MKTG 1030 WEEK 7
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
What is a business’ objective?
deliver shareholder profit
What does PLC stand for?
Product Life Cycle
What is the PLC?
tool managing product stage
What are the PLC factors?
never in success
remain in stage
global difference
varied marketing method
What is an example of a short PLC product?
computer
What is an example of a long PLC product?
jewelry
kitchen
What are the PLC stages?
intro
growth
maturity
decline
What is the first PLC stage?
introduction
What is the second PLC stage?
growth
What is the third PLC stage?
maturity
What is the fourth PLC stage?
decline
What PLC stage has the highest marketing cost & lowest profit?
introduction
Why does the first PLC stage have the highest marketing cost & lowest profit?
R&D
Who has distribution access in the first PLC stage?
early adopter
What is penetration pricing?
price strategy
low initial price
What is penetration pricing’s use?
encourage customer to try product
What is skimming pricing?
high initial price
What is skimming pricing’s use?
quick initial investment recovery
What PLC stage accepts the product by the market?
growth
What PLC stage encourages competition?
growth
Why does the second PLC stage encourage competition?
increased sale
attractive profit
What does the second PLC stage require to ensure availability?
expanded distribution
increased production
True or False: Pricing during the second PLC stage fluctuates.
False: Pricing during the second PLC stage remains constant.
Why do sales level off in the third PLC stage?
eroded demand
replacement / repeat sale > new customer
What PLC stage only has the strongest suppliers survive?
maturity
What are the ways to extend life cycles on existing products?
enter new market
modify target market & marketing strategy
add new feature
What comprises the second PLC stage packaging strategy?
redesign
What comprises the second PLC stage quality strategy?
add new feature extending use
What comprises the second PLC stage quantity strategy?
increased amount for equal price
What are the ways to extend life through new markets?
global
online
substitute
What obsoletes products in the fourth PLC stage?
tech
True or False: Product sales decrease at an increasing rate.
True
What is product harvest?
reduce cost to maintain profit
How might a business avoid the fourth PCL stage?
modify product during maturity
What does the BCG Matrix look like?
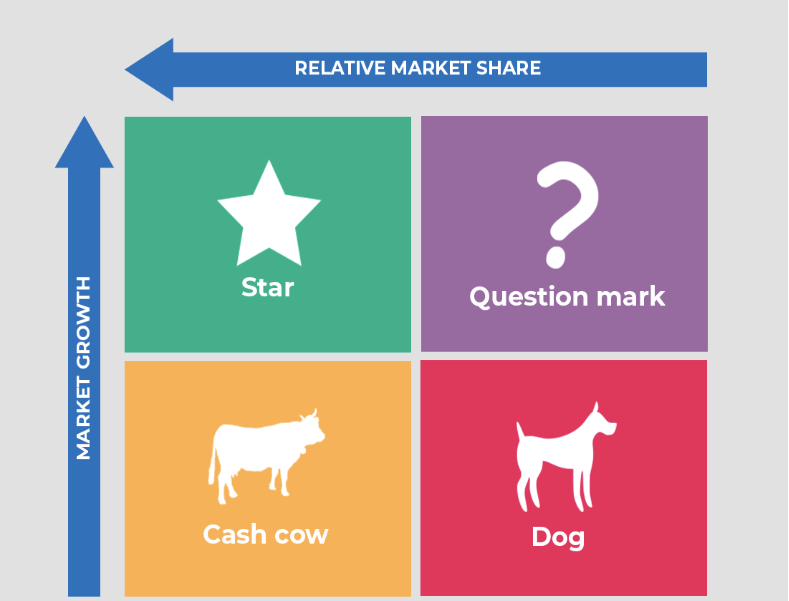
What is the BCG matrix’ x-axis?
relative market share
What is the BCG matrix’ y-axis?
market growth
What comprises a star?
high relative market share
high market growth
What comprises a question mark?
low relative market share
high market growth
What comprises a cash cow?
high relative market share
low market growth
What comprises a dog?
low relative market share
low market growth
What is the BCG matrix question mark’s strategic option?
opportunity development
How can the BCG matrix question mark undertake its strategic option?
select investment = star OR dog
identify niche & strategy
What is the BCG matrix star’s strategic option?
growth investment
How can the BCG matrix star undertake its strategic option?
aggressive marketing
selling
advertising
pricing
promoting
What is the BCG matrix cash cow’s strategic option?
earnings management
How can the BCG matrix cash cow undertake its strategic option?
expand successful / divest unsuccessful product line
differentiate & maintain / increase brand awareness / loyalty
price stability key
What is the BCG matrix dog’s strategic option?
harvest / divest
How can the BCG matrix dog undertake its strategic option?
harvest: target niche
save operation / distribution cost
What are the business growth ways?
acquisition
organic growth
What are some acquisition examples?
product
tech
business
What are some organic growth examples?
inhouse development
What are the organic innovation kinds?
incremental
radical / disruptive
What is incremental / sustaining innovation?
add to existing business / product / tech
What is radical / disruptive innovation?
target different & unattractive market
rely on different performance characteristic
require different business model
transform chain / asset value role & skillset
What do performance trajectories look like?
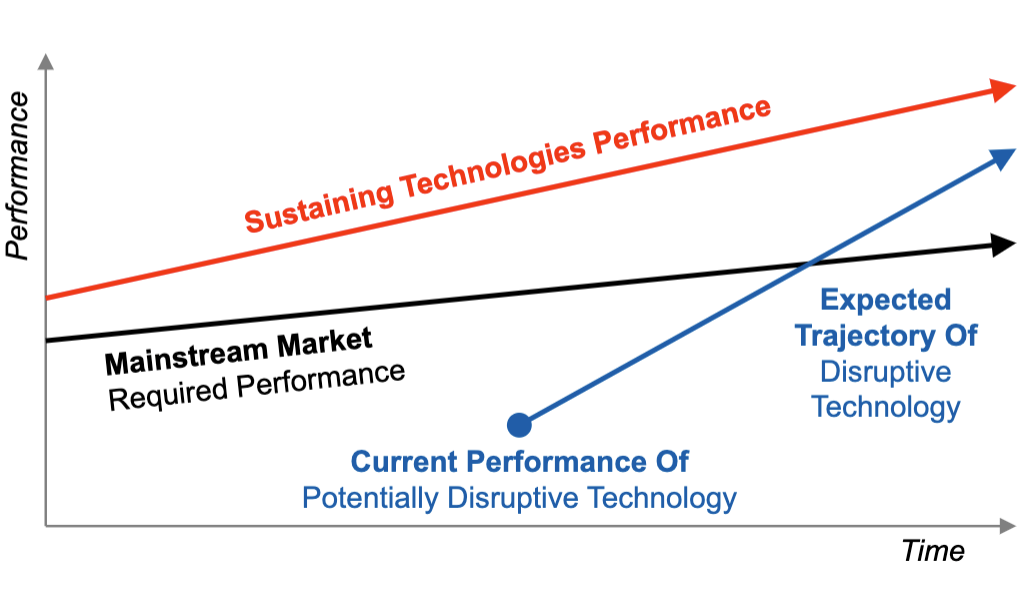
What is the current performance trajectory relationship?
disruptive > mainstream > incremental
What is the expected performance trajectory relationship?
mainstream > disruptive > incremental
What does the Ansoff matrix look like?
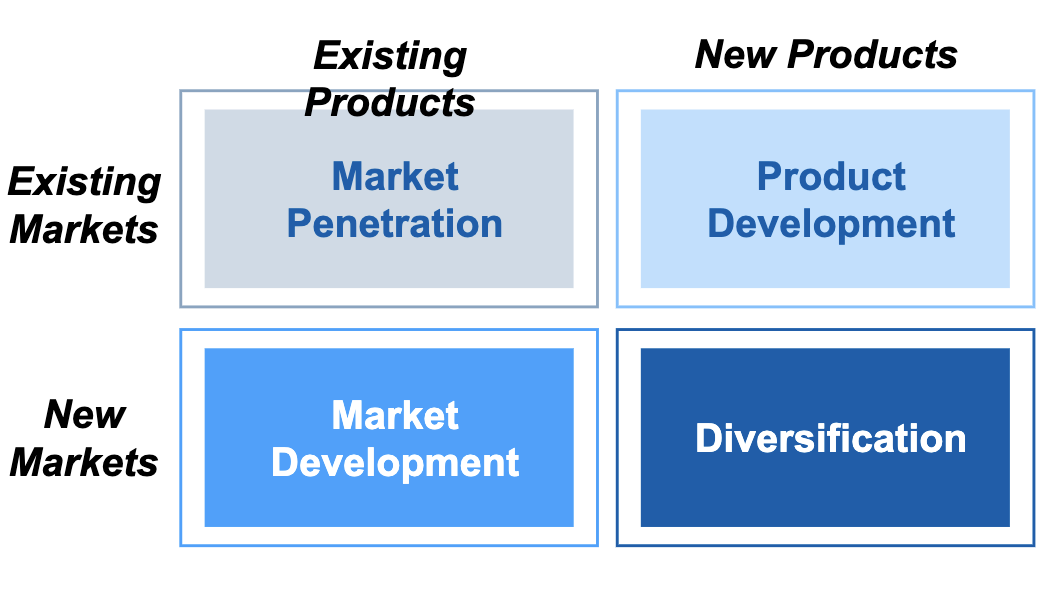
What is the Ansoff matrix?
product & marketing entry strategies
What is on the Ansoff matrix’ x-axis?
existing / new product
What is on the Ansoff matrix’ y-axis?
existing / new market
What comprises market penetration?
existing product
existing market
What comprises product development?
new product
existing market
What comprises market development?
existing product
new market
What comprises diversification?
new product
new market
What is the Ansoff matrix?
strategy tool helping business decide how to grow
What are the new product development key factors?
potentially large & growing market
market expertise
proven process
What are a growing market’s characteristics?
higher demand
creative room
fund access
quick scale
early brand
lower barrier
Why is increased demand a growing market characteristic?
get business by being there without taking from competitor
Why is creative room a growing market characteristic?
undefined rules
Why is fund access a growing market characteristic?
investor knows markets promise high potential returns
Why is quick scale a growing market characteristic?
doesn’t require cheaper / better business
Why is early brand a growing market characteristic?
no entrenched incumbent
Why is lower barrier a growing market characteristic?
few rules
What entrepreneur expertise obtains higher success?
manager experience
effective family entrepreneur
unique knowledge
unique employee knowledge
What does the Booze Allen Hamilton Study conclude?
no R&D and …
growth
profitability
shareholder return
relationship
True or False: The process identifying and bringing market opportunities is less important than the cost.
False: The process identifying and bringing market opportunities is more important than the cost.
What are the consumer purchase process stages?
need recognition
info search
product evaluation
product choice & purchase
post-purchase use
disposal
What are the new product process stages?
opportunity identification
concept
product & plan
business
What comprises the opportunity identification stage?
scan option
What comprises the concept stage?
develop (concept)
What comprises the product & plan stage?
develop venture
What comprises the business stage?
upscale venture
What is a new product process decision point?
decide to continue venture
What are the new business creation factors?
perception = reality
branding = most important product differentiation aspect
single strategy
understand web
What are the Lemon Coast Soap (P&G) case study key takeaways?
marketconsumer perception = realitybehaviour & preference insight = innovation tool
try something
What are the Universal Music case study key takeaways?
brand >
stand for … something > everything
media = variable cost
endorsement differentiates
What are the Mill Street Brewery case study takeaways?
strategy: what you aren’t = what you are
small = nimble / responsive / proactive
right niche can win
innovation can go back
don’t be afraid to give what customer asks for
What are the Colleges Ontario case study key takeaways>
figure out in category
emotional connection = key opportunity
relationship + leveraged function benefit = powerful package
What are some ways to understand customers?
focus group
survey
1-on-1 interview
ethnography
netnography
What questions does the Ansoff matrix ask?
should we sell more of what we already have?
should we try something new?
What PLC stage associates with BCG matrix stars?
intro
What happens to BCG matrix stars with more investment?
be future cash cow
What PLC stage associates with BCG matrix question marks?
growth
What must businesses decide with BCG matrix cash cows?
invest
or
drop
What happens to BCG matrix question marks with more investment?
be future star
What PLC stage associates with BCG matrix cash cows?
maturity
What comprises a BCG matrix cash cow?
steady income
low investment
What PLC stage associates with BCG matrix dogs?
decline