Microevolution and population genetics (2)
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Microevolution
genetic changes within populations
Basic Evolution
Change through time
Decent with modification
Descent with modification
Evolutionary changes that have accumalted over time since two lineages split
Change in environment → natural pressures → remove those that are not fit → those who do fit reproduce and pass on genes
Environment is always changing and not known
Pangenesis
Incorrect
Gametes are result of gemmules (features of every facet of organism) produced small packages of what they are → go into offspring → create a new organism
Believed acquired characteristics (scars, skills) were inherited
Why is Pangnesis incorrect?
acquired characteristics are developed over a life time
Acquired traits result from changes in an organism's phenotype, not its genotype. Since they don't change the genetic code, they can't be passed on to the next generation.
genotype
The genetic makeup of a cell or organism; the particular combination of alleles present in an individual.
ATGC, actual DNA sequence
Individuals genotype is set of alleles possessed by the individual
genotype frequency
The proportion of a specified genotype among all the genotypes for a particular gene or set of genes in a population.
genotype-by-environment interaction
Unequal effects of the environment on different genotypes, resulting in different phenotypes.
ex: Height potential part of genotype, but environment (ex: malnutrion) can change phenotype?
What is biological evolution
change in allele or genotype frequencies in populations over time
Why do islands show evolution so well?
geographically isolated from mainland → large ecological opportunity, no comp, genetic variation → radiated across islands → specification events across diff. Environments on islands
Adaptive radiation
when Organisms diversify rapidly from an ancestral species when a change in the environment makes new resources available, creates new challenges, or opens new environmental niches
Phenotype
The expressed physical, behavioral, and biochemical traits of an individual, including height, weight, eye color, and so forth.
phenotypes are underlined by genotype frequencies and allele frequencies
Selection pressure genotype vs. phenotype
Phenotype: Natural selection acts on an organism’s phenotype (observable features)
Phenotype is often largely a product of genotype (the alleles, or gene versions, the organism carries).
When a phenotype produced by certain alleles helps organisms survive and reproduce better than their peers, natural selection can increase the frequency of the helpful alleles from one generation to the next – that is,
it can cause microevolution.
Who created penicillin?
Alexander Fleming, 1928
What is penicillin a product of?
Product of Penicillium mold
What kind of drug is penicillin?
• First antibiotic drug based on a naturally occurring substance
What issue occurred with penicillin?
• Represents an evolved response to bacteria
the spread of antibiotic resistant in bacteria reduced effectivess of penicillin over time
Microevolution
Changes within species,
Pushed by Natural selection and Other evolutionary forces
what does microevolution depend on"?
heritable variation in population genetics
What is a population?
individuals on species at same time and place
Need to Produce fertile offspring and productive
what are traits under?
can be under strong natural selection
e.g. antibiotic resistance
what is phenotypic variation?
heritable variation in appearance and/or function
What is qualitative variation
Type of phenotypic variation
characteristics with distinct states
what are polymorphisms?
Any genetic difference among individuals that is present in multiple individuals in a population.
Under qualitative variation
distinct variants of character
e.g., presence of spines = Yes or No
How are polymorphisms impact by natural selection?
States can be more useful in certain times and places
Ex: red ladybug survives because they are predated less on than black ladybug population
Quantitative variation
type of phenotypic variation
Characteristics with a range of variation
Controlled by multiple genes
Can be measured (e.g., height)
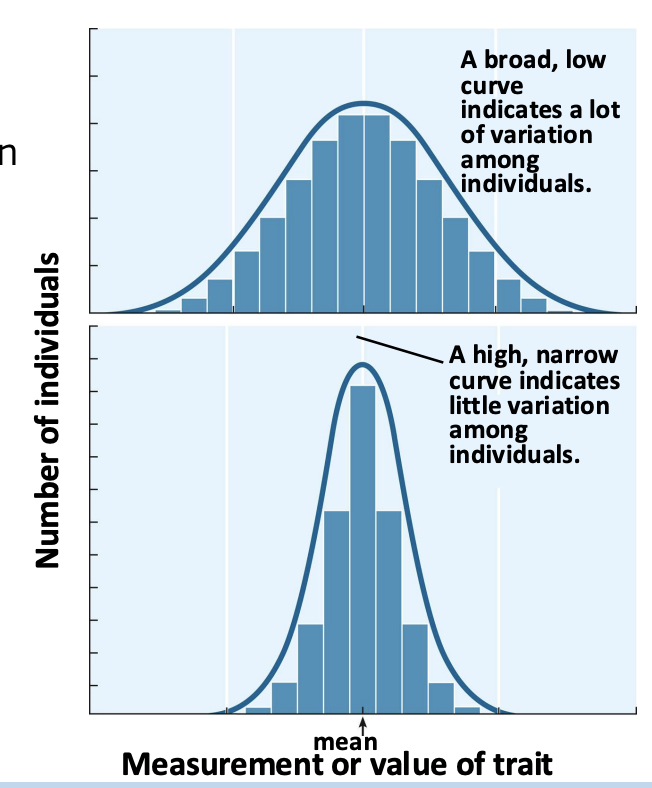
when do characteristics have a wider range?
Trait does not have strong pressure to conform to a certain way
When do characteristics converge to a mean?
There is strong natural selection for that specific trait
Are genotypes and phenotypes completely correlated?
Phenotypic variation is due to genetics, environmental differences, or both
Only genetic component of phenotype are heritable
Are there experiments we can use to determine connection between phenotypes and genotypes?
Keep genetics constant (clones), vary environment
Breeding and selection experiments
how to determine if variation is influenced by genetics
Evolution can only act on heritable variation
Law of segregation
Organisms carry two alleles per trait, which segregate during gamete formation, so each gamete carries one allele per trait. Offspring receive one allele per parent.
sex cell formed —> alleles segregate —> each gamete (sex cell) will have one allele for each trait (ex: Y or y)
two allele for each genes, one from each parent
Law of independent Assortment
The inheritance of one trait is independent of the inheritance of another, as long as the genes for the traits are on different chromosomes.
Law of dominance
In a pair of alleles, one may be dominant, masking the effect of the other, which is recessive
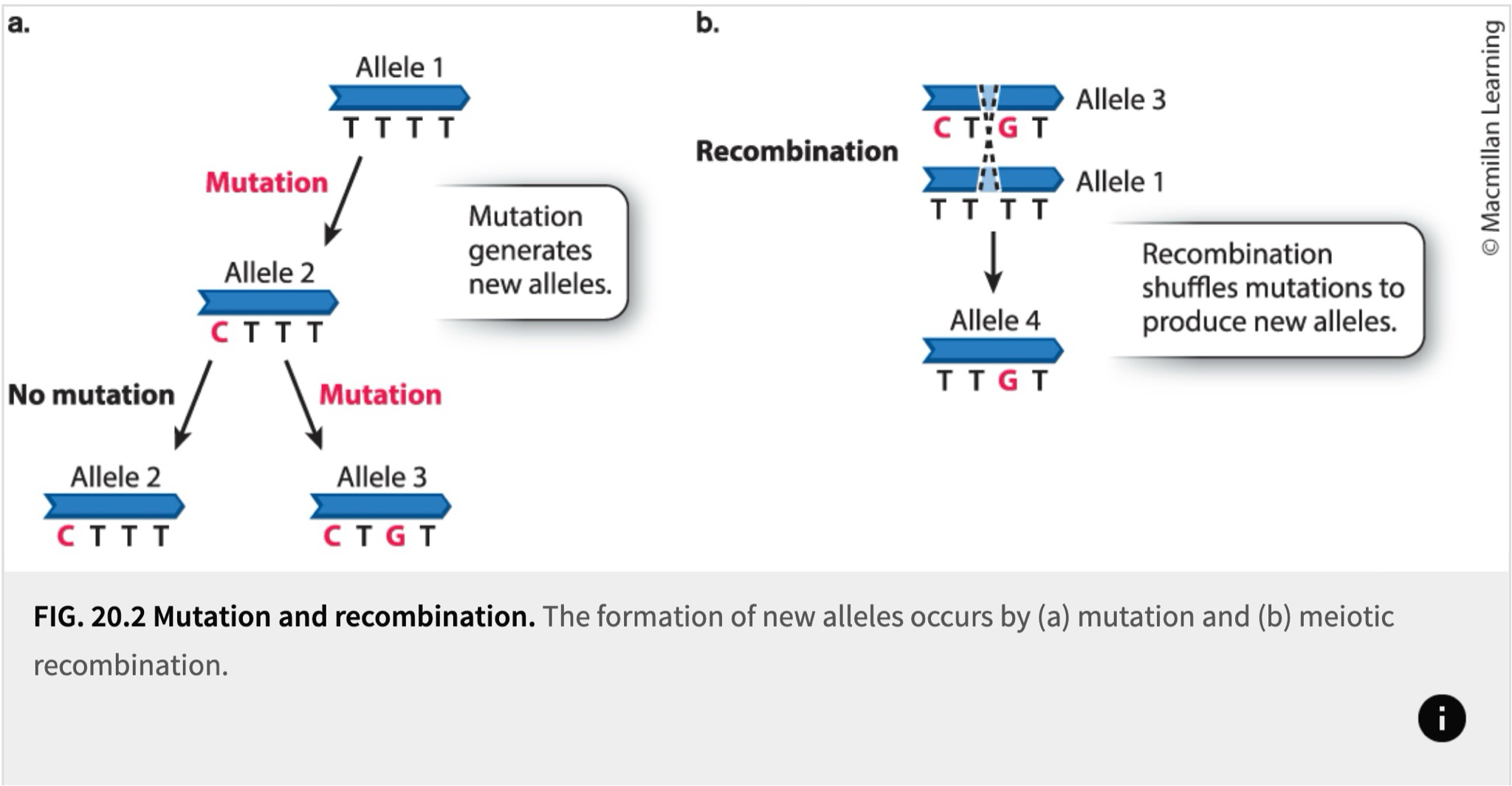
What causes genetic variation?
new alleles from mutations
Recombination followed by segregation of homologous chromosomes during meiotic cell division shuffles to create new combinations
what are Germ-line mutations?
occur in reproductive cells and present in sperm or eggs
passed down to the next generation
What is recombination?
occurs when genetic variation is already present
takes place in meiosis production of sperm and eggs
causes segments of DNA to be shuffled from chromosome to chromosome
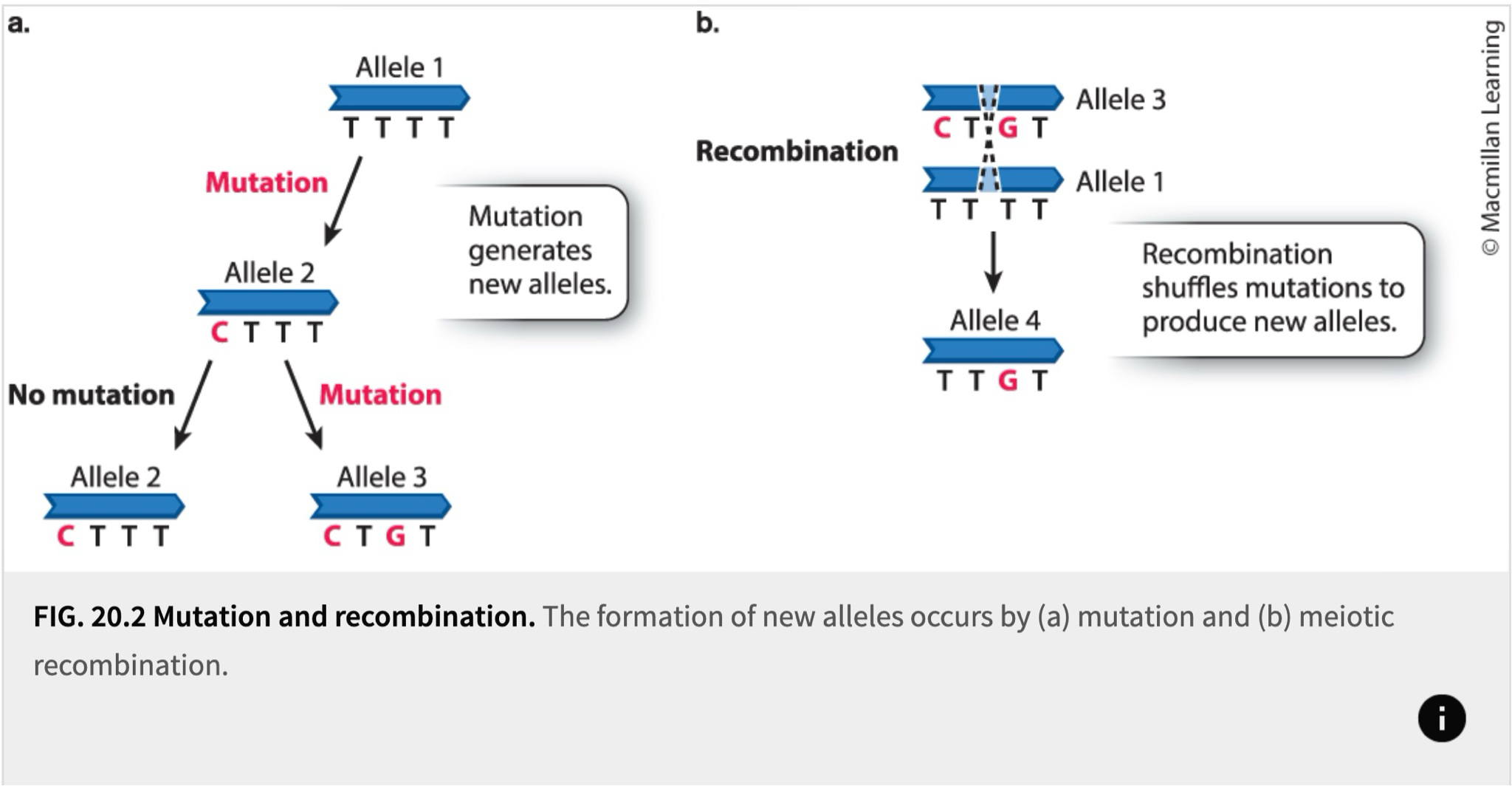
What can recombination occur from?
organisms crossing over
independent assortment
random fertilization
What is population genetics?
The study of patterns in genetic variation in populations
For evolution to occur, individuals within a population must differ genetically
Individuals within a population are more closely related to each other than members of other populations
What happens when individuals on the same species are isolated from each other?
Different populations of the same species may be isolated from each other such that gene flow is rare
What is the gene pool?
The sum of all alleles at all gene loci in all individuals within a population
Characterizes a population’s genetic makeup
Used to identify the genotypes and calculate genotype frequencies
How will variation be inherited?
variation that can be inherited and is best suited for environment will be disproportionately passed to the next generation
What is environmental variation?
variation among individuals due to different enviroments
What is genetic variation?
difference in genetic material that is transmitted to offspring
How does genetic variation impact physical differences?
difference in DNA —> difference in RNA and proteins —> affects molecular formation of cell —> lead to physical difference we can observe
What causes variation in sexual organisms?
fertilizations = unique combinations of genes
What is evolutionary theory?
predicts new species arise by divergence of populations through time from a common ancestor
closely related species look like each other more than distant relatives
What is the tree of life?
full set of evolutionary relationships
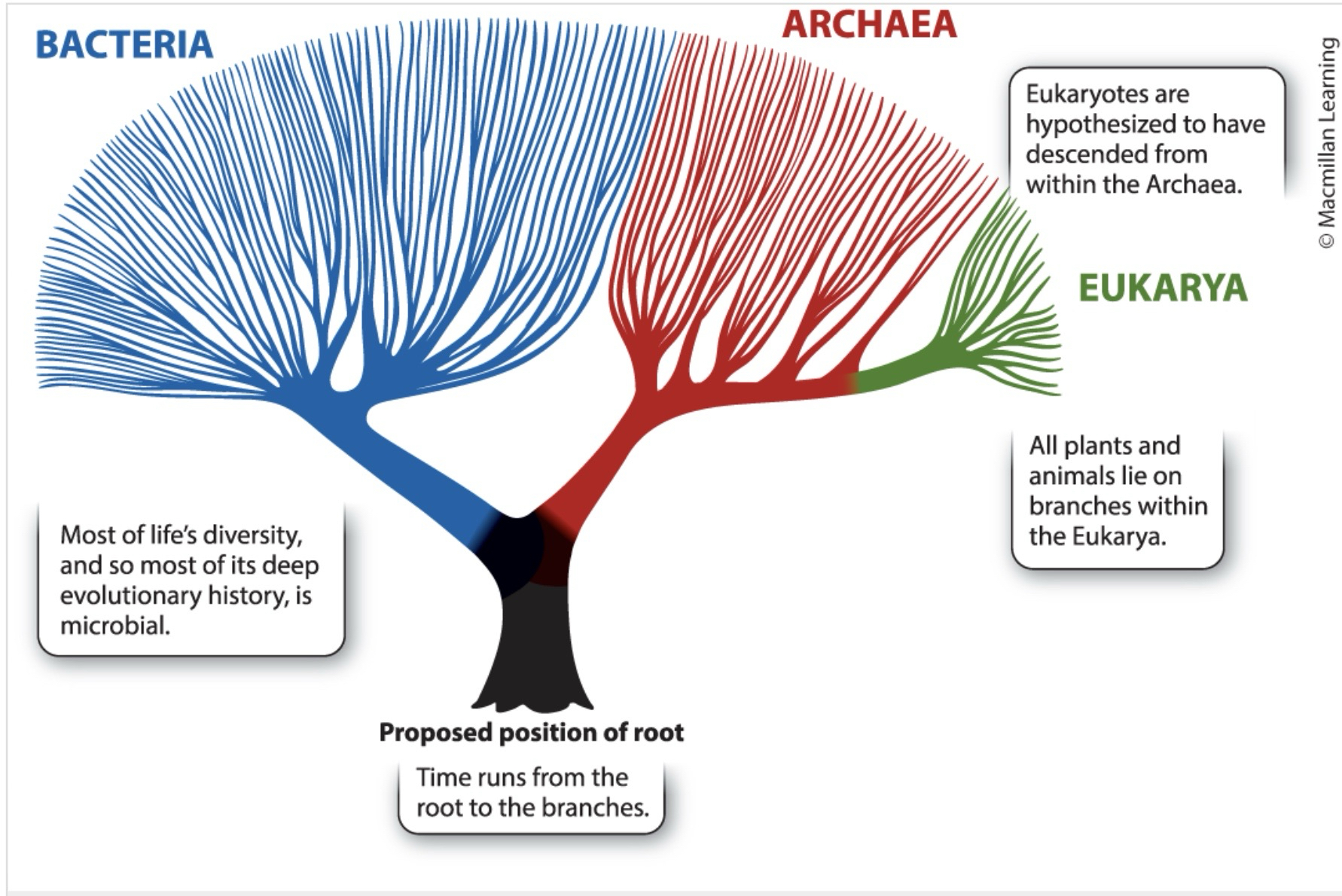
What are the major parts of the three of life?
Two major branches
bacteria
Archaea and Eukarya
most plants and animals are only two branches in Eukarya
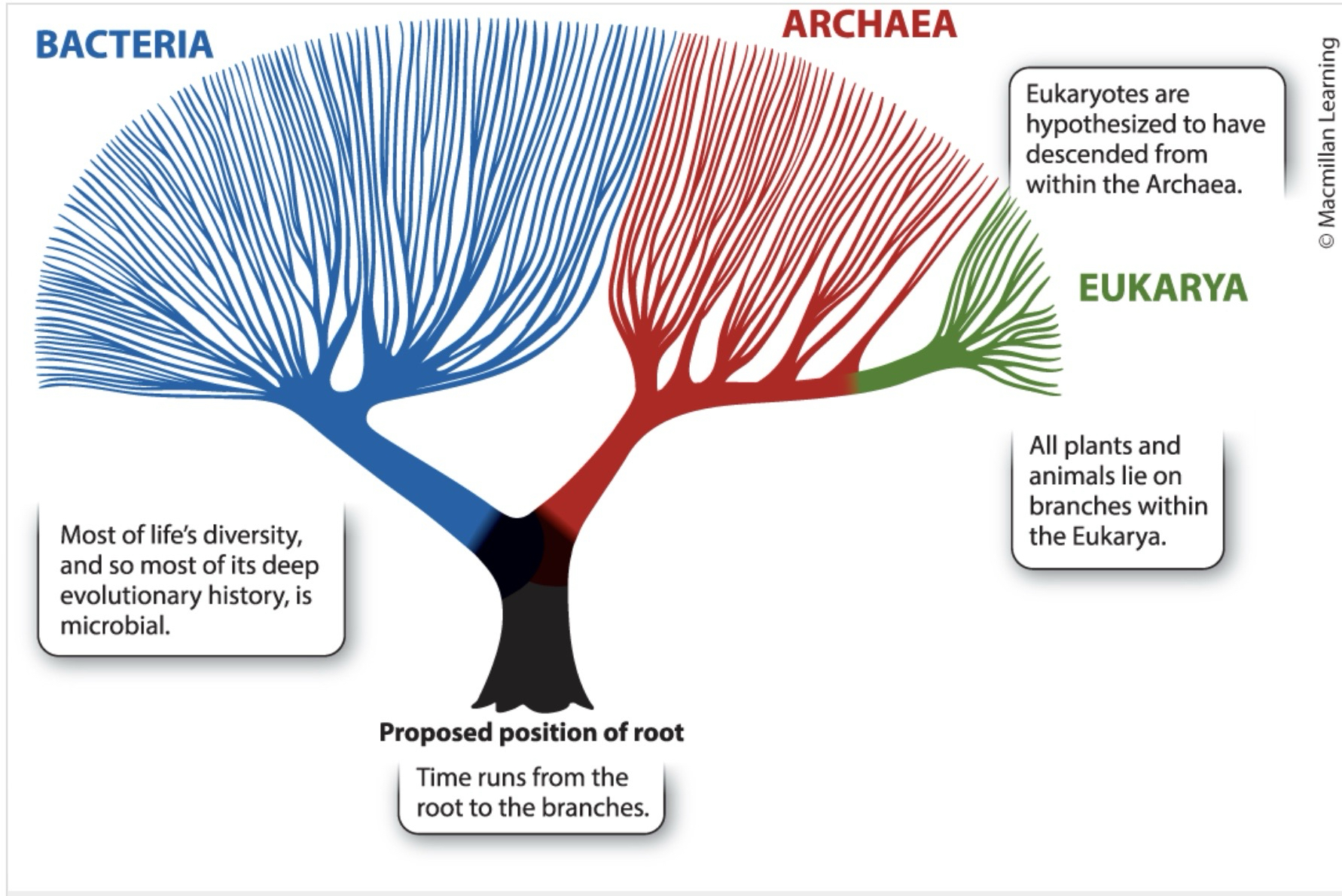
What are most branches on the tree of life?
Microorganisms
What is represented at the root of the tree of life?
The last common ancestor of all organisms
Evidence of evolutionary theory
nested patterns and succession of fossils in geological records
How to alleles interact with phenotype?
offspring inherit one allele from each parent (two alleles total)
allele in same location in chromosome determine observable trait
Species definition?
group of individuals capable, through reproduction, of sharing alleles with one another
what do individuals in species represent?
Individuals represent different combinations of alleles drawn from the species gene pool.
What are somatic mutations?
occurs in body tissue nonreproductive cells
only affects cells descended from one cell where mutation originally rose —> affects only that one individual
What are neutral mutations?
have little to no effect
silent mutation that does not alter amino acids
or amino acid change but no change to protein function
What are deleterious mutations?
harmful effect on organisms
large portion of mutations that occur in protein-coding regions of genome
What are advantageous mutations?
improve chances of survival and reproduction
results in species adapting to environment
What is the most rare mutation?
Advantageous mutations
What can happen to the population with advantageous mutations?
can increase in frequency in population until carried by every member of spices (fixation)

What is the best qualitative variation?
Ladybugs —> two distinct states
B and C= quantitative variations (range)