PPFA 7- states of matter and their transformation
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
What are the 3 state of matters ?
Three primary states : solid, liquid and gases
why are these important - help to understand pharmaceutical formulation , stability and packaging
What are some examples of medications in these states and their properties ?
What are intermolecular forces ?
-Secondary forces between molecules, weaker than covalent/ionic bonds.
-These forces also critically affect the structure and stability of biomolecules (e.g.,
proteins, DNA) in pharmaceutical and biotech applications.
-Types of intermolecular forces vary in strength and pharmaceutical impact.
What are intermolecular forces essential for ?
Essential for:
Drug formulation → tablet compression, powders, aerosols.
Drug delivery → solubility and dissolution control.
Stability → solid-state polymorphism and amorphous stability.
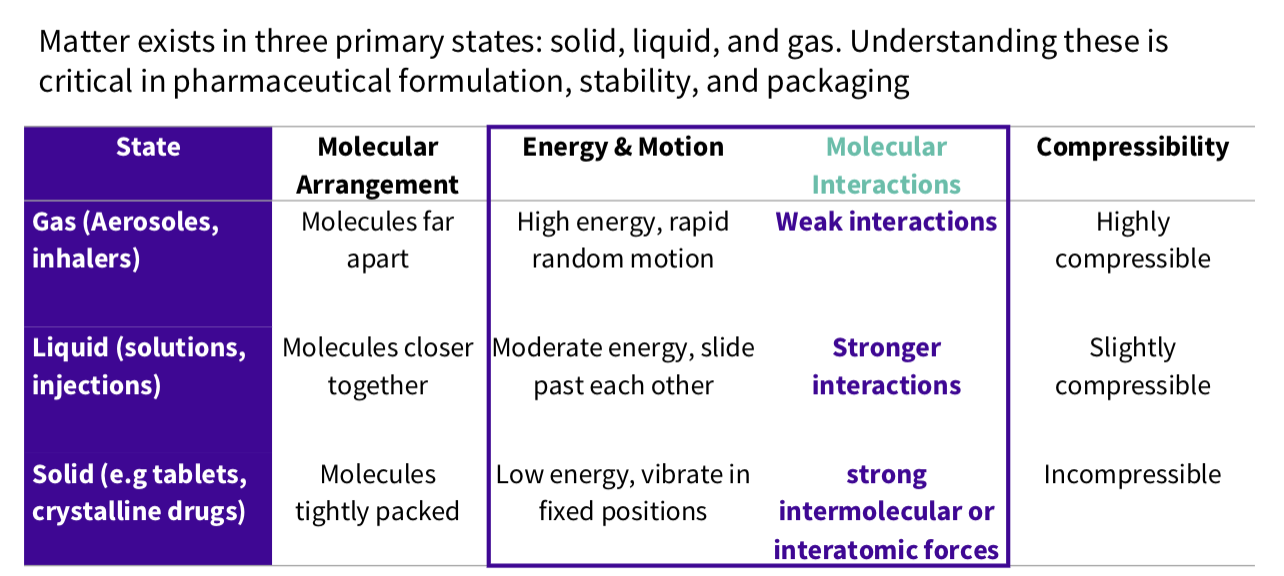
What is are repulsive vs attractive forces?
Molecules experience two opposing forces :
Attractive - hold molecules together
Repulsive - prevent collapse
Describe a repulsive forces
When two particles approach, their electric double
layers overlap, causing repulsion
What is the pharmacy relevance of repulsive forces ?
Pharmacy relevance:
Stabilizes colloidal drug suspensions (e.g.,
emulsions, liposomes).
Prevents aggregation of particles in
formulations.
When does repulsion dominate?
At Very Short Distances
Repulsion dominates strongly
-This creates an energy barrier that prevents
particle aggregation
Describe a attractive forces
Attractive Forces dominates at intermediate
distance → Molecules are pulled closer
What is the relevance of attractive forces ?
Pharmacy relevance:
Promotes aggregation if repulsive forces are
weak.
Important for powder compaction in
tablets and aerosol stability.
Note- energy approx. 0 = no significant interaction
What do these forces control?
These forces control physical properties
like:
Melting and boiling points
Density
Solubility
Vapor pressure
What is Van der waals ?
Weak intermolecular forces that relate to non ionic interactions between molecules,yet they involve charge – charge interactions.
Partial charges can be permanent or be induced by neighbouring groups
What are the types of van der waals forces?
Types of Van der Waals Forces:
Keesom Forces (Dipole–Dipole)
Debye Forces (Dipole-Induced Dipole)
London Dispersion Forces (Induced Dipole-Induced Dipole)
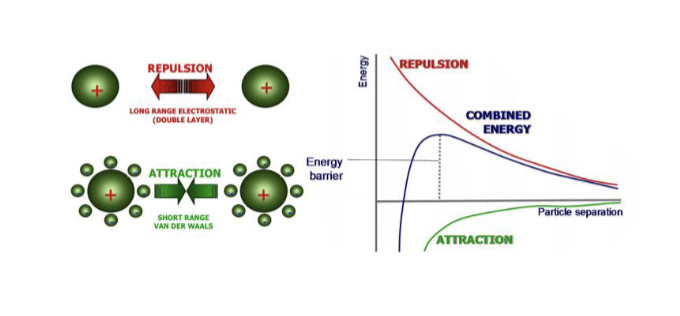
What is a keesom forces and describe it ( dipole - dipole ) ?
Occur between permanent dipoles in polar molecules.
The permanent dipoles interact
with one another in an ion-like
fashion.
Because the charges are partial,
the strength of bonding is much
weaker
What is the pharmaceutical relevance of keesom forces?
Pharmaceutical Relevance
Solubility: Polar drug molecules dissolve better in
polar solvents.
Tablet stability: Dipole interactions between
excipients help with powder compaction
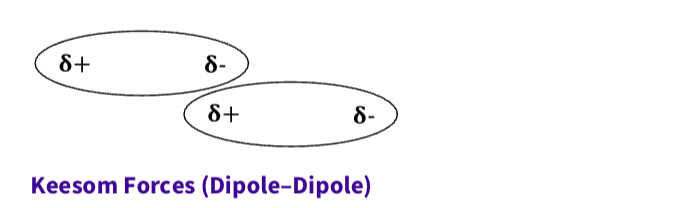
What is debye forces ( dipole - induced dipole)
A permanent dipole induces polarity in a nearby non-polar molecule, creating attraction
Show the ability of a permanent
dipole to polarize charge in a
neighbouring nonpolar easily
polarizable molecule.
What is london dispersion forces ( induced dipole- induced dipole) ?
Caused by temporary dipoles due to fluctuations in electron distribution.
why is it important - Important in non-polar molecules like
hydrocarbons and biological membranes
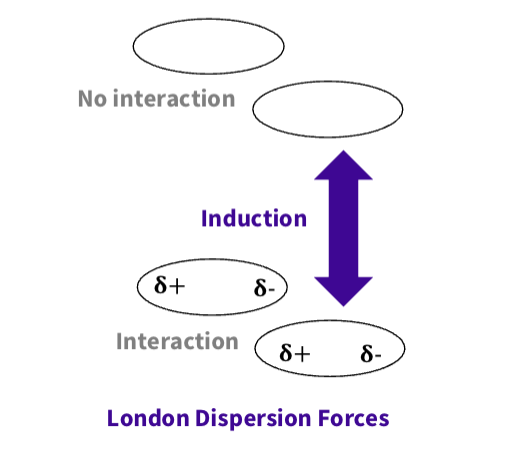
What is orbital overlap ( π - π interactions) ?
-type of dipole - dipole force
-the interaction between π electron orbitals in systems
eg - aromatic-aromatic interactions can occur when the double bonded π -orbitals from two rings overlap
Whta is a hydrogen bond ?
-The interaction between H
and highly electronegative
atoms (O, N, F)
stronger than van der waals stronger
What is the applications of hydrogen bonds in pharmacy ?
Applications in pharmacy:
• Improves solubility of polar
drugs.
• Stabilizes crystalline forms.
• Governs polymorphism → affects
bioavailability.
What is the ion - dipole and ion- induced dipole forces ?
Occur between polar or nonpolar molecules and ions
Example - Ion-induced dipole forces
are involved in the formation of the
iodide complex.
What is the role of ion- dipole?
ion-Dipole
▪ Major role in dissolution of
salts.
▪ Example: NaCl dissolving in
water.
This effect can clearly influence the solubility of solute and play
important role in dissolution process
What is ion-ion interaction?
Strongest interaction.
Relevant for salt forms of drugs to enhance stability and solubility.
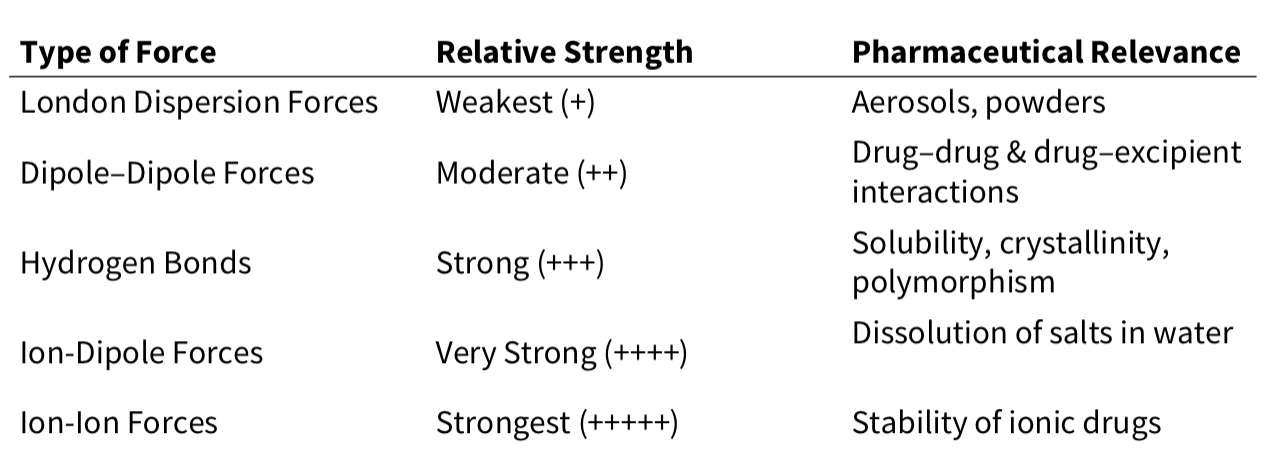
Intermolecular interactions - summary
What is gibbs phase rule ?
This rule tells us how many variables we can control while maintaining equilibrium, which
is key when formulating stable products:
F = C − P + 2
F = degrees of freedom — how many variables we can change independently
C = number of components,
P = number of phases in equilibrium
What is gibbs phase rule - single component
If we have liquid water only (P=1, C=1) ⟶ What is F?
we can vary both temperature and pressure freely
F = 2
What is gibbs phase rule - two components ?
f we have liquid + vapor (P = 2, C=1) ⟶ What is F?
we can only change one variable without disturbing equilibrium
F = 1
What is gibbs phase rules- 3 components ?
At the triple point (solid + liquid + vapor, P = 3, C=1) ⟶ What is F?
we can't change anything without shifting the phases
This is why the triple point of water has a fixed temperature and fixed pressure
F = 0
Phase diagram
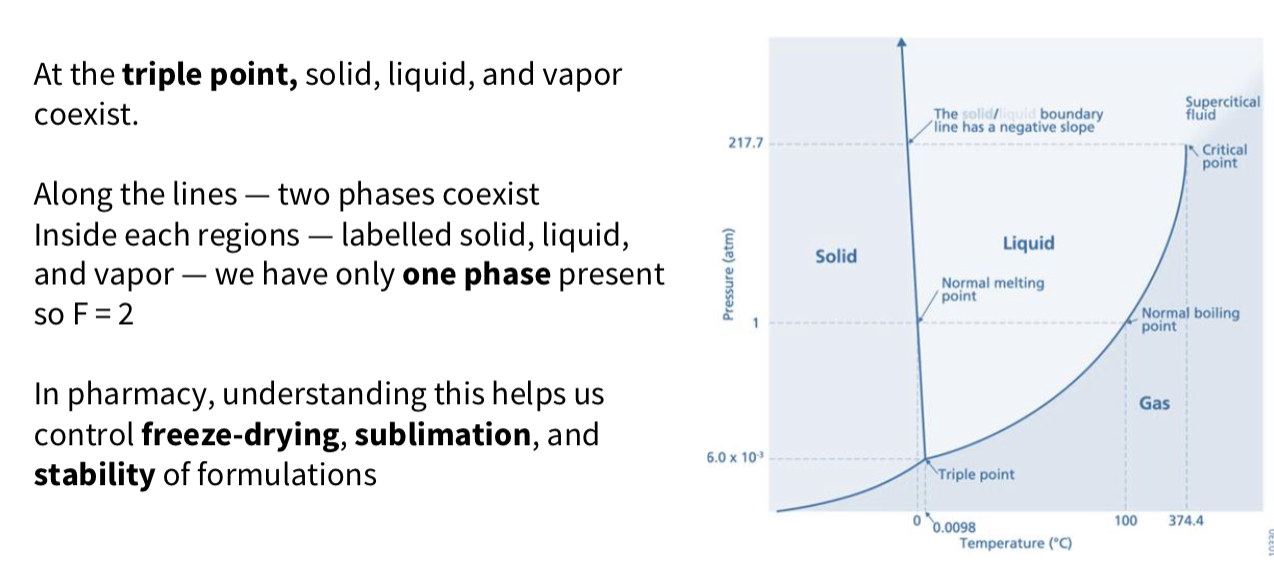
What is a phase diagram ?
Phase diagrams show relationships between
temperature, pressure, and composition
What is phase equilibrium ?
Phase equilibrium: stable coexistence of
phases without net change.
Pharmacy relevance:
▪ Predict drug stability & storage conditions
▪ Guide formulation development
▪ Understand solubility & melting behavior
What is freeze - drying ( lymphilization) ?
Direct transition from solid - gas without becoming liquid
used in pharmaceuticals for dry heat - sensitive materials
What is the process for freeze drying ?
Process-
material is frozen
placed under vacuum
ice sublimes, leaving dry product
Advantages - preserves structure , stability and potency of drugs
Scenario - application
A batch of a monoclonal antibody arrives ,but its stored as a freeze-dried powder ( lyophilized vial) instead of a liquid .
antibody - biologic
-protein = can denature
-solid - more stable than liquid ,limited in conditions ,stable longer
-heat sensitive - FD better method so convert S-G ( avoid high temp)
-Before given - reconstituted with sterile water
-Extended shelf life
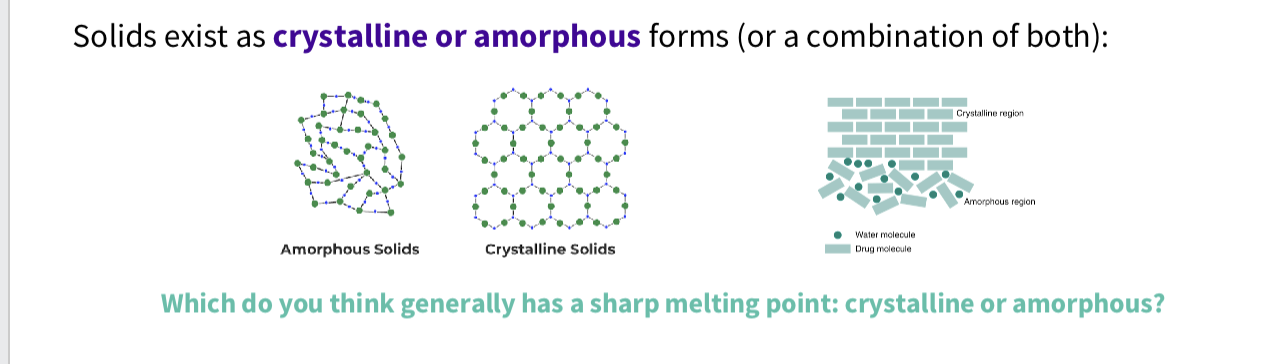
How do pharmaceutical solids exist ?
solids exist as crystalline or amorphous forms ( or a combination of both)
What is a amorphous solids?
irregular arrangement , higher solubility but lower stability
( easily changes overtime)
What is a crystalline solid ?
highly ordered , definite melting points - more sharp melting points ,to break all of these bonds
crystals - with weak forces have low melting points
crystals with strong lattices ( ie strong attractive forces) have high melting points
How do crystals form?
Two main routes:
Cooling molten material (e.g. suppositories, creams)
From solution → requires supersaturation
Ways to induce crystallization from solution:
Evaporation (↑ concentration)
Cooling (↓ solubility)- enhanced by heating ,than cooling might leave some crystals
Antisolvent addition (↓ solubility)
Crystal formation steps:
Nucleation (first tiny cluster)
Growth (molecules add on)
Crystallization = supersaturation → nucleation → growth → ordered solid
What is the main crystallization equation?
Crystallization = supersaturation → nucleation → growth → ordered solid
What is polymorphism?
Polymorphism is the ability of a substance to exist in multiple crystalline forms, each with different properties
What is pharmaceutical importance of polymorphism ?
Pharmaceutical importance:
• Affects solubility, dissolution, and bioavailability.
• Impacts drug formulation and stability.
Polymorphs will convert to the stable form over
time.
Regulatory authorities require control of
polymorphs primarily for this reason
What links polymorphism and tablet manufacture ?
Polymorphs affect not just dissolution but also
physical properties
Paracetamol: high-dose drug with poor
compression → difficult to make tablets
Limited excipient can be added (tablet size
constraint)
Researchers explore alternative polymorphs
with better compressibility to improve tablet
manufacture
What is a hydrate crystals ?
Hydrate = crystal lattice with water molecules trapped in fixed
ratio (e.g. monohydrate, dihydrate).
~11% of known compounds exist as hydrates.
Most common: monohydrate > dihydrate > trihydrate
What is solvate crystals ?
Solvate = lattice contains other solvents (e.g. ethanolate).
Rarely used in pharma (risk of toxicity/impurity).
What are some properties of hydrates ?
Hydrates can behave like polymorphs
(“pseudopolymorphism”).
What is the effect on dissolution rate (solubility)?
Dissolution rate may be faster or slower than anhydrous
form:
Theophylline: anhydrous dissolves faster
(supersaturated → reverts to hydrate equilibrium).
Erythromycin: hydrates dissolve faster (water
disrupts lattice).
Key point: Hydrate vs anhydrous form changes dissolution and bioavailability, so must be
carefully controlled in drug development