Science Section 1 Academic Decathlon 25-26
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
William Gilbert (1544-1603)
Philosopher
Discovered "electric force" in 1600 by rubbing amber together
Amber
Elektron (In Greek)
Used in William Gilbert's experiment for the electric force
Old Western basic elements
Water, earth, fire, air
Fundamental elements cannot be made of anything because everything is made of it
Elements
From the Periodic Table
Made of smaller pieces
Atom
Atom = indivisible
All matter was made of atoms
Creates elements
Benjamin Franklin (1706-90)
Drafted Declaration of Independence
Kite & Thunderstorm experiment
Popular in France
Leyden Jar
Device that stores electricity and gives an electric shock
Inspired Ben Franklin's kit experiment
Electrical Fire
Benjamin Franklin
Attracted and repelled things
Electric charge in conserved
Actually electrically charged particles moving from atom to atom
Kite and thunderstorm experiment
Benjamin Franklin
Attached key to stand surrounded by small shelter
Measured static electricity buildup on key
Proved lightning was electrical
Particle
Fundamental piece of matter of which everything else is made
Nucleus
Center of atoms
Protons & neutrons
Protons
Positively charged
Similar mass to neutron
Made of quarks
Neutrons
Neutrally charged
Similar mass to proton
Made of quarks
Mass
Measured in kilograms
Determines object's response to forces
Like inertia
Kilograms
Measure of mass
1kg~1L Water
Avg person = 60-70kg
Inertia
Resistance to changes in motion
Like mass
Electron
Negatively charged
Surrounds nucleus
Equal number to protons, can be different
Electric Charge
Fundamental quality of a particle
Can be zero
Opposites attract, same repels
Newton's 1st Law of Motion
An object's inertia will allow it to keep going as long as there are no forces to stop it
Force
Interactions between objects
How one object can change the motion of another object
Measured in Newtons
1 Newton = Weight of 1 Apple
Newton's 2nd Law of Motion
Object feeling a force will accelerate in the direction of that force
More mass=more resistance
F=MA
Newton's 3rd Law of Motion
Every action has an equivalent reaction
Gravity of planets, attraction between protons/electrons
Quark
Makes up protons and neutrons
Positive Scientific Notion
10^1= 10
10^2= 100
10^3= 1000
Power = # Zeros After 1
Multiplying by 10
Negative Scientific Notion
10^-1= 0.1
10^-2= 0.01
10^-3= 0.001
Dividing by 10
Scientific Notation Conversions
1kg= 1,000 g = 1x10^3 g
1g= 1x10^-3 kg
1km= 1,000 m = 1x10^3 m
Fundamental Forces
Strong Nuclear Force & Weak Nuclear Force (Only occurs within nucleus)
Gravitational Force
Electromagnetic Force
Strong Nuclear Force
Keeps protons & neutrons within nucleus (otherwise they would repel or be unstabilized)
Only occurs within nucleus
Weak Nuclear Force
Transforms particles into other particles
Radioactive Decay
Only occurs within nucleus
Gravitational Force
Pulls mass towards other mass
Strength depends on masses & distance apart
FG=G(m1m2/r^2)
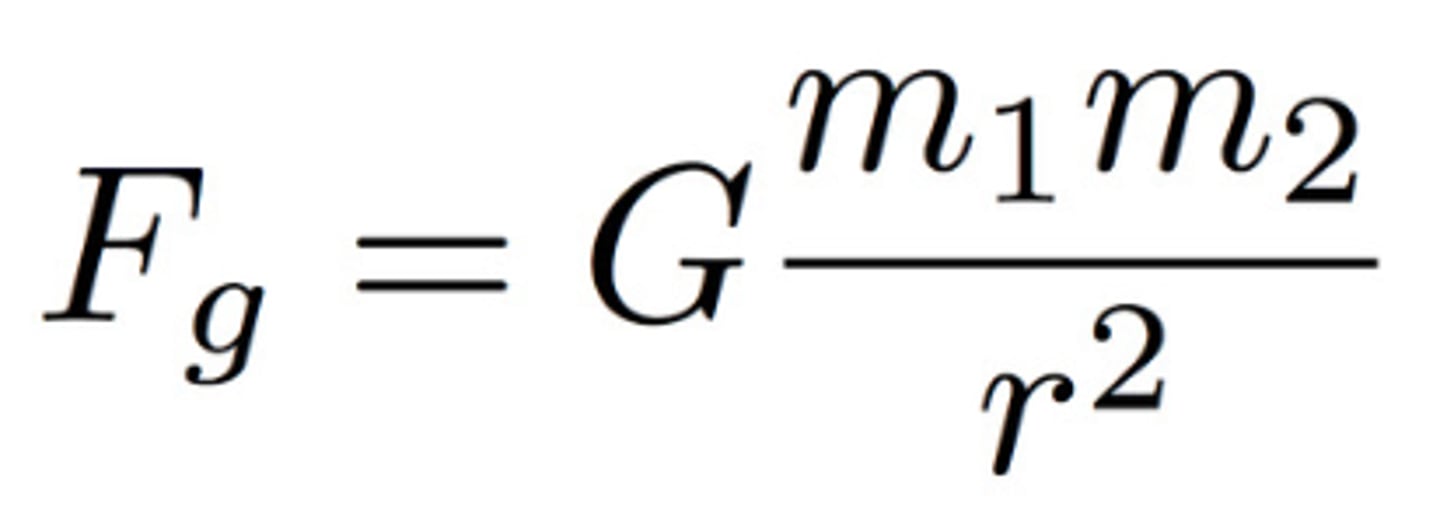
Electromagnetic Force
Attracts and repels charged particles
Keeps atoms together
Gravitational Force Equation
m= masses of 2 objects; r= distance between 2 objects; FG= Force of Gravity; G= Gravitational Constant (6.67x10^-11 N m^2/kg^2)
Inverse Square
Sensitive to changes in distance than mass
Only attractive
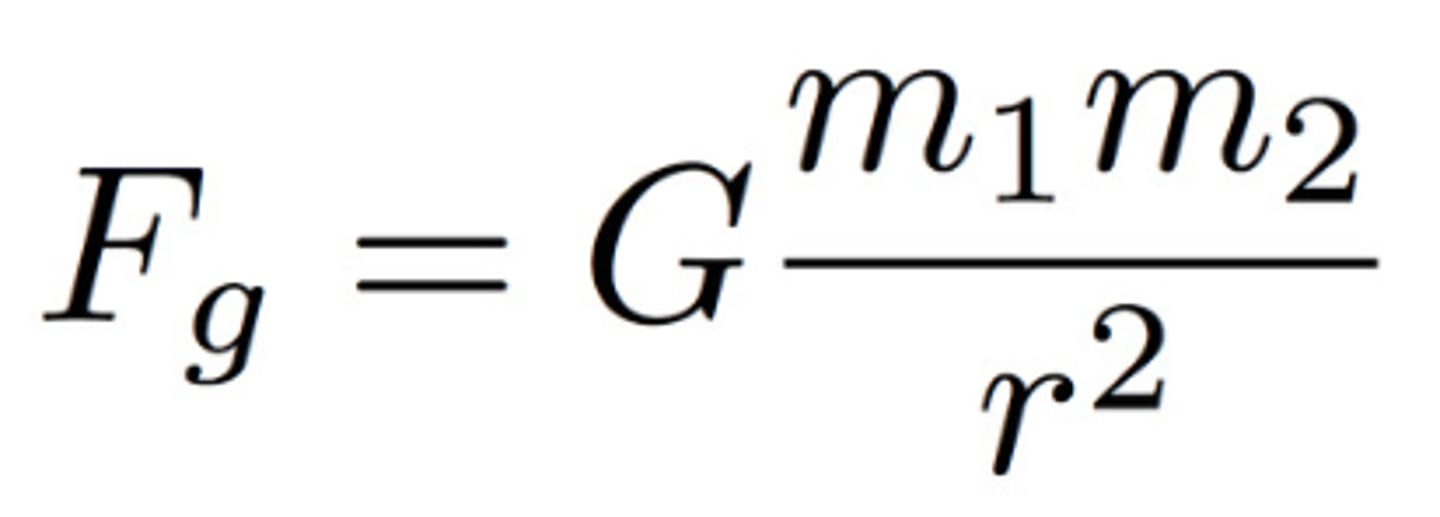
Inverse Square Law
Solves for a quantity that is inversely proportional to the distance squared
Jupiter, Sun, Earth
Jupiter is 5x further from the sun than Earth
Jupiter gets 1/25th the amount of light the Earth gets
Example of the Inverse Square Law
Gravitational Constant
aka Newton's Constant
Tells how strong a force you get
6.67x10^-11 N m^2/kg^2
Very small
Earth's Force
6x10^24
Mass of Proton
1x7x10^-27
Mass of an electron
9.1x10^-31
Coulomb's Law
q= Amount of charge on two objects; r= distance apart; k=constant (8.99x10^9 N m^2/C^2)
Electricity can attract and repel
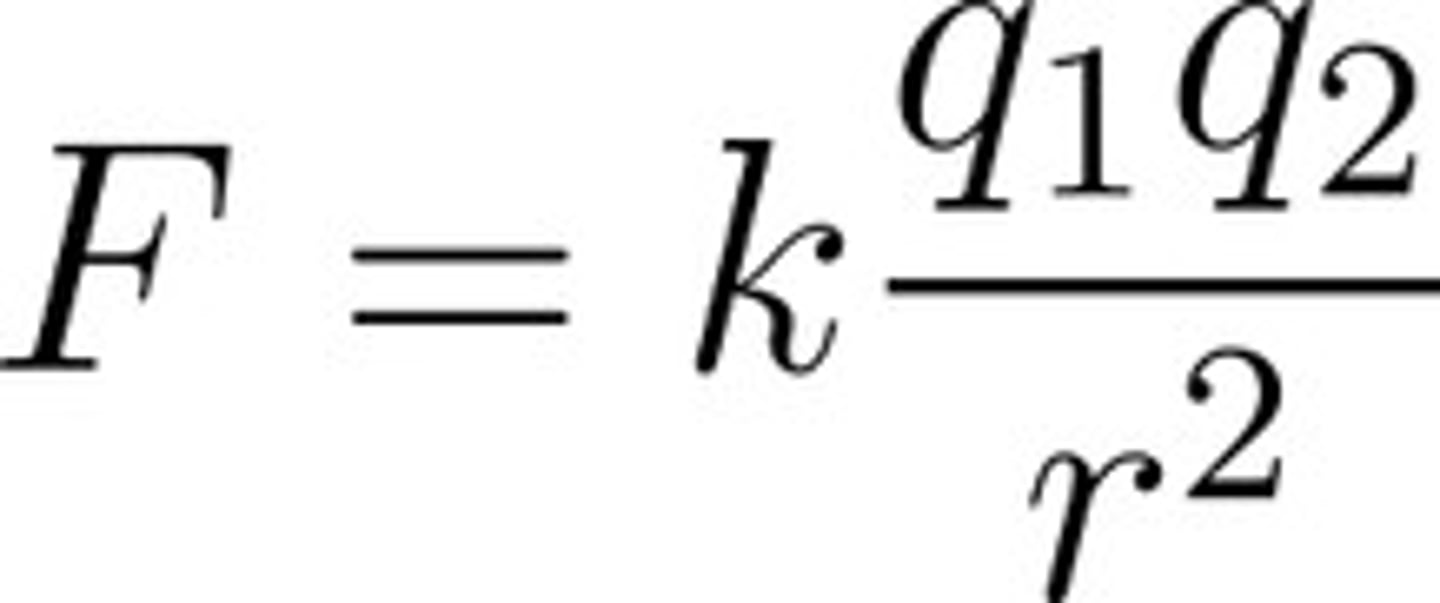
Discovery of Coulomb's Law
Charles Coulomb, 1785
Torsion balance with a charged rod suspended by a string, twisted by electric forces from rod
Coulomb
Measurement of electric current
Very big compared to proton or electron (+-1.7x10^-19 coulombs)
Coulomb's Constant
k= 8.99x10^9 N m^2/C^2
Electric v. Gravitational Force
Electric force is much stronger (by more than 10^40)
Less noticeable because most atoms are electrically neutral, while everything has positive mass
Cloth & glass rod
Glass picks up a positive charge, cloth is negative charge due to stealing glass's electrons
Vector
Magnitude & Direction
EX Wind, Gravity
Scalar
Magnitude
EX Temperature
Simplified Gravitational Equation
FG=mg
m=mass; g= strength of gravitational field created by earth (depends on mass/distance of object, often 9.8 newtons/kg)
g decreases with square of distance
Satellite Gravity
g=90% of earth's
Moons gravity
g<1% of earth's
Simplified Electrical Force Equation
FE=qE
q=charge; E=electric field (newtons/coulomb), how much force a particle with charge q will feel at that location
Positive mass follows direction of gravity
Positive charge goes in the same direction as E, neg opposite
Positively charged object's electric field
Points away from object
Negatively charged object's electric field
Points towards object
Strength of proton's electric field
E=kq/r^2
Calculating a large object's electric field
Electric fields from multiple objects can be added together
2 Protons Electric field
Add together, looks like field w 2x strength of proton
In between (@ = magnitude) P1 points L, P2 points R, cancels out (0 force)
Proton/Electron Electric field
Very weak, looks like charge of zero
In between, proton points R, electron point R, reinforce
Around, points away from proton and towards Electron
Electric Dipole
Large, flat sheet with proton
Flat sheet is positively charged -> proton is pushed upwards & diagonal (cancelled out)
Gauss's Law
Find out what the electric field looks like for extended objects
Closed geometric shape, calculate the amount that passes through the "Gaussian Surface"
εo= Permittivity of free space; q=total charge within surface (=σA); φE= Electric Field Flux (=2EA)
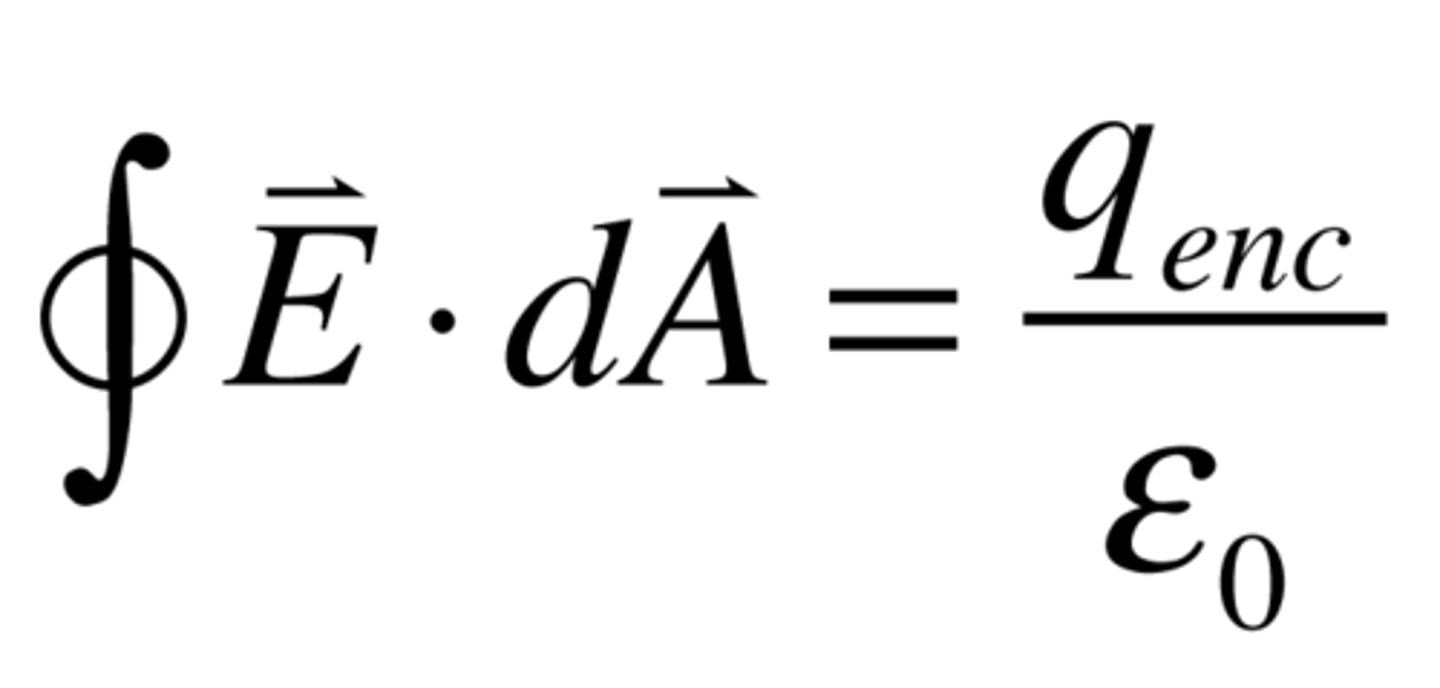
Permittivity of Free Space (εo)
1/4(pi)k
Electric Field Flux (φE)
Scalar
φ=phi
Amount that passes through a given area
Depends on strength of electric field & orientation of relative to field
Normally E (strength of electric field) * A (surface area)
Large, flat sheet & cylinder
Top & Bottom of cylinder (same flux) :2 EA =q/εo
How much charge : 2 EA = σA/εo
Cancel out A: E = σ/2εo
σA
Charge Density
Van de Graff Generator
Vertical conveyor belt, continuously rubs two materials together at the bottom of a tower -> stray electrons gather at top, in a metal ball
Static Electricity
Two different materials rubbing against each other, one steals the others electrons and looks for a way out to prevent buildup
Electrically Polarized
When an object is neutral, but the positive nucleus is off to one side and the electrons are off to another
Electrons continue to be repelled, protons continue to be attracted
Ions
Uneven # of protons/electrons
Conductor
Quickly exchanges heat energy and charge with surroundings
Outer electrons are loosely bound to nucleus, allows them to freely jump
Metals (aluminum, copper)
Outer orbital shells are unfilled
Insulators
Do not allow electrons to move freely
Conductor that gains a net electric charge
Electrons are as far spread a part as they can be
Electric field = 0
(non zero=keep moving)
Faraday Cage
Sheilds the inside from electromagnetic radiation
Corners V Circles
Corners = more charge density of