Bios 1300 Exam 4
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/180
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:57 AM on 11/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
181 Terms
1
New cards
What does muscle contraction depend on?
ATP... No other energy source can serve its place
2
New cards
What does the supply pf ATP depend on?
Availability of O2
Organic energy :glucose, fatty acids, glycogen)
Organic energy :glucose, fatty acids, glycogen)
3
New cards
What are the two ways that ATP is synthesized?
Aerobic fermination
Aerobic respiration
Aerobic respiration
4
New cards
What do we have to have ATP for?
-for cross bridge contraction formation and release
-Pump Ca+2 back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum
-Na+/ K+ pumps
-Pump Ca+2 back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum
-Na+/ K+ pumps
5
New cards
What happens when you take the P off of ADP and add it to another ADP?
the ADP with added P becomes AMP and ADP
6
New cards
Immediate ATP source
-Phosphogen System
-borrows Phosphate groups from other MC and transfers then to ADP
-this happens in two methods
1.take P from ADP transfers to another ADP making AMP and ATP
2.Takes creatine P. trans. to ADP making creatine and ATP
-borrows Phosphate groups from other MC and transfers then to ADP
-this happens in two methods
1.take P from ADP transfers to another ADP making AMP and ATP
2.Takes creatine P. trans. to ADP making creatine and ATP
7
New cards
1st method for immediate ATP source: Phosphogen system
-Takes P from ADP and transfers it to another ADP molecule
-Makes AMP and ATP
ENZYME: myokinose
-Makes AMP and ATP
ENZYME: myokinose
8
New cards
2nd method from immediate ATP sources: Phosphogen system
-Takes from creatine phosphate and transfer it to ADP
-creates creatine and ATP
-ENZYME: creatine kinase= pull PO4 off CP & adds to ADP
-muscle contains LARGE amounts of this enzyme
-creates creatine and ATP
-ENZYME: creatine kinase= pull PO4 off CP & adds to ADP
-muscle contains LARGE amounts of this enzyme
9
New cards
What source of making ATP is very limited and how long does it give energy for?
Immediate Source: Phosphogen System
10- 15 seconds for intense exercise
*Not dependent on availability of O2*
10- 15 seconds for intense exercise
*Not dependent on availability of O2*
10
New cards
Anaerobic Fermination
-requires no O2
-short term energy supply
-causes build up of lactic acid which contributes to muscle fatigue
-short term energy supply
-causes build up of lactic acid which contributes to muscle fatigue
11
New cards
Aerobic Respiration
-produces far more ATP that anaerobic fermentation
-NO LACTIC ACID
-requires a continual supply of O2
-glucose oxidations
-extracts ATP from other organic sources
-NO LACTIC ACID
-requires a continual supply of O2
-glucose oxidations
-extracts ATP from other organic sources
12
New cards
Short term energy= steps
-glycogen- lactic acid system
-until cardiopulmonary sys. can catch up... anaerobic ferm. takes over
-blood glucose= obtained from blood and glycogen is utilized from storage
-muscle cell undergoes anaerobic gylcolisis (in cytoplasm)
-Lactic acid is generated as byproduct
-only produces enough energy from 40 seconds
-until cardiopulmonary sys. can catch up... anaerobic ferm. takes over
-blood glucose= obtained from blood and glycogen is utilized from storage
-muscle cell undergoes anaerobic gylcolisis (in cytoplasm)
-Lactic acid is generated as byproduct
-only produces enough energy from 40 seconds
13
New cards
How many ATP yield during anaerobic glycolysis
-2 ATP yield from breakdown of 1 glycogen molecule
-requires no O2
-requires no O2
14
New cards
Steps during long term energy
-aerobic respiration
-provided by aerobic cellular respiration occurring in the mitochondria
-nutrient source : glucose and fatty acids from triglyceride.
-requires O2
-CO2 is by- product
-36 ATP produced from one glucose molecule
-utilized for light exercise and rest *fatty acids*
-provided by aerobic cellular respiration occurring in the mitochondria
-nutrient source : glucose and fatty acids from triglyceride.
-requires O2
-CO2 is by- product
-36 ATP produced from one glucose molecule
-utilized for light exercise and rest *fatty acids*
15
New cards
What nutrient is required during aerobic fermentation?
glucose and fatty acid from triglycerides
(broken down)
(broken down)
16
New cards
What happens with triglyceride during intense exercise?
-triglyceride doesn't break down fast enough to provide enough ATP to supply energy
*must rely on blood glucose*
*must rely on blood glucose*
17
New cards
Glycogen Depletion
-hits the wall feeling in 400m race
18
New cards
What increases during muscle fatigue?
-PO4 ion concentration from phosphogen system
-interferes with Pi release from the myosin heads and CA+2 released from SR
-interferes with Pi release from the myosin heads and CA+2 released from SR
19
New cards
Nervous Fatigue
-in untrained people
-nerve is unable to sustain the high frequency signal
-nerve is unable to sustain the high frequency signal
20
New cards
Fatigue is not caused by what?
An ATP lack
21
New cards
How are muscles classified?
-contraction speed and resistance to fatigue
22
New cards
What determines muscle contraction speed?
the form of myosin in each type
23
New cards
What contributes to oxygen diffusion in muscle fibers?
the thickness of the muscle fiber and amount of blood vessels
24
New cards
Slow twitch fibers
-type 1 (slow oxidative fibers)
-slow twitch myosin splits ATP slowly
-doesn't return calcium to the SR quickly
-rely on AEROBIC metabolism to get ATP
-have more mitochondria
-resist fatigue
-RED= more blood vessels to deliver more O2
-diffusion of O2 from the BV of cell is faster
-muscle fiber is THINNER
-increased dwarfism
-slow twitch myosin splits ATP slowly
-doesn't return calcium to the SR quickly
-rely on AEROBIC metabolism to get ATP
-have more mitochondria
-resist fatigue
-RED= more blood vessels to deliver more O2
-diffusion of O2 from the BV of cell is faster
-muscle fiber is THINNER
-increased dwarfism
25
New cards
Fast twitch fibers
-type 2 (glycotic fibers)
-splits ATP quickly
-stores more glycogen
-generates quick twitch which results in more contractile cycles in a given time
-ANAEROBIC termination for ATP sources
-have less blood vessels
-diffusion of O2 from BV to muscle fibers is slower
-THICKER
-WHITE
-splits ATP quickly
-stores more glycogen
-generates quick twitch which results in more contractile cycles in a given time
-ANAEROBIC termination for ATP sources
-have less blood vessels
-diffusion of O2 from BV to muscle fibers is slower
-THICKER
-WHITE
26
New cards
Are muscles only fast twitch or slow twitch?
-all muscles have both fibers in them
27
New cards
Is smooth muscle voluntary or involuntary?
involuntary= no conscious control
28
New cards
Where is smooth muscle found?
hollow organs and tissues
29
New cards
Smooth muscle
-capable of hypertrophy and hyperplasia and mitosis
-increases number of cells in pregnant women
-involuntary
ex: dermis, eye, organs
-increases number of cells in pregnant women
-involuntary
ex: dermis, eye, organs
30
New cards
Microscopic anatomy of smooth muscle
-small and fusiform
-no striations
-ends overlap the larger middle area of adjacent cell
-no T tubeless or motor end plate
-no motor unit
-sparse sarcoplamsic reticulum (holds Ca+2 ions)
-no striations
-ends overlap the larger middle area of adjacent cell
-no T tubeless or motor end plate
-no motor unit
-sparse sarcoplamsic reticulum (holds Ca+2 ions)
31
New cards
What is the fuel of aerobic exercise?
Fatty acids
(talking while we are exercising)
(talking while we are exercising)
32
New cards
Tryptophan
-amino acid
-makes you tired
-has to be converted into a different MC
-crosses the blood brain barrier
*converted in the brain into SEROTONIN*
(causes tiredness)
-makes you tired
-has to be converted into a different MC
-crosses the blood brain barrier
*converted in the brain into SEROTONIN*
(causes tiredness)
33
New cards
If you increase the intensity of a nerve A.P. will this change the contraction strength of twitches?
No... ALL OR NONE METHOD
34
New cards
If you increased the length of the muscle will the contract. strength twitch change?
Yes... about length tension relationship
35
New cards
If you increase the temperature of a muscle will the contraction strength twitch change?
Yes... a warmer muscle increases in temp. causes enzymes to work faster and increase speed of cross bridge formation.
36
New cards
If you change the state of muscle hydration will this alter the contraction strength of the twitch?
Yes... dehydration= less blood flow and nutrients to that muscle.. decrease O2..
-lose intRAcellular H2O
-lose intRAcellular H2O
37
New cards
If you change the pH of a muscle will this affect the contraction strength of muscle twitches?
Yes... pH of SR decreases- increase of [H+] ions
-changes the shapes of proteins
-troponin> Ca+2
-lactic acid form O2
-changes the shapes of proteins
-troponin> Ca+2
-lactic acid form O2
38
New cards
Is smooth muscle always innervated?
No
39
New cards
What is smooth muscle with nerve supply called?
Autonomic Nervous System
40
New cards
What is the parasympathetic nervous system neurotransmitter?
ACh
-relaxing and calming NS
-relaxing and calming NS
41
New cards
What is the sympathetic N.S. neurotransmitter?
NE
-norepinephrine
- "fight or flight NS"
-norepinephrine
- "fight or flight NS"
42
New cards
Explain contraction of Smooth Muscle
-contraction can be slow
-stays contracted for a LONG period of time
EX: bladder maintaisn tension for extended period of time
-stays contracted for a LONG period of time
EX: bladder maintaisn tension for extended period of time
43
New cards
How is smooth muscle classified?
How it's activated
-multi- unit
-single- unit
-multi- unit
-single- unit
44
New cards
Multi- Unit smooth muscle contraction
-each myocyte contracts independently
-single cell contraction
-not linked electrically through junction
-relies on neuron
-EX: B.V., iris, arrector pili muscle
-single cell contraction
-not linked electrically through junction
-relies on neuron
-EX: B.V., iris, arrector pili muscle
45
New cards
Single- Unit smooth muscle contraction
-contracts as a unit
-connected electrically to each other via gap junctions
-AP spreads out
EX: visceral smooth muscle
-connected electrically to each other via gap junctions
-AP spreads out
EX: visceral smooth muscle
46
New cards
Electrical excitation of smooth muscle
-autonomic fibers
-neuron stimulates
-neuron stimulates
47
New cards
What are the modes of excitation for smooth muscle?
electrical means
chemical means
temperature
stretch
audtorhythmicity
chemical means
temperature
stretch
audtorhythmicity
48
New cards
Chemical means excitation of smooth muscle
-hormones (oxytocin and epinephrine)
-histamine (releases nitric oxied)
-nitric oxide
-low pH (acidosis contraction )
-histamine (releases nitric oxied)
-nitric oxide
-low pH (acidosis contraction )
49
New cards
What are the hormones that chemically excite smooth muscle?
-oxytocin- labor contraction of uterus
-epinephrine- releases smooth muscle overlap in tract B.V. in ost visceral organs
-epinephrine- releases smooth muscle overlap in tract B.V. in ost visceral organs
50
New cards
Oxytocin
labor contraction of uterus
51
New cards
Epinephrine
releases smooth muscle
overlaps BV of most visceral smooth muscle
overlaps BV of most visceral smooth muscle
52
New cards
how does nitric oxide excite smooth muscle
-gas is synthesized in endothelial
-vasoconstrictor and releases nitric oxide & caused reaction to allow muscle to contract
-vasoconstrictor and releases nitric oxide & caused reaction to allow muscle to contract
53
New cards
How does temperature excite smooth muscle?
cold- stimulates smooth muscle (arrector pili, scrotum, areola)
heat- releases
heat- releases
54
New cards
How does stretch excite smooth muscle
-smooth muscle is NOT subject to length- tension- relations
-it contracts fully when it's stretched (bladder, uterus)
-NO z- discs to prevent additional shortening and no lack of myosin heads in the center or thick filaments
-it contracts fully when it's stretched (bladder, uterus)
-NO z- discs to prevent additional shortening and no lack of myosin heads in the center or thick filaments
55
New cards
What does smooth muscle lack that skeletal muscle has ?
-length tension relationship
-Z- discs
-Z- discs
56
New cards
How does audtorhythmicity excite smooth muscle?
-myocytes act as pacemaker cells that spontaneously depolarize @ regular time intervals
EX: intestines- no innervation needed
EX: intestines- no innervation needed
57
New cards
Is there troponin in smooth muscle?
No
58
New cards
Steps of smooth muscle contraction?
-Ca+2 from SR & entry of Ca+2 into cell binds to protein called calmodulin (CaM)
-this activates an enzyme on myosin to split ATP into ADP and Pi (hydrolyze)
-causes sliding of thin filaments over thick filaments, actin attaches to dense bodies on P. membrane
-Relaxation of smooth muscle is slow
-this is important b/c smooth muscle must continuous tone
-very fatigue resistant
-this activates an enzyme on myosin to split ATP into ADP and Pi (hydrolyze)
-causes sliding of thin filaments over thick filaments, actin attaches to dense bodies on P. membrane
-Relaxation of smooth muscle is slow
-this is important b/c smooth muscle must continuous tone
-very fatigue resistant
59
New cards
Does contraction of smooth muscle pull on cell membrane at many diff. junctions at once or single junctions at once?
Multiple junctions at once
60
New cards
Is continuous conduction in unmyelinated axons fast or slow?
Slow
61
New cards
Axolemma
Axoplasm
Axoplasm
plasma membrane of motor neuron
CYTOPLASM
CYTOPLASM
62
New cards
what is needed for axonal transport?
-proteins made in the soma
-needed by the axon
-needed to return back to the cell body for recycling
-needed by the axon
-needed to return back to the cell body for recycling
63
New cards
Fast axonal transport
anterograde= away from cell body (material required for synapse)
retrograde= toward cell body (harmful waste materials)
-400 mm a day
-movement along microtubules
- "train track" increased ATP needs
retrograde= toward cell body (harmful waste materials)
-400 mm a day
-movement along microtubules
- "train track" increased ATP needs
64
New cards
Slow axonal transport
-0.1- 3mm a day
-results from flow of axoplasm
-ONLY anterograde movement
-development of regenerating neurons
-enzymes, no axolemma
-results from flow of axoplasm
-ONLY anterograde movement
-development of regenerating neurons
-enzymes, no axolemma
65
New cards
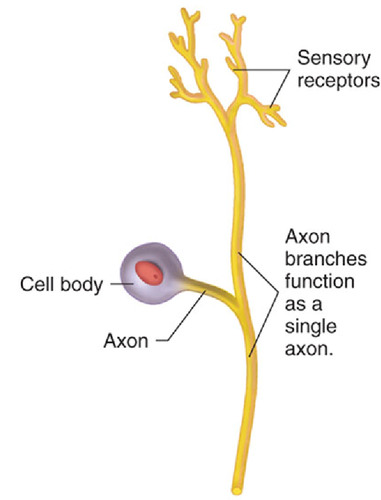
Multipolar axon
-multiple entries and one single axon
66
New cards
Bipolar
Rare, 1 dendrite and 1 axon
-retina and olfactory nerves
-retina and olfactory nerves
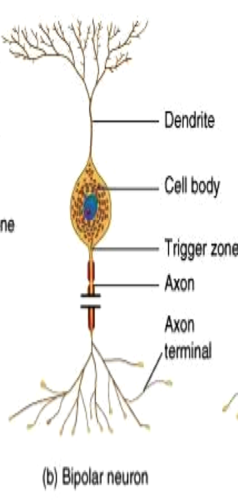
67
New cards
Unipolar
-many dendrites
-single fused axon that emerges as "T" from cell body (sensory)
-single fused axon that emerges as "T" from cell body (sensory)
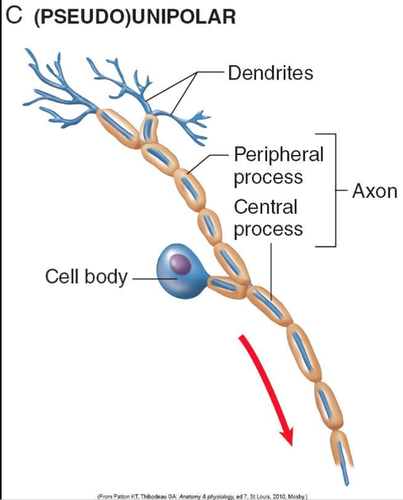
68
New cards
Does the terminal absorption have myelin?
no
69
New cards
Herpes virus, polio, and rabies with neurons
-enters neuron @ synaptic knob
-hitches a ride to the cell body
-replicates at the end
-hitches a ride to the cell body
-replicates at the end
70
New cards
Primary infection and the neuron
-infection
-retrograde
-replicates
-Latent (sits)
-phyorolytic stress
-reach
-retrograde
-replicates
-Latent (sits)
-phyorolytic stress
-reach
71
New cards
Neuroglia
-smaller than neurons
-hold them together like glue
-far outnumbered neurons 10:1 ratio
-capable of mitosis
-do NOT transmit nerve signals but instead assist in their functions
-hold them together like glue
-far outnumbered neurons 10:1 ratio
-capable of mitosis
-do NOT transmit nerve signals but instead assist in their functions
72
New cards
Astrocytes
-neuroglia of CNS
-starlike and most abundant
-large w/ many branches
-touch capillary walls and neurons
-starlike and most abundant
-large w/ many branches
-touch capillary walls and neurons
73
New cards
What are the neuroglia of the CNS
-astrocytes
-oligodendrocytes
-microglia cella
-ependymal cells
-oligodendrocytes
-microglia cella
-ependymal cells
74
New cards
Functions of astrocytes?
-F(X): form blood- brain barrier w/ their feet, form structural network by their cytoskeleton, reg. tissue fluid composition (controls movement of MC and ions from blood)
-converts glucose to lactate and supplies to neurons
-when neurons die, they fill in the space by astrocyte mitosis (sclerosis, or astrocytosis)
-converts glucose to lactate and supplies to neurons
-when neurons die, they fill in the space by astrocyte mitosis (sclerosis, or astrocytosis)
75
New cards
Ependymal cells
-look like ciliated simple cuboidal w/ roots
-NO BASEMENT MEMBRANE
-line the ventricles of brain and central canal of the spinal cord
-NO BASEMENT MEMBRANE
-line the ventricles of brain and central canal of the spinal cord
76
New cards
Functions of ependymal cells?
-they produce cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)- clear
-ependymal cells + nearby blood capillaries make coracoid plexus
-cilia of these cells help circulate CSF
-as blood passes through the coracoid plexus it only allows certain things through
-ependymal cells + nearby blood capillaries make coracoid plexus
-cilia of these cells help circulate CSF
-as blood passes through the coracoid plexus it only allows certain things through
77
New cards
Microglia Cells
-small cells w/ slender branches
-phagocytic cells of the immune system
-wander through the CNS and replicate in response to infection
-develop from monocyte line that also makes macrophages
-phagocytic cells of the immune system
-wander through the CNS and replicate in response to infection
-develop from monocyte line that also makes macrophages
78
New cards
Oligodendrocytes
-large bulbous body w/ many arm- like extensions
-each extension goes to a different neuron and wraps around its axon
-this wrapping is called *myelin sheath*
-covering prevents ions from passing through the axonal membrane
-protects the nerve from ECF
*electrical tape around a wire*
-1 oligodendrocytes wraps around many CNS axons
-each extension goes to a different neuron and wraps around its axon
-this wrapping is called *myelin sheath*
-covering prevents ions from passing through the axonal membrane
-protects the nerve from ECF
*electrical tape around a wire*
-1 oligodendrocytes wraps around many CNS axons
79
New cards
Which spinal nerves are the musculocutaneous?
C5, C6, C7
80
New cards
Where do sensory fibers come from?
Posterior or dorsal root
81
New cards
Where do motor fiber come from?
Anterior or ventral roots
82
New cards
What are the 2 types of cells of the PNS?
satellite cells
schwann cells
schwann cells
83
New cards
Satellite Cells
-flattened cells around cell bodies in a ganglion (sensory)
-physically separate the cell bodies and provide insulation
-physically separate the cell bodies and provide insulation
84
New cards
Schwann Cells
-flatten cells that may wind repeatedly around an axon to form a myelin sheath
-they can also assist in regeneration of damaged nerve fibers
-node of ravine is between 2 Schwann cells
-they can also assist in regeneration of damaged nerve fibers
-node of ravine is between 2 Schwann cells
85
New cards
Myelin or myelin sheath
-insulating covering around the axon that consists of repeating concentric layers of p. membrane of glia cells
-20% protein
-80% lipid
-LIKE TAPE
-20% protein
-80% lipid
-LIKE TAPE
86
New cards
Myelination
-process by which part if an axon is wrapped with myelin
CNS: oligodentrites
PNS: Schwann cells
CNS: oligodentrites
PNS: Schwann cells
87
New cards
When does myelination occur?
-14th fetal week
-little myelin at the time of birth
-need increased fat content (nutrition)
-little myelin at the time of birth
-need increased fat content (nutrition)
88
New cards
Process of myelin in the PNS
-schwann cells circles 1mm of a PNS axon
-as it wraps around it squeezes cytoplasm & nucleus to outside
-gaps between schwann cells= nodes of ranvier
-as it wraps around it squeezes cytoplasm & nucleus to outside
-gaps between schwann cells= nodes of ranvier
89
New cards
What is the neurilemma and what is external to it?
-cytoplasm & nucleus & last layer of P. membrane
-endoneurium
-endoneurium
90
New cards
Myelination in CNS
-oligodendrocyte can myelinated 1mm of MANY axons @ same time
-cytoplasmic extension wrap repeatedly around a portion of an axon
-NO NUERILEMMA OF ENDONEURIUM
-nodes of ranvier are created still
-cytoplasmic extension wrap repeatedly around a portion of an axon
-NO NUERILEMMA OF ENDONEURIUM
-nodes of ranvier are created still
91
New cards
What's the difference between myelination in the CNS vs. PNS
-no neurilemma or endonuerium are formed in CNS but they are in the PNS
92
New cards
Unmyelinated axons in PNS
-associated with schwann cells
-no myelin sheath to cover them
-axon rests in depressed portion of schwann cells
-no myelin sheath to cover them
-axon rests in depressed portion of schwann cells
93
New cards
Unmyelinated axons in the CNS
NOT associated with oligodendrocytes
94
New cards
What are two diseases associated with myelin?
-multiple sclerosis
-Gillian- Barre syndrome
-Gillian- Barre syndrome
95
New cards
Multiple Sclerosis and myelin
-pathologic and autoimmune
-CNS
-demyelination of axons in CNS and destroys oligodendrocytes (antibodies attack them)
-A. potential conduction is disrupted which impairs sensory and motor
-Sclerosis= hardening (repeated inflammatory reaction)
-young adults 18- 40
-CNS
-demyelination of axons in CNS and destroys oligodendrocytes (antibodies attack them)
-A. potential conduction is disrupted which impairs sensory and motor
-Sclerosis= hardening (repeated inflammatory reaction)
-young adults 18- 40
96
New cards
What are the first signs of multiple sclerosis?
-blurred vision
-numbness or tingling
-loss of balance
-fatigue (unrelated to amount of sleep)
-bowel or bladder
-thinking of clarity of thought
-numbness or tingling
-loss of balance
-fatigue (unrelated to amount of sleep)
-bowel or bladder
-thinking of clarity of thought
97
New cards
Guillian- Barre syndrome (GBS)
-autoimmune attack to schwann cells
-PNS
-actue, flu- like illness
-peripheral nerve axons affected
-symmetrical weakness in lower limbs (rubbery legs)
-starts distally and moves proximally
-pain is often present
-PNS
-actue, flu- like illness
-peripheral nerve axons affected
-symmetrical weakness in lower limbs (rubbery legs)
-starts distally and moves proximally
-pain is often present
98
New cards
Prognosis of Guillian- Barre Syndrome
-ICU
-pneummia
-bed sores
-can take weeks or months
-pneummia
-bed sores
-can take weeks or months
99
New cards
Which type of cell cannot regenerate? (CNS or PNS)
CNS
100
New cards
Regeneration of PNS cells
-axon can regenerate cell body only if it remains in tact
-schwann cells play a role in regeneration
-depends on 2 things :
1= amount of damage
2= distance b/w site of damage & structure it innervates
-schwann cells play a role in regeneration
-depends on 2 things :
1= amount of damage
2= distance b/w site of damage & structure it innervates