Chapter 1: Evolutionary Biology of HIV
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
What foundational concept will be emphasized in the course?
Population genetics.
What are some key topics covered in the course?
Speciation, adaptation, classification, microevolution, and macroevolution.
What is the significance of evolutionary concepts in biology?
They are relevant to all facets of biology, including human health.
What is the course's approach to teaching evolutionary biology?
It emphasizes basic principles and theory with examples rather than being purely descriptive.
What are the course objectives regarding population genetics?
To understand selection, genetic drift, linkage, and gene flow.
What does the course aim to teach about speciation?
The mechanisms of speciation and diversification.
What is the definition of evolution provided in the notes?
Change in allele frequencies over time; descent with modification and diversification.
What processes enable evolution?
Chance (random genetic drift), mutation, and natural selection.
How does evolution relate to survival and reproduction?
It directly influences aspects of organisms' lives, including survival and reproduction.
What societal issues are discussed in relation to evolutionary biology?
Negative societal consequences and inequities that persist in science.
What case study is introduced to teach about evolution in this course?
The study of HIV.
What is one question the course aims to answer regarding HIV treatments?
Why did initial HIV treatments ultimately fail?
What is the significance of Darwin's quote mentioned in the notes?
It highlights the historical context of evolutionary theory and its implications.
What is the importance of evolutionary biology in medical research?
It aids in understanding health issues and the evolution of diseases.
What is the expected outcome of studying evolutionary biology?
A deeper understanding of the principles of evolution and their applications.
What is HIV?
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) is an obligate, intracellular parasite that attacks the immune system.
When was HIV first described in the United States?
HIV was first described in the United States in 1981.
What percentage of HIV cases are found in Sub-Saharan Africa?
68% of all HIV cases are found in Sub-Saharan Africa.
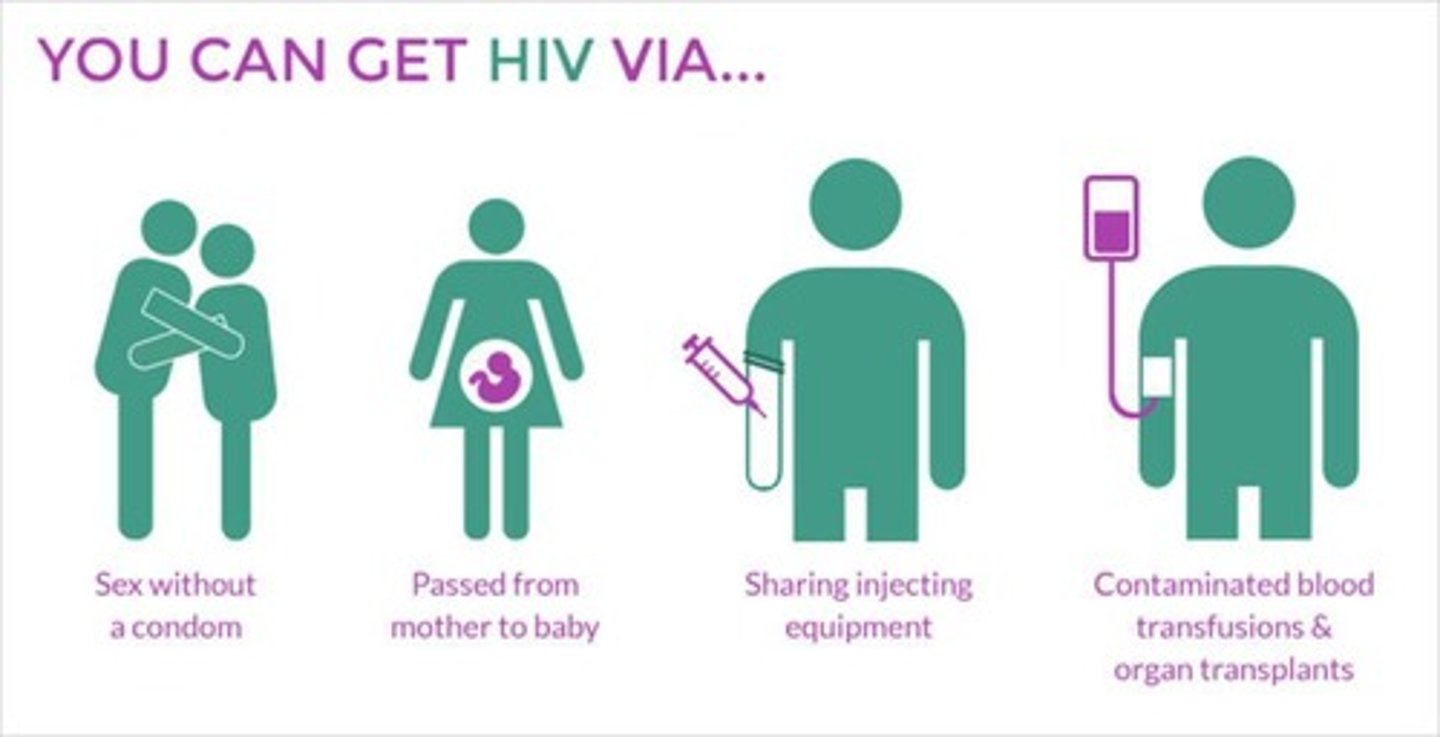
What are the primary modes of HIV transmission?
through bodily fluids via sexual intercourse, needle sharing, transfusions, breastfeeding, and childbirth.
How does HIV cause AIDS?
By destroying the immune system's T cells, leading to a collapse of the immune response.
What is the typical timeline from HIV infection to AIDS?
Usually occurs about 10 years after HIV infection.
What is the role of reverse transcriptase in HIV?
It allows HIV to convert its RNA into DNA, facilitating its replication within host cells.
Why did AZT treatment fail in the long run?
It failed because HIV evolved resistance due to mutations in reverse transcriptase that allowed the virus to survive despite the drug.
What is the error rate of reverse transcriptase?
Approximately 1 mutation per 1700 nucleotide incorporations.
What is HAART?(Highly Active Anti-Retroviral Therapy)
involves using more than two drugs to treat HIV.
What is Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP)?
Is a medication taken to prevent acquiring HIV, effective at 99% when exposed.
What happens to HIV populations in the absence of AZT?
In the absence of AZT, HIV populations return to being error-prone and can evolve new mutations.
What are coreceptor inhibitors?
Block HIV from attaching to host cells.
What is the significance of the CD4 and CCR5 co-receptors for HIV?
Are critical for HIV entry into immune cells, specifically T cells.
What is the impact of HIV on global health?
Since the beginning of the HIV epidemic, approximately 91 million people have been infected, and 44 million have died.
What are integrase inhibitors used for?
They block the incorporation of viral DNA into the host's DNA.
What is the primary goal of therapies targeting HIV?
To prevent HIV from replicating and to stop the progression to AIDS.
How does natural selection affect HIV treatment outcomes?
It leads to the survival of HIV strains that have mutations allowing them to resist treatment, such as AZT.
What is the relationship between HIV and evolutionary biology?
The study of HIV illustrates principles of evolution, such as mutation, natural selection, and adaptation.
What is the consequence of high mutation rates in HIV?
lead to rapid evolution of the virus, making it difficult to develop long-lasting treatments.
What is the role of protease inhibitors in HIV treatment?
Protease inhibitors block the enzyme that cleaves precursor proteins necessary for the maturation of virions.
Why is prevention considered the best strategy against HIV?
Because it stops the virus from spreading and reduces the number of new infections.
What are entry/fusion inhibitors?
These inhibitors that prevent HIV from entering host cells.
What challenges do researchers face in treating HIV?
The rapid mutation of the virus and the development of drug resistance.
How does the immune system respond to HIV infection?
It attempts to destroy virions and kill infected T cells and macrophages.
What is the significance of opportunistic infections in AIDS?
They occur when the immune system is compromised, leading to severe health complications.
What is the expected outcome after the onset of AIDS?
Death and it usually occurs within 2 years due to opportunistic infections.
How can PrEP be administered?
It can be taken as a pill or a shot.
What is the effectiveness of PrEP against HIV?
99% effective at avoiding HIV when exposed.
What are HAART cocktails?
Highly Active Anti-Retroviral Therapy, which consists of more than two drugs.
Why doesn't HAART cure HIV?
Dormant virions in resting T cells contribute to the persistence of the virus.
What is the significance of the Δ32 allele in HIV resistance?
Individuals with the Δ32 allele on CCR5 co-receptors are resistant to HIV infection.
What percentage of people with European ancestry have the Δ32 allele?
9% of people with European ancestry have the Δ32 allele.
What is the origin of HIV in humans?
HIV likely originated from SIV in primates, specifically from chimpanzees and sooty mangabeys.
When did HIV-1 likely evolve?
Around 1931, between 1915 and 1941.
What are the two main types of HIV?
HIV-1 and HIV-2.
What is the primary difference between HIV-1 and HIV-2?
HIV-1 is more widespread and deadly, while HIV-2 is primarily found in West Africa and is less deadly.
What historical event contributed to the spread of HIV in the 1980s?
New sexual practices in the 1970s led to increased transmission rates.
What does the Transmission Rate Hypothesis suggest?
The virulence of a virus is influenced by the transmission dynamics of the host population.
What is the role of promiscuity in the evolution of HIV virulence?
Increased promiscuity can select for more virulent strains of HIV.
What was the outcome of the Louisiana v. Richard J. Schmidt case?
Dr. Schmidt was found not guilty of purposefully infecting his ex with HIV.
What is the significance of T-cell escape variants in HIV treatment?
They dominate the latent reservoir in chronic phase-treated patients, complicating treatment.
What evidence supports the cure of HIV in the Berlin Patient?
Bone marrow transplants from donors with the Δ32 allele.
What was the outcome for the Berlin Patient?
He was cured of HIV after a bone marrow transplant.
What is the current status of HIV-2 in southern Asia?
HIV-2 is increasing in virulence due to high rates of promiscuity.
What are Long-Term Nonprogressors in HIV infection?
Individuals who become infected with HIV but do not progress to AIDS.
What is the relationship between HIV replication rate and host virulence?
High replication rates can lead to increased transmission but may also result in host death.
What is the significance of the phylogeny of HIV and SIV?
It helps trace the evolutionary history and origins of HIV in humans.
What are the four groups of HIV-1?
Group M, Group N, Group O, and Group P.
What is the primary mode of HIV transmission?
Through sexual contact, sharing needles, or from mother to child.
How does the mutation rate of HIV affect its evolution?
HIV has a high mutation rate, leading to diverse viral populations within hosts.
What are the implications of HIV's high mutation rate for treatment?
It complicates treatment and vaccine development due to rapid viral evolution.
What is the role of evolutionary biology in understanding HIV?
It helps in tracing the history of HIV diversification and understanding resistance mechanisms.