ORGS 2100 - Class 10: Organizational Culture
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
What is organizational culture?
shared social knowledge
…
regarding rules
…
shaping employee attitude
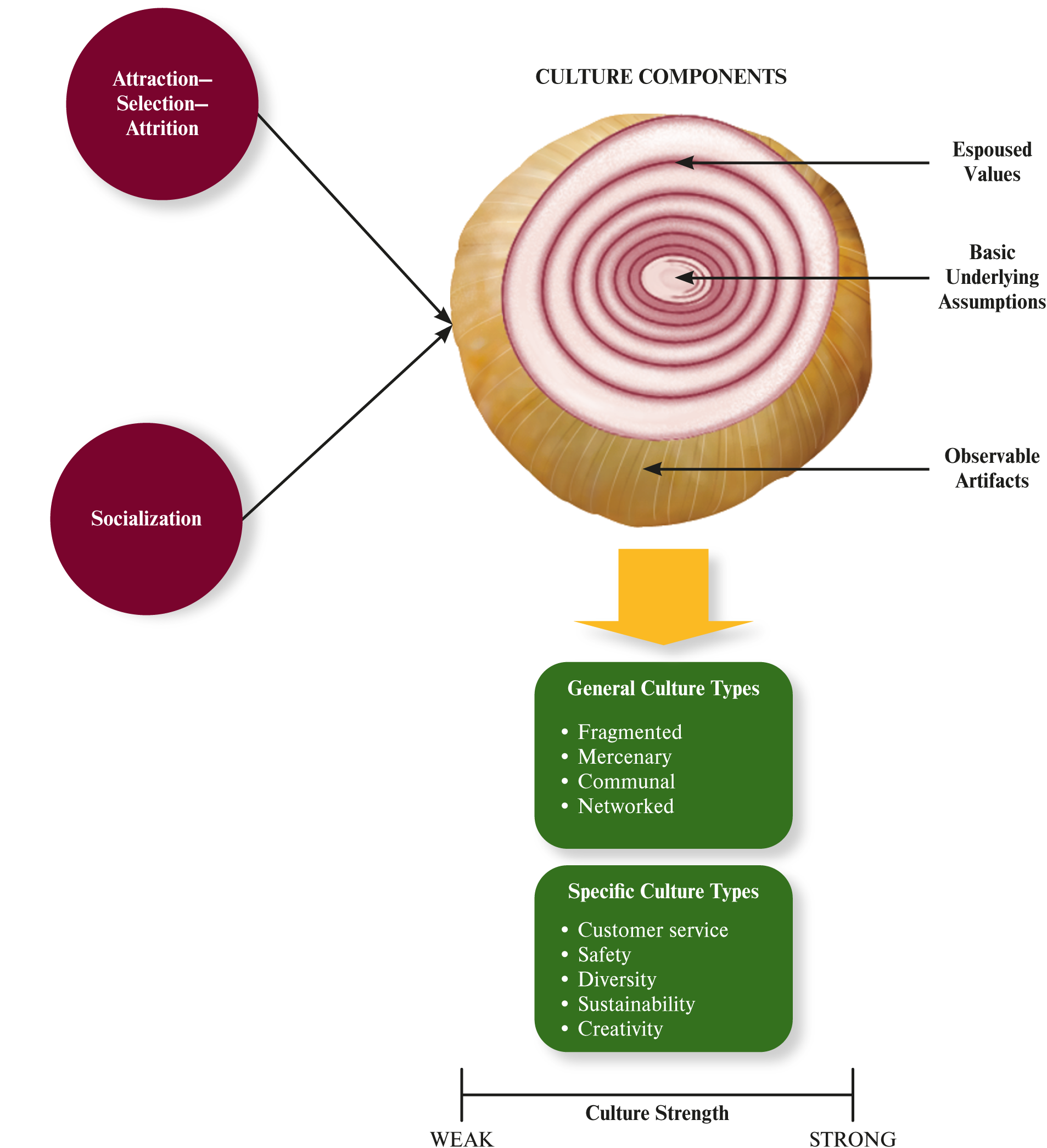
What are the organizational culture components?
observable artifact
<
espoused value
<
underlying assumption
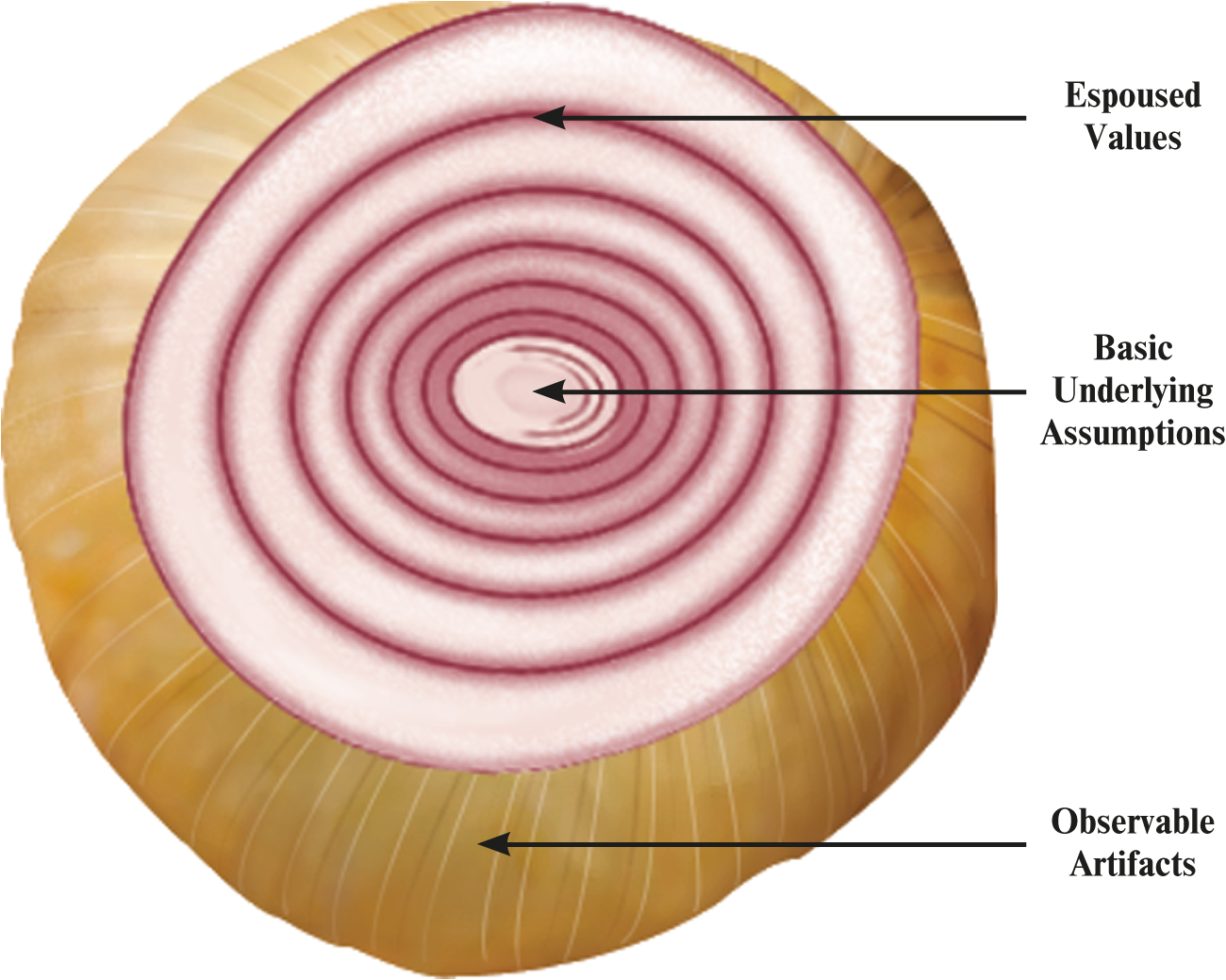
What are observable artifacts’ primary means?
transmit organizational culture to workforce
What are the major observable artifact types?
symbol
structure
language
story
ritual
ceremony
What differentiates espoused and enacted … values?
espoused
say that thing’s important
v.s.
enacted
act like thing’s important
… value
What are underlying assumptions’ extent?
question behaviour validity act
What is an organizational culture typology example?
solidarity
sociability
What are the solidarity & sociability typology descriptions?
fragmented
mercenary
networked
communal
… culture
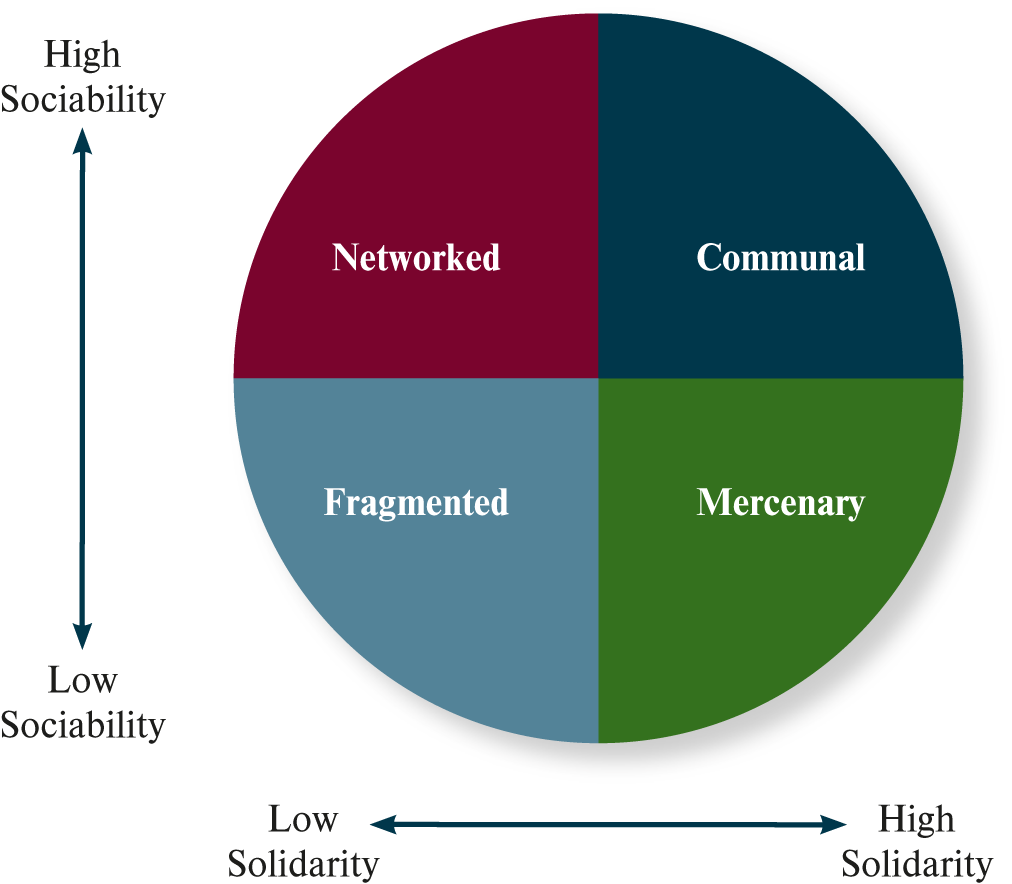
What is a fragmented culture?
low solidarity
low sociability
What is a mercenary culture?
high solidarity
low sociability
What is a networked culture?
low solidarity
high sociability
What is a communal culture?
high solidarity
high sociability
What is the organizational culture & organization size relation?
small: communal
v.s.
large: networked
… culture
What are some organizational culture examples?
service
safety
diversity
sustainability
creativity
… culture
What is the service culture process?
service-oriented leader behaviour
service culture
service-oriented employee behaviour
customer satisfaction
sale

What is perhaps the greatest safety culture lesson?
CEO sets priority
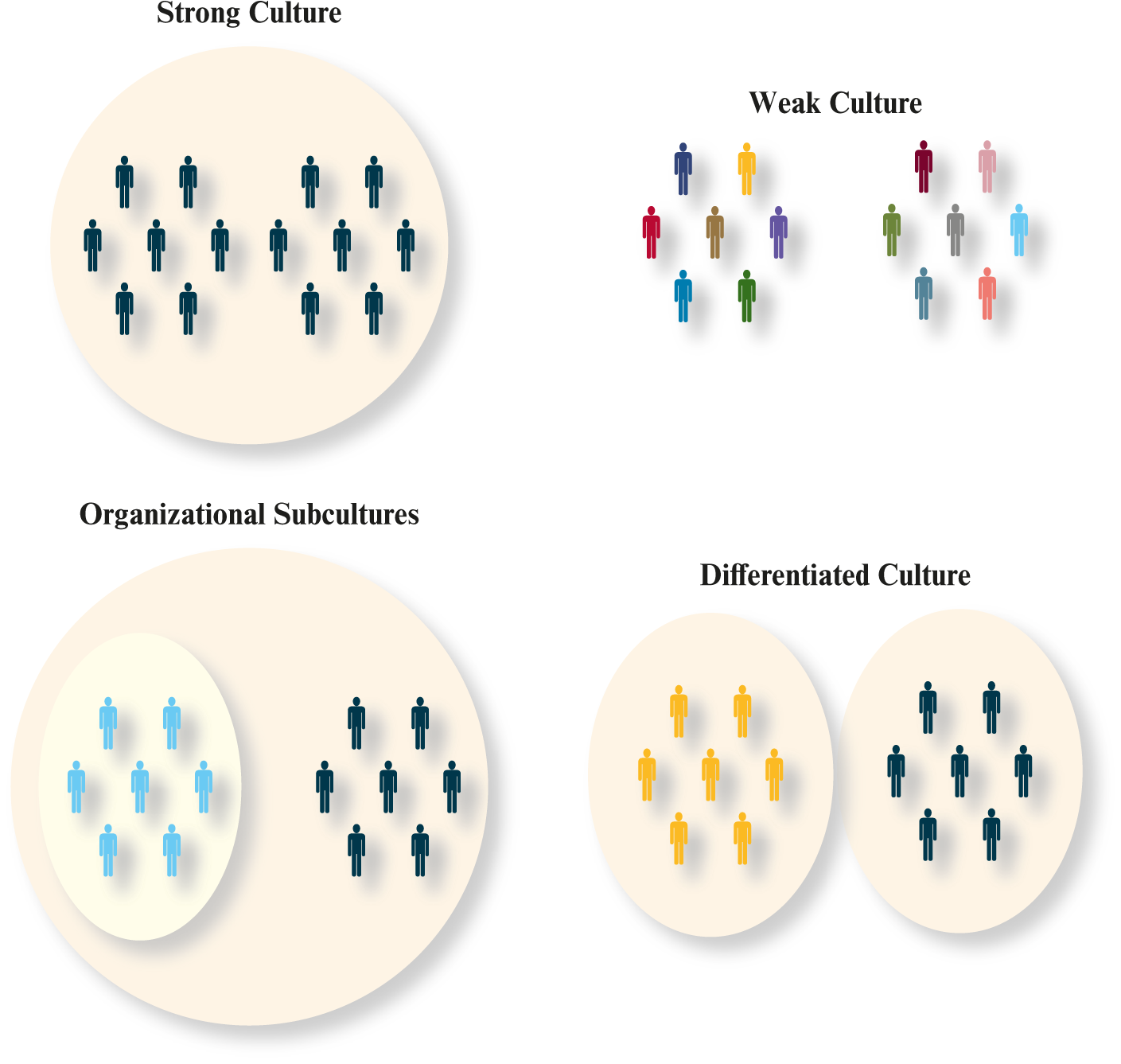
What is culture strength?
degree that employee agrees about how thing should happen & accordingly behave
What characterizes high culture strength?
high consensus
high intensity
What does culture strength do?
unite
direct
… employee
What are the culture strengths and subcultures?
strong
v.s.
weak
… culture strength
organizational
v.s.
differentiated
… subculture
What are some culture strength advantage examples?
organizational culture efficiency
differentiate
self-identify
facilitate
stabilize
What are some culture strength disadvantage examples?
adapt inability
difficult to merge & adapt
limit thought diversity
too much of good thing
What is the reason for subcultures?
leader & group engendering different norm
What is the reason for countercultures?
subculture value doesn’t match organization
What processes keep culture strength?
attraction-selection-attrition
socialization
What is attraction-selection-attrition?
|:| ASA
theory that employee will be drawn to culture matching
What is socialization?
process
employee learns social knowledge to adapt to organizational culture
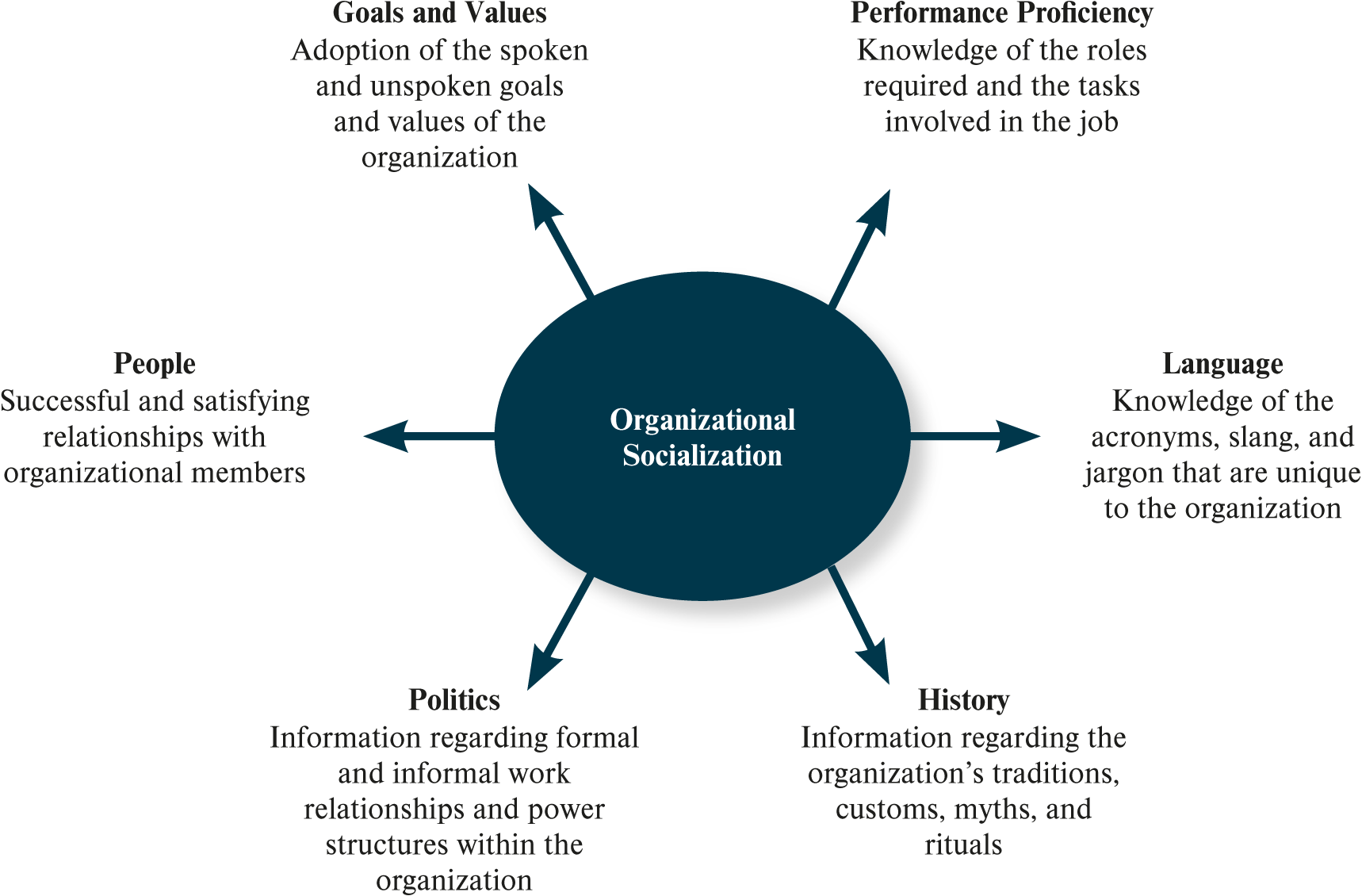
What ways are socialization dimensions important?
job performance
organization commitment
person-organization fit
What are the socialization dimensions?
goal / value
performance proficiency
language
history
politics
people
What are the socialization stages?
anticipatory
encounter
understanding / adaptation
What is the anticipatory stage?
socialization stage
potential employee develops work image
What is the encounter stage?
socialization stage
employee outside info v.s. inside info
reality shock
What is understanding & adaptation?
socialization stage
employee learns & internalizes norms
What explains why some organizations have different cultures?
What are the organization change stages?
unfreeze
change initiative
refreeze
W
What is unfreezing?
organization change stage
unacceptable status quo
What is change initative?
organization change stage
introduce new …
leader
reward
training
What is refreezing?
organization change stage
harden new attitude = new norm
What are the culture change attention questions?
if / what change = needed
if / what change = resisted
change appropriateness
if successful change
What is culture analysis’ primary focus?
gather / interpret info
interview
focus group
structured assessment
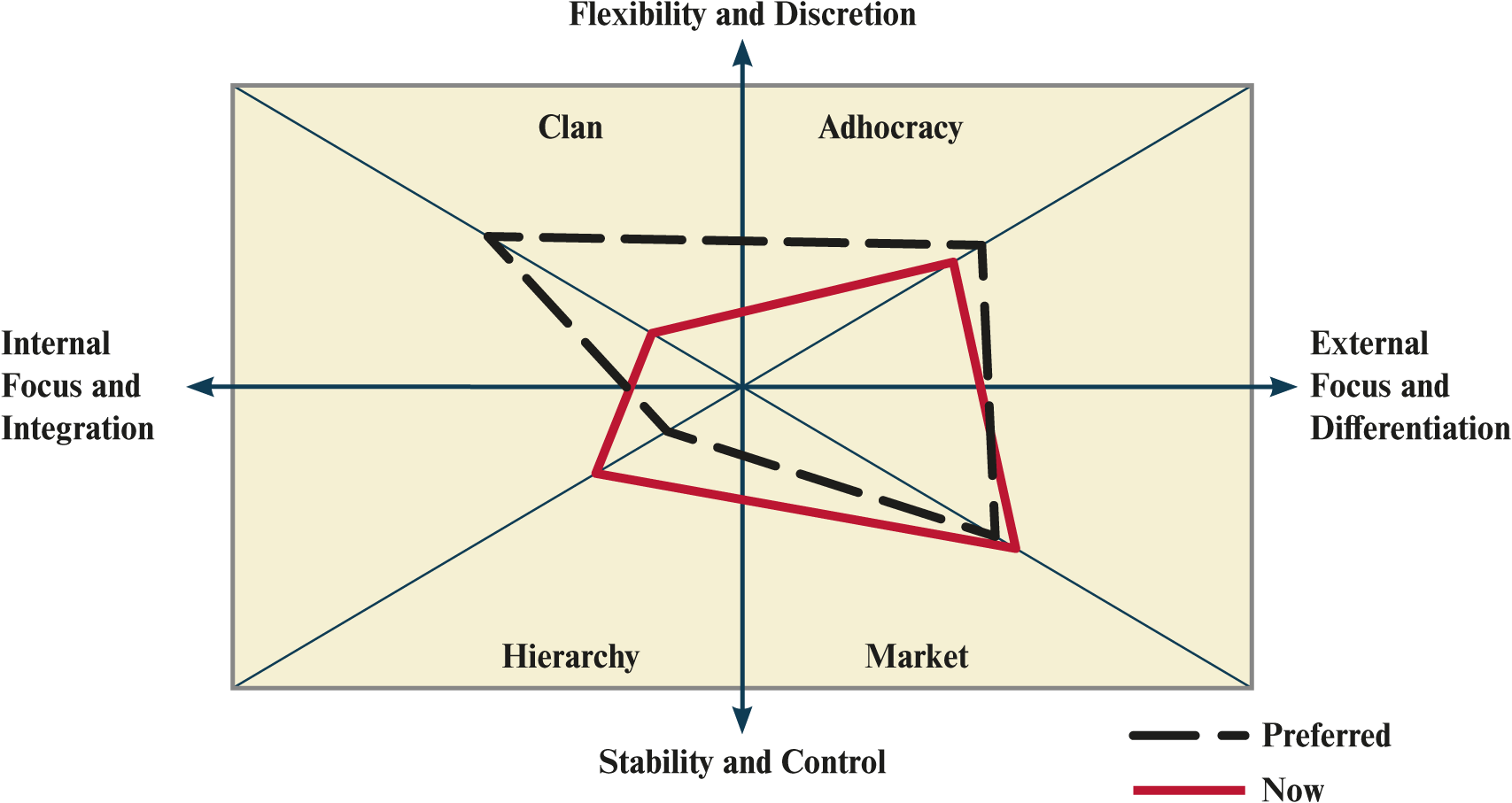
What is the OCAI?
structured approach
|:| organizational culture assessment instrument
categorize organization culture in relation to core value
What are the OCAI primary dimensions?
flexibility / discretion / dynamism v.s. stability / order / control
internally
integration
coordination
cohesion
externally
risk taking
entrepreneurship
results
differentiation
… oriented
What are the culture clusters?
clan
adhocracy
hierarchy
market
… -oriented
What is clan-oriented?
culture cluster
personal
mentor
nurture
participation
What are the clan-oriented dimensions?
flexibility / discretion
internal focus / integration
What is adhocracy-oriented?
culture cluster
dynamic
entrepreneurial
risk taking
innovation
What are the adhocracy-oriented dimensions?
flexibility / discretion
external focus / differentiation
What is hierarchy-oriented?
culture cluster
structure
control
coordination
efficiency
stability
What are the hierarchy-oriented dimensions?
stability / control
internal focus / integration
What is market-oriented?
culture cluster
results
competition
achievement
What are the market-oriented dimensions?
stability / control
external focus / differentiation
What is the OCAI diagnosis process?
depict 2 culture profiles
What explains why the majority of change efforts fail?
resistance
What are some resistance examples?
reduced …
… task performance
… citizenship behaviour
elevated …
… counterproductive …
… withdrawal …
… behaviour
culture properties
deviate from status quo
What can increase readiness?
involve member in plan
encourage participation
answer question
provide info
explain change importance
→ minimize apprehension & strengthen trust
What are the change interventions?
selection
training
performance management
leader change
mergers & acquisitions
What change interventions have low resistance & slow speed?
selection
training
What change interventions have moderate resistance & speed?
performance management
What change interventions have high resistance & fast speed?
leader change
mergers & acquisitions
What are selection advantages?
change value / skill / behaviour mix
What are selection disadvantages?
slow change
What are training advantages?
expand skill type / level
increase explicit / tacit knowledge
content / process flexibility
What are training disadvantages?
costly
slow implement
gradual change
What are performance management advantages?
focus on thing that matters most
facilitate learning
motivating
What are performance management disadvantages?
manager requires training
gradual change
erode motivation
win / lose culture
What are leader change advantages?
fast implement
What are leader change disadvantages?
disrupt existing relation
uncertainty
threat for some member
What are mergers & acquisitions advantages?
fast implement
What are mergers & acquisitions disadvantages?
difficult adjust
significant job loss
slow benefit
no way to know culture after
What answers the ‘if successful change’ question?
re-administer OCAI
assess change initiative effectiveness
look at organization evidence
What explains why culture change can be difficult to evaluate?
change initiative desired effect has poorly chosen metrics to detect
change initiative specific behaviour effect not detected using general measure
short timeframe measure might miss real change
What is a more realistic change approach?
diagnosis / analysis
intervention design / implementation
follow-up → facilitate learning
What is person-organization fit?
degree
personality / value = organization culture
What are the socialization approaches?
encourage …
strong culture
v.s.
discourage …
culture change
… adaptation
What are some encourage adaptation tactic examples?
orient newcomer with other
put newcomer through orientation apart from current member
provide hurdle prior to membership & role model
remind newcomer that they are part of group helping define who they are
What are some discourage adaptation tactic examples?
orient newcomer by themself
allow newcomer to interact with current member while oriented & membership regardless of whether requirement = met
use no example of what one’s supposed to be
affirm newcomer to be themself chosen for who they are
What are some other socialization examples?
RJP
orientation
mentor
What is RJP?
|:| realistic job preview
process
newcomer understands positive & negative aspect
What socialization stage does RJP occur?
anticipatory
What creates organizational culture?
external / internal shock
founder & employee value / action
industry demand
What plays a role in maintaining organizational culture other than ASA & socialization?
leader
employee
performance management
What is a systems approach?
organization = interdependent system where elements influence others
What are the system approach elements?
leadership
employee
communication
physical environment
process
What are other examples of how adapting elements can change organizational culture?
training
reward
symbol / story
What is 1 example of why DEI efforts might fail?
don’t tackle broad issue
What organization elements are integral for inclusion?
leadership
communication
training
What are some DEI intervention examples that rarely achieve change?
mandatory bias training
grievance system
top-down compliance
What proves effective in long-term inclusion?
voluntary engagement
mentorship
sponsorship
cross-functional / diversity task … team
→ ownership / accountability / momentum
In 1992, Schein introduced two causes of culture creation. These are... (Quiz)
Actions and values
Performance management and reward systems
Leaders and employees
External and internal shocks
According to one perspective, first introduced by Schein in 1992 - one of the early scholars of organizational culture - the culture of an organization is created through the process of encountering external and internal challenges (or "shocks")...
The American Institute of Architects (AIA) initiated culture change in response to what? (Quiz)
#Black Lives Matter
#Me Too
The deep water horizon oil spill
A hospital safety concern
It has been argued that organizations that have a _____________________ organizational culture benefit from it as a competitive advantage (Quiz)
rare and inimitable
weak
strong
competitive
Organizations that rank employees based on performance and give rewards only to high-ranking employees are likely to cultivate a _____________________ organizational culture. (Quiz)
collaborative
competitive
safety
creative
Which of the following is the correct definition of organizational culture, according to your textbook? (Quiz)
The knowledge within an organization regarding how the leader's values shape that of employees
The knowledge within an organization regarding how fellow colleagues' values shape that of employees
The shared social knowledge within an organization regarding the rules, norms, and values that shape the attitudes and values of employees
Individual differences in how employees think about the norms, rules, and values of the organization
In reference to artefacts of an organizational culture, which of the following is an example of a symbol? (Quiz)
Company's official motto
Company's logo
Art and paintings hung on the company's wall
All of the above
Which of the following best characterizes how culture can be shaped from the "bottom-up"? (Quiz)
Culture can be shaped by leaders' values and actions
Culture can be shaped by employees' values and actions
Culture can be shaped by external and internal schocks
Culture change can only occur within bottom levels of the organizational hierarchy
In reference to creating inclusive cultures, Catarina Rivera emphasized the ________________________. (Quiz)
Internal shocks
External shocks
Conversations between coworkers
Physical environment
The physical environment and accessibility in particular
According to the systems approach to organizational culture change, all of the following are elements of an organization that are important to consider for culture change EXCEPT: (Quiz)
Leadership
Employees
Physical environment
None. All of the above are elements
When referring to processes that maintain organizational culture, what does the acronym ASA stand for? (Quiz)
Attraction-selection-attrition
Socialization
Attrition-selection-attraction
Association for social adaptation