2. Fermentation
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Different types of processes by secreted enzymes acting on substrate
Proteolysis: digestibility, flavor and taste
Lipolysis: flavor
Amylolysis: digestiblity, acid formation
Pectinolysis: digestibility
Cellulolysis: digestibility
What kind of metabolites do microorganisms produce?
Flavor compounds
acids, alcohol, esters, acetoin
Coloring substnaces
Carotenoids
Vitamins
B-vitamins
Yeast extract
Antimicrobial compounds
Acids, alcohols, carbon dioxide
Hydrogen peroxide
Reuterin, bacteriocins, killer-toxins
Conversion of carbohydrates into lactic acid
Produces:
yoghurt
cheese
vegetables
sausages
not efficient; not all the substrate is used

Types of lactic acid bacteria
Homofermentative: can switch between the following types of fermentation
Homolactic fermentation → only produces lactate as an end product.
Mixed acid fermentation
Heterofermentative
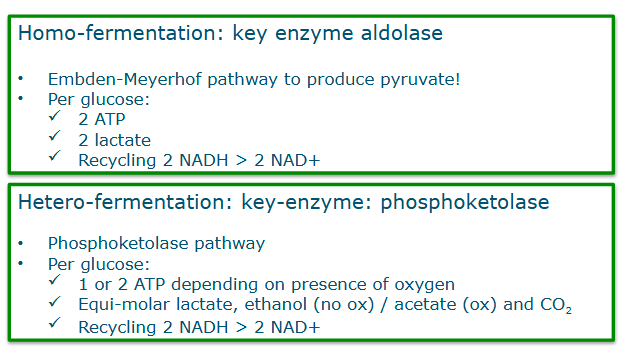
Homo-fermentation vs. heterofermentation
no CO2 in homo
How to ferment alcohols
Use yeast
Steps of alcoholic fermentation
EM pathway: common glycolysis.
EM pathway is found in: bacteria & yeast.
Net yield: 2ATP, 2NADH, 2pyruvate
EtOH production: pyruvate reduction
Net yield: 2CO2, 2NAD+, 2ethanol
Fusel alcohols
Alcohols with a higher number of C atoms
Whisky, brandy, and rum rely on fusel alcohols (and their esters) for depth, body, and fruity/spicy notes.
Isoamyl alcohol → used to make isoamyl acetate (“banana oil”) for flavorings and fragrances.
How are fusel alcohols made?
Following the Ehrlich pathway
Transamination
→ The amino acid loses its nitrogen (–NH₂) group.
→ This turns it into a keto acid.Decarboxylation
→ The keto acid loses a carbon (as CO₂).
→ What’s left is an aldehyde.Reduction
→ The aldehyde is reduced (adds hydrogen) using NADH.
→ That turns it into a fusel alcohol.