Endurance Training: Effects on VO2 Max, Performance, and Muscle Adaptations
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is the primary training method to increase VO2 max?
Endurance training involving large muscle groups in dynamic activity for 20-60 minutes, at least 3 times a week, at ≥50% VO2 max.
What is the average expected increase in VO2 max from training?
15-20% increase, with 2-3% in those with high initial VO2 max and up to 50% in those with low initial VO2 max.
What is the Fick equation used for?
Calculating VO2 max.
What is the primary physiological factor causing differences in VO2 max across populations?
Differences in stroke volume (SV) max.
What are the expected improvements in VO2 max from short duration training (~4 months)?
26% increase in VO2 max, primarily due to increased stroke volume (SV) over a-vO2 difference.
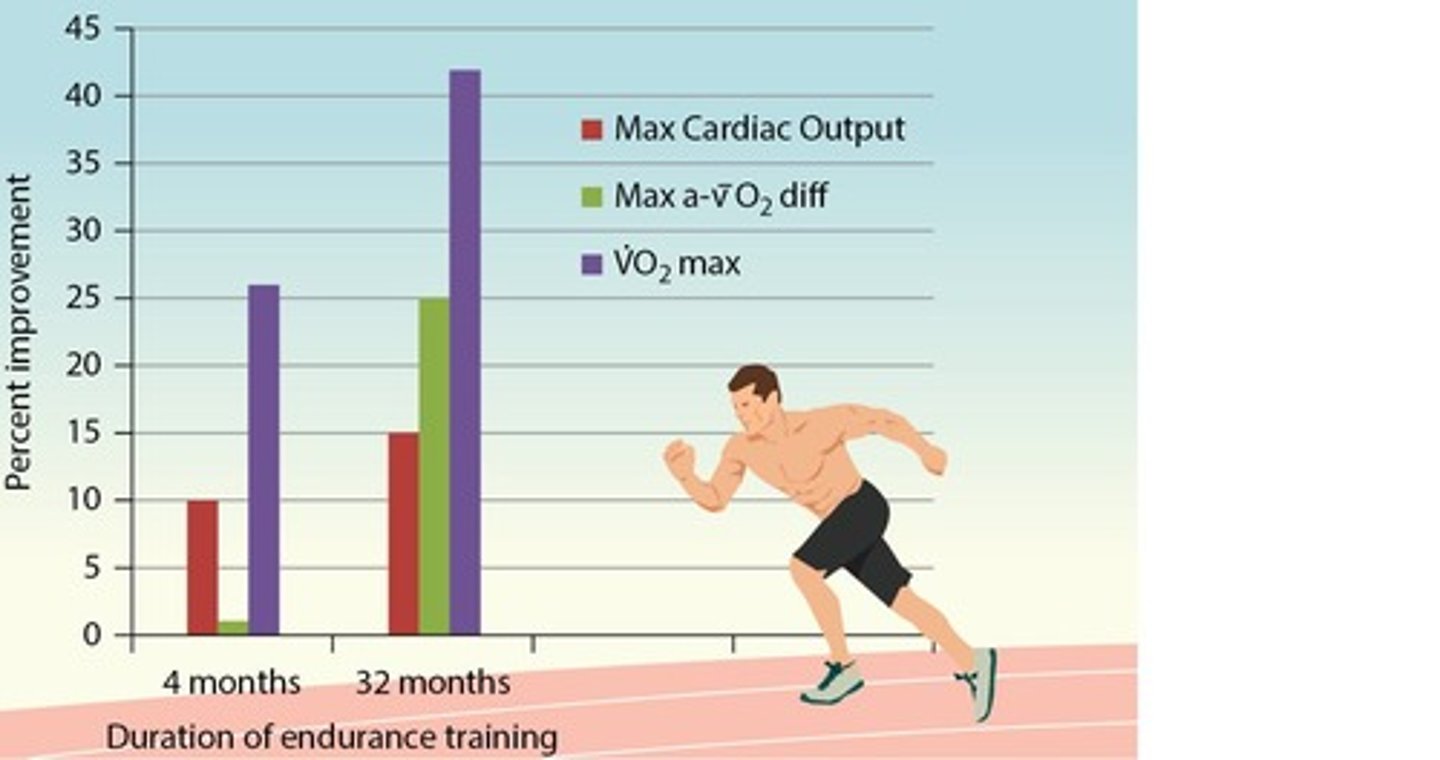
What are the expected improvements in VO2 max from longer duration training (~28 months)?
42% increase in VO2 max, with a-vO2 difference improving more than stroke volume.
What components are included in the VO2 max equation?
Heart rate max (HR max), stroke volume max (SV max), and a-vO2 difference max.
What factors contribute to increased maximal stroke volume from training?
Increased preload, plasma volume, venous return, and ventricular volume, along with decreased afterload.
What is the effect of endurance training on arteriovenous O2 difference?
Increased muscle blood flow, reduced sympathetic nervous system vasoconstriction, and improved oxygen extraction by muscles.
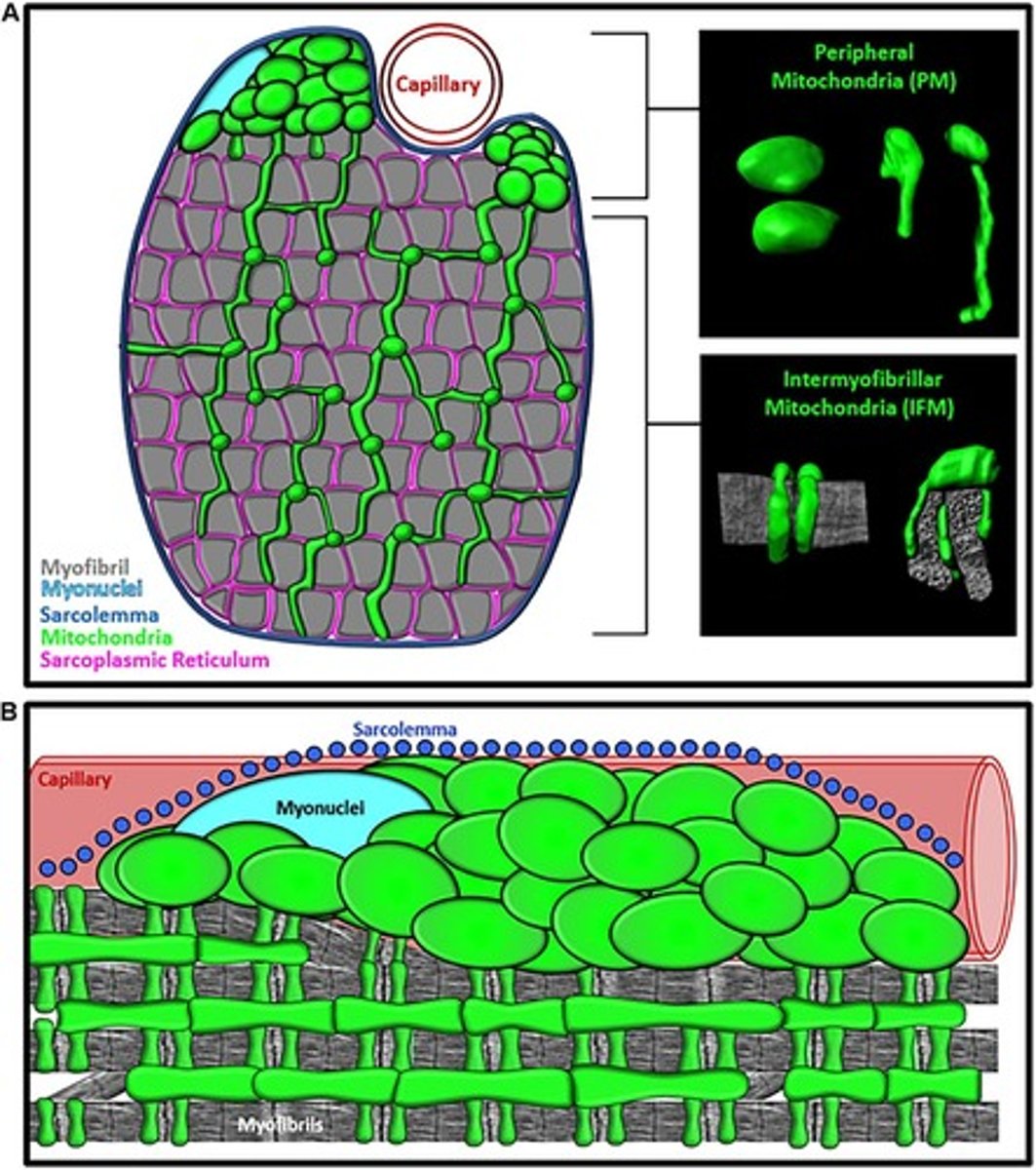
What adaptations occur in muscle fibers due to endurance training?
Fast-to-slow shift in muscle fiber type, increased capillary density, and enhanced oxygen diffusion.
What are the two populations of mitochondria found in muscle fibers?
Subsarcolemmal mitochondria located below the sarcolemma and intermyofibrillar mitochondria located around contractile proteins.
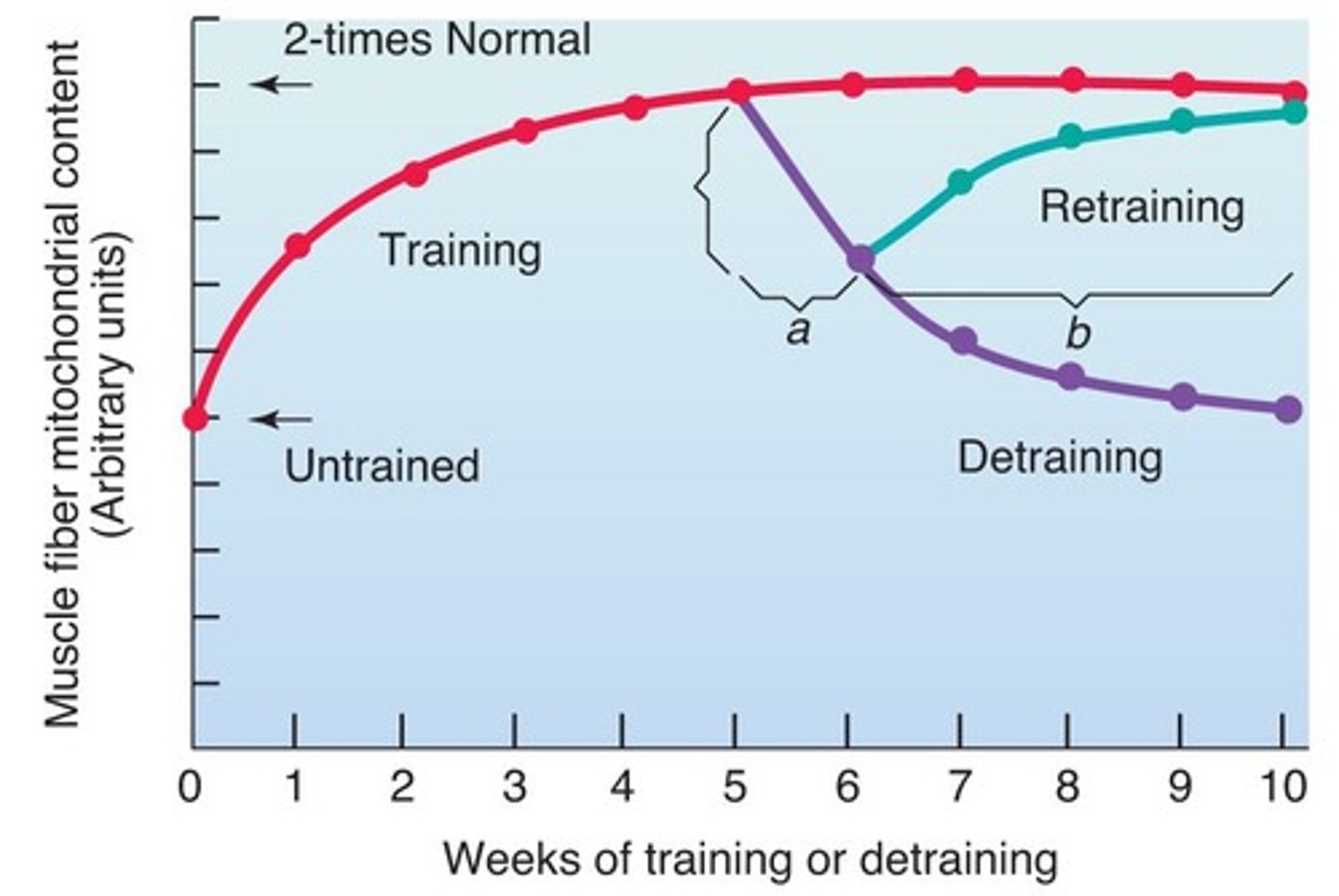
How quickly can mitochondrial content increase with training?
Mitochondrial content can increase 50-100% within the first 6 weeks of training.
What is the relationship between ADP levels and mitochondrial ATP production after training?
Lower ADP levels are needed to increase ATP production and VO2 after training.
What changes occur in muscle fuel utilization due to exercise training?
Increased utilization of fat and sparing of plasma glucose and muscle glycogen.
What physiological responses are influenced by biochemical adaptations to training?
Reduced sympathetic nervous system activity, lower heart rate, and decreased ventilation.
What happens to VO2 max during detraining?
VO2 max decreases by approximately 8% within 12 days and 20% after 84 days.
How quickly do muscle mitochondria adapt to retraining?
Muscle mitochondria can double within 5 weeks of retraining.
What is the impact of detraining on mitochondrial adaptations?
50% of training gains can be lost within 1 week of detraining, with the majority lost in two weeks.
What is the significance of capillary density in endurance training?
Increased capillary density enhances the diffusion of oxygen and improves waste removal from muscles.
What is the effect of endurance training on lactate and H+ formation?
Endurance training results in less lactate and H+ formation during exercise.
What is the role of fatty acid binding protein in muscle fuel utilization?
It facilitates the transport of free fatty acids (FFA) into the muscle for oxidation.