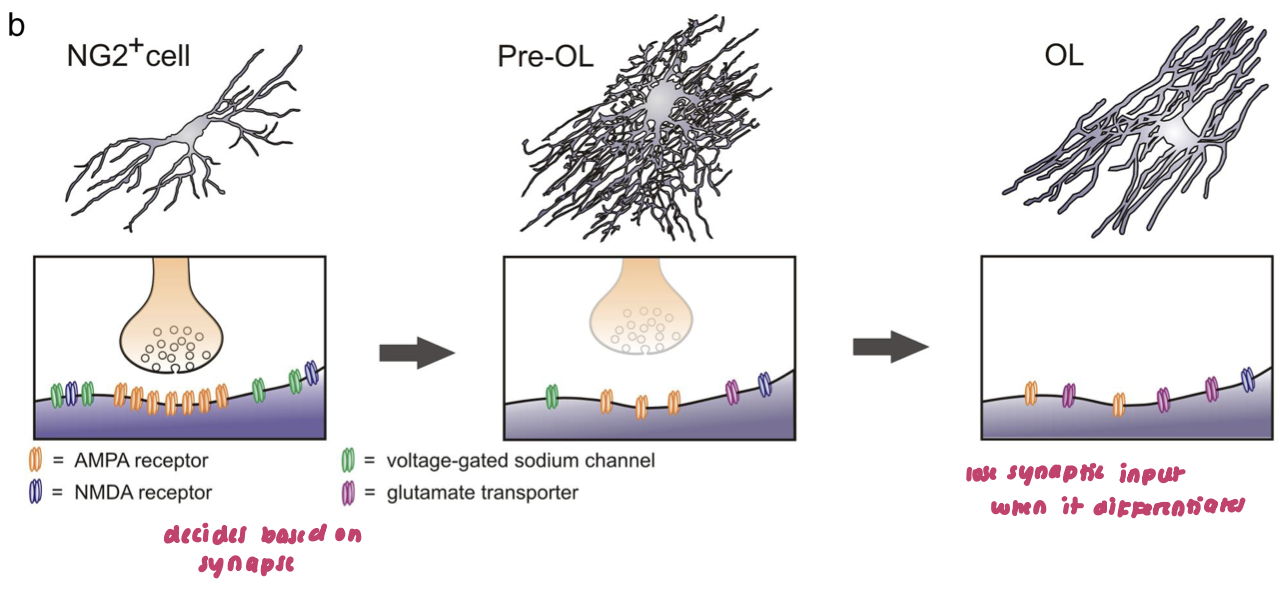
glutamatergic synapses on oligodendrocyte precursor cells in the hippocampus (OPCs)
OPCs receive synaptic inputs to sense neural activity to determine if they need to differentiate into a mature oligodendrocyte and myelinate axons
no AP
OPC to OL differentiation model (2)
As an OPC (or NG2 cell) differentiates to become a mature Oligodendrocyte, they lose their synaptic contacts and lose their ionotropic glutamate receptors.
disruption of process impairs memory consolidation