IGCSE Com Sci - UNIT 3: Hardware
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
What is the purpose of the CPU?
The purpose of the CPU is to fetch, decode and execute instructions.
Define the term microprocessor.
A microprocessor is a type of integrated circuit on a single chip.
What does CPU stand for?
CPU stands for Central Processing Unit.
True or False? The CPU is only used in desktop computers.
False. The CPU is used in various devices including laptops, desktops, games consoles, and mobile devices.
Input
Data and commands inputted by the user using an input device.
Process
The execution of instructions by the CPU to manipulate data.
Output
The results of processing displayed to the user via an output device.
What are the three main steps in computer data processing?
The three main steps in computer data processing are input, process, and output.
True or False? The terms CPU and microprocessor can be used interchangeably.
True. The terms CPU and microprocessor can be used interchangeably.
What is the Von Neumann Architecture?
The Von Neumann Architecture is a design of the CPU proposed by John Von Neumann in the 1940s, which most general-purpose computers are built upon.
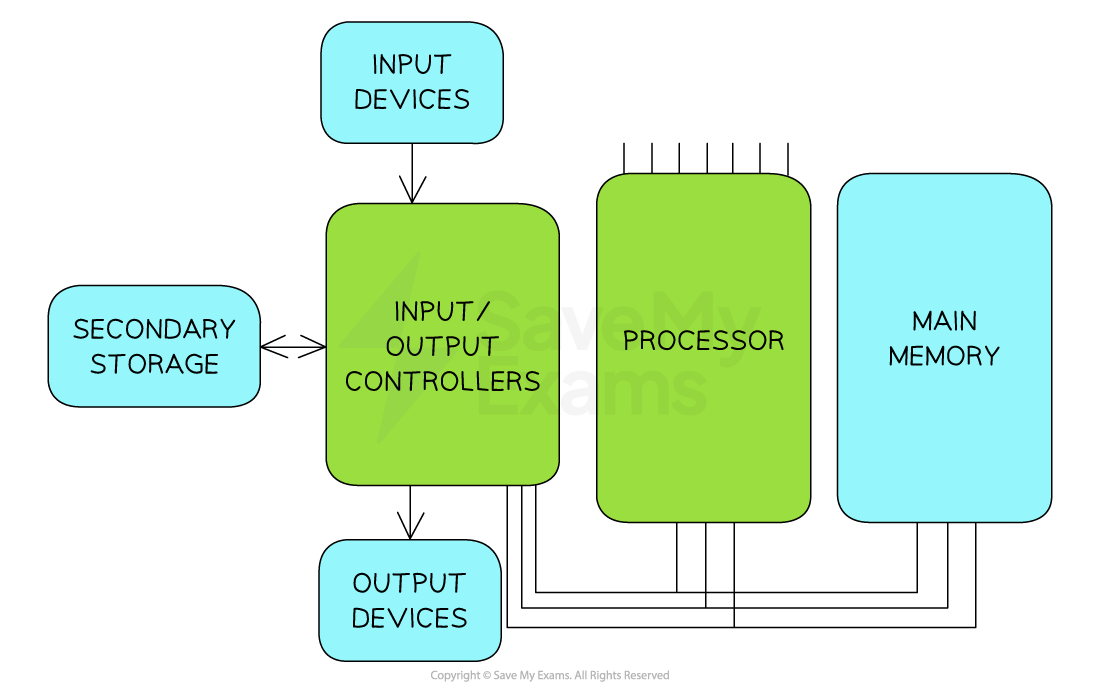
Program Counter (PC)
Holds the memory address of the next instructions to be executed.
Memory Address Register (MAR)
Holds the memory address of where data or instructions are to be fetched from in memory.
Memory Data Register (MDR)
Stores the data or instruction which has been fetched from memory.
Current Instruction Register (CIR)
Stores the instruction the CPU is currently decoding or executing.
Accumulator (ACC)
Stores the results of any calculations that have taken place in the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU).
What is a bus in computer architecture?
A bus is a set of parallel wires through which data/signals are transmitted from one component to another.
Name the three types of buses in computer architecture.
The three types of buses are address bus, data bus, and control bus.
What is the function of the address bus?
The address bus carries location data (addresses), data is written to/read from.
True or False? The data bus is unidirectional.
False. The data bus is bidirectional, carrying data or instructions in both directions.
What is the Fetch-Decode-Execute Cycle?
The Fetch-Decode-Execute Cycle is the cycle that the central processing unit (CPU) runs through billions of times per second to make a computer work.
What are the three main stages of the FDE Cycle?
The three main stages are Fetch, Decode, and Execute.
In the fetch stage, what register holds the address of the next instruction?
In the fetch stage, the Program Counter (PC) holds the address of the next instruction to be fetched from memory.
What happens to the Program Counter after an instruction is fetched?
The Program Counter increments by 1 so it is pointing to the next instruction to be executed.
Opcode
The part of an instruction that specifies what operation to perform.
Operand
The part of an instruction that specifies what to perform the operation on.
What happens during the decode stage?
During the decode stage, the CPU works out what is required from the instruction by splitting it into opcode and operand.
True or False? The execute stage always involves performing a calculation.
False. The execute stage can involve performing a calculation, storing a result, or fetching data from memory, depending on the instruction.
What is the purpose of the Control Unit (CU) in the fetch stage?
The Control Unit sends a signal along the control bus to initiate the read operation from main memory.
How many times per second does a modern CPU typically perform the Fetch-Decode-Execute cycle?
A modern CPU typically performs the Fetch-Decode-Execute cycle billions of times per second.
What are the three common characteristics of the CPU that impact its performance?
The three common characteristics are: Clock Speed, Cache Size, Number of Cores.
Define clock speed.
Clock speed is measured in Hertz (Hz) and measures the number of fetch-decode-execute cycles that can take placein 1 second.
True or False? Modern computers have a clock speed measured in Gigahertz (GHz), meaning billions of cycles per second.
True. Modern computers have a clock speed in Gigahertz (GHz), meaning billions of cycles per second.
What is the impact of a faster clock speed?
The faster the Clock Speed, the more instructions can be fetched and executed per second.
What does a Clock Speed of 3.5GHz mean?
A Clock Speed of 3.5GHz means it can perform up to 3.5 billion instructions per second.
What is cache used for?
Cache is used as temporary storage to provide quick access to frequently used instructions and data.
What is the benefit of a larger cache size?
The larger the Cache Size, the more frequently used instructions or data can be stored, resulting in fewer fetch cycles from RAM and improved performance.
Define number of cores.
Each core works like its own CPU, so multiple cores allow multiple processing units to fetch, decode and execute instructions simultaneously.
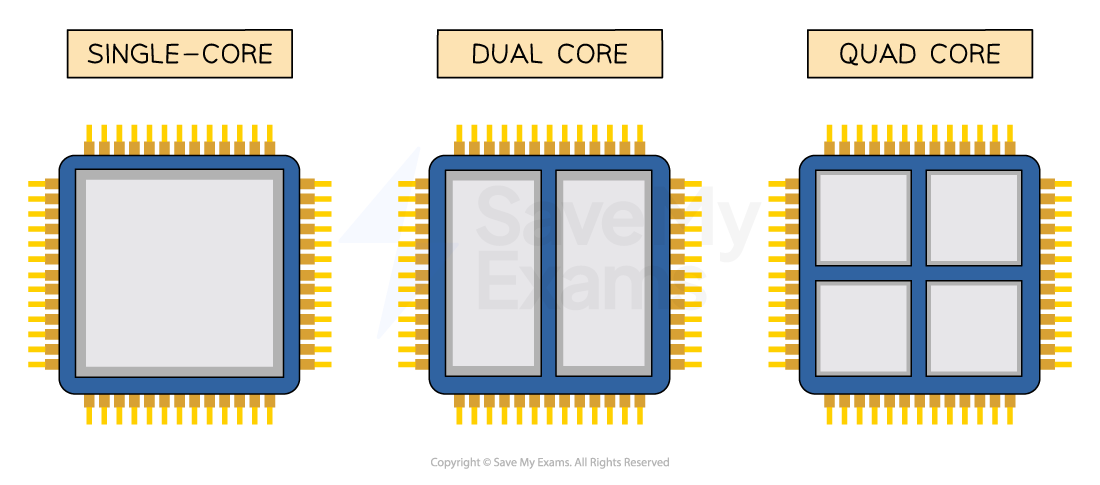
True or False?
A dual-core CPU with a Clock Speed of 3.6GHz can fetch, decode & execute more instructions in 1 second that a quad-core CPU with a Clock Speed of 2.5GHz?
False.
A dual-core CPU (2 cores) running at 3.6GHz can perform 2 x 3.6 billion instructions = 7.2 billion instructions per second.
A quad-core CPU (4 cores) running at 2.5GHz can perform 4 x 2.5 billion instructions = 10 billion instructions per second.
For a dual-core 2.5GHz processor, what does "dual-core" mean?
For a dual-core processor, "dual-core" means there are two cores (processing units) that can fetch, decode and execute instructions.
What is an instruction set?
An instruction set is a list of all the commands that can be processed by a CPU.
Machine code
The binary code representation of a CPU instruction.
What are the two parts of a machine code instruction?
The two parts of a machine code instruction are the operation code (opcode) and the operand.
What is a mnemonic in the context of CPU instructions?
A mnemonic is a short, human-readable code that represents a machine code instruction.
True or False? CPU instruction sets are universal across all processors.
False.
Instruction sets are machine-specific and can vary between different processor manufacturers.
What does the ADD instruction typically do?
The ADD instruction typically adds a value to the value currently stored in the accumulator (ACC).
What does the LDA instruction typically do?
The LDA instruction typically loads the value stored in a memory location into the accumulator.
What does the HLT instruction typically do?
The HLT instruction (halt) typically stops the program.
Define embedded system.
An embedded system is a computer system with a single function, inside a larger mechanical unit.
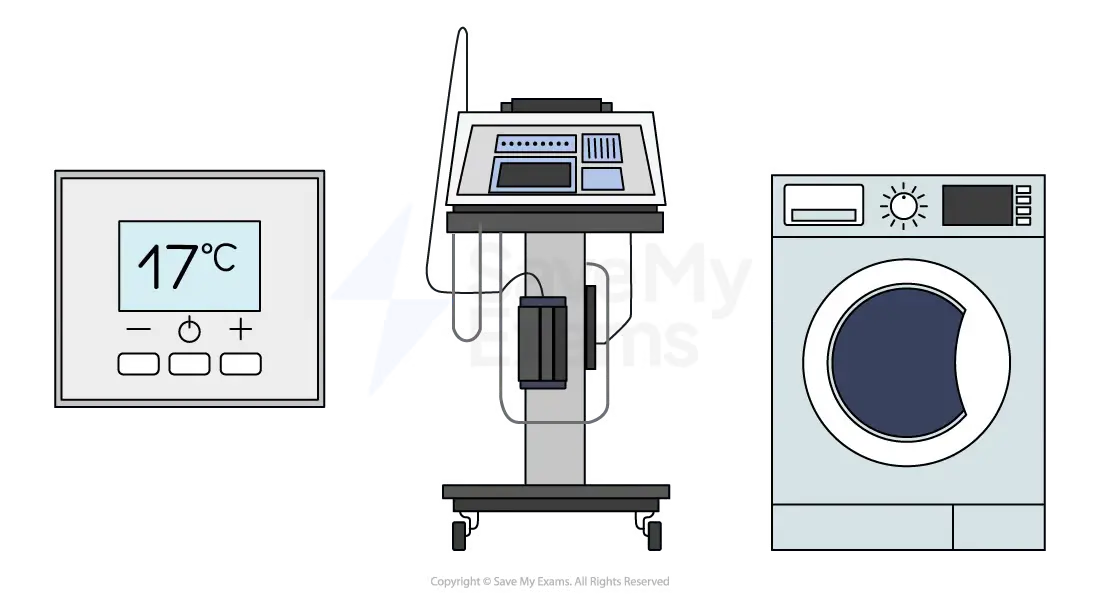
What are three examples of embedded systems?
Examples of embedded systems include: Heating thermostats, Hospital equipment, Washing machines.
What are the three key properties of an embedded system?
The three key properties of an embedded system are:
small size
use less power than general-purpose computers
lower cost
True or False? A laptop is an example of an embedded system.
A laptop is not an example of an embedded system. A laptop is an example of a general-purpose computer.
Why do embedded systems use less power?
They have a single dedicated function rather than being general-purpose computers.
True or False? A fridge is an embedded system.
False. While a fridge has a single main function, it does not contain a CPU, so it is not considered an embedded system.
Are mobile phones considered embedded systems?
Mobile phones are general-purpose computing devices, not single-function embedded systems.
What is an input device?
An input device is a hardware component that allows users to interact with a computer system by inputting data or commands.
Keyboard
A keyboard is an input device that allows users to input text and commands by pressing keys.
What is the primary function of a mouse?
The primary function of a mouse is to navigate the computer screen and click on items.
Touchscreen
A touchscreen is an input device that allows users to interact with the device by touching the screen, commonly found on smartphones and tablets.
What is the main purpose of a scanner?
The main purpose of a scanner is to digitise physical documents or images, converting them into a format that the computer can process.
Biometric device
A biometric device is an input device used for security purposes to verify a user's identity, such as fingerprint scanners or facial recognition systems.
What is a graphics tablet used for?
A graphics tablet is used to allow artists and designers to draw or sketch directly onto a computer, particularly useful for graphic design and 3D modelling.
True or False? A joystick is primarily used for word processing.
False. A joystick is primarily used for computer games, especially flight simulators, allowing users to control movement more fluidly than with a keyboard or mouse.
Barcode scanner
A barcode scanner is an input device that scans barcodes, typically used in retail and inventory management.
What is the main function of a microphone as an input device?
The main function of a microphone as an input device is to capture audio input, which can be used for voice commands, recording audio, or video conferencing.
What is an output device?
An output device is a hardware component that receives information from a computer system and presents it to the user in a comprehensible form.
Monitor
A monitor is an output device that displays visual output from the computer, including text, images, and videos.
What is the primary function of a printer?
The primary function of a printer is to produce a hard copy of digital documents or images.
Speakers
Speakers are output devices that output audio from the computer, such as music, sound effects, or voice.
What is a Braille display used for?
A Braille display is used to output information in Braille, allowing visually impaired users to read text from the computer.
Plotter
A plotter is an output device used for printing large, high-quality diagrams and designs, often used in engineering or architecture.
What is the main purpose of a projector?
The main purpose of a projector is to project the computer's display onto a large screen or wall, useful for presentations or movie viewing.
True or False? Headphones are considered input devices.
False. Headphones are considered output devices that output audio directly to the user, providing a more personal and potentially immersive experience.
Virtual Reality (VR) Headset
A Virtual Reality (VR) Headset is an output device that provides an immersive visual and audio output, primarily used for gaming and virtual simulations.
What is an example of a computer-controlled machinery output device?
An example of a computer-controlled machinery output device is an actuator.
What is a sensor?
A sensor is an input device that measures a physical property of its environment such as light levels, temperature, or movement.
Monitoring system
A monitoring system is a system that tracks the state of a system, gathers data, and may issue warning messages.
What is a control system?
A control system is a system that controls based upon the input from sensors, such as starting a heater when water temperature falls below an acceptable level.
Feedback loop
A feedback loop is a process where outputs are recycled and used as inputs, creating a continuous cycle.
What does an acoustic sensor measure?
An acoustic sensor measures sound levels.
Accelerometer
An accelerometer is a sensor that measures acceleration rate, tilt, and vibration.
What is the typical use of a humidity sensor?
A humidity sensor is typically used to monitor humidity in greenhouses.
True or False?
An infra-red sensor is used to detect motion or a heat source.
True.
An infra-red sensor is used to detect motion or a heat source.
pH sensor
A pH sensor is a device that measures the acidity or alkalinity of a substance.
What type of sensor would be used to help drivers when reversing?
A proximity sensor would be used to help drivers when reversing.
What is primary storage?
Primary storage is directly accessed by the CPU and holds the data and instructions that the CPU needs to access while the computer is turned on.
True or False?
Primary storage is always volatile.
False.
Primary storage is volatile with the exception of ROM.
RAM
RAM is Random Access Memory, a type of primary storage that holds data and instructions currently in use, is volatile, and has fast access times.
What does ROM stand for?
ROM stands for Read Only Memory.
True or False?
RAM is faster than secondary storage.
True.
RAM is faster than secondary storage.
What is stored in ROM?
ROM stores the first instructions a computer needs to start up (Bootstrap) and the BIOS (Basic Input Output System).
True or False?
ROM is volatile.
False.
ROM is non-volatile.
What is the main difference between RAM and ROM in terms of data persistence
RAM is volatile and loses its contents when power is turned off, while ROM is non-volatile and retains its contents.
BIOS
BIOS is the Basic Input Output System stored in ROM.
True or False?
RAM has a larger capacity than ROM.
True.
RAM has a larger capacity than ROM.
What is secondary storage?
Secondary storage is non-volatile storage that retains digital data within a computer system when the power is turned off.
Name the three types of secondary storage.
The three types of secondary storage are magnetic, solid state, and optical.
True or False?
Secondary storage has a smaller capacity than primary storage.
False.
Secondary storage has a larger capacity than primary storage.
Magnetic storage
Magnetic storage is a type of non-volatile media that uses magnets (polarity) to store binary 0s and 1s.
Solid state storage
Solid state storage is a type of non-volatile media that uses electronic circuits to store binary 0s and 1s.
Optical storage
Optical storage is a type of non-volatile media that uses lasers to burn the surface of a disk, creating pits and lands suitable for storing binary 0s and 1s.