Neural Basis of Rehab Exam 1
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms

Action Potential conduction velocity increases with increasing atonal diameter

It provides electrical insulation

The axon hillock
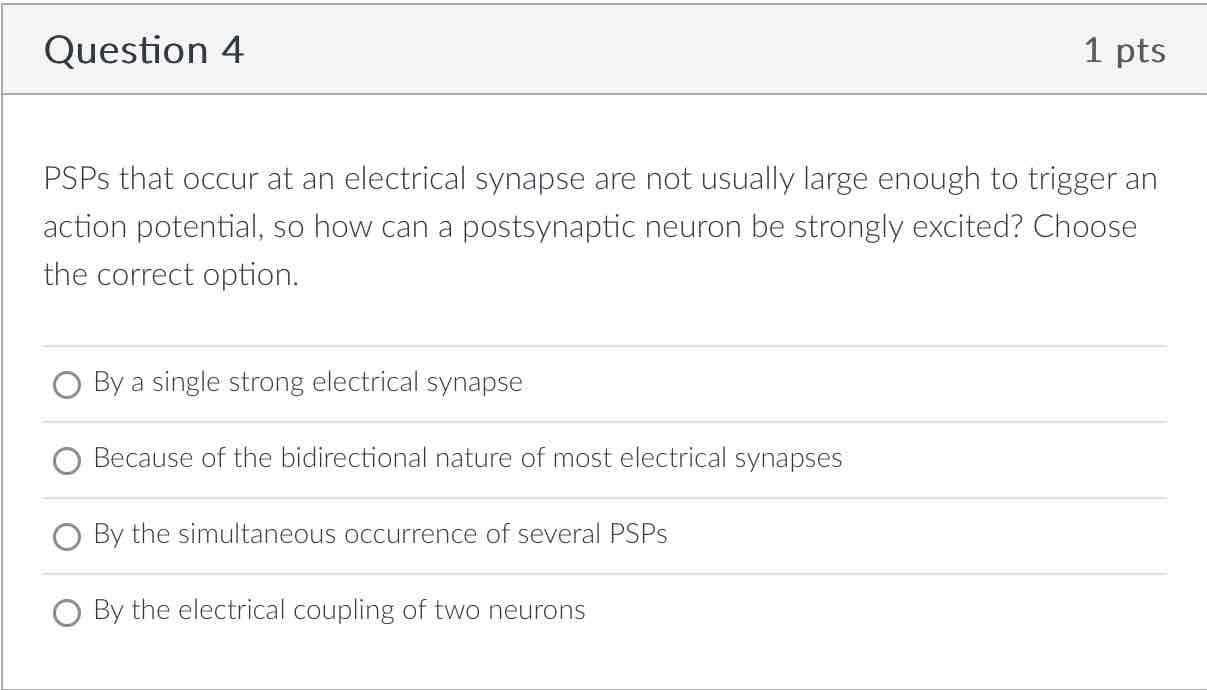
By the simultaneous occurrence of several PSPs
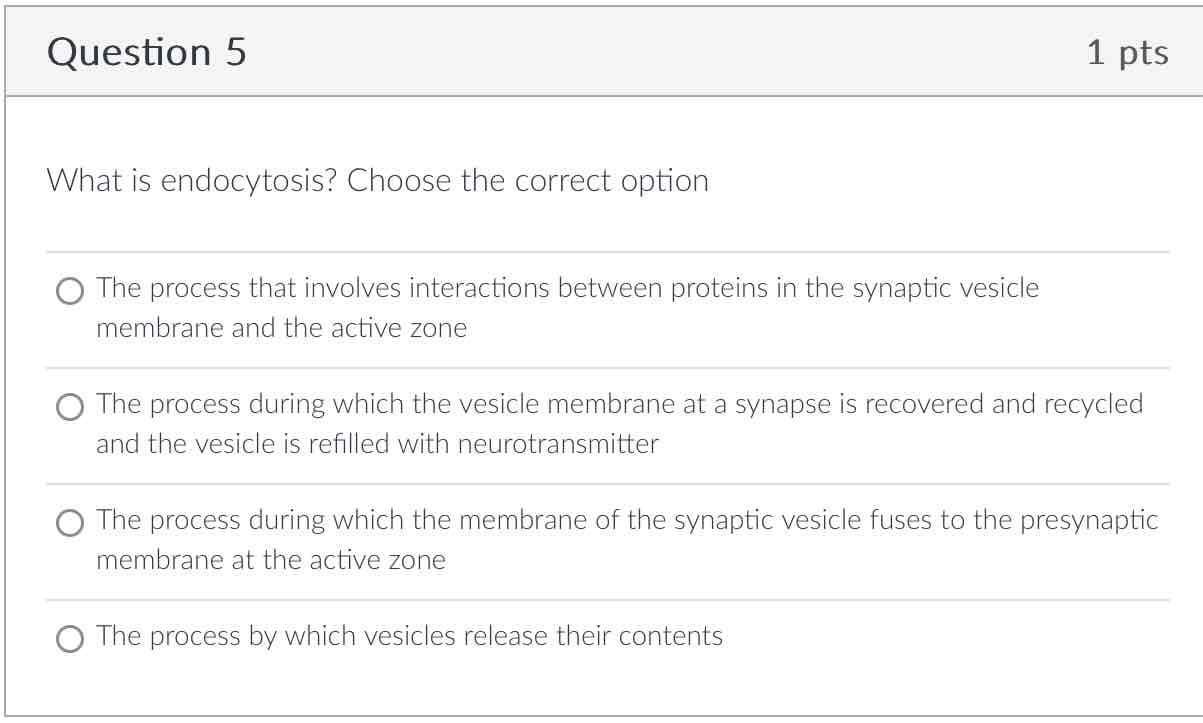
A process during which the vesicle membrane at a synapse is recovered and recycled and the vesicle is refilled with neurotransmitter

A process during which the same synapse fires action potentials in quick succession and individual EPSPs add together

Electrical synapse between neurons

Molecules that activate additional enzymes in the cytosol
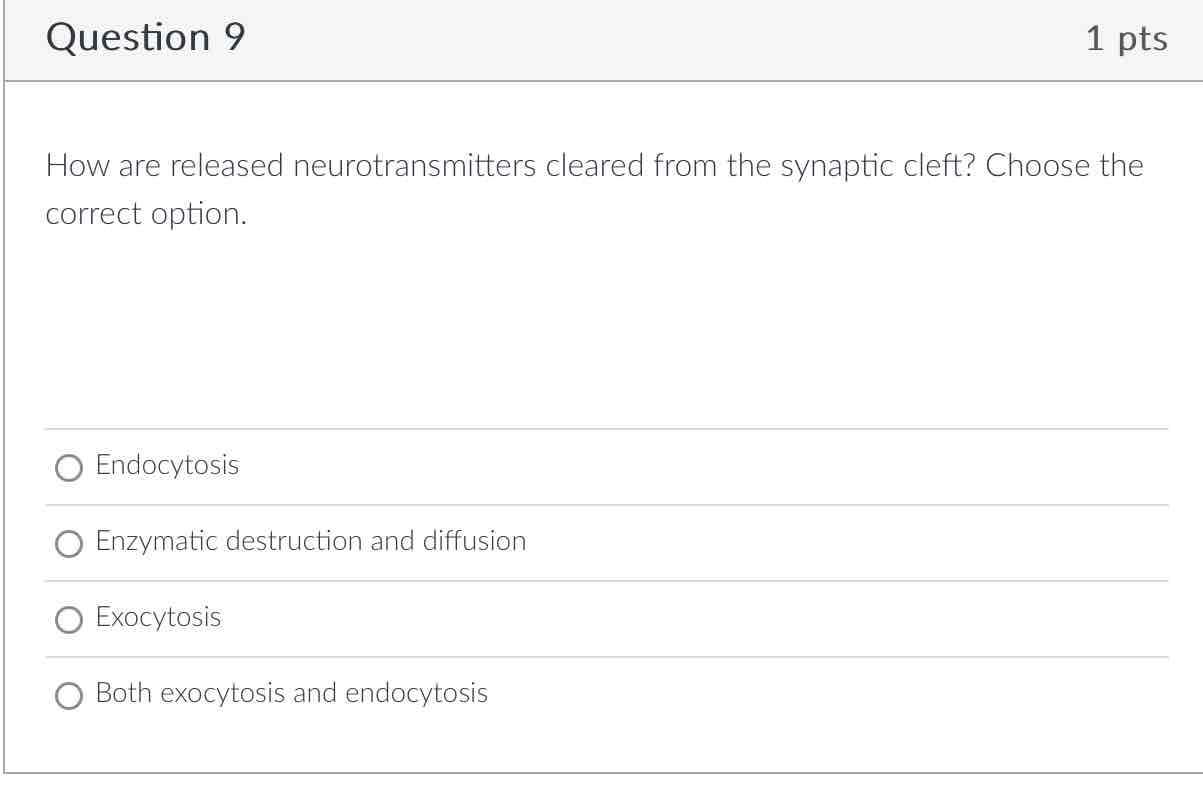
Enzymatic destruction and diffusion

Activate effector proteins such as ion channels or those that synthesize second messengers



Retrograding signaling
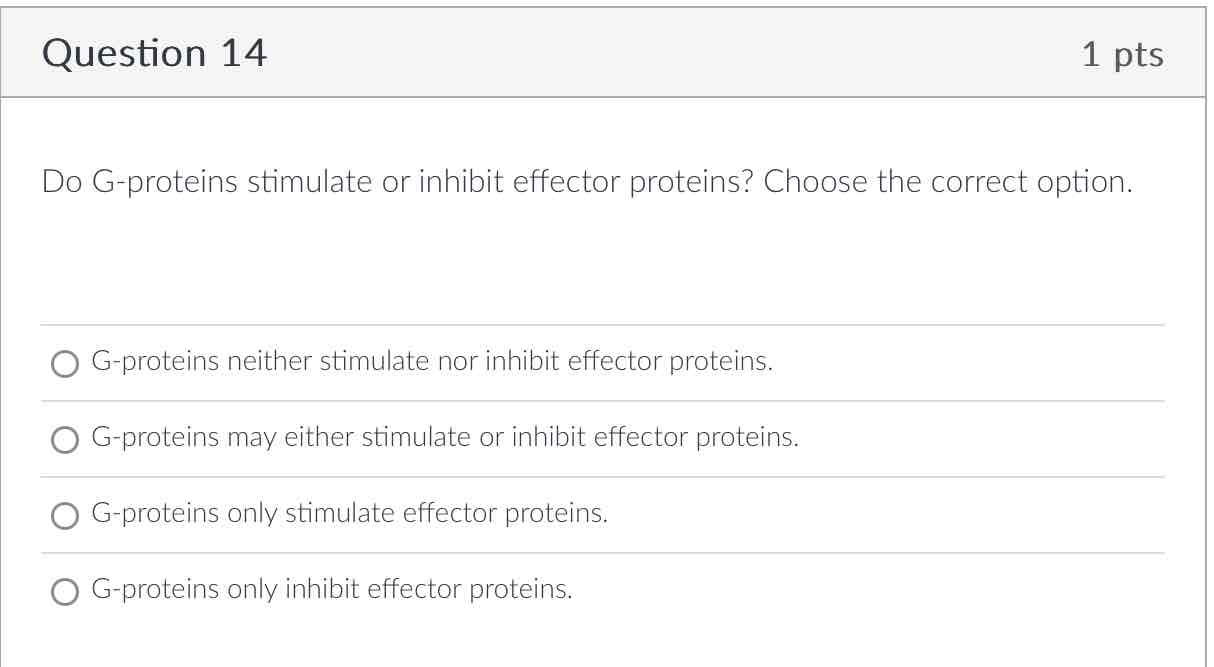
G-protiens may either stimulate or inhibit effector protiens

The shortcut pathway includes three elements: the receptor, G-protien, and the ion channel

The ability of one transmitter to activate more than one subtype of receptor

They are retrograde messengers by which postsynaptic neurons act on presynaptic terminals
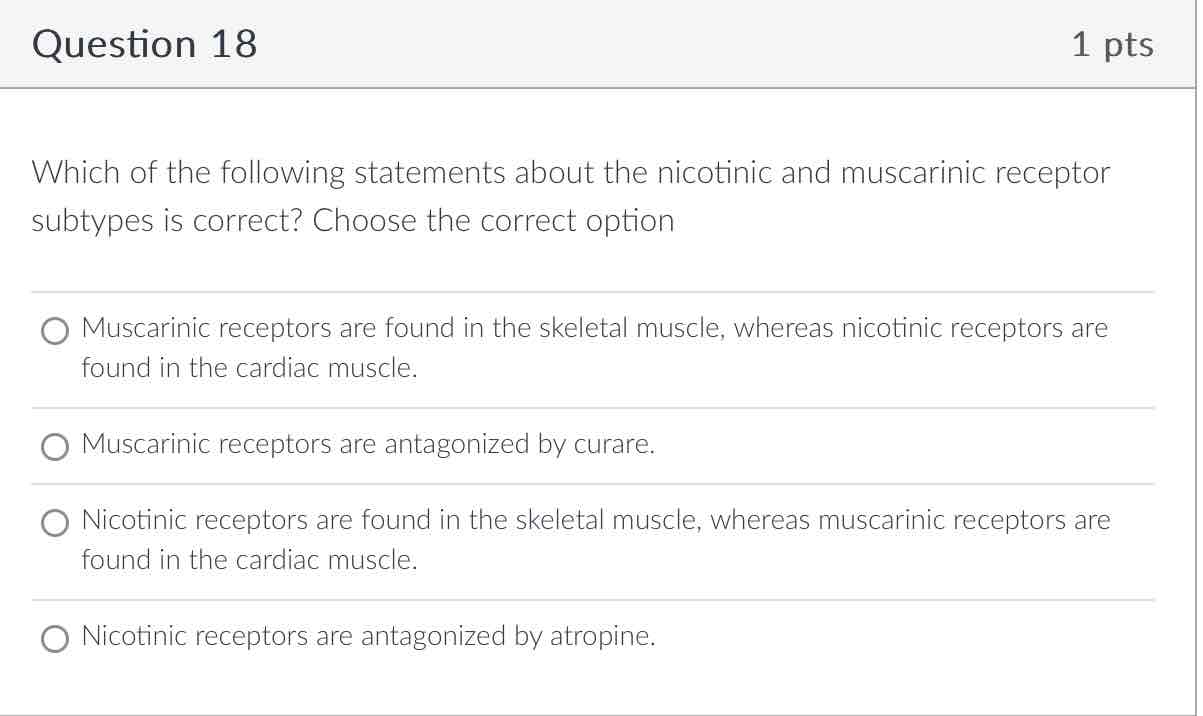
Muscarinic receptors are found in the skeletal muscle, whereas nicotinic receptors are found in cardiac muscle
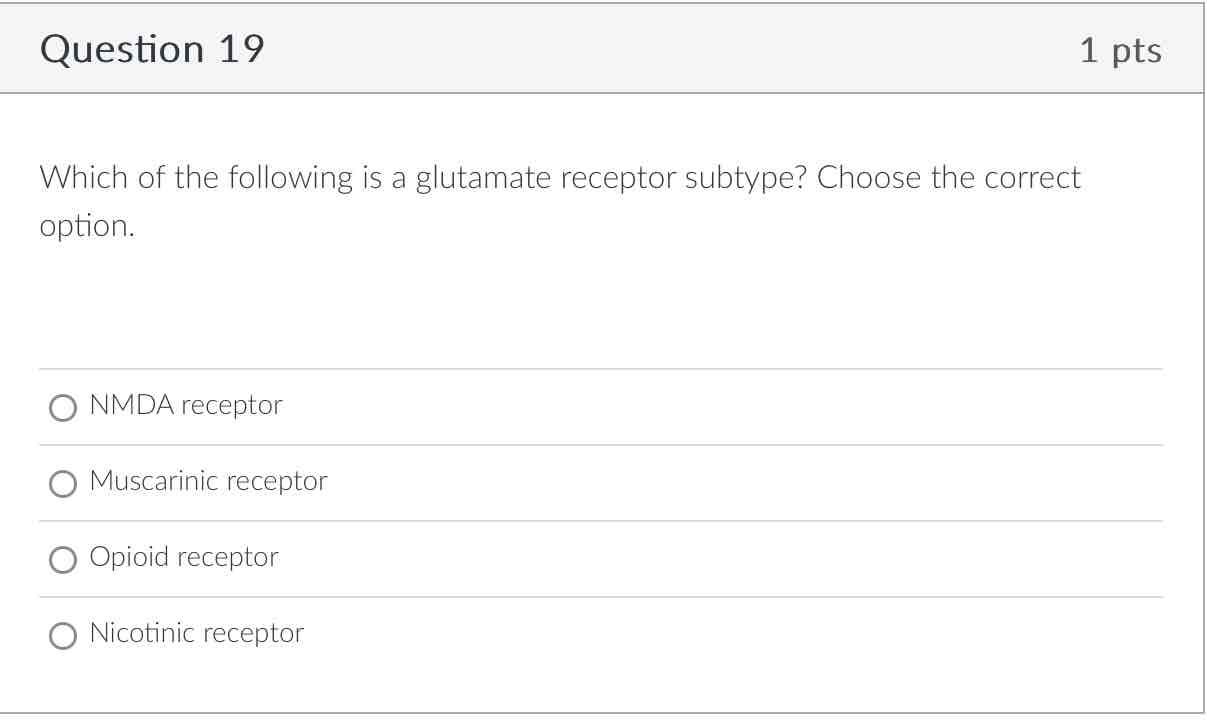
NMDA receptor
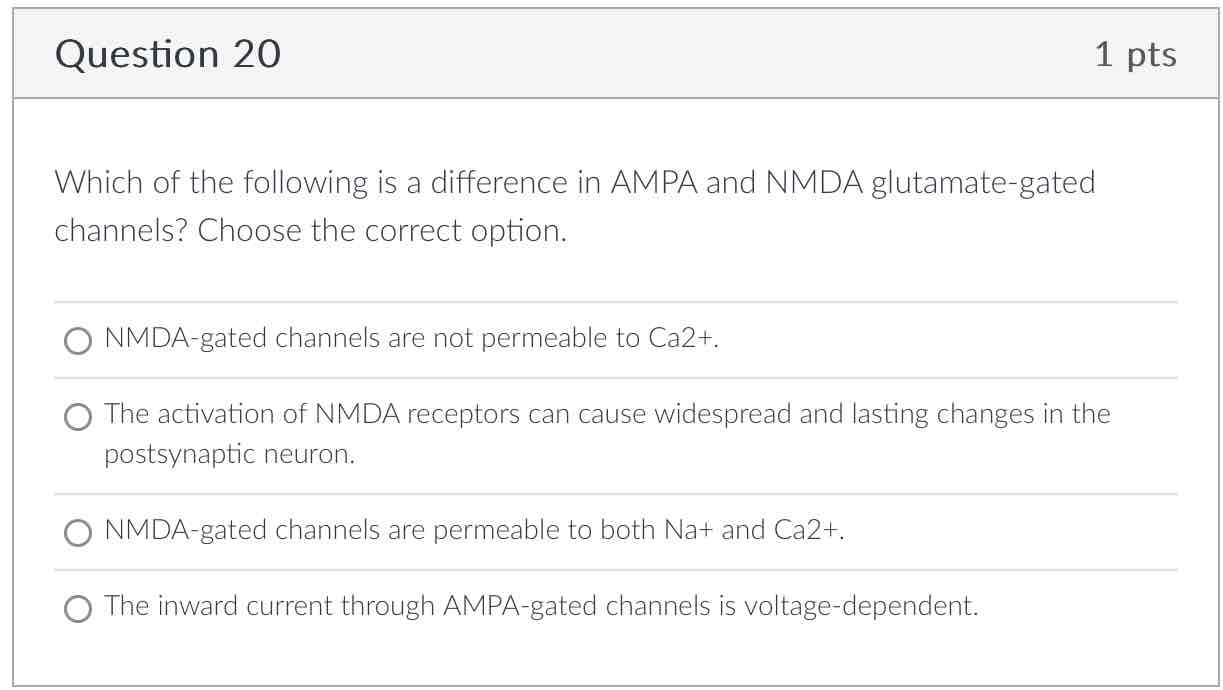
NMDA-gated channels are permeable to both Na+ and Ca2+

Tyrosine s the precursor for three catecholamine neurotransmitters: dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine
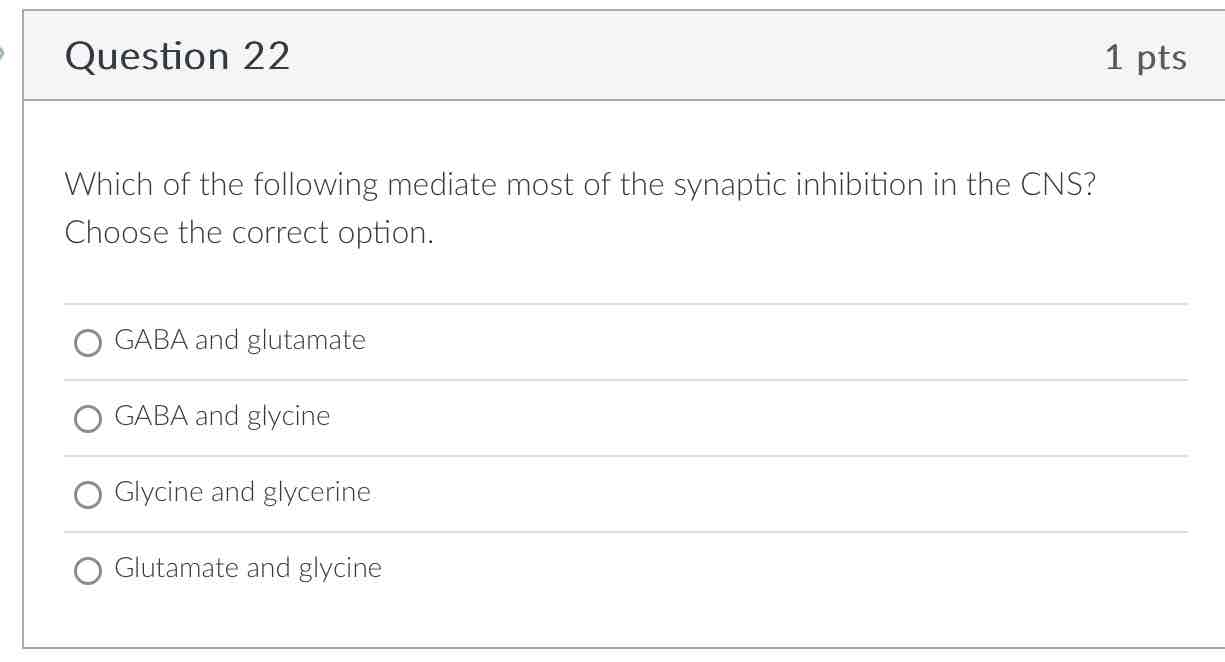
GABA and glycine



Insulating, supporting, and nourishing neurons

Dendrites receive incoming signals from other neurons, whereas axons carry the output of neurons

Region where axonal membrane is exposed
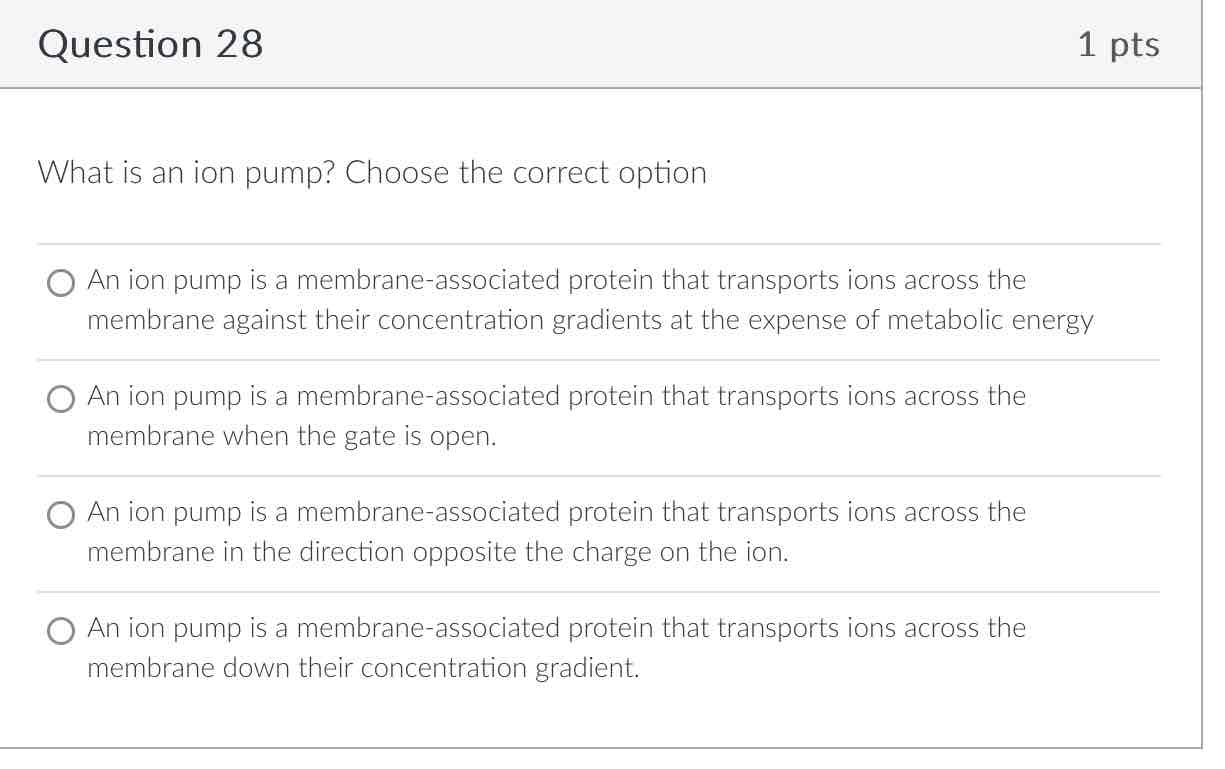
An ion pump is a membrane-associated protein that transports ions across the membrane against their concentration gradients at the expense of metabolic energy

Selective ionic permeability

Critical level of depolarization required to trigger an action potential

Voltage-gated potassium channel restore negative membrane potential after the spike
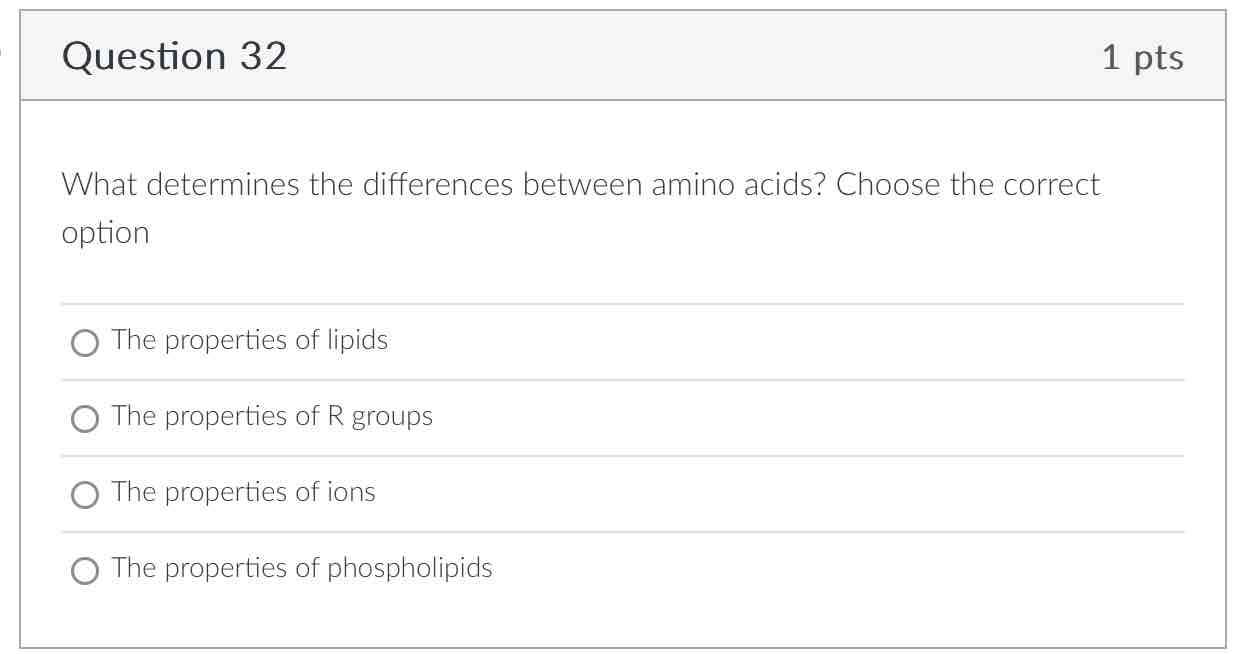
The properties of R groups

Nature of the R groups lining the ion channel
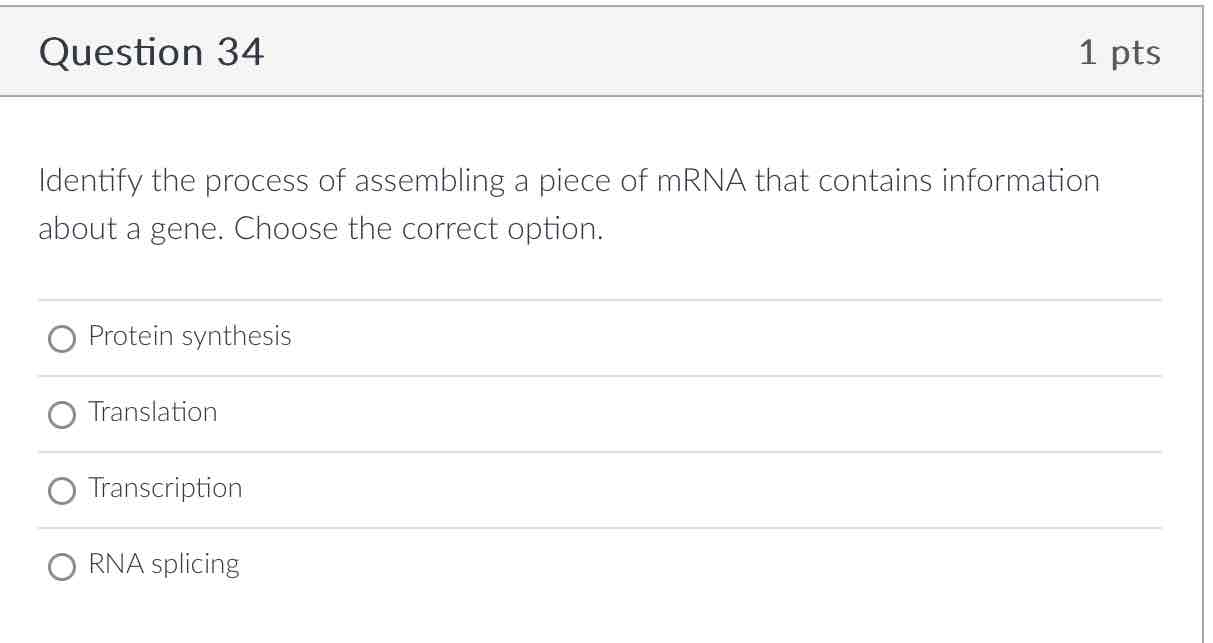
Transcription


If you were to study the structure of an entire neuron, which stain or method would you choose?
Golgi Stain
Nissl Stain
Golgi and Nissl stain combined
Electron Microscopy
Golgi Stain
What is the region where the axon begins?
Soma
Axon hillock
Axon collateral
Axon terminal
Axon hillock
Neuron:
all have the same number of dendrites
usually have several axons
are all remarkably similar in size
have only one axon
have only one axon
The ______ is the core region of the cell that contains the nucleuss.
dendrite
axon
Golgi body
Soma
Soma
The blood-brain barrier is made up ____ attached to neurons and blood vessels.
astrocytes
microglia
Schwann cells
ependymal cells
astrocytes
____ operate as part of the brain’s immune system.
astrocytes
microglia
oligodendroglia
ependymal cells
miroglia
Myelin is produced by:
oligodendroglia and Schwann cells
oligodendroglia and microglia
astroglia and Schwann cells
microglia and astroglia
oligodendroglia and Schwann cells
What molecular arrangement in the phospholipids bilayer forms a barrier to water-soluble ions?
The hydrophobic tails face the extracellular space and the cytosol. The hydrophilic tails face each other.
The hydrophobic heads face the extracellular space, and the hydrophobic tails face the cytosol.
The hydrophobic heads face the extracellular space and the cytosol. The hydrophobic tails face each other.
The hydrophilic heads face the extracellular space and the cytosol. The hydrophobic tails face each other.
The hydrophilic heads face the extracellular space and the cytosol. The hydrophobic tails face each other.
Which of the following influences ionic movement through membrane channels?
Only diffusion
Only electricity
Ohm’s law
Diffusion and electricity
Diffusion and electricity
What is resting membrane potential?
Difference in electrical charge across the membrane at rest
Generation of conduction of action potential at rest
Positive charge of the membrane at rest
Isolation of the cytosol from extracellular matrix
Difference in electrical charge across the membrane at rest
What is the meaning of an ion’s equilibrium potential?
Net movement of ions from a region of high concentration to region of low concentration
Electrical potential difference that exactly balances an ionic concentration gradient
Difference between the real membrane potential and equilibrium potential for a particular ion
Difference in concentration between a region with a high ionic concentration and a region with a low ionic concentration
Electrical potential difference that exactly balances an ionic concentration gradient
Why are action potentials said to be “all-or-none"?
Continuous application of depolarization generates many action potentials in succession
Application of current through a microelectrode depolarizes the cell only to threshold levels, not beyond
Depolarizing the neuronal membrane has no effect until membrane potential crosses a threshold
Continuous application of depolarizing current into the neuron crats only one action potential
Depolarizing the neuronal membrane has no effect until membrane potential crosses a threshold
The movement of what ion occurs in the rising phase of the action potential? (Referring to the cell)
Inward Na+
Outward Na+
Inward K+
Outward K+
Inward Na+
What accounts for the falling phase of the action potential?
The inward movement of sodium channels
Sodium channels close quickly once the membrane potential becomes positive during the action potential. At the same time, the potassium channels open.
Switching the dominant membrane permeability from K+ to Na+
Increased membrane permeability for both potassium and sodium
Sodium channels close quickly once the membrane potential becomes positive during the action potential. At the same time, the potassium channels open.
Why do action potentials travel in only one direction?
The membrane just behind the action potential is refractory due to inactivated potassium channels
The membrane just behind the action potential is refractory due to inactivated sodium channels
Membrane proteins are destroyed when an action potential fires and it takes time to replace them
There is not enough sodium in the extracellular space after an action potential has just fired
The membrane just behind the action potential is refractory due to inactivated sodium channels
Which of the following channels in the active zones of the synaptic terminal open when the membrane depolarizes and causes the release of synaptic vesicles?
Sodium channels
Voltage-gated sodium channels
Voltage-gated calcium channels
Potassium channels
Voltage-gated calcium channels
What types of cells can a neuron communicate with at a synapse?
Only muscle
Another neuron, muscle cell, or glandular cell
Only another neuron
Only a glandular cell
Another neuron, muscle cell, or glandular cell
Into what categories are neurotransmitter receptors classified?
Transmitter-gated ion channels and G-protein-coupled receptors
Over a hundred chemical categories
Over a hundred protein categories
All in the same category: neurotransmitter receptors
Transmitter-gated ion channels and G-protein-coupled receptors
Why are G-protein-coupled receptors referred to as metabotropic receptors?
Because they are actived by receptor proteins
Because the receptor is an ACh-gated ion channel hat is permeable to Na+
Because they can trigger widespread metabolic effects
Because the metabotropic ACh receptor is coupled by a G-protein to a potassium channel
Because they can trigger widespread metabolic effects
What is synaptic integration?
A method of comparing the amplitudes of miniature postsynaptic potentials
A process by which multiple synaptic potentials combine within one postsynaptic neuron
Adding together all IPSPs generated by a single neuron
Adding together all EPSPs generated by a single neuron
A process by which multiple synaptic potentials combine within one postsynaptic neuron
What is the term used for neurons hat use neurotransmitter acetylcholine?
Glutamatergic
GABAergic
Cholinergic
Noradrenergic
Cholinergic
What is the consequence of inhibiting acetylcholine esterase (AChE)?
Inhibiting AChE induces ACh synthesis in all motor neurons in the spinal cord and brain stem
Inhibiting AChE limits how much ACh can be synthesized in the axon terminal because it is the rate-limiting step in ACh synthesizes
Inhibiting AChE prevents ACh breakdown, disrupting neurotransmission at cholinergic synapses
Inhibiting AChE transfers an acetyl group from acetyl CoA to choline
Inhibiting AChE prevents ACh breakdown, disrupting neurotransmission at cholinergic synapses
What is the effect of amphetamine and cocaine on dopamine and norepinephrine synapses?
They promote catecholamine reuptake
The prolonged the presence of the neurotransmitter in the synaptic cleft
They convert tryptophan into an intermediary called 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP)
They regulate mood, emotional behavior, and sleep
They prolong the presence of the neurotransmitter in the synaptic cleft
Which type of neuron is the major source of synaptic inhibition in the nervous system?
Adrenergic neurons
GABAergic neurons
Glutamatergic neurons
Serotonergic neurons
GABAergic neurons
At what stage does signal amplification occur in the G-protein-coupled second messenger cascade?
At the point where cAMP molecules activate kinases
At the point where receptor activates a G-protein
At several stage of the cascade
At the point where G-protein activates an adenylyl cyclase
At several stage of the cascade
Why does ACh slow the heart rate?
It stimulates muscarinic receptors that open potassium channels
It stimulates muscarinic receptors that close potassium channels
It stimulates nicotinic receptors that open potassium channels
It stimulates nicotinic receptors that close potassium channels
It stimulates muscarinic receptors that open potassium channels
Which of the following regulates vital bodily functions as breathing?
Cerebellum
Brain stem
Meninges
Cerebrum
Brain stem
Which side of the cerebellum is concerned with movements of the right hand?
Left
Dorsal
Frontal
Right
Right
In what lobes do we find auditory, visual, somatosensory, and motor cortex?
Temporal (auditory), occipital (visual), parietal (somatosensory), and frontal (motor cortex)
Temporal (visual), occipital (auditory), parietal (somatosensory), and frontal(motor cortex)
Temporal (somatosensory), occipital (auditory), parietal (visual), and frontal(motor cortex)
All sensory cortex is in the parietal lobe, and the motor cortex is in the frontal lobe
Temporal (auditory), occipital (visual), parietal (somatosensory), and frontal (motor cortex)
When you place your hand on a speaker while playing loud music, which mechanoreceptor enables you to “feel” the speaker’s vibration?
Meissner’s corpuscles
Ruffini’s endings
Pacinian corpuscles
Cutaneous mechanoreceptors
Pacinian corpuscles
Which of the following has large receptive fields that may cover an entire finger or half of the palm?
Merkel’s disk
Pacinian corpuscles
Meissner’s corpuscles
Krause end bulbs
Pacinian corpuscles
What are mechanoreceptors?
Sensitive to high-frequency vibrations
Sensitive to smooth, mechanical surface
Sensitive to physical distortion
Sensitive to temperature change
Sensitive to physical distortion