plant organisation
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
is the leaf an organ?
yes
transpiration
the loss of water by evaporation from leaves through the stomata
transpiration process
water vapour from leaf cells evaporates through stomata (on underside of leaf) into surrounding air
water potential inside cells of leaf lowered (due to loss of water)
water moves from xylem to leaf cells down water potential gradient
water pulled up xylem due to (strong) cohesive forces between molecules, forming continuous column of water
water moves into xylem from root cells, lowering water potential inside root cells so water moves into them by osmosis
transpiration stream
a continuous column of water and dissolved minerals through a plant, from the roots up to the leaves, and out into the atmosphere as water vapour
factors affecting rate of transpiration (3)
temperature
humidity
wind speed
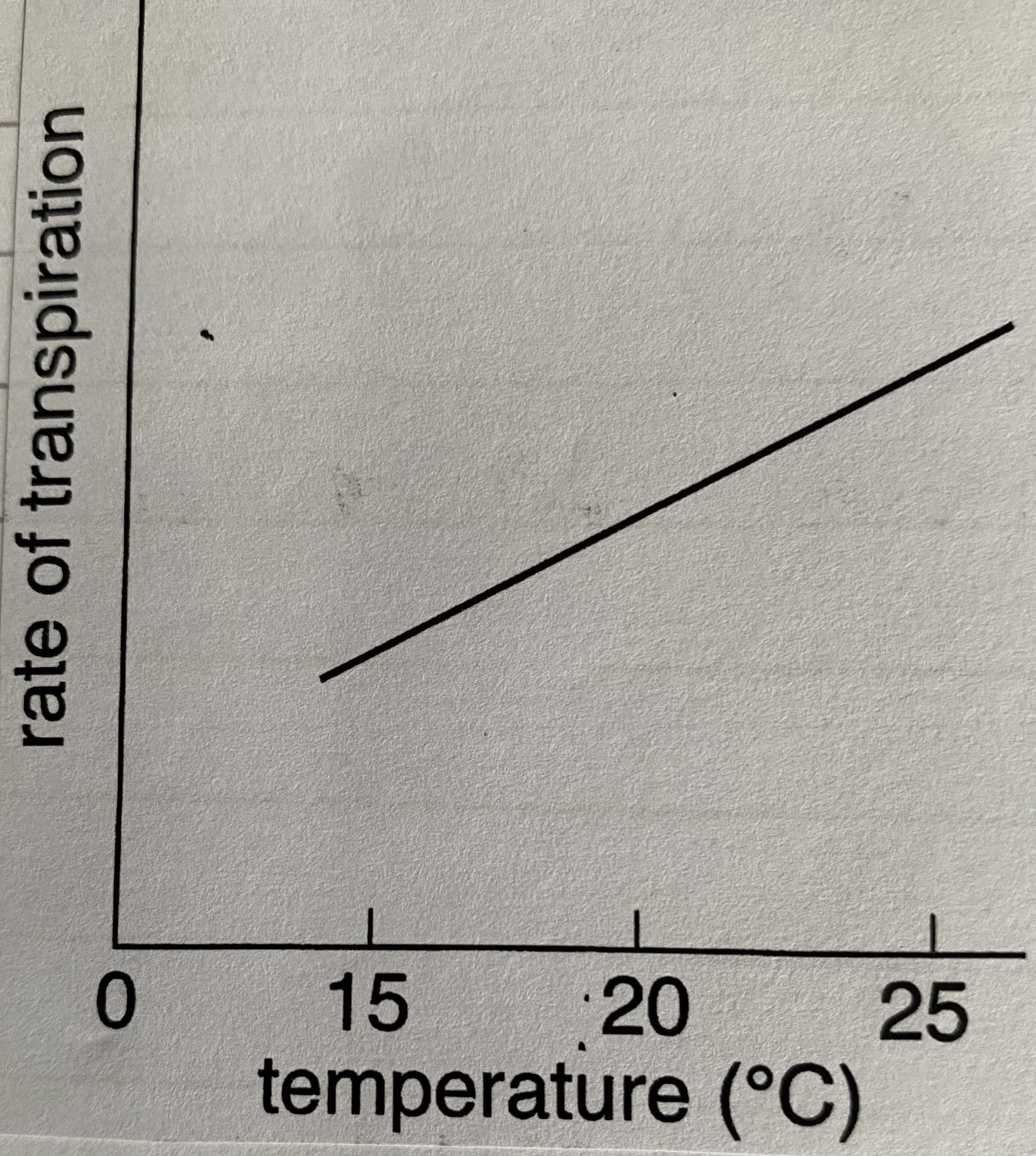
how does temperature affect the rate of transpiration?
as temperature increases rate increases (KE of particles has increased) but in extreme temperatures stomata will close so rate stops (conserves water but prevents photosynthesis)
what is humidity?
how saturated the air is
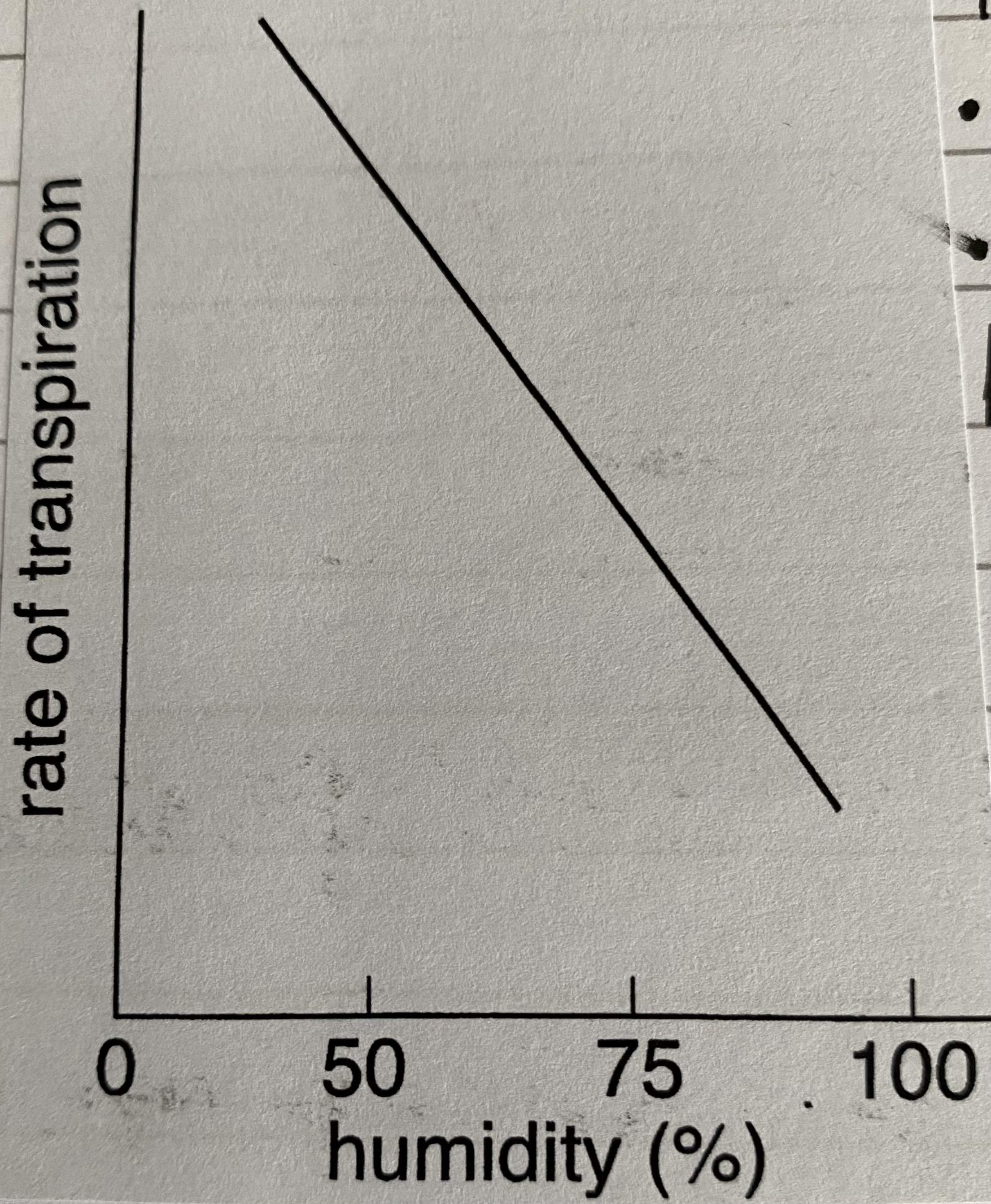
how does humidity affect the rate of transpiration?
as humidity increases rate decreases due to osmosis (high humidity = shallow gradient)
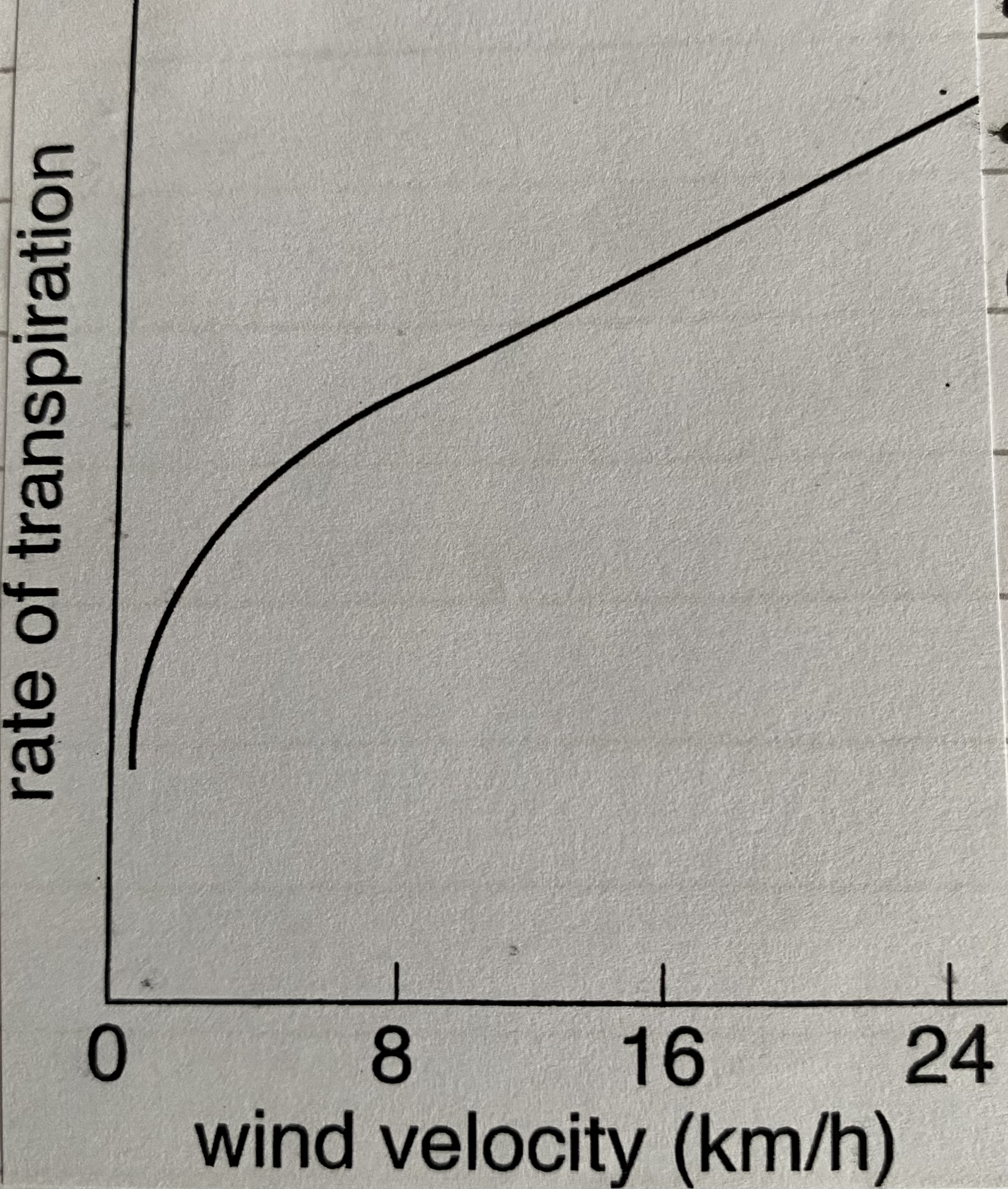
how does wind speed affect the rate of transpiration?
as wind speed increases rate increases as wind moves water vapour in boundary layer (allowing more water vapour to take its place)
translocation
the movement of food molecules through the phloem tissue
role of xylem
transports water and dissolved mineral ions around plant
direction of movement in xylem
always UP plant:
roots —> stem —> leaves
role of phloem
transports dissolved sucrose (from leaves for immediate use or storage) and amino acids around plant
direction of movement in phloem
either upwards OR downwards
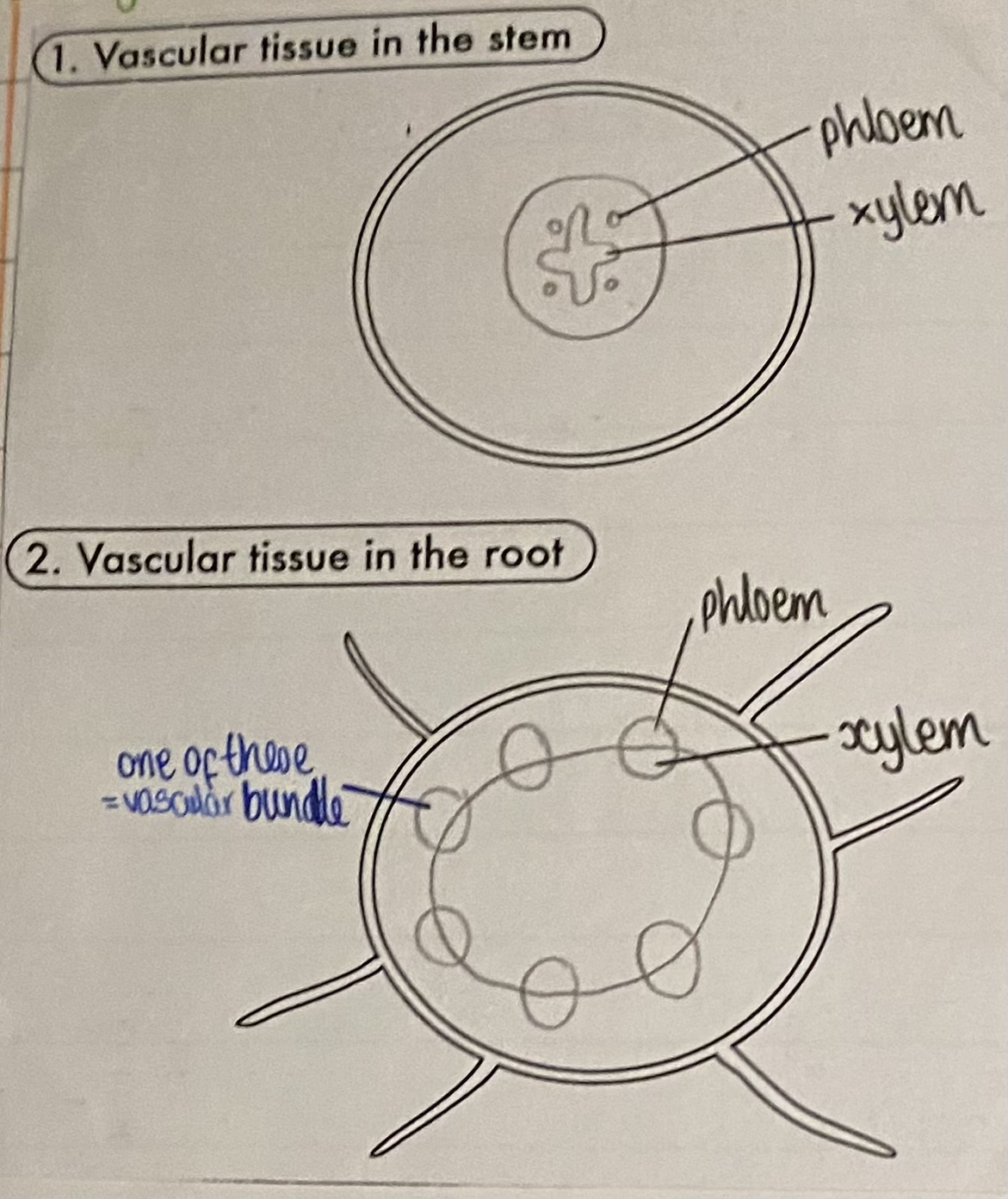
xylem and phloem arrangement
arranged together in vascular bundles in roots, stem and leaves
leaf structure
see image
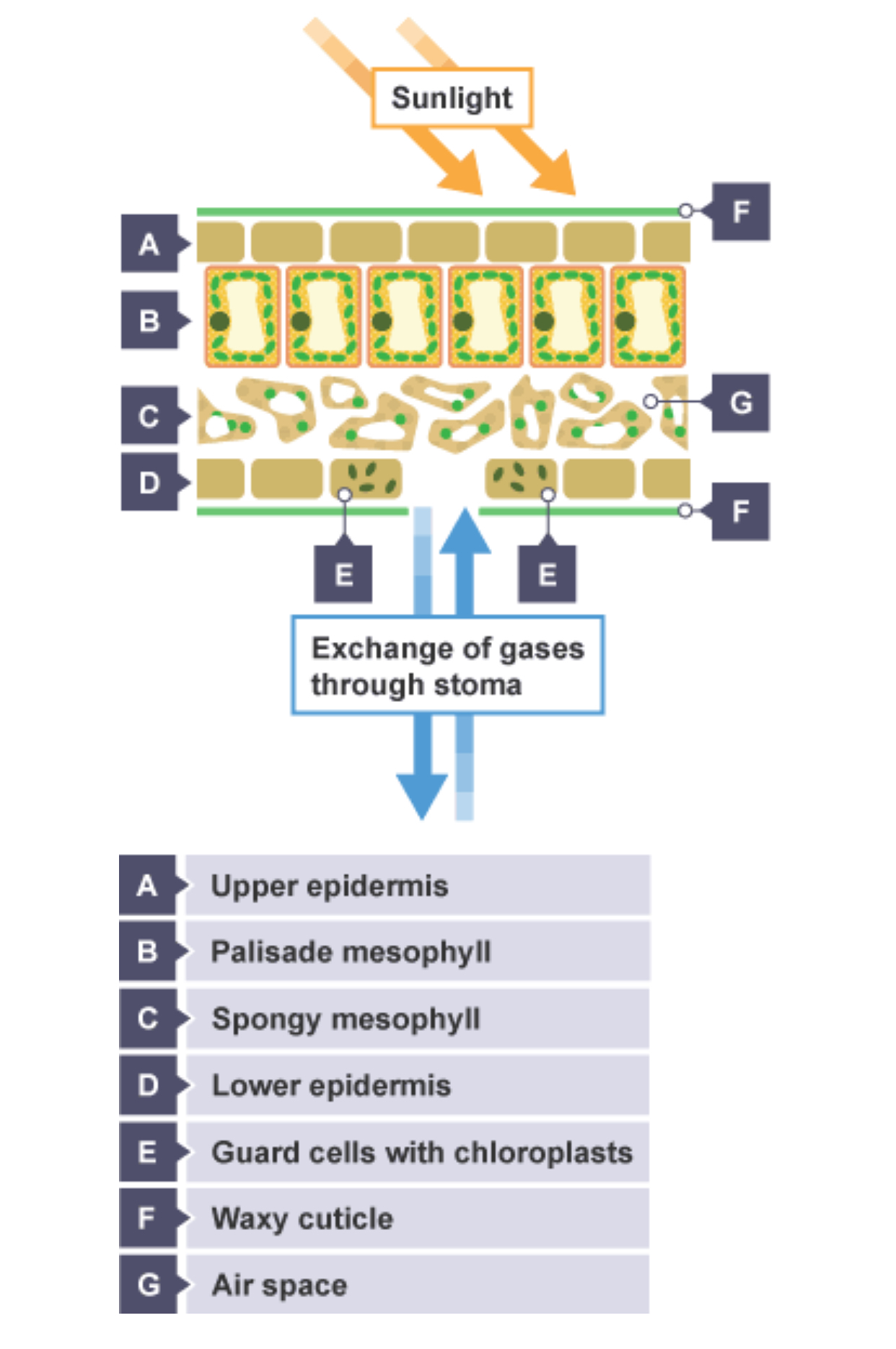
what is the palisade mesophyll adapted for?
adapted to absorb light efficiently (for photosynthesis)
how is the palisade mesophyll adapted?
many chloroplasts
column shaped and arranged closely together
towards upper surface of leaf
what is the spongy mesophyll adapted for?
adapted for efficient gas exchange
how is the spongy mesophyll adapted?
tissue loosely packed
cells covered by thin layer of water (gases dissolve in this so diffuse easily)
what is the waxy cuticle adapted for?
reduces water loss by evaporation
how is the waxy cuticle adapted?
is a waterproof waxy layer on top leaf
what is the upper epidermis adapted for?
lets light straight through to palisade cells
how is the upper epidermis adapted?
single layer of cells covering too of leaf
are clear
lower epidermis
single layer of cells covering bottom of leaf
what are stomata?
tiny holes in lower epidermis
role of stomata
control water loss and gas exchange
how are the stomata controlled?
guard cells surround stomata which allow stomata to open and close
what does a potometer measure?
the rate of water uptake by a plant
how does a potometer measure this?
by estimating the rate of transpiration (as most water absorbed by a plant is lost through transpiration)