UCM Quiz - Hon Physics Review
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
The time that it takes to complete one time around a circular path
Period (T), measured in seconds
Formula for speed in uniform circular motion
V= 2(pi)r/T
Formula for centripetal acceleration based on speed and radius
A=v²/r
When an object travels in a curved path, the velocity vector is always pointing ______ to the curve.
Tangent
Centripetal means…
“Center seeking“
The direction of acceleration during circular motion is
Towards the center of the circle
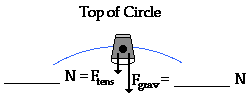
The object has a mass of 1.5kg and is moving 4 m/s at the top of a loop with a 1m radius. Determine the acceleration, net force, weight, and tension force.
A= 16m/s², down; Fnet = 24N, down; Fgrav = 14.7N, down; Ftens = 9.3N, down
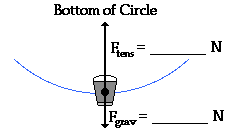
The 1.5kg object is moving 6m/s at the bottom of a loop with a 1m radius. Determine the acceleration, net force, weight, and tension force.
A= 36m/s², up; Fnet= 54N, up; Fgrav= 14.7N, down; Ftens= 68.7N, up
Write Newton’s 2nd Law for an object moving at constant speed v around a circle with radius r.
Fnet = mv²/r
Which force causes centripetal acceleration when a car travels around a flat, circular road?
Friction
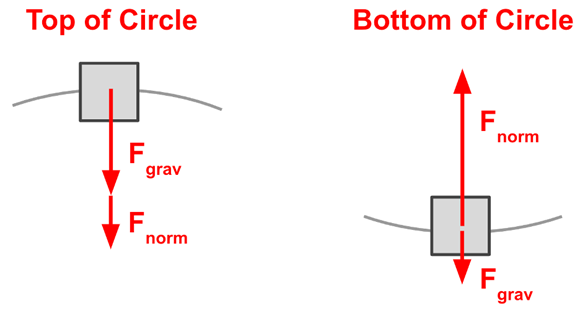
What is a situation that could produce the following two free body diagrams (FBD)?
Roller coaster with a loop (the seats would have to be upside down at the top in order to produce a downward normal force)
What happens to centripetal acceleration when speed doubles but radius stays the same?
Acceleration increases by a factor of 4
What happens to centripetal acceleration when speed stays constant but radius doubles?
Acceleration gets cut in half
What must be happening if an object that is moving at a constant speed is also accelerating?
Its direction of motion is changing
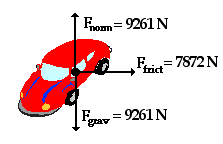
For the car shown, what is its mass? What is its acceleration? If the frictional force makes it go around a circle with radius of 35m, how fast is it going?
M= 945kg; a= 8.33m/s²; v=17.1 m/s
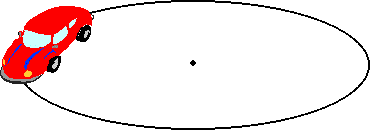
If you were riding in the car shown, which direction is closest to the direction of the net force acting on you at this moment-left, right, up, down, forward, backward?
Right
When an object on the end of the string is whirled in a vertical circle, is the tension at the bottom of the circle greater than, less than, or equal to the weight of the object?
Tension is greater than the weight so that the net force is pointing upwards, which is the direction of centripetal acceleration at this point
What is the magnitude of acceleration for an object traveling at a constant speed of 10m/s while going around a circular path with a radius of 25 meters?
4m/s²
When a car travels over the top of a hill, is the normal force on the car greater than, less than, or equal to its weight?
The normal force is less than the weight so that the net force points down, which is the direction of the centripetal acceleration at this point
From a physics perspective, why is it bad to have curved roads with a small radii of curvature?
Small radius makes centripetal acceleration big, meaning large forces are required to keep cars on these curved paths