X-rays
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
The electronvolt(eV)
Energy lost or gained by an electron when it accelerates through a potential difference of one volt.
A photon
A discrete amount of electromagnetic radiation.
What is an X-Ray?
A photon of electromagnetic radiation of very high frequency.
How are X-Rays produced?
When high speed electrons strike a metal of high melting point.
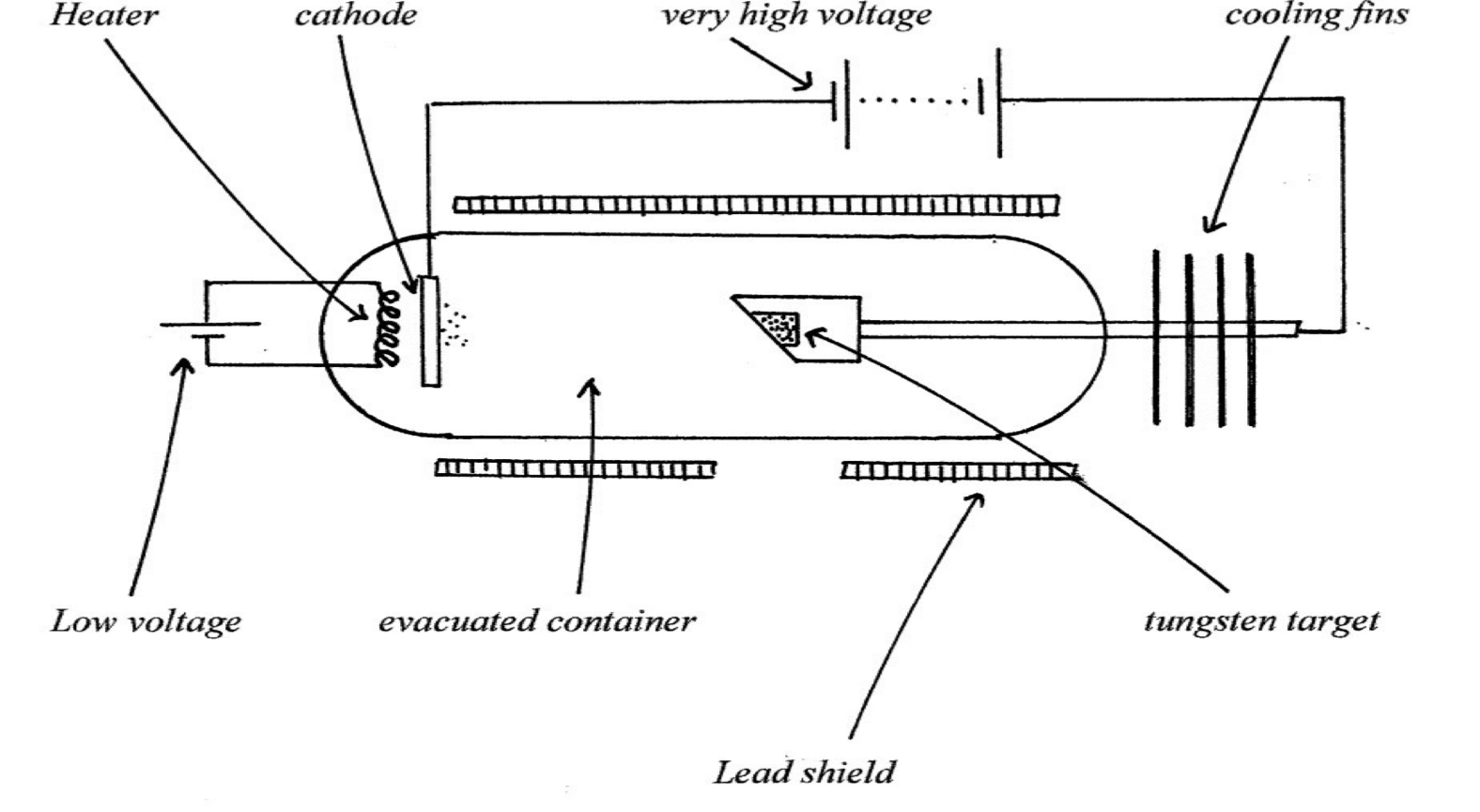
Operation of an X-Ray tube
Electrons are emitted from the cathode by the thermionic effect.
They are accelerated to a very high speed by the high voltage
They hit the tungsten target and X-rays are emitted
The lead shield protects the user from the harmful effects of X-rays.
Properties of X-Rays
The speed of an X-ray is the same as the speed of light in a vacuum. (3x10^7 m/s )
They ionise the molecules of a material through which they pass. X-rays are regarded as ionising radiation
If the air molecules above a negatively charged gold leaf electroscope are ionised then the positive ions would come in contact with the cap of the electroscope. The charge on the electroscope would be reduced. The deflection of the gold leaf would decrease.
X-rays are not deflected in magnetic fields and are not deflected in electric fields.
Therefore X-rays have no charge and are neutralX-rays cause a chemical reaction with film in a similar way to light. X-ray photographs are therefore possible.
X-rays have a very high frequency and will eject electrons from a metal surface by the photoelectric effect. X-rays would exceed the threshold frequency of many metals.
X-rays can cause fluorescence i.e. they strike certain substances and emit photons of a longer wavelength, very often photons of visible light.
Penetration(Hardness) of X-rays
The ability of X-rays to pass through materials of different thickness or density of Material.
Intensity of an X-ray beam:
Refers to the number of X-rays in the beam.
How are X-rays the inverse of the photoelectric effect?
With the production of X-rays, electrons hit the tungsten target and photons are emitted. With the photoelectric effect, the photons fall on a metal and electrons are emitted.
Uses of X-Rays
Medicine: to detect broken bones
Industry: to detect breaks in industrial pipes
Hazards of X-Rays
They can ionise atoms into the body, causing them to become abnormal, which can lead to cancer.