Lens, Uvea, Vitreous
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
lens provides ____ of total dioptric power of eye
1/3
what type of stimulation starts the process of accommodation
parasympathetic
what does parasympathetic stimulation do in the lens
causes contraction of the ciliary muscle
when the ciliary muscle contracts, what happens to the lens zonules
decrease in tension
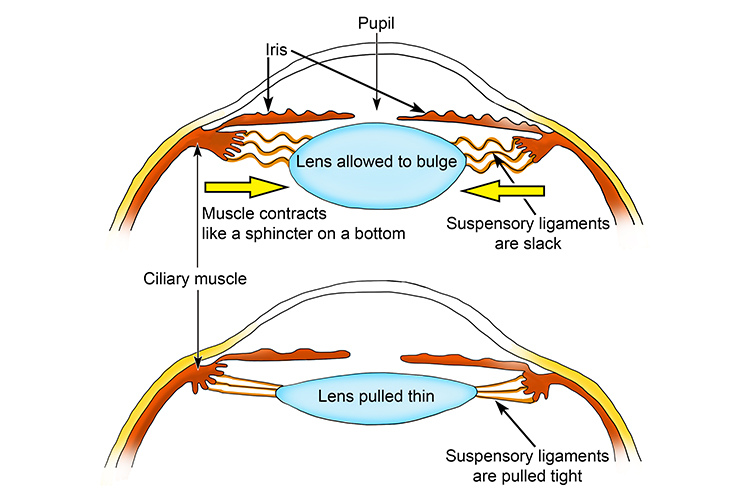
during accommodation lens anterior pole moves (forward/backward), and anterior curvature (increases/decreases)
forward, increases
during accommodation lens posterior pole moves (forward/backward), and posterior curvature (increases/decreases)
backward, increases
during accommodation, lens thickness (increases/decreases) and anterior chamber depth (increases/decreases)
increases, decreases
during accommodation, lens diameter (increases/decreases) and lens power (increases/decreases)
decreases, increases
what does accommodation do to IOP and why
initially can cause decrease in IOP when CM contraction pulls on the scleral spur and opens up the TM
can then cause an increase in IOP due to a decrease in AC depth when the anterior pole moves forward
what can happen to narrow angle patients during accommodation and why
pupillary block
AC depth decreases and lens thickens
lens can push forward on iris and block the TM outflow at the angle due to narrow chamber depth
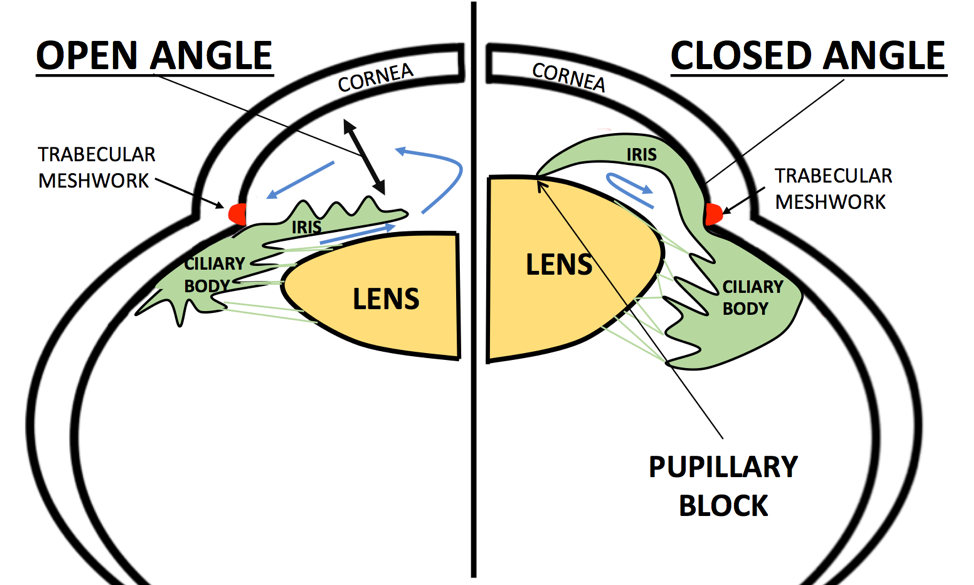
what kind of drugs can cause pupillary block in narrow angle patients
give a drug example
miotics like pilocarpine
accommodation in triad of miosis, convergence, and accommodation can lead to pupillary block
lens is (vascular/avascular)
avascular
lens has the largest concentration of ______ of any structure in the body
proteins
where does lens get glucose and oxygen
aqueous
lens is so packed with proteins that it needs to get oxygen and glucose elsewhere
what 2 lens functions does the lens need glucose and oxygen for
producing new lens fibers and proteins
maintaining the Na+/K+ ATPase
role of the Na+/K+ ATPase in the lens
maintaining lens dehydration and transparency by balancing water and ions in the lens
how does the Na+/K+ ATPase work in the lens
epithelial cell pump moves Na+ into the aqueous humor and K+ into the lens
water follows Na+ into the AH
water follows _____ out of the lens to maintain lens transparency
Na+
what ion enters the lens via the Na+/K+ ATPase
K+
over 70% of glucose used by the lens is produced through _____________
anaerobic glycolysis
what part of the lens is supplied by glucose via aerobic metabolism
lens epithelium only
what is the first step of aerobic and anaerobic respiration
conversion of glucose to glucose 6-phosphate via hexokinase enzyme
what happens if hexokinase is not available to convert glucose to glucose 6-phosphate
glucose is converted to sorbitol via aldose reductase
what happens if excess sodium accumulates in the lens
osmostic gradient is created that favors movement of water into the lens
causes lens swelling, lens fiber damage, and cataracts
__________ converts glucose to glucose 6-phosphate
__________ converts glucose to sorbitol
hexokinase
aldose reductase
why do diabetic patients experience cataract formation
excess glucose leads to sorbitol accumulation in the lens
accumulation of sorbitol causes lens damage and early cataracts
other than cataract formation, what side effect of sorbitol accumulation in the lens do diabetic patients experience
lens swelling that causes refractive shift
what is the main protector against oxidative damage in the lens
glutathione
how does glutathione protect against oxidative damage in the lens
acts as a reducing agent (donates electron) to detoxify hydrogen peroxide
how does the lens get glutathione
transported into the lens from the aqueous
synthesized by lens epithelial cells and superficial fiber cells
what happens to glutathione diffusion with age
glutathione diffusion decreases with age
factor in cataract formation
another name for vitamin c
ascorbic acid
is ascorbic acid found in higher quantities in the lens or aqueous
much higher in the lens
role of ascorbic acid in the lens
helps protect the lens from oxidative damage
2 main proteins in the lens
glutathione
ascorbic acid
how is oxidative damage detrimental to the lens
it reduces lens clarity
how do lens fiber cells help maintain lens transparency
minimize light scatter because they lack membrane-bound organelles
packed very close together and uniformly spaced
cytoplasm of lens fiber cells have crystallins that minimize light scatter via destructive interference
what ion needs to be limited inside the lens to prevent cataract formation
Ca2+
list factors that help maintain lens transparency
Na+/K+ ATPase pumps that move K+ into the lens and Na+ out of the lens
avascular nature of lens to minimize light scatter
lens fiber cell arrangement, lack of membrane-bound organelles, and crystallin content
transport processes that monitor and limit Ca2+ concentration in lens
what forms the embryonic nucleus
primary lens fibers of the posterior epithelium
what facilitates growth of the lens after the embryonic nucleus is formed
secondary lens fibers of the anterior epithelium
where does mitosis of lens fiber cells occur
germinative zone of the anterior lens epithelium
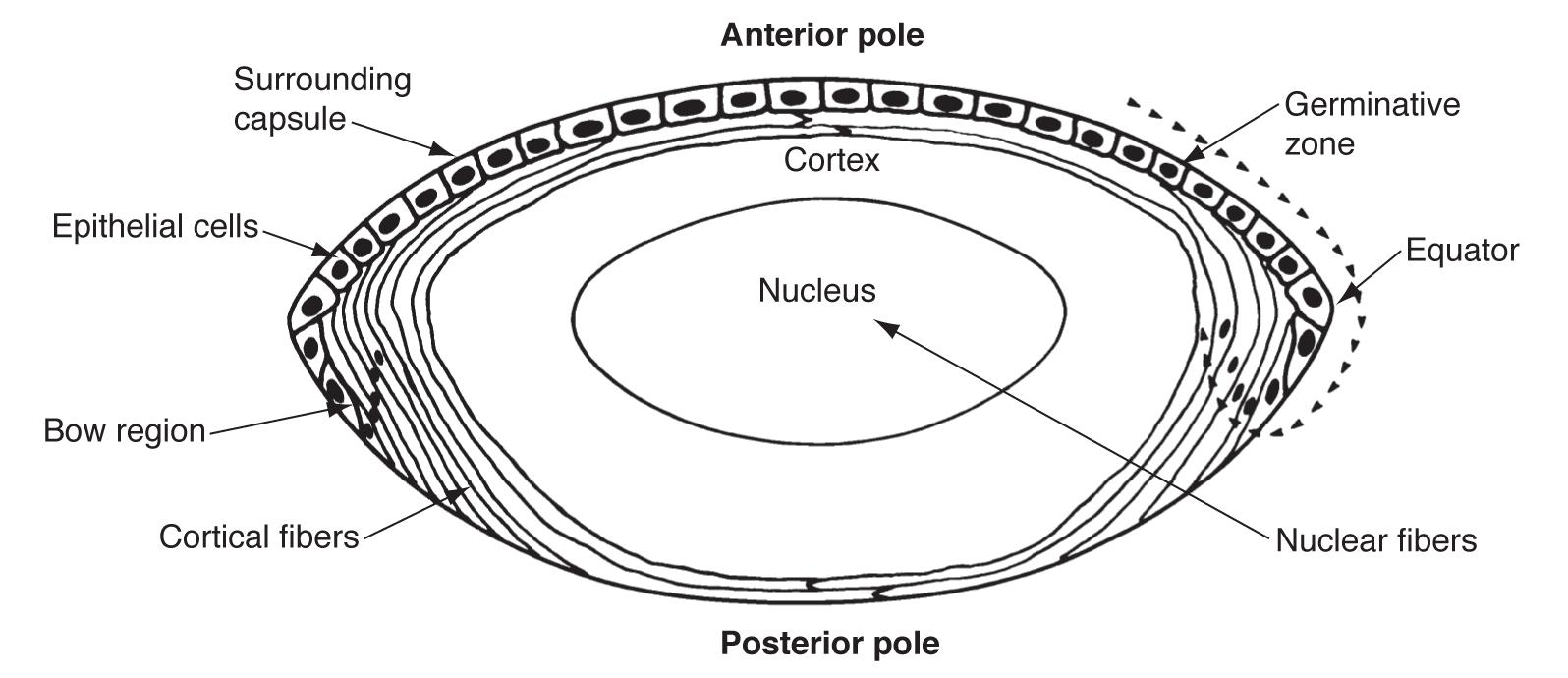
what happens to lens fiber cells after mitosis
fiber cells move from germinative zone through transition zone and into lens equator, where fiber elongation occurs
where does lens fiber elongation occur
lens fiber cells
during lens fiber elongation what happens to lens fiber cells
they lose their membrane bound organelles and gain crystallins (allows for lens transparency)
in what part of the lens aerobic respiration occur
anterior lens epithelium
what part of the lens has the greatest metabolic demand and why
anterior lens epithelium
this is the area where mitosis of fiber cells occurs
the _______________ has the greatest demand of all lens components and therefore contains a significant amount of __________ to provide energy for mitosis
anterior lens epithelium
mitochondria
how are nutrients provided to the anterior lens epithelium
aqueous humor travels over the lens and provides nutrients
______________ is responsible for transporting nutrients from the AH to the lens
anterior lens epithelium
crystallins are (soluble/insoluble) lens proteins
soluble
what happens to crystallins with age and why
crystallins decrease and insoluble lens proteins increase
due to increase in cross-linking between lens fiber cells
what happens when there is increased cross linking in the lens
insoluble lens protein aggregates form
alters amount of water in the lens
__________ within the lens decrease a lot with age
alpha crystallins
by what age are there no more alpha crystallins in the lens
45
molecular chaperones
alpha crystallins
prevent degradation of other crystallins
what happens when alpha crystallins in the lens begin to degrade
lens fiber cells begin to degrade and cataracts can start to form
how much does lens thickness increase per year
0.02 mm
what happens to lens diameter with age
relatively stable after teen years
what happens to anterior and posterior lens capsule thickness with age
anterior: increases with age
posterior: relatively stable with age
where is the lens capsule the thickest and thinner
thickest: anterior mid-peripheral part of the lens (pre-equatorial)
thinnest: posterior pole
(T/F): Lens is the thickest BM in the body
true
what type of collagen makes up the lens
type IV
what happens to lens radius of curvature with age
decreases (lens becomes more convex)
how should refractive error change with increased lens thickness and why doesn’t it
since lens becomes more convex (+), patient should become more myopic with age
change in gradient refractive index of lens prevents this from happening
what happens to AC depth with age
decreases as anterior lens moves further forward
state if amino acids, glutathione, Na+, Ca2+, H2O, and crystallins increase or decrease with age
amino acids: decrease
glutathione: decrease
Na+: increase
Ca2+: increase
H2O: increase
crystallins: decrease
what happens to nuclear fibers with age
lose nucleus and organelles
become more yelloww
where does nuclear sclerosis begin
embryonic nucleus
expands to fetal and adult nucleus
what is the center of the lens called
embryonic nucleus
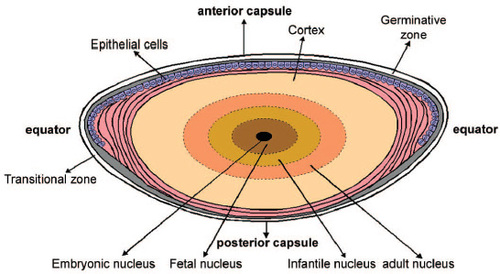
what part of the lens has the highest refractive index and why
embryonic nucleus
has the highest concentration of crystallins
what demarcates the boundaries of the fetal nucleus
y sutures
main function of iris
regulates pupil size
benefits of small pupil size
reduces spherical and chromatic aberrations
increases depth of field
(miosis/mydriasis) is more difficult with age
mydriasis
2 results of aging of the iris
increased pigment deposition on the anterior structures of the eye
increased resistance to dilation due to aging of the iris sphincter and dilator muscles
what part of the iris causes increased pigment deposition with age
posterior pigmented iris epithelium
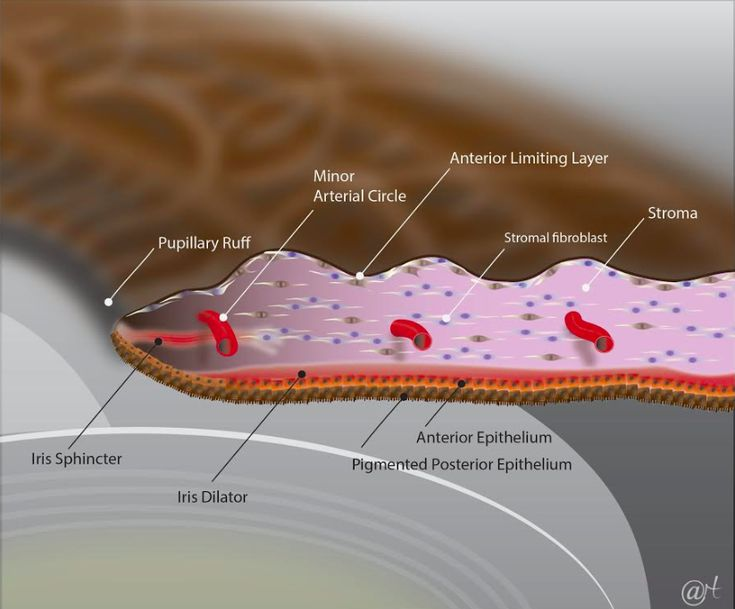
2 main functions of the ciliary body
accommodation via ciliary muscle
production and secretion of AH
what part of the CB contributes to AH drainage
ciliary stroma via uveoscleral meshwork
what happens to AH formation with age
decreases
what happens to CB contraction with age
does not decrease
why does accommodation decrease with age (presbyopia)
changes in the lens
not in the contraction of the CB
2 main functions of the choroid
provides nutrients to outer retinal layers
has pigment that absorbs excess light that passes through RPE
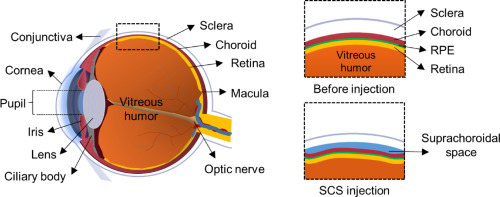
where is the suprachoroidal space and what is it used for
space on top of the choroid between the choroid and sclera
site of passageway for nerves and arteries from the back of the eye to the front
also used for suprachoroidal space injections
the choroid has a (higher/lower) protein content than the retina
higher
what does the protein gradient between the retina and choroid do
since the choroid has higher protein content, the protein gradient allows absorption of excess water from the retina into the choroid
what happens to bruch’s membrane with age
thickens
what happens to the choriocapillaris with age
decreases in thickness
what happens to over choroid thickness with age
decreases
list 4 functions of the vitreous
transparent medium for light
UV filter for the retina
structure and cushion for the globe (absorbs external forces/vibrations)
storage for ions and nutrients for the retina and lens
what wavelength of light does the vitreous filter out
300-350
how does the vitreous impact drug absorption
gel-like consistency of vitreous decreases the bioavailability of topical drugs in the posterior segment
total volume of the eye
5 mL
total volume of the vitreous
4 mL (80% of the eye)
weight of the vitreous
4 grams
what is the main type of collagen in the vitreous
type 2
what is the vitreous composed of
99% water, type 2 collagen fibrils, hyaluronic acid
what is hyaluronic acid
a non-sulfated GAG
what is the role of hyaluronic acid in the vitreous
supports collagen fibrils and helps maintain proper spacing, maintains vitreous viscosity
vitamin C concentration is (higher/lower) in the vitreous than blood plasma
higher
vitreous has more vitamin C