Biology EOY
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Biological molecules, photosynthesis, and organising systems covered
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
Function of carbohydrates
Provides energy. Found in pasta, rice, and sugar
Function of lipids (fats and oils)
Provides energy, acts as an energy store, and provides insulation. Found in butter and oily fish
Function of proteins
Needed for growth and repair of tissue and to provide energy in case of emergencies. Found in mainly meat and fish but occasionally in beans
Function of vitamin A
Improves vision, keeps skin healthy, and keeps hair healthy. Found in carrots, liver
Function of vitamin C
Needed to prevent scurvy. Found in fruits, especially citruses like oranges
Function of vitamin D
Absorbs calcium and maintains bone health. Found in sunlight, fish, and eggs
Function of calcium (minerals)
Needed to make and strengthen bones and teeth. Found in dairy products
Function of iron
Essential for hemoglobin production and oxygen transport in the blood. Found in red meat, beans, and spinach.
Function of water
Essential for chemical reactions to take place in cells. Found in beverages and foods.
Function of fibre
Provides bulk (roughage) for the intestine to push food through it. Found in whole grains and vegetables
Energy requirement regarding age
Children and teenagers need more energy compared to older people as they need energy to grow and are generally more active
Energy requirement for pregnancy
Pregnant women need more energy than other women as they have to provide energy for their babies to develop alongside them–they practically have to provide energy for two people
Structure or carbohydrates
Made up of simple sugars (monosacharides) like glucose or maltose. Contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (C,H,O)
Structure of proteins
Proteins are made up of amino acids. Contains carbon, nitrogen, hydrogen, and oxygen (C,N,H,O)
Structure of lipids
Lipids are made up of fatty acids and glycerol. Contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (C,H,O)
Test for starch
Add iodine solution to starch. If starch present it becomes blue-black; if not, it stays brown
Test for proteins
Add biuret raegant to the food sample. If protein is present, it turns to purple; if not it will stay blue.
Test for lipids (layers)
Add Sudan III stain solution. If lipids are present, a separate bright red layer will form at the top; if not, the solution stays mixed
Test for lipids (emulsion)
Add ethanol to the solution. If lipids are present, the solution emulsifies and turns cloudy; if not, no lipids are present
Test for glucose
Place test tube with food sample in a hot bath at 75°C for five minutes. Then add drops of Benedict's solution. Leave it for 5 minutes. Concentration of sugar is based on the colour: green/yellow is low concentration, orange is medium concentration, red is high concentration
Enzyme definition
Enzymes are biological catalysts made from protein that break down foods chemically
Lock and key model
Enzymes are specific and only bind with one substrate so only substrates that have a complementary shape to the active site will be broken down by it
Anabolic enzymes
Links together two different substrates
Catabolic enzymes
Breaks down substrates into smaller molecules
Temperature's effect on enzymes
As temperature increases, so does kinetic energy, leading to more enzyme-substrate complexes formed. However, when it is past the optimum, the active site denatures and the substrate can no longer bind to the active site
pH's effects on enzymes
Different enzymes work well at different optimum pH. If the pH is too high or too low, the active site will denature, making substrates unable to bind to the active site
Define denature
When an active site changes shape due to bonds bejng broken
Explain photosynthesis
Plants use chlorophyll to absorb sunlight which acts as a catalyst to convert CO₂ and H₂O into glucose–a plant's source of energy–as well as a waste product of O₂. This process occurs in chloroplasts.
Word equation for photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide + water —> glucose + oxygen
Symbol equation for photosynthesis
6CO₂ + 6H₂O —> C₆H₁₂O₆ +6O₂
Effect of temperature in photosynthesis
Enzymes are involved in photosynthesis so if temperature goes past the optimum, the enzymes’ active sites become denatured and rate of photosynthesis drops
Effect of light in photosynthesis
As light intensity increases, so does the rate of photosynthesis linearly. But after a certain point, light intensity is no longer a limiting factor, something
Effect of CO₂ concentration in photosynthesis
As CO₂ concentration increases, does the rate of photosynthesis linearly. But after a certain point, CO₂ concentration is no longer a limiting factor, something else is
Test light necessity in photosynthesis
Deprive plant from light for 48 hours
Take leaf from plant and test for starch (iodine)
No starch has been made meaning no photosynthesis has occurred: light is necessary
Test chlorophyll necessity in photosynthesis
Take variegated (green and white) leaf exposed to light for a bit
Test leaf for starch (iodine)
Only green parts (parts with chlorophyll) has turned blue-black. Chlorophyll is a necessity
Test CO₂ necessity in photosynthesis
Place plant and soda lime (absorbs CO₂) in sealed bell jar with light outside
After a while test leaf for starch (iodine)
Plant doesn't turn blue-black. CO₂ is necessary
Name leaf structure from top to bottom
Epidermal tissue—>palisade mesophyll tissue—>spongy mesophyll layer
Adaptations of epidermal tissue
Secretes waxy substance (waxy cuticle)—> protection from water and dirt
Transparent—> light can go through
Thin—> easy gas diffusion
Adaptations of palisade mesophyll layer
at top to maximise sunlight absorption
packed for as many palisade cells (plant cells) as possible
many chloroplasts for maximum sun absorption
Adaptations for spongy mesophyll layer
contains some chloroplasts for photosynthesis
has space for easy gas diffusion
Adaptations of the stomata
Two guard cells which open up when swollen with water (to let it in) and open during the day when photosynthesis occurs. Typically found at bottom of leaf
Skeletal system
Protects and supports body organs and provides a framework the muscles use to support movement. Made up of bones and joints
Respiratory system
Responsible for exchanging oxygen in and carbon dioxide out through diffusion (gas exchange).
Circulatory system
Pumps blood around the body
Nervous system
The network of nerve cells and fibres that transmits nerve impulses between parts of the body.
Lymphatic system
Composed of a network of vessels, ducts, nodes, and organs. Provides defence against infection.
Digestive system
Breaks down food into absorbable units that enter the blood for distribution to body cells.
Excretory system
Removes waste from your body and controls water balance
Muscular system
Enables movement of the body and internal organs
Why do we have so many different organ systems?
To live we have to carry out all the life processes: nutrition, excretion, movement, sensitivity, growth, reproduction, and respiration. Multiple systems allow complex organisms to carry out different jobs at the same time
Function of liver
Produces bile which breaks down dead blood cells and digests cholesterol (build up may lead to blocked arteries). Also stores glycogen which balances blood sugar levels.
Function of kidney
Regulate the water content in the blood. They excrete/remove the toxic waste products of metabolism (chemical reaction of changing food to energy)
Function of large intestines
Absorbs water and salts from the liquid waste and turns it into solid waste (stool)
Function of small intestines
Digests food further and absorbs nutrients into the blood
Function of lungs
Gas exchange and breathing
Function of stomach
Digests food using peristalsis (mechanical) and enzymes (chemical). Has HCl maintaining pH needed for enzymes to work and kills of bacteria
Function of heart
Pumps blood around the body
Function of brain
Coordinates nervous response
Function of bladder
Stores urine
Function of ciliated cells
Has many tiny hairs called cilia which 'flick' mucus and other materials out the trachea
Function of goblet cell
Produces mucus to trap harmful bacteria and dust. Found in the trachea
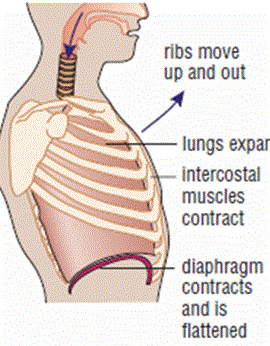
Describe the change in the body during inhalation
diaphragm contracts
intercostal muscles contract
volume of ribcage increase
pressure in chest decreases
air moves inside lungs.
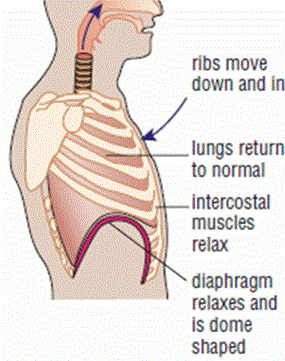
Describe the change in the body during exhalation
diaphragm contracts
intercostal muscles relax
volume of ribcage decreases
pressure increases
air moves out of lungs
Composition of inhaled air
21% Oxygen
79% Nitrogen
0.04% Carbon Dioxide
Composition of exhaled air
16% Oxygen
79% Nitrogen
4% Carbon Dioxide
Word equation for respiration
Glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy (ATP)
Balanced equation for respiration
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O2 -> 6CO₂ + 6H₂O
Label the respiratory system
Location of gas exchange
alveoli
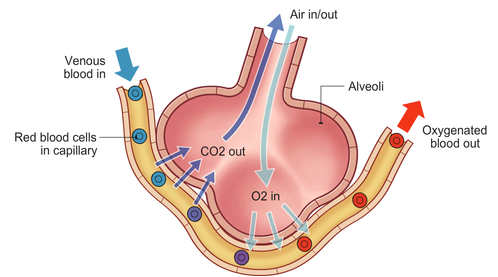
Adaptations of alveoli
Thin walls (just one cell thick) to reduce the diffusion distance
Large surface area for maximum exchange of gases
Moist surface for the dissolving of gases in alveolar air so that they can diffuse across the alveolar walls
Rich blood supply to remove diffused gases and maintain a concentration gradient for further diffusion
Peristalsis
Constriction and relaxation of the muscles of the intestine, trachea, or another canal, pushing digested food forwards
Function of mouth
Food is chewed here to be broken down mechanically. Enzymes begin to break it up the food into smaller molecules chemically
Function of oesophagus
Connects the mouth to the stomach, transporting food and liquids.
Function of rectum
Stores faeces until it is excreted
Function of anus
Muscle which excretes faeces
Villi
Finger-like extensions of the intestinal mucosa that increase the surface area for absorption (taking in nutrients broken down by enzymes)
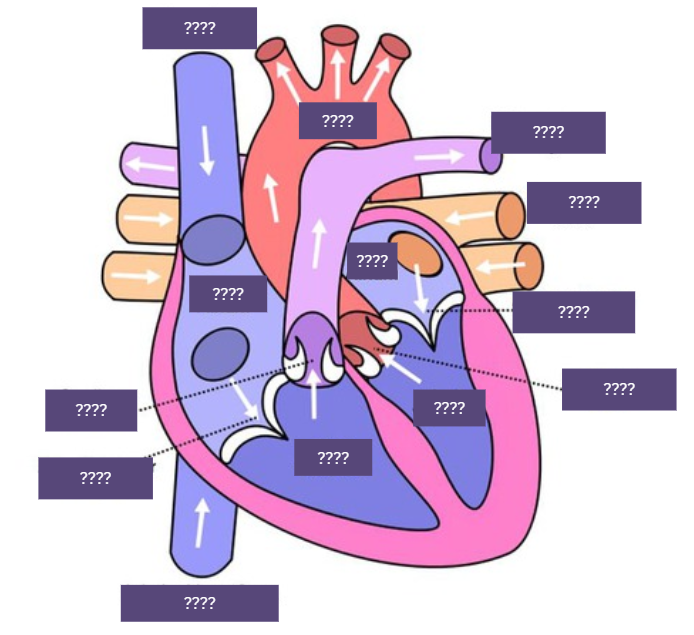
Heart diagram (unlabelled)
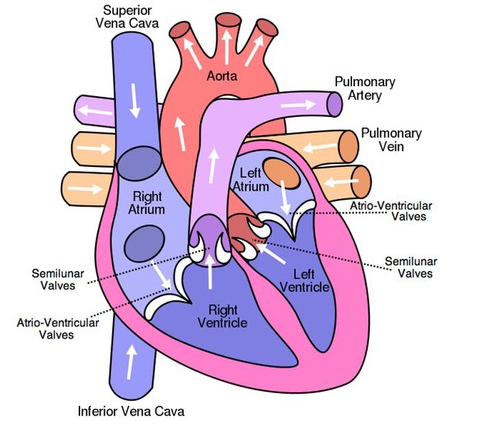
Heart diagram (labeled)
Direction of blood flow
Oxygenated blood from lungs to left side of heart
Oxygenated blood from heart to rest of body
Deoxygenated blood from body to left side of heart
Deoxygenated blood from heart to back to lungs
Double circulatory system
Blood passes twice through the heart in one complete cycle, one pump to send blood to the body and the other to pump it back to the lungs. This ensures that the body is never out of supply for oxygen by constantly sending out and obtaining oxygenated blood
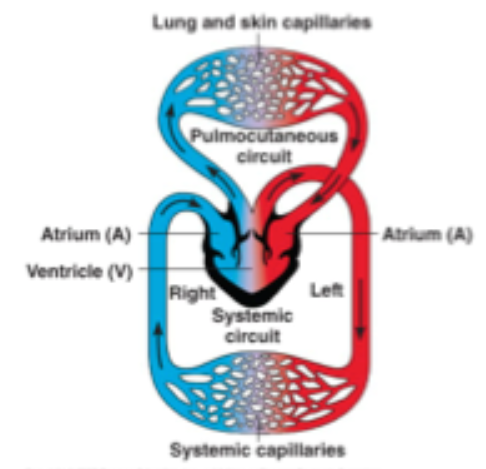
Cardiovascular disease
The narrowing/blocking of blood vessels which can lead to a heart attack, chest pain, or stroke
Explain atherosclerosis
When fat cholesterol builds up, the fat dries up and turns into plaque, leading to atherosclerosis, leading to an increase in blood pressure as the heart tries to pump the blood through, possibly leading to a heart attack
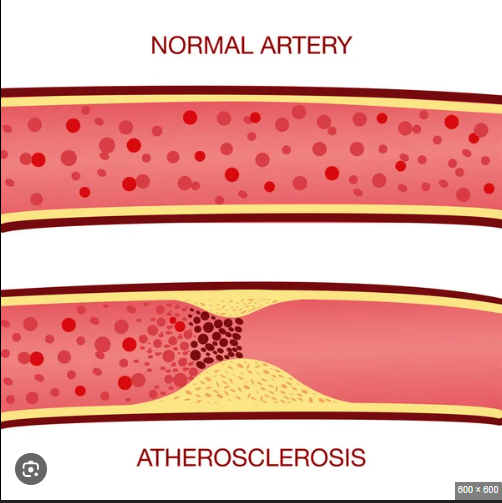
Causes of cardiovascular disease
Genetic variation
Poor diet—>increases cholesterol and plaque build up
High blood pressure—>friction narrows and damages vessels, making it more prone to plaque build up
Smoking—>chemicals from smoking damages vessels, making it more prone to plaque build up
Sedentary lifestyle—>reduces blood circulation, leading to build up of cholesterol and plaque
Age—>cholesterol levels naturally increase overtime
Alimentary canal
The passage which food passes through (all the digestive system excluding gallbladder, liver, pancreas, and appendix)
Muscular walls
Contracts (squeeze) and relaxes to send blood throughout your body
Atrioventricular valves
Allows blood to flow from the arteries to the ventricles, but prevent flow in the opposite direction.
Semilunar valves
Allows blood to flow from the ventricles to the arteries and prevent the flow in the opposite direction
Septum
It forms a barrier in the four-chamber of heart, preventing oxygenated and deoxygenated blood from mixing.
Coronary arteries
Supply the heart muscle with blood high in oxygen, branching off the aorta
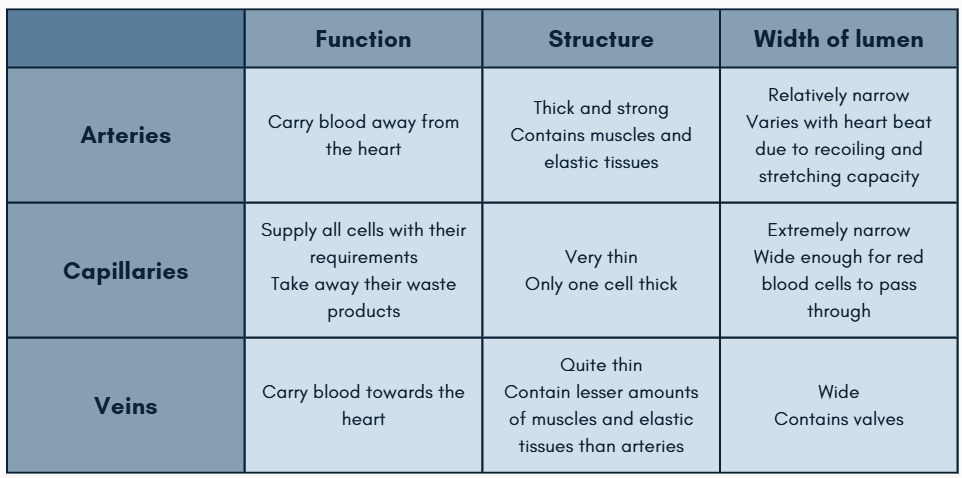
Function, structure, and width of lumen of arteries
Carries blood away from the heart
Thick and strong, containing muscles and elastic tissues
Lumens are relatively narrow, varying with heart beat due to recoiling and stretching capacity
Function, structure, and width of lumen of veins
Supplies all cells with their requirements and takes away their waste products
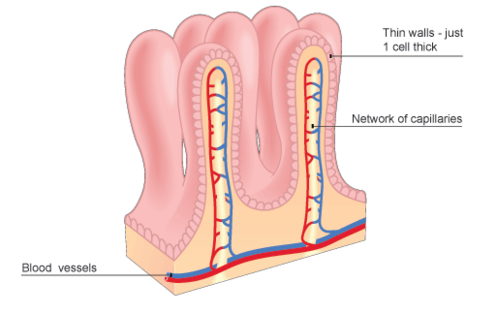
Very thin; only one cell thick
Lumens are extremely narrow, wide enough for red blood cells to pass through
Function, structure, and width of lumen of capillaries
Carries blood towards the heart
Quite thin, containing smaller amounts of muscles and elastic tissues than arteries
Lumens are wide, containing valves
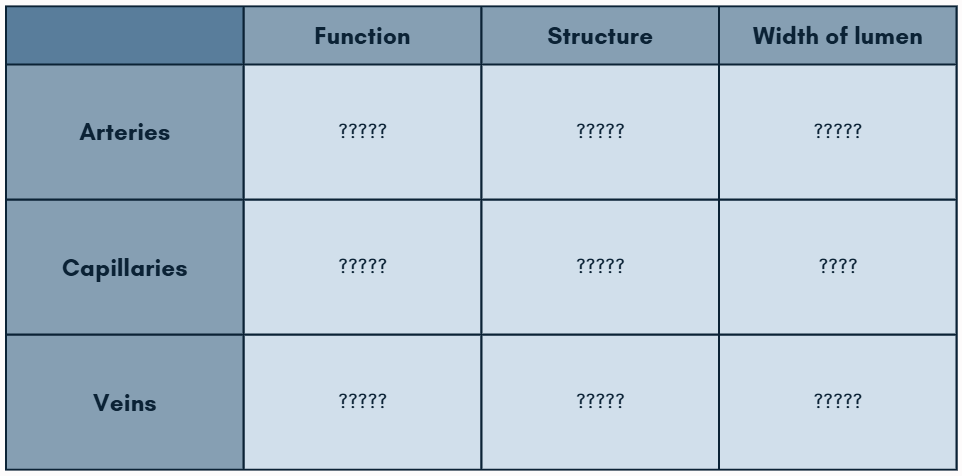
Fill in the table