Econ 102 - Chapter 6: Taxes, Prices Controls, and Quantity Regulations
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Government Intervention
The government can affect market outcomes with laws, taxes, and regulations.
Goal: shape costs and benefits, not stop supply & demand.
Taxes
Result: buyers pay more, sellers receive less → both share burden.
Tax on Sellers
shifts supply curve up (higher cost of production).
Tax on Buyers
shifts demand curve down (lower willingness to pay).
Statutory Burden
who (pays) legally sends tax to the government.
Economic Burden
who actually bears the cost after price changes.
(determined by elasticity)
Tax Incidence
how the economic burden is divided between buyers & sellers.
Depends on elasticity, not statutory burden.
More Inelastic (steeper) = More Burden
If demand is inelastic → buyers pay more.
If supply is inelastic → sellers pay more.
Four-Step Recipe for Analyzing Taxes
Identify which curve shifts (supply or demand).
Determine shift direction (up/down).
Compare pre- and post-tax equilibrium.
Determine which side is more inelastic (demand/supply)
Subsidies
government payment for making a specific choice.
Acts like a negative tax → increases quantity, lowers price for buyers, raises price for sellers.
Example: Pell Grants (college students).
More inelastic side captures more benefit.
Inelastic
pays more tax / gains more subsidy.
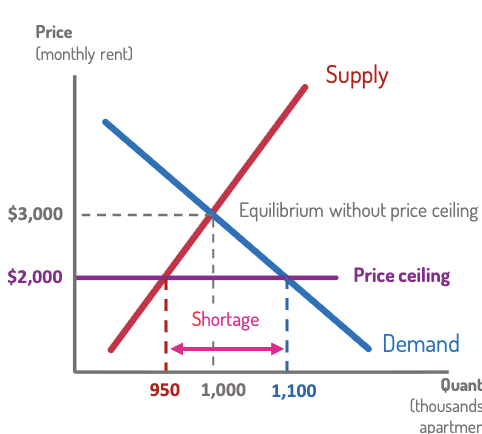
Price Ceiling
maximum legal price.
Binding if set below equilibrium → causes shortage.
Example: Rent control.
Lowers rent → fewer apartments available.
Leads to black markets, bribes, poor maintenance.
Ceilings go below equilibrium.
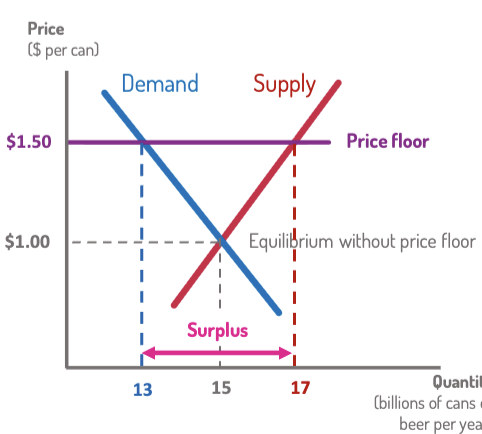
Price Floor
minimum legal price.
Binding if set above equilibrium → causes surplus.
Examples:
Minimum Wage: raises worker pay, may reduce jobs.
Minimum Alcohol Price (Scotland): reduces consumption.
Floors go above equilibrium.
Quantity Regulation
government sets a minimum or maximum quantity.
ex: Mandate or Quota
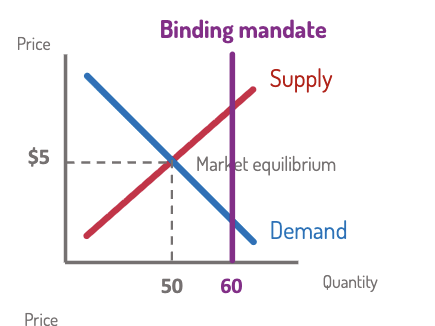
Mandate
minimum quantity that must be bought/sold.
Binding if above equilibrium quantity → increases quantity.
Increases the quantity bought or sold.
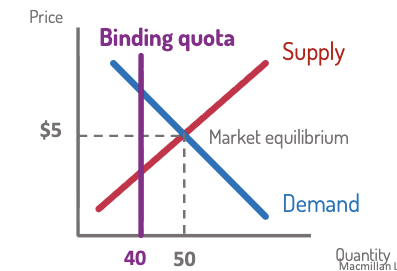
Quota
maximum quantity allowed
Binding if below equilibrium quantity → decreases quantity.
Decreases the quantity bought or sold