Respiratory and Metabolic Diseases of Sheep and Goats
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Ovine Progressive Pneumonia (OPP)/Maedi- Visna
Retrovirus- life long infection
Transmission: OPP
Direct contact
Fomites
Feed/water
Milk/Colostrum**
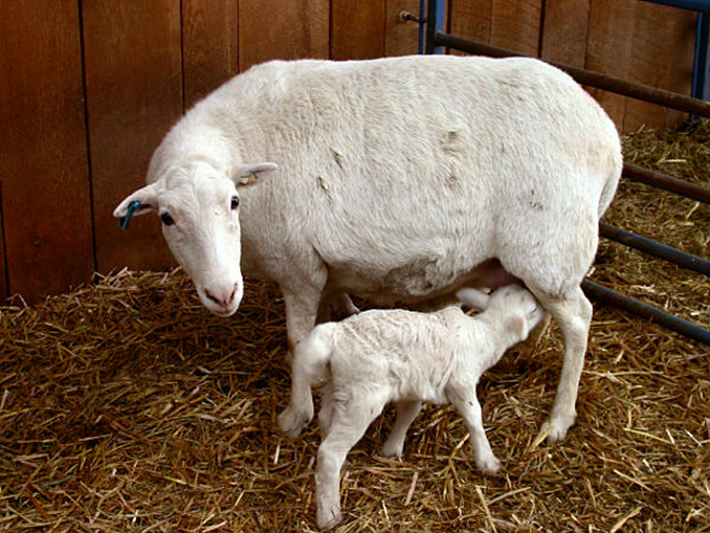

Clinical Signs: OPP
“Thin ewe syndrome”
Progressive pneumonia
“Hard bag”
Lameness
Posterior paresis
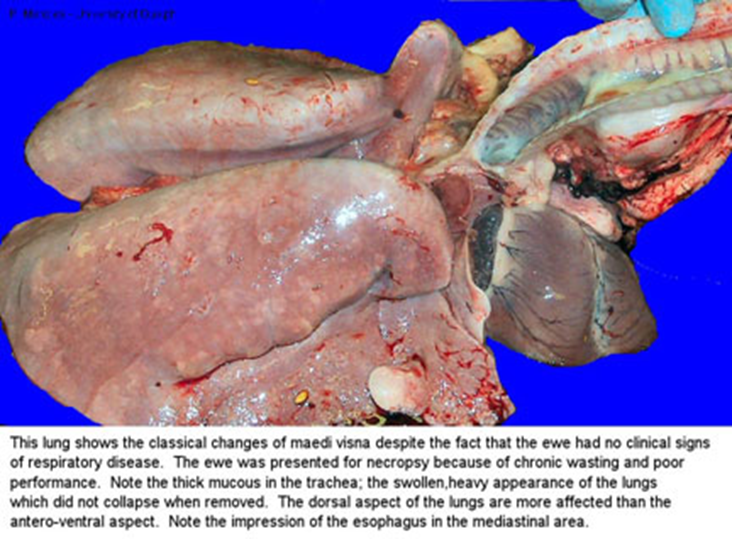
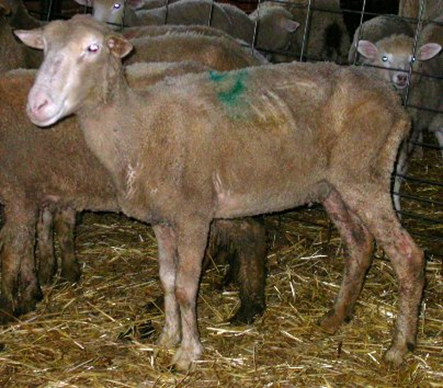
Treatment/Prevention: OPP
NONE
Most die within a year of first exhibited

Nutritional Myodegeneration (White muscle disease)
Selenium and/or Vitamin E deficiency
cardiac and skeletal muscle disease
Lambs, calves, kids, foals

Clinical signs: White muscle disease
Cardiac syndrome- sudden death
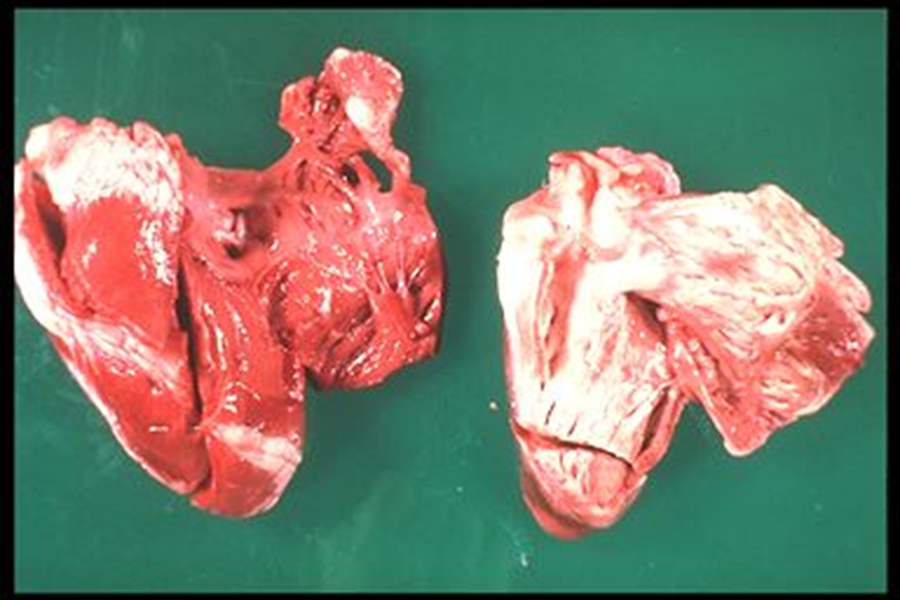
Skeletal muscle syndrome: slower onset
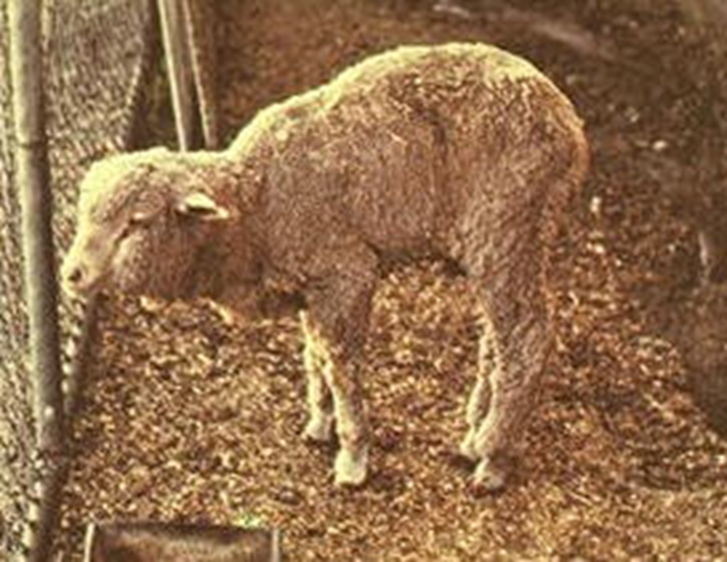

Treatment/Prevention: White Muscle Disease
Cardiac syndrome
NONE
Skeletal muscle syndrome
Bo-Se
Prevention
Supplementation
Periodic blood sampling
Properly prepared and store hay/grain
Access to high-quality green forage- Vitamin E
Copper Toxicosis
Growing lambs most susceptible
Copper accumulation —> liver damage —> Stress —> Massive amts of Cu released —> Interference w/ RBC membrane proteins —> —> HEMOLYSIS
Clinical Signs: Copper Toxicosis
Jaundice
Anemia
Weakness
Sudden death
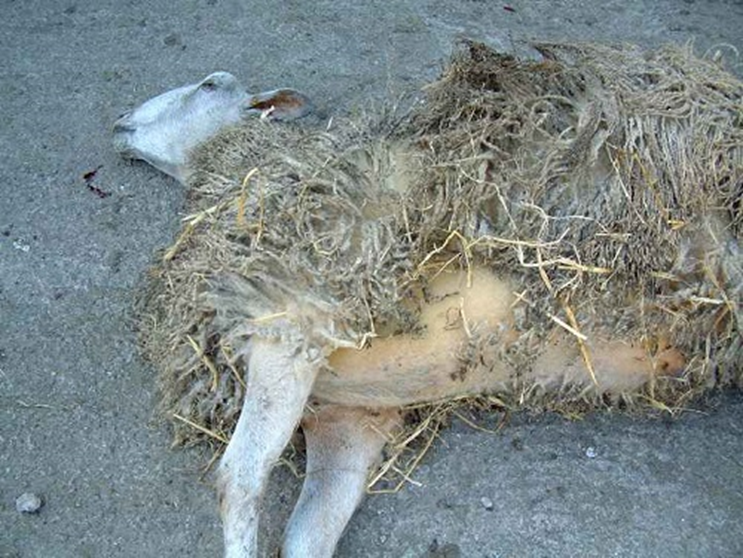
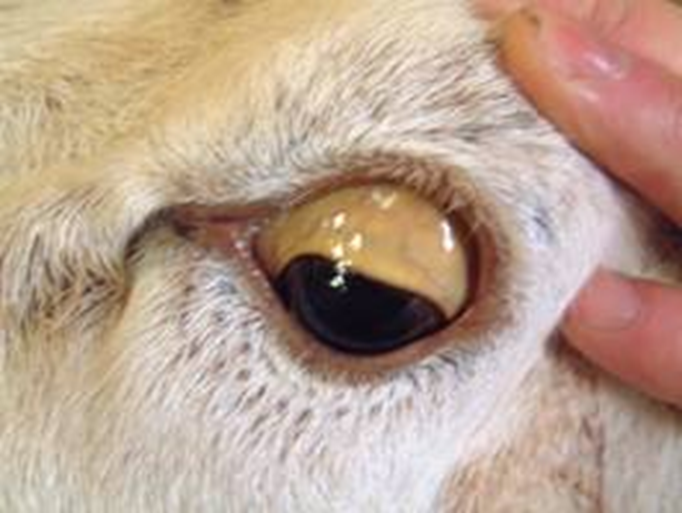

Treatment/Prevention: Copper Toxicosis
IV fluids
Oxygen
Blood transfusion
Chelator therapy
Supplement with Molybdenum

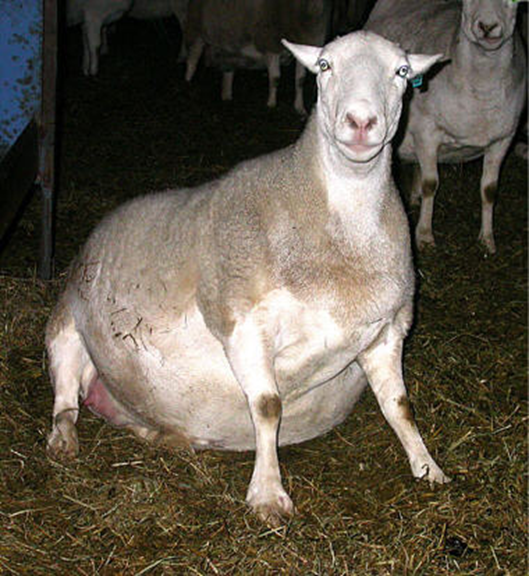
Pregnancy Toxemia of Ruminants (Twin lamb disease; Ketosis)
Thin/Obese ewes
Carrying multiple fetuses
Stress precipitates
Bad weather
Shipping
other
Late gestation
Pregnancy Toxemia- Pathogenesis
Inadequate energy intake in late gestation —> decrease blood glucose level —> Depletion of liver glycogen reserves —> Mobilization of stored fat as NRG sources —> Formation of ketones (toxic byproducts) in bloodstream —> Metabolic acidosis and CNS toxicity
Clinical Signs: Pregnancy Toxemia
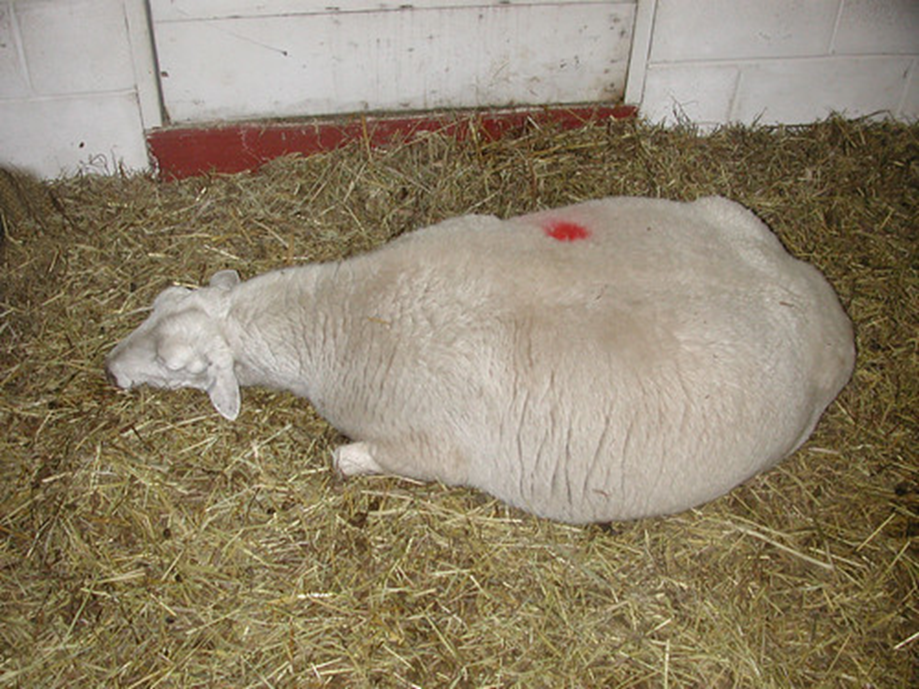

Treatment/Prevention: Pregnancy Toxemia
Treatment
C-section* esp if neurologic, thin or fat
Cannot manage fetal demands in late pregnancy
Glucose PO or IV
Propylene glycol
Change diet slowly
Grave prognosis in recumbent ewes
Prevention
Don’t let ewes become fat
Progressive increase of plane of nutrition during last 1/3 gestation
Exercise

Guinea Pig Pregnancy Toxemia
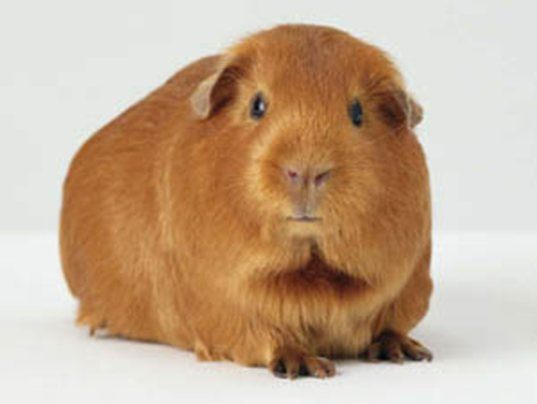

Circulatory- Preeclampsia
Abnormal vascular changes that lead to ischemia of the uteroplacental unit
Metabolic- nutritional form
Fasting/anorexia