THE BASIC SUBJECTIVE ROUTINE Session 5
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
THE SUBJECTIVE ROUTINE
Uses “question and answer” techniques to establish a refractive correction which appears to give the patient the most comfortable vision.
In most cases, an objective starting point is used, which can be refined and modified using subjective methods.
Where do we start?
prev rx
retinoscopy
auto-refraction/ photo refraction
symp
ophthalmoscopy
Estimate of refractive error from visions.
Most cases – we are starting from retinoscopy result
If ret is better – subjective easier
Remember ret doesn’t equal subjective
Ret can be different to Rx or difficult so you might have to spend more time on subjective
EXAMPLE

L chart Vision 6/24 R 6/12. Lets assume this patient has a spherical Rx (no astigmatism)
How could we work out approx. Rx just using visions alone? We know that 0.25DS a line so that 1.25 (5 lines of blur)
Lets say the RHS is just a cyl Rx (no sph) What approx. would the cycl rx be?
Cyl – 0.50 DC to blur one line 3 lines of blur so ~1.50DC
Go back and revisit this, Snellen charts (no logmar)

THE BEST SPHERE
This is the most plus/ least minus spherical lens which gives us the best possible VA.
In an astigmatic error, the best sphere is achieved when the circle of least confusion is at the retina.
added plus lenses to blur, then we used minus lenses. We discussed giving MOST PLUS LEAST MINUS
Bs fine tune your ret. When ret has gone wrong or quite simply the ret does not equal the subjective –
Visions after ret – 6/18, BS offer plus then minus to improve the SPH component of the Rx
It can improve the vision even if ASTIG not found – to give you a better starting point
How to find the best sphere
Start c best vision- Ret should have improved it.
Monocularly
Offer plus (0.50) watch terminology.
does it help you read the line below
additional
Place spherical / highest power lenses closest to the eye (back cell in trial frame).
With plus lenses, insert replacement lenses before removing old lens (patient will experience fleeting blur).
V important – high powered lens
Relevance – control accom
+2.00 take it out (they will accommodate) +2.25 will cause blur -only relevant to + lenses
so only for + prescription put +2.25 c+2.00 then take out +2.00
DUOCHROME OR BICHROMATIC TEST

Subjective tests - Duo R/G
Diff wavelengths of light to establish ematropia
Alternate sph component – dontn touch cyls
Filters BRITISH STANDARD
Duochrome test
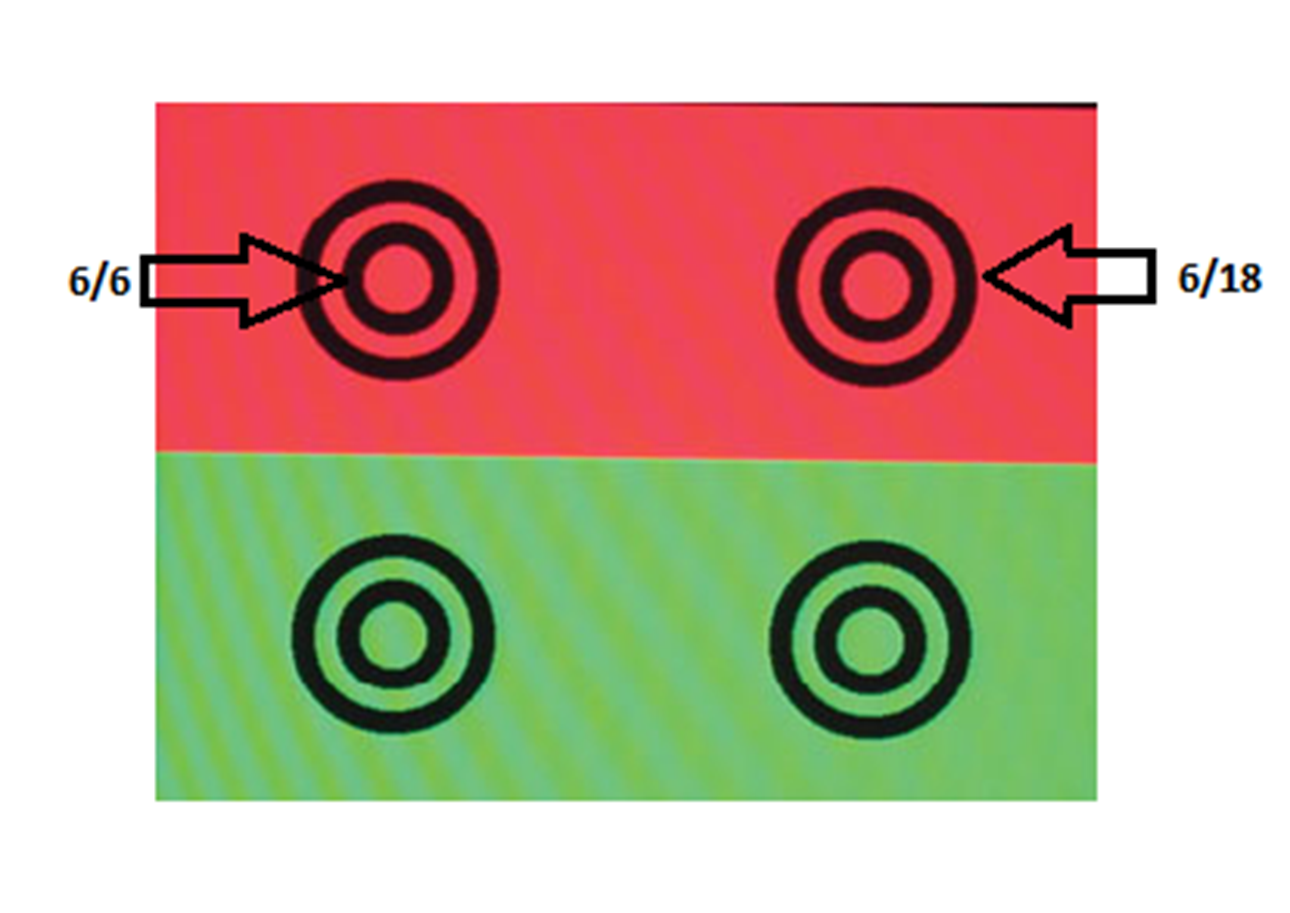
This is the target – same as we used for ret with circles minimsed to make non accom target
5/5 small curcel
6.18 large circle
Change size of target if px cant see it if less than 6/18
looking at the circles do they appear clearer rounder sharper against the red or green background
what does duo test mean
Relative to the best focus of the eye (yellow 570nm), the green filter of the bichromatic test (535nm) is 0.20DS in front, the red filter (620nm) is 0.24 DS behind.
Therefore black test targets on the red and green filters appear equally clear for an emmetrope or a corrected ametrope.
What about the uncorrected hyperope and myope and the colour defective?
R= g when yellow light focussed in the right place – green sl in front, red sl behind the circles appear equally clear
uncoorrected hyperope/ accom – Needs plus…focus behind retina, the one in front is clearest - so green
Uncorrected myope/over corrected –red (opposite as above)
Colour defective – this test does work CA but can be sl bias (less reliable)
If yellow light is in focus at the retina (ie when the spherical Rx is correct), then due to chromatic aberration, there will be a green focus 0.20DS in front of the retina, and a red focus 0.24DS behind the retina.
The 2 filter colours will appear equally bright providing colour vision is normal.
If red is clearer, this indicates too much +.
If green is clearer, this indicates too much -.
Duochrome Principles:
Duochrome Principles: The picture to the left shows an eye with light focussed on the Retina. The focus for green and red light is approximately equidistant from the retina (one in front, one behind) and so both appear equally clear.
The picture to the right shows a myopic eye which is not corrected. Here the focus for the red light is closer to the retina than the green light so the red side will appear clearer.
NOTE: If both red and green are too far from the retina then they will both be lured and hard to differentiate (Duochrome test is only for fine tuning)
Duochrome drawbacks
Patient must look at detail (usually circles), not be distracted by the colours.
•Only useful close to the final result.
•Older patients may have red bias due to yellowing of the crystalline lens.
•Many young patients with active accommodation have red bias.
•Colour deficiency – strong protanopes.
No subjective test is perfect – hence ehy we have a series of tests
String protanoes have green bias
+1.00 DS TEST
If best sphere achieved, +1.00DS will blur, either by 4 lines (from perfect VA) to 6/18, or back to 6/18 anyway if perfect vision has not yet been achieved due to astigmatism or pathology.
If less or more blur occurs, sphere can be adjusted accordingly.
•Easy to understand so often very useful.
subjective test
Using principles we are already using ans aware of
sph error is approx. 0.25 / line - so add 0.25
May not work in unstable hypermetropes or incipient myopes due to unstable accommodation.
•Needs careful explanation - if patient squints or tries to hard- they will see better than
•Small pupils - elderly may not work
•We haven’t corrected astigmatism yet – might not work
‘I’ve added a blur lens, this is supposed to blur your vision - looking at the chart without squinting or screwing your eyes up what would be the smallest line you can see?’
if vision not improved
If PH still improves VA, will need to use techniques to test for astigmatism.
Use check tests to ensure result correct, ie +1.00 DS test and/or Duochrome test.
Remember, accommodation is not static.
If after all of this – ret, BS, Duo and +1.00
TECHNIQUES FOR DETECTION OF ASTIGMATISM
¡There are 2 methods for detection of astigmatism:
¡the JACKSON CROSSED CYLINDER,
¡the BLOCK AND FAN.
JACKSON CROSSED CYLINDER,
Convenient.
Can use +ve or –ve cyls.
Head tilt does not affect result.
Some patients find technique hard to follow and need a more direct comparison.
NB: Method will be demonstrated in practical session.
working w cyl
CROSS CYL : Points to remember
For this technique the circle of least confusion is sited at the retina.
Which side of duochrome should you leave the patient on before commencing crossed cyls??
circle of least focus confusion on retina
always want be slightly green
if they said red - accom relaxed place -0.25 and induce accom and it should shift to green - keep placing -0.25 till on green
if too much on green put +0.25 so just on green
Use of minus cyls will also help.
Ret Vision BS, Duo, Cross cyl, +1.00 then a binocular test
cross cyl
can be twirled
Sphere power must always be re-checked at the end.
Push the plus!
Any monocular routine will need to be followed by binocular balancing…
