Enzymology - Tutorial 3: Enzyme Regulation, Electron Transport Chain (ETC) and Oxidative Phosphorylation
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
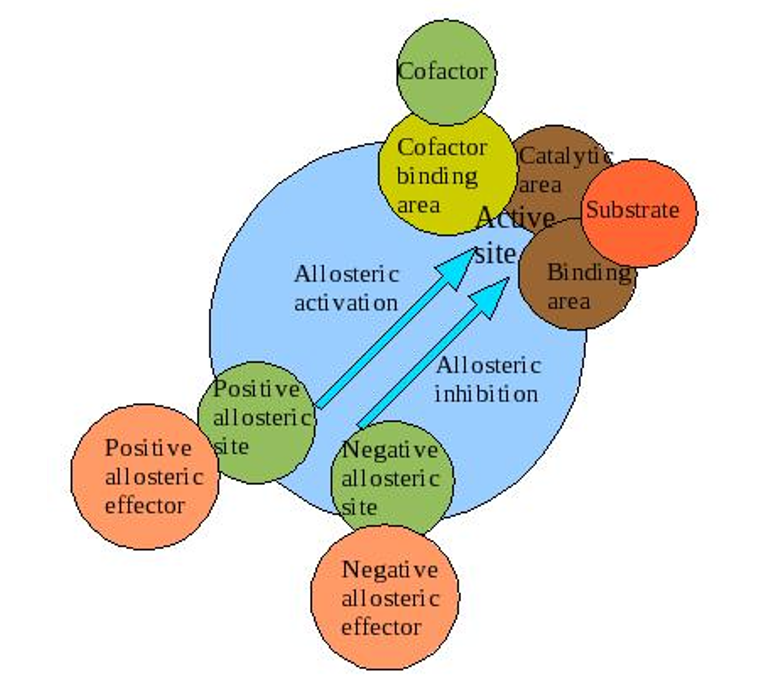
What are the characteristics of an allosteric enzyme?
An enzyme that changes its conformational ensemble upon binding of an effector
binding of an effector results in change in binding affinity at different ligand binding site
follow sigmoidal curve
usually composed of multiple subunits
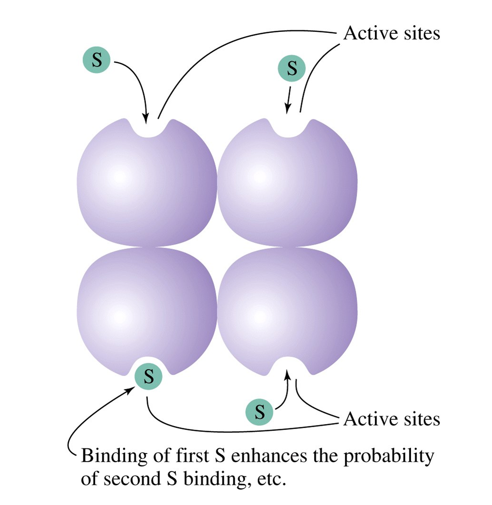
What happens when a homotropic effector binds?
binding of the first substrate enhances the probability of second substrate binding
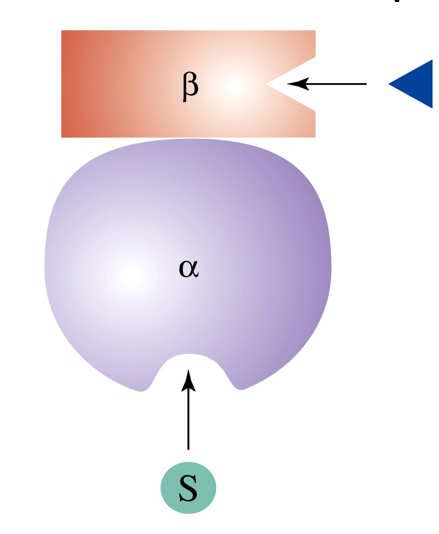
What happens when a heterotropic effector binds?
effector molecule binds to site on regulatory subunit which sends a message to the catalytic subunit
substrate binds more or less depending on whether the effector is positive or negative
What is a zymogen?
in active form/precursor of enzyme
How is a zymogen activated?
activated by the removal of a polypeptide unit
What is the process of breaking down nutrients to release energy to change ADP to ATP?
Catabolism
What is the process of changing simpler components to more complex ones with ATP?
Anabolism
What’s the difference between ΔG and ΔGo?
ΔG = change in free energy
ΔGo = change in free energy under standard conditions
all reactants and products are at an initial concentration of 1.0 M
pressure of 1.0 atm
temperature of 25 C
What happens if a reaction has negative ΔG?
favorable (spontaneous) reaction
exergonic reaction
What happens if a reaction has positive ΔG?
unfavorable (non-spontaneous) reaction
endergonic
What happens if a reactions ΔG = 0?
reaction is at an equilibrium
Which ETC inhibitors inhibit complex I?
rotenone
Which ETC inhibitors inhibit complex III?
antimycin A
Which ETC inhibitors inhibit complex IV?
cyanid and carbon monoxide
What prevents the influx of protons through ATP synthase?
oligomycin
What is the function of dinitrophenol?
a chemical uncoupler, uncouples ETC from OX. Phosphorylation
What happens when an allosteric activator stabilizes the enzyme in its high affinity form?
enzyme activity
What happens when an enzyme subject to allosteric activation is in its uncomplexed form?
allosteric activation is less active
uncomplexed form has low affinity for the substrate
What happens when an enzyme subject to allosteric inhibition is in its uncomplexed form?
allosteric inhibition is active
uncomplexed form has high affinity for the substrate
What happens when an allosteric inhibitor stabilizes the enzyme in its low affinity form?
little or no activity
What is the process of creating ATP from ADP?
phosphorylation
Which enzyme helps turn ATP to ADP?
kinase
What is the function of phosphatase?
removes a phosphate group
opposite of kinase
How are enzymes regulated by covalent modification?
ubiquitination
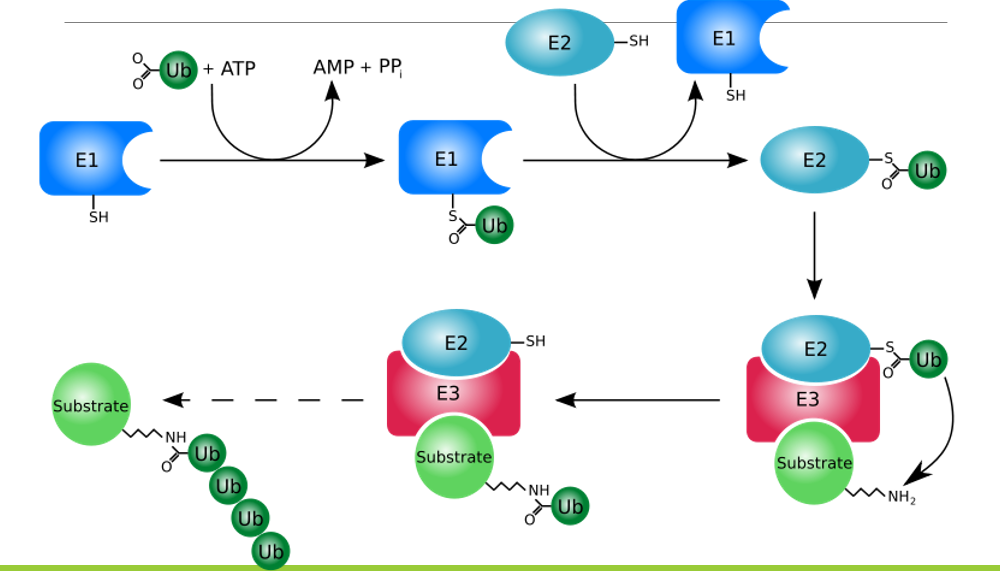
How are enzymes regulated by protein-protein interactions?
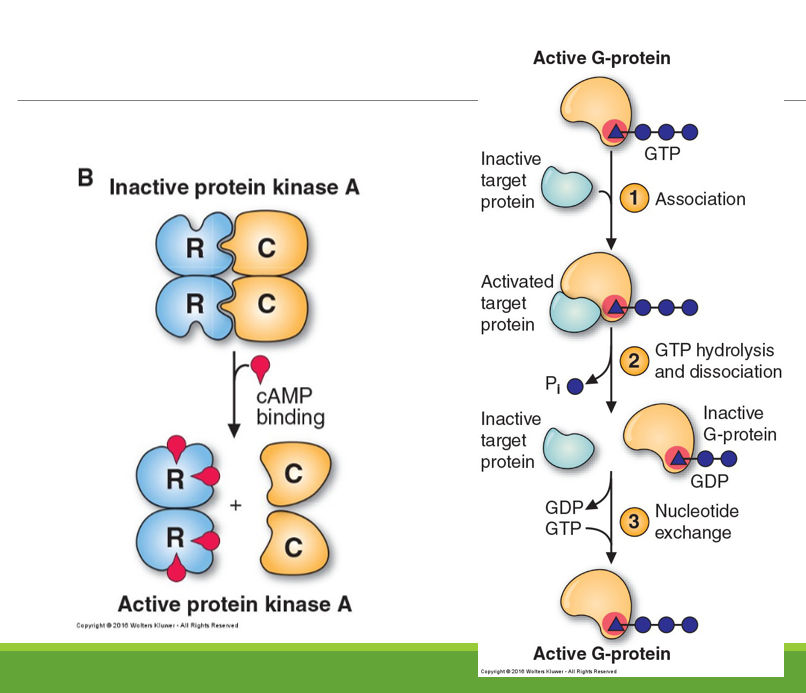
What is the induction and repression of enzyme synthesis?
induction: increased synthesis of an enzyme
repression: reduced synthesis of an enzyme
used for enzymes needed under special physiological conditions
What are the properties of isoenzymes?
enzymes with different molecular forms\
have similar amino acid sequences but not identical
may differ in kinetics (Km and Vmax)
may have different regulators
may differ in coenzyme preference
may have different cellular distribution
may have different development distribution
What are the isoenzymes of creatine kinase (CK)?
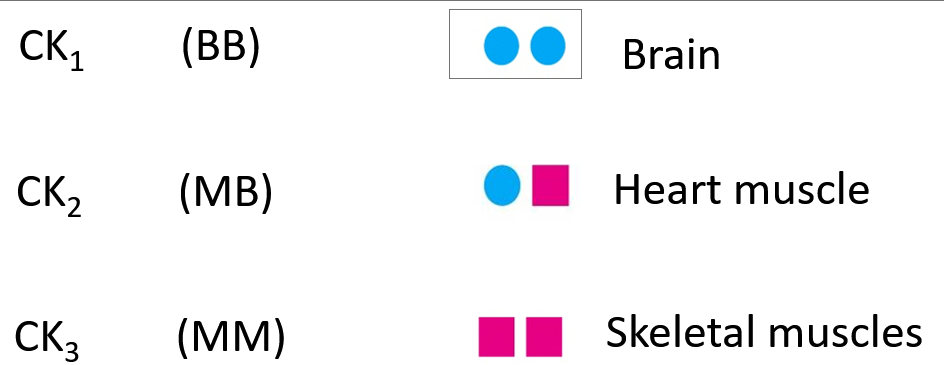
How are enzymes used in clinical diagnosis?
increased plasma level of certain enzymes can be used for setting a clinical diagnosis
How does the ETC work?
Complex I accepts electrons from NADH, and passes them to coenzyme Q (CoQ) which also receives electrons from complex II
CoQ passes electrons to complex III, which passes them to cytochrome c (cyt c)
Cyt c passes electrons to Complex IV, which uses the electrons and hydrogen ions to reduce molecular oxygen to water
What is the most important factor in the regulation of ETC?
ADP, referred to as respiratory control