(MTM) MCB 2.7 - DNA Damage Mutation Repair
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
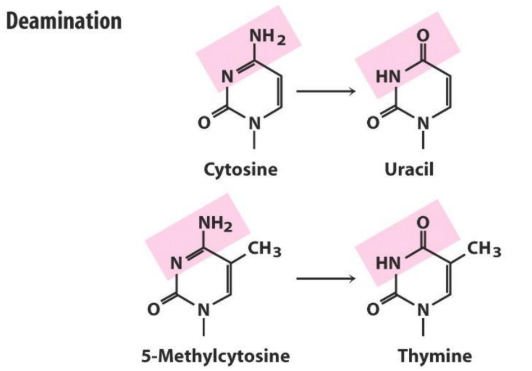
cytosine to uracil
in spontaneous dna damage, deamination is a loss of an amino group on the base, usually ___ to ___
thymine
-5’-CG-3’ sequences have a tendency to mutate to 5’-TG-3’
-MUTATION HOTSPOTS
when 5’ methylcytosine (DNA methylation) is deaminated, it becomes ___
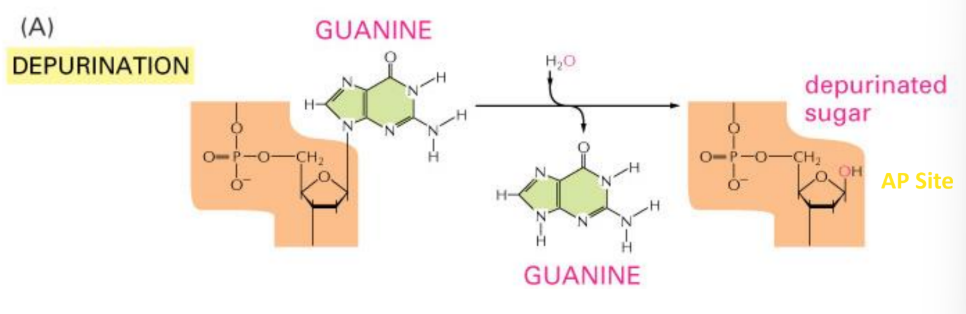
depurination
in spontaneous dna damage, ___is a loss of an entire purine and creates an AP site
methyl
methylguanine
in induced DNA damage, alkylating agents add ___ groups to bases. ____ mis-pairs with T (instead of cytosine) resulting in replication errors
insertions, deletions, and frameshifts
in induced DNA damage, intercalating agents (planar molecule) slide between bases, pushing them apart resulting in ___,___, and ____
free radicals
in induced DNA damage, ionizing radiation such as x rays and gamma rays generate ___ that introduce double strand breaks
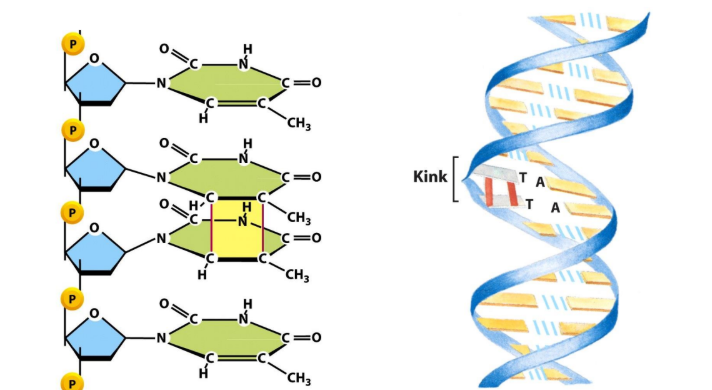
pyrimidine dimers
covalent
in induced DNA damage, UV rays causes ____ which introduces ___bonds on the same strand
phosphodiester
in induced DNA damage, ROS cleaves ____ bonds which breaks single and double stranded DNA
mutagenesis
The process by which a stable change in the genetic information of an organism occurs
null mutation
what type of mutation results in a complete loss of function or a completely nonfunctional protein is produced
partial loss of function mutation
A mutation that reduces but does not completely eliminate the protein activity
loss of function
Complete or partial decrease in protein activity
gain of function
Increase in protein activity, or creation of a new activity
dominant negative mutations
type of mutation that result in mutated proteins that interfere or block the function of wild type protein
Dominant Negative > Null > Partial loss of function
order these from most severe to least severe clinical presentation:
null
partial loss
dominant negative
Genome > Chromosomal > Gene
order from most common type of level mutation to least:
genome
gene
chromosome
silent mutation
-nucleotide has changed by the codon for the protein is the same
mutation that does not alter the amino acid sequence of a protein
Nonsense mutation
mutation that introduces stop codon
null
nonsense mutation in eukaryotes result are considered __ due to mRNA degradation
conservative missense
a mutation where the mutated amino acid has similar properties to the original amino acid
nonconservative missense
a mutation where the mutated amino acid is different than the original
non-stop mutations
a mutation that replaces a stop codon with an amino acid coding codon resulting in longer proteins
null mutations
splice site mutations result in insertions or deletions in the coding sequence that results in a frameshift. they introduce premature termination codons and result in mRNA degradation and are usually ___ mutations
5’ end
GU
splice donor is at the ___ end of the intron and the bases are __
3’ end
AG
splice acceptor is at the ___ end of the intron and the bases are __
acceptor
intron retention is when a splice ___ is lost and an intron is retained in the mRNA
acceptor
exon skipping is when a splice ___ is lost and an exon is removed in the mRNA
cryptic splice site
a new splice acceptor or donor site, causing abnormal mRNA splicing. This is caused by a single base mutation
frameshift
-Null mutation
-premature termination codon (PTC)
a mutation that the number of bases inserted or deleted is NOT a multiple of 3
short tandem repeat
___ sequences (microsatellites /VNTRs) are prone to expansion or contraction as they are passed from parent to offspring
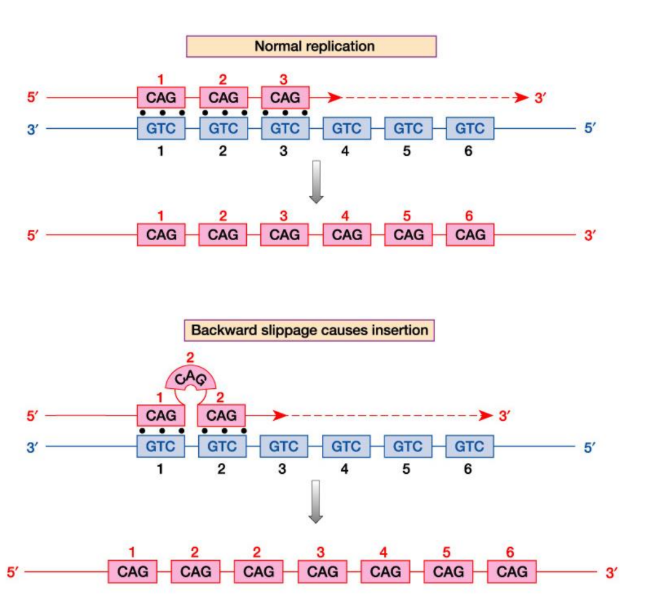
expansions
in replication: Backward slippage in slipped-strand mispairing results in ___
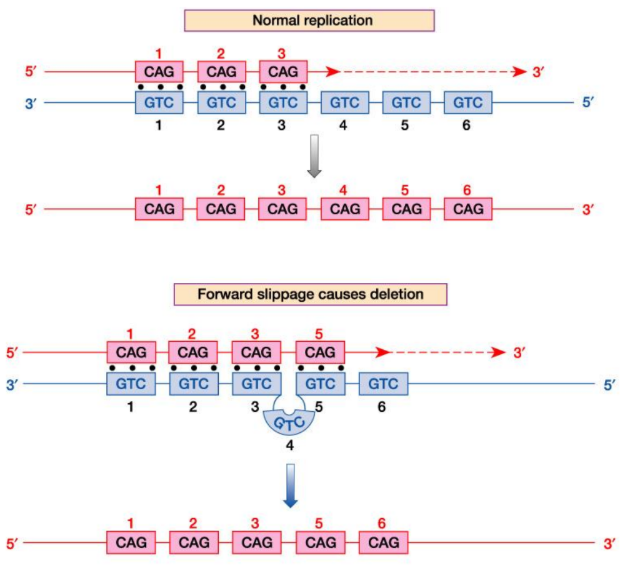
Contractions
in replication Forward slippage in slipped-strand mispairing results in ___
mismatch repair
-corrects slippages in tandem repeats
corrects replication errors (wrong bases or small insertions/deletions) by excising the newly made DNA segment and replacing it
detecting differential hemi-methylation of adenine in the old (correct) strand
-Mut factor
mismatch repair in prokaryotes can distinguish the old (correct) strand from the incorrect (new) by ___
Mut factor
in mismatch repair of prokaryotes, what factor recognizes the hemi-methylation of the old (correct) strand and nicks the new strand
MSH and MLH
in mismatch repair of eukaryotes, what repair proteins recognize the single strand DNA break of the new strand
MSH and MLH
expansions
lynch syndrome is due to a mutation in which repair proteins which causes microsatellite ____ that were supposed to be corrected
colorectal cancer
Lynch syndrome or HNPCC has an increased risk for ____ cancer
bulky
-example:
pyrimidine dimers (UV rays)
bulky adducts
nucleotide excision repair (NER) corrects ____ damage to a (single or double) strand of DNA
XPB and XPD helicase
in NER, which enzymes remove the bulky damage?
UV-induced pyrimidine dimers
xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) is caused by a mutation in the XP genes which results in the inability to remove ___
Base excision repair (BER)
repairs specific bases that were deaminated, alkylated, depurinated, and oxidized
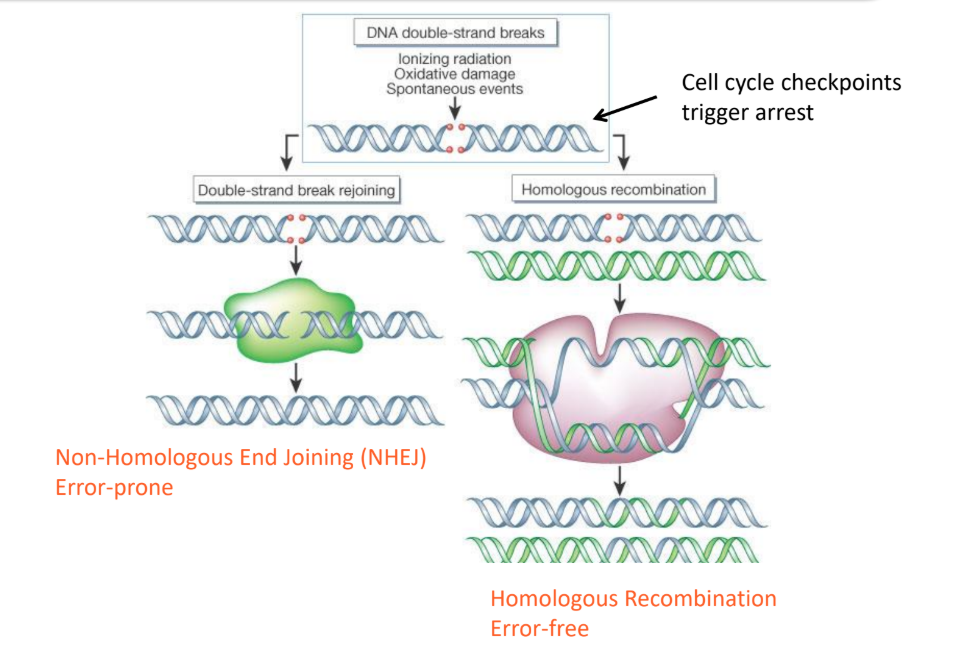
non-homologous end joining (NHEJ)
is an error-prone mechanism to repair double stranded DNA breaks
-the ends are directly joined
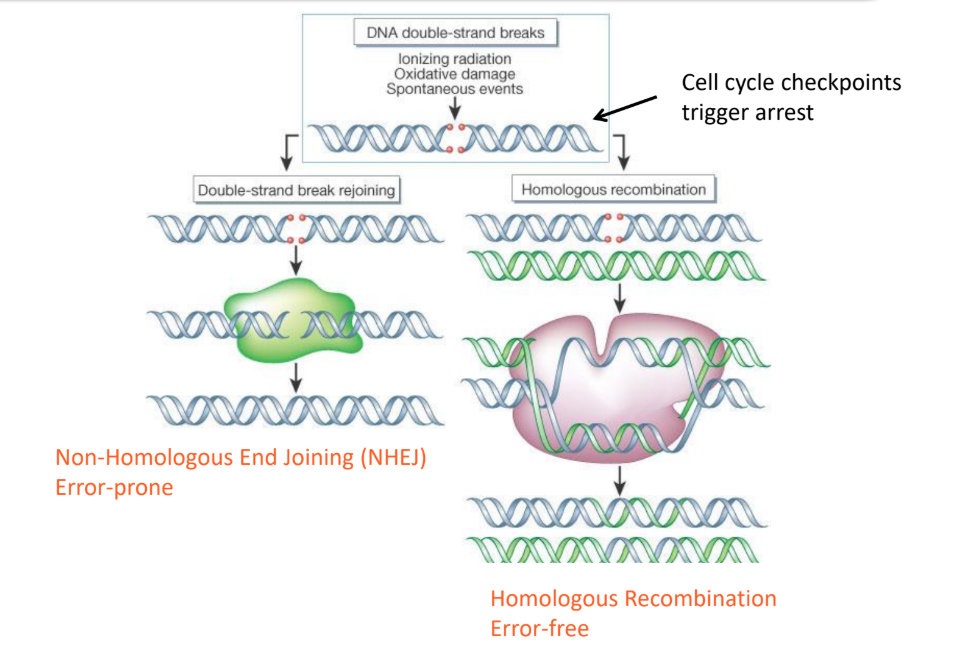
homologous recombination
repairs double-strand breaks accurately by using a sister chromatid as a template through strand invasion and DNA synthesis.
BRCA1 and BRCA2
in homologous recombination, what genes are involved in dsDNA break repair?
BRCA1 and BRCA2
breast cancer is due to a mutation and loss of function of which genes?
NBM
in Nijmegen Breakage Syndrome, the ___ gene that encodes for nibrin is mutated which prevents the repair of dsDNA
autosomal recessive
Chromosome Instability Syndromes are all what type of mode of inheritance?
nondisjunction
most common cause of aneuploidy is ___
unequal crossing over
most common cause of chromosomal rearrangement is ____
ATM
-cell does pause for repair (fails checkpoint)
Ataxia Telangiectasia has a defect in the ____ protein that detects dsDNA. Therefore in homologous recombination, it is unable to repair the dsDNA
BLM
bloom syndrome has a mutated ___ genes that causes increased sister chromatid exchange
WRN
Werner syndrome has a mutated ___ gene that shortens telomeres
FA
fanconi anemia has a mutated ____ genes which causes increased interstrand crosslinks