Dental X-Ray Image Characteristics: Density, Contrast, Sharpness, and Distortion
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Dental X-Ray Image
A dental image appears as a black and white image or picture with varying shades of gray.
Radiolucent
The portion of the processed image that is dark or black; a structure that appears black on film lacks density.
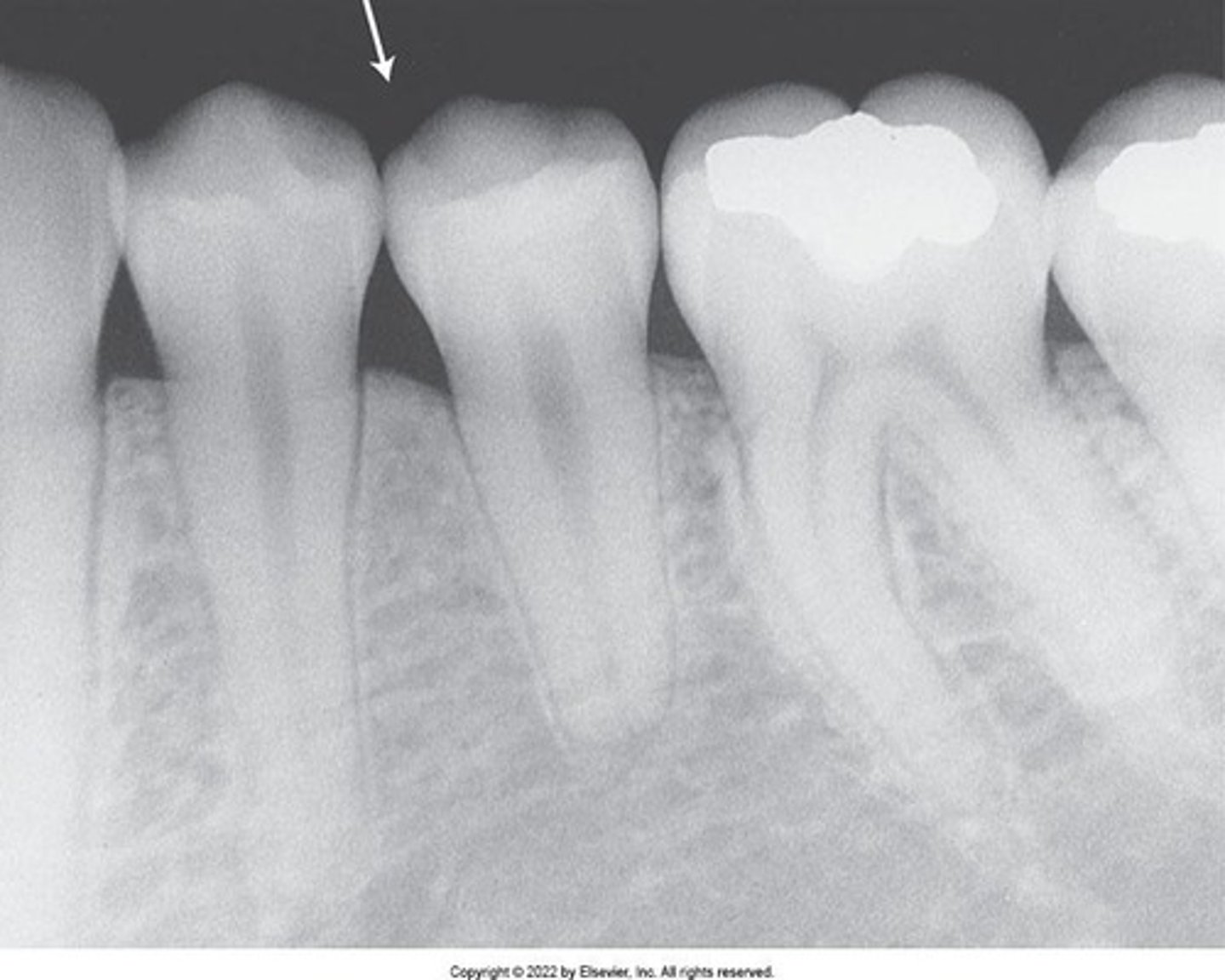
Radiopaque
The portion of the processed image that appears white; a structure that appears white on film is dense and absorbs or resists passage of the x-ray beam.
Diagnostic Image Characteristics
In a diagnostic image, the images have proper density and contrast, have sharp outlines, and are of the same shape and size as the object radiographed.
Visual Characteristics
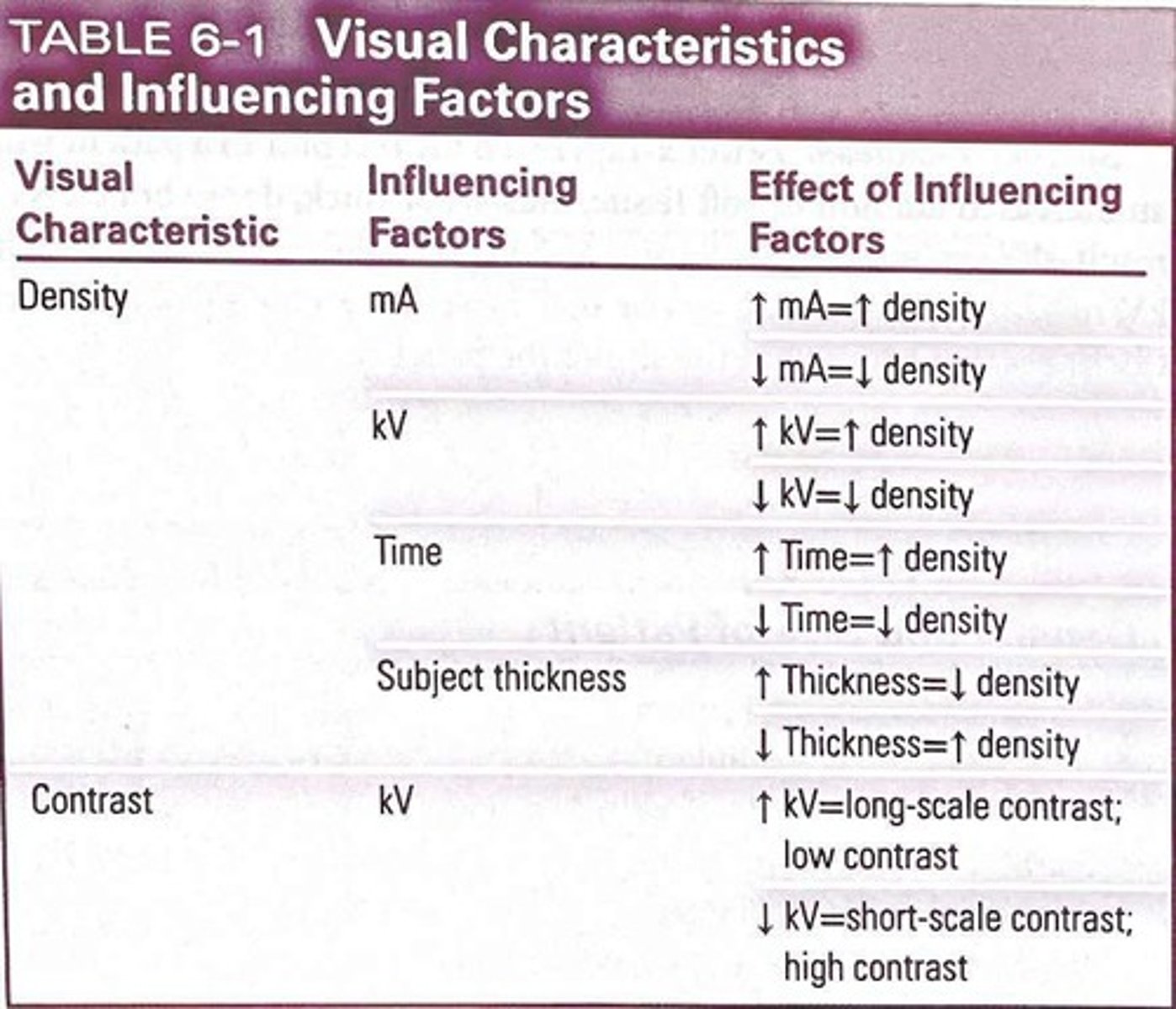
Density and contrast are the two visual characteristics that influence the quality of a dental image.
Density
The overall darkness or blackness of a dental image; the relative transparency depends on distribution of black silver particles in the emulsion.
Influencing factors of Density
Kilovoltage, milliamperage, exposure time, subject thickness.
Contrast
Contrast is the difference in degrees of blackness between adjacent areas.
Preferred Film Contrast
A film that is a compromise between low contrast and high contrast is preferred.
Influencing factors of Contrast
Increasing the kilovoltage affects image contrast by increasing the mean or average energy of the x-rays and by producing higher energy x-rays.
High Contrast
A dental image that does not have very dark and very light areas but instead has many shades of gray.
Low Contrast
A dental image that has very dark areas and very light areas.
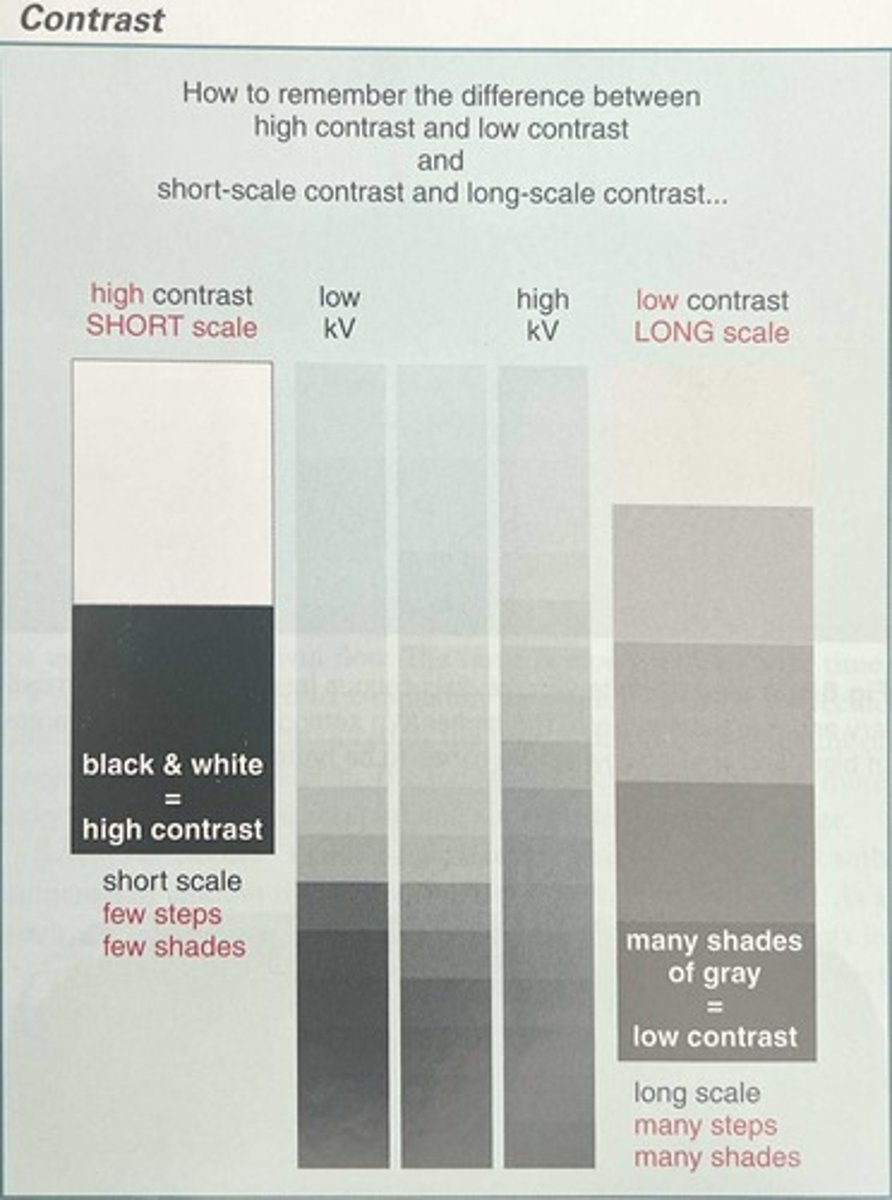
Scales of Contrast
The range of useful densities.
Short-scale Contrast
An image with only two densities, black and white; occurs with machines functioning at low kVp.
Long-scale Contrast
An image with many densities, many shades of gray; occurs with machines functioning at high kVp.
Aluminum Stepwedge
An aluminum stepwedge can demonstrate short-scale and long-scale contrast; it consists of uniform layered thicknesses of an x-ray absorbing material.
Sharpness
Sharpness is the capability of the x-ray receptor to reproduce the distinct outlines of an object.
Penumbra
A certain lack of image sharpness is present in every image.
Influencing factors of Sharpness
Focal spot size, film composition, movement.
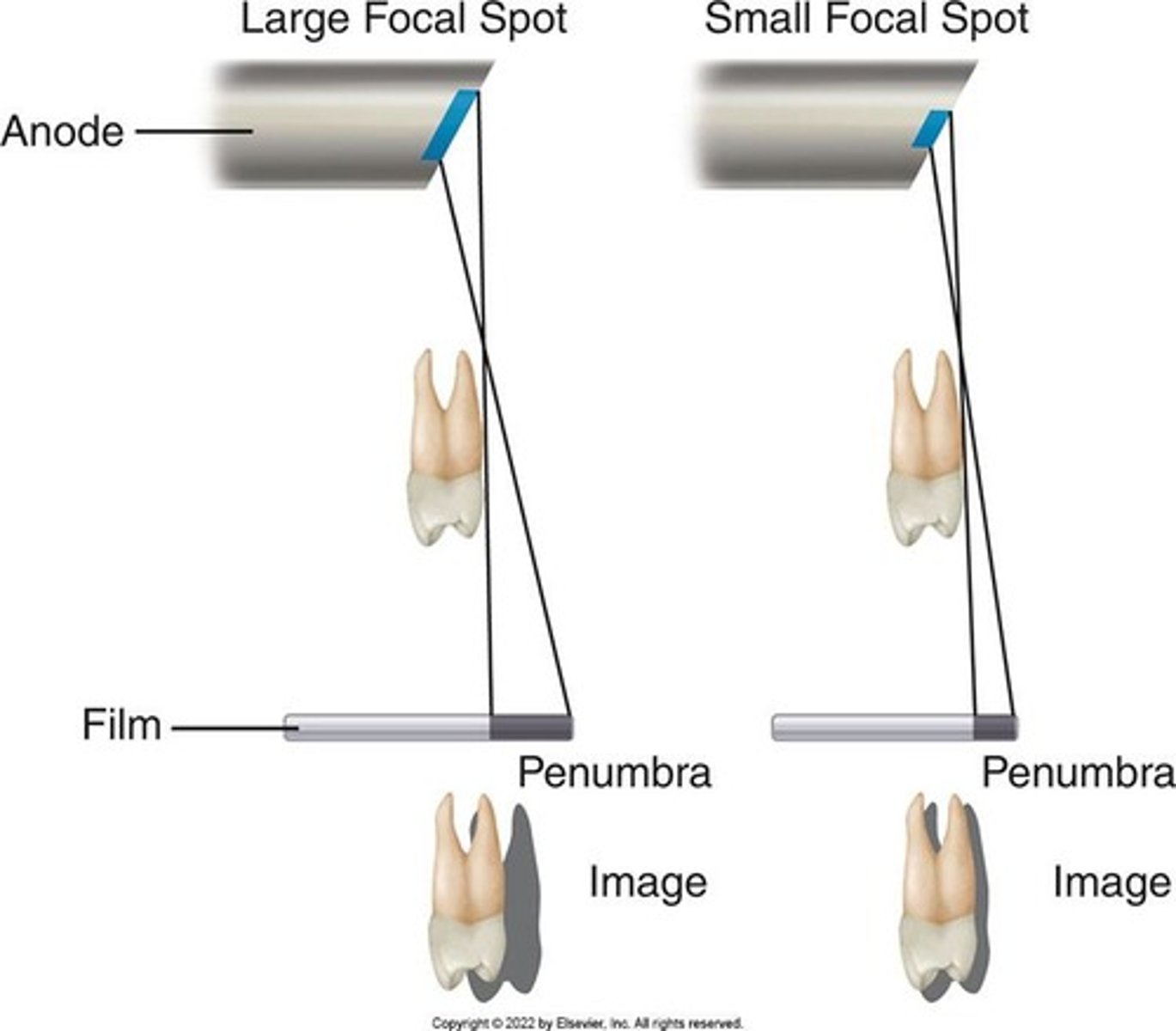
Magnification
Results from the divergent paths of the x-ray beam as they radiate from the focal spot.
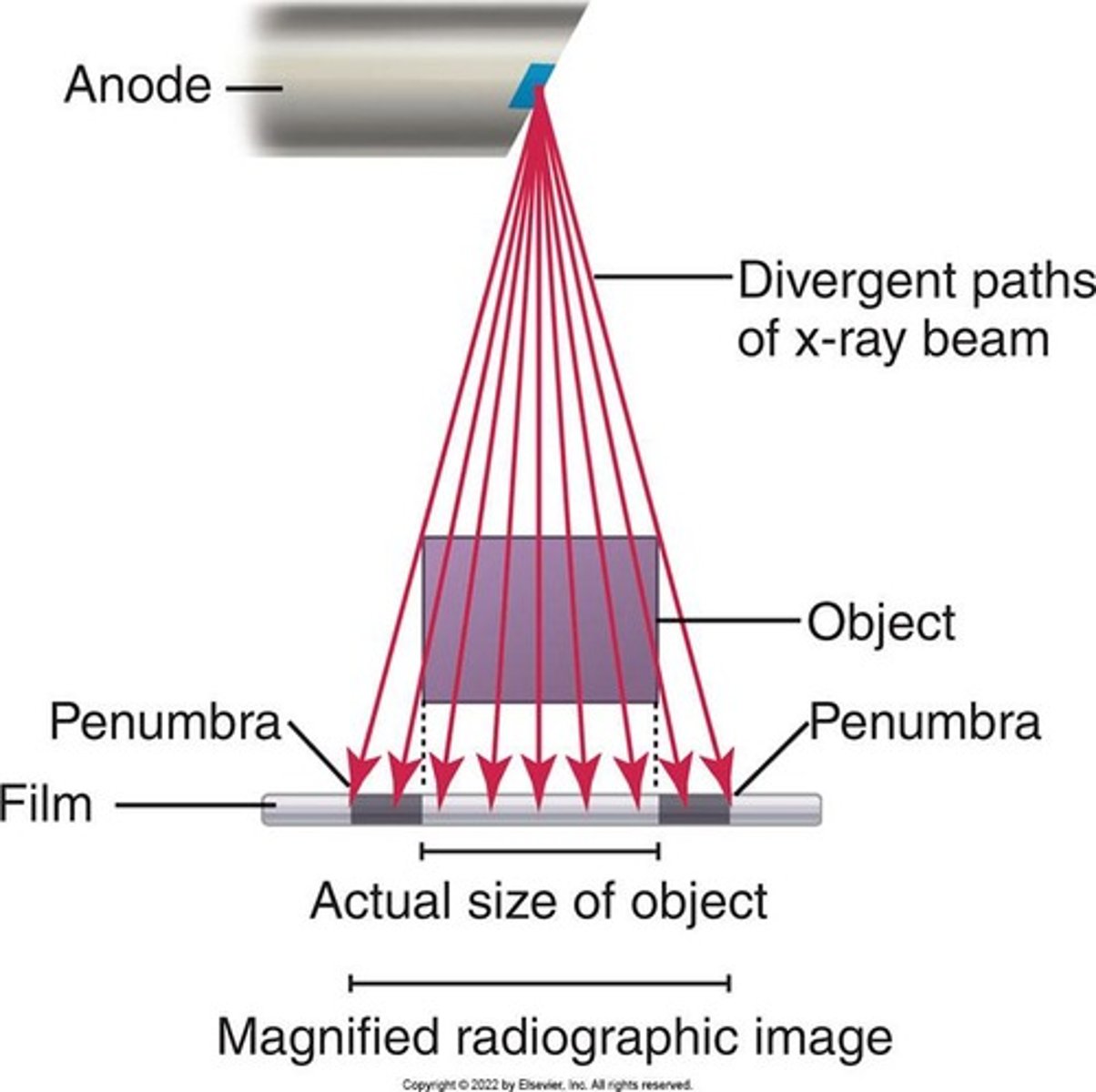
Influencing factors of Magnification
Target-receptor distance and object-receptor distance.
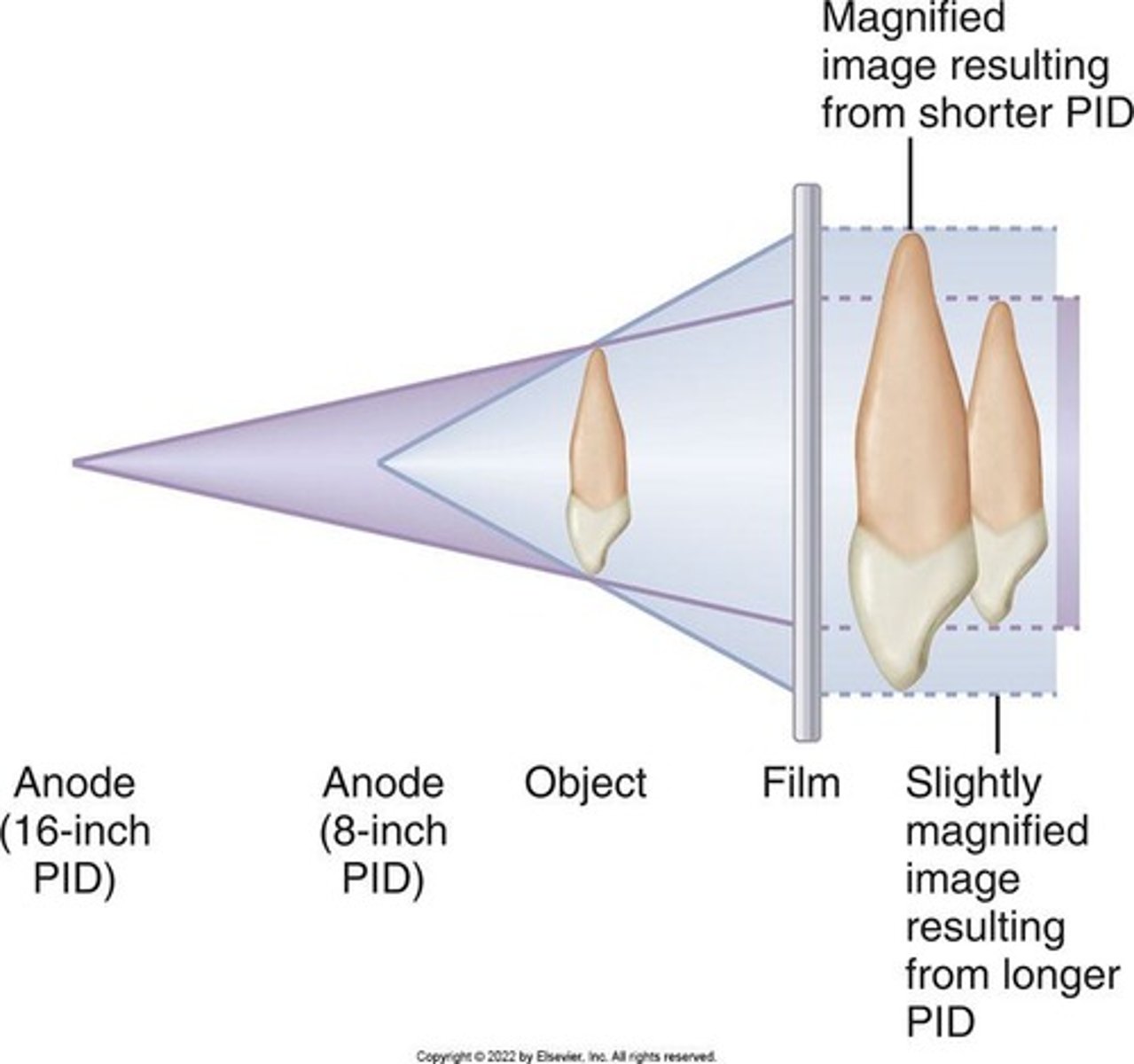
Distortion
A variation in the true size and shape of the object being radiographed.
Influencing factors of Distortion
Object-film alignment and x-ray beam angulation.