AP Human Geography AMSCO Ch.3, Ch.4, and Ch.5 Key Terms Flashcards
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Bolded = definition; Italic = Sentence; Underline = Example
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
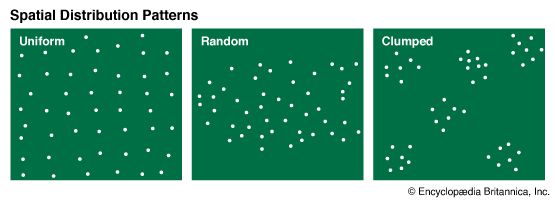
Population Distribution
Definition: The pattern of human settlement — the spread of people across earth.
Sentence: "Population distribution varies greatly between urban and rural areas."
Example Location: Urban areas often have higher population distribution than remote regions.
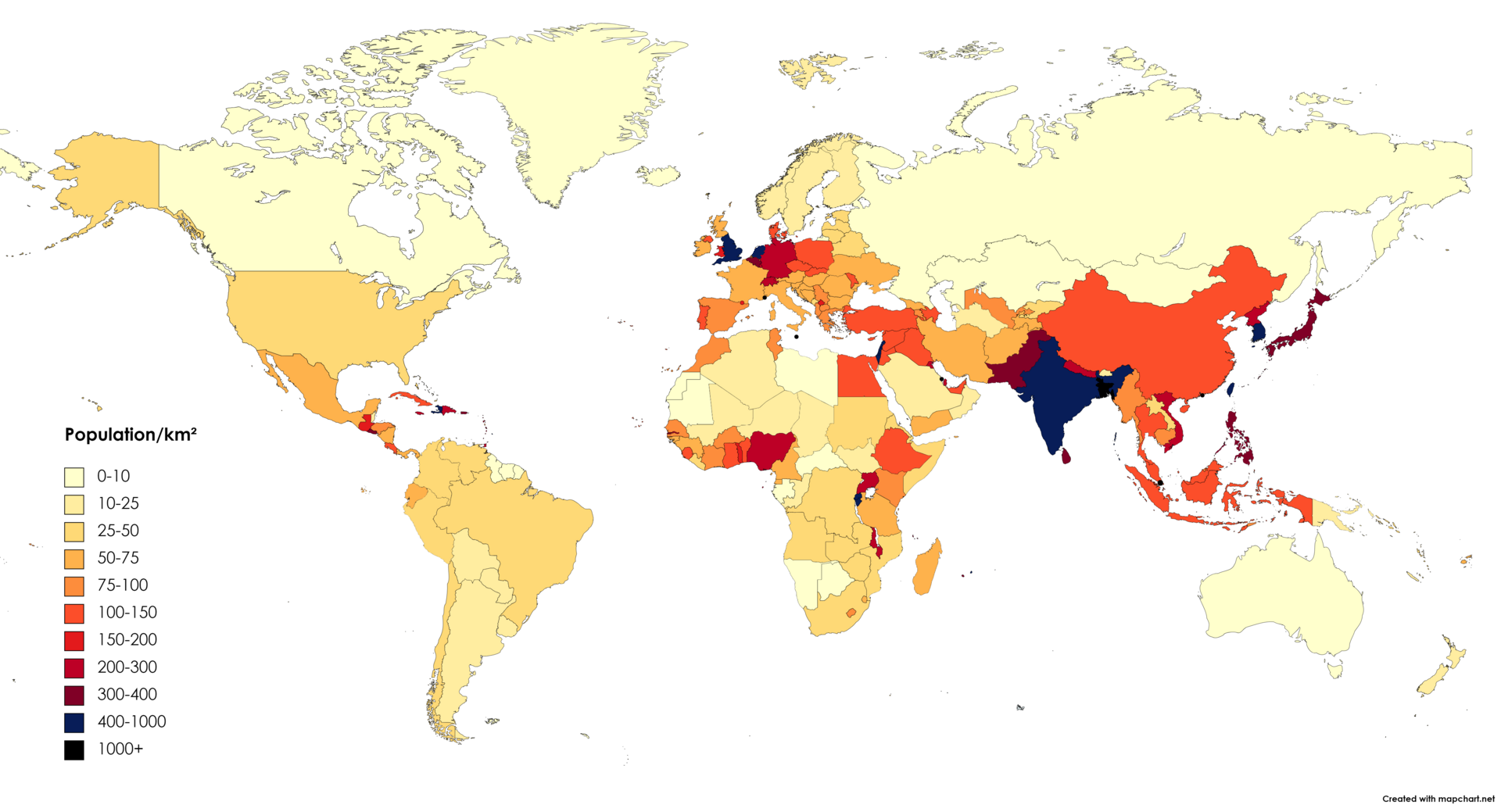
Population density
Definition: A measure of the average population per square mile or kilometer of an area. It measures how crowded a place is.
Sentence: "The population density of New York City is much higher than that of rural Montana."
Example Location: Cities like Tokyo and Mumbai have high population densities.
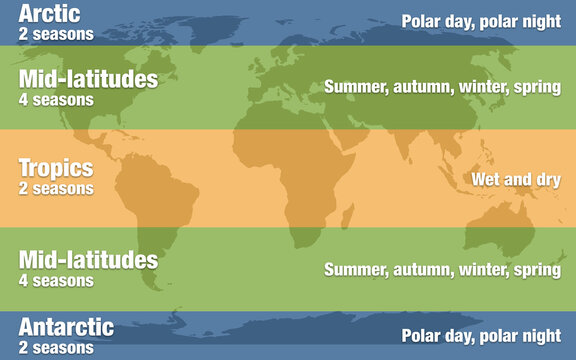
Midlatitudes
Definition: Regions between 30N and 60N and between 30S and 60S. Moderate climates and better soils than do regions of higher or lower attitudes. Most people live in midlatitudes.
Sentence: "Most of the world’s population resides in the midlatitudes due to favorable living conditions."
Example Location: Europe and the northern United States are in the midlatitudes.
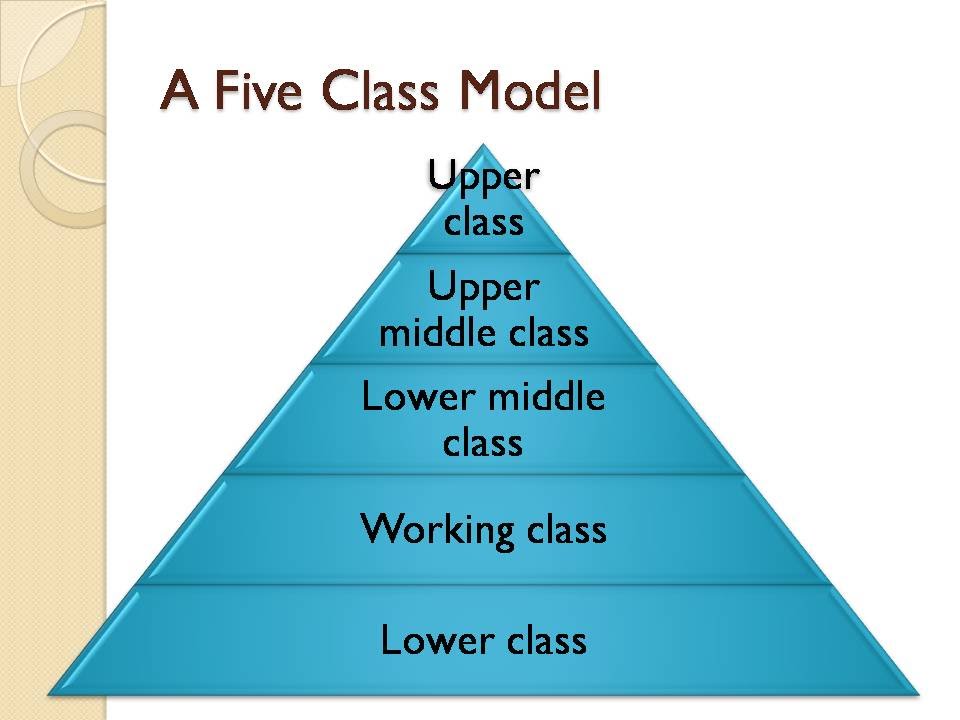
Social stratification
Definition: The hierarchical division of people into groups based on factors such as economic status, power, ethnicity or religion.
Sentence: "Social stratification is visible in many societies, where income divides different social classes."
Example Location: Social stratification can be seen in caste systems in South Asia.
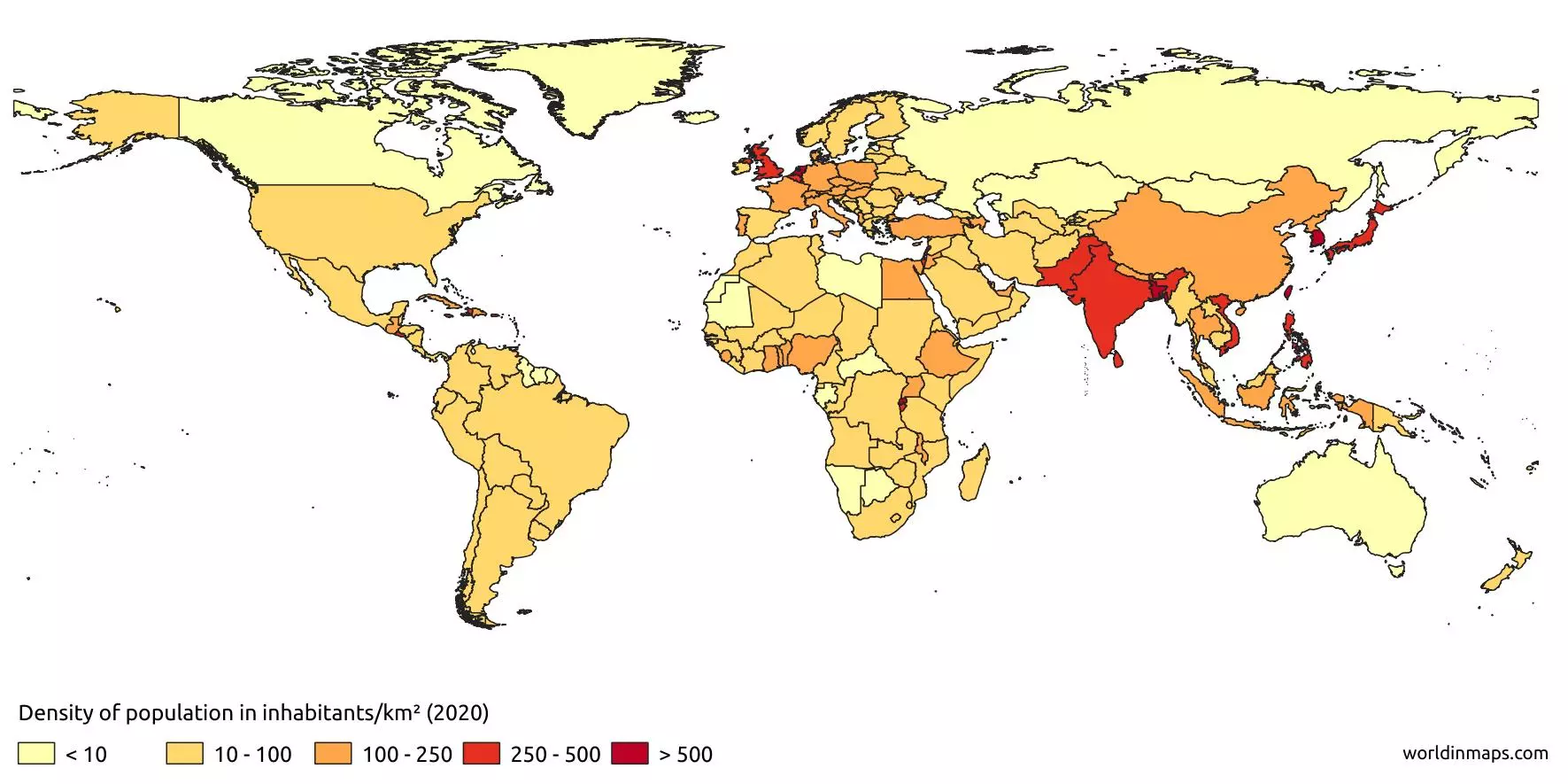
Arithmetic population density
Definition: The most commonly used population density, calculated by dividing a region's population by its total area.
Sentence: "Arithmetic population density helps to determine how crowded a region might be."
Example Location: Calculated for countries like China or the U.S. to understand population spread.
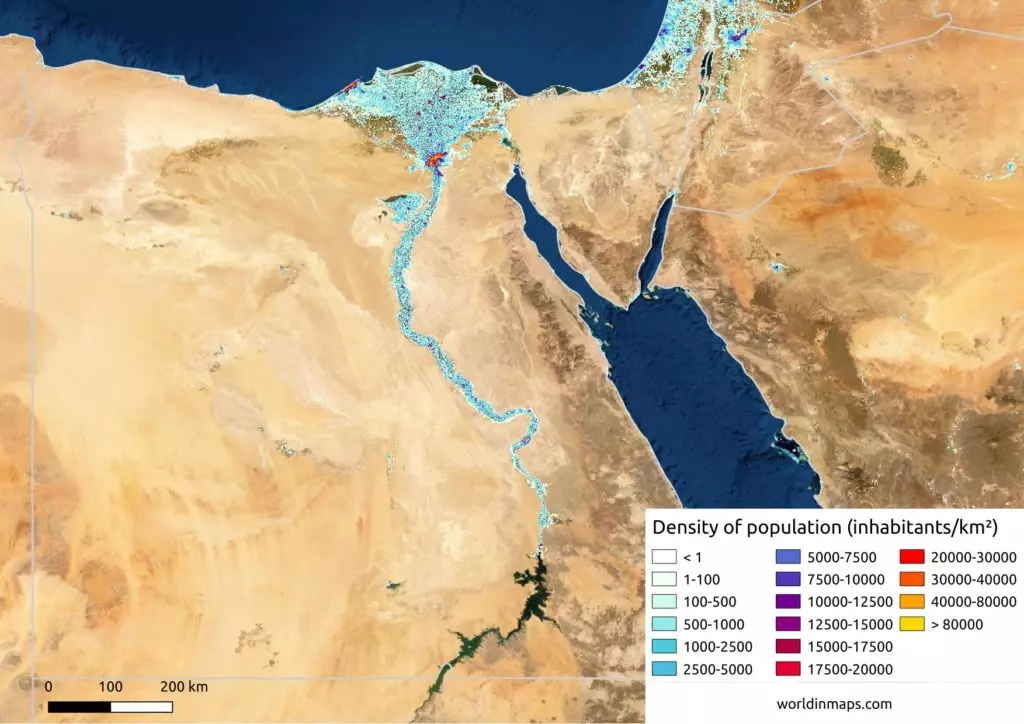
Physiological population density
Definition: Calculated by dividing the population by the amount of arable land.
Sentence: "Egypt has a high physiological population density because most of its population lives near the Nile River."
Example Location: Egypt, where the majority of people live on fertile land near water sources.

Arable
Definition: Land suitable for growing crops.
Sentence: "Farmers seek arable land to cultivate crops and support their livelihoods."
Example Location: The Great Plains in the U.S. have large areas of arable land.
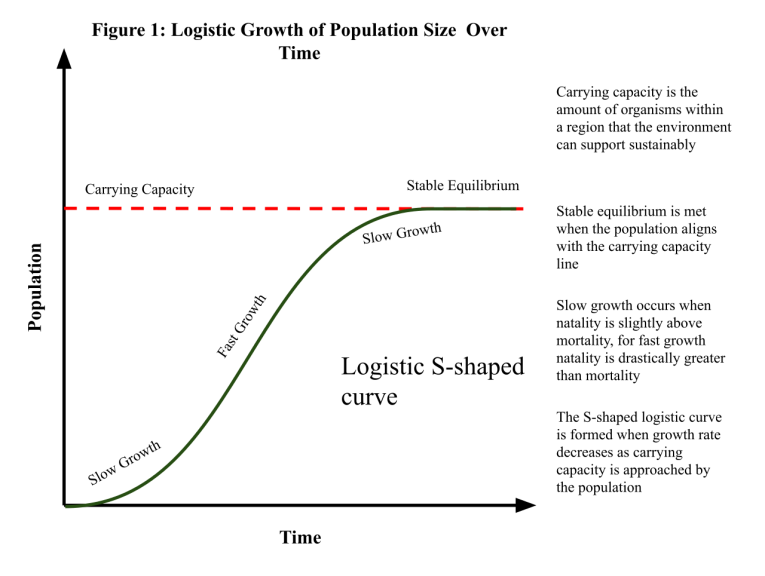
Carrying capacity
Definition: The population a region can support without significant environmental deterioration.
Sentence: "The carrying capacity of an island is limited due to its finite resources."
Example Location: Small islands, where resources are limited, often have low carrying capacities.
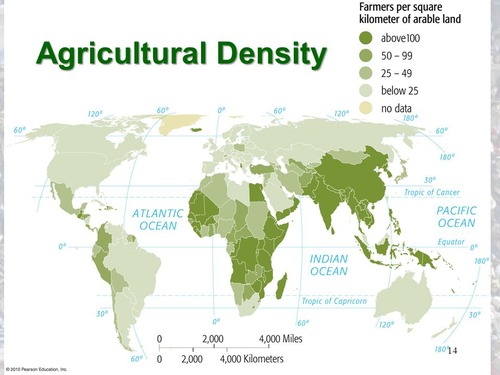
Agricultural population density
Definition: The population a region can support without significant environmental deterioration.
Sentence: "The carrying capacity of an island is limited due to its finite resources."
Example Location: Small islands, where resources are limited, often have low carrying capacities.
Redistricting
Definition: When urban area are increasing in population and rural areas are shrinking. Result in physically smaller urban districts and larger rural districts.
Sentence: "Population shifts require redistricting to ensure fair political representation."
Example Location: Common in the United States after each census.

Overpopulation
Definition: When a region has more people than it can support — partially dependent on its population distribution and density.
Sentence: "Overpopulation can lead to resource depletion and pollution."
Example Location: Cities like Dhaka, Bangladesh, often experience the effects of overpopulation.
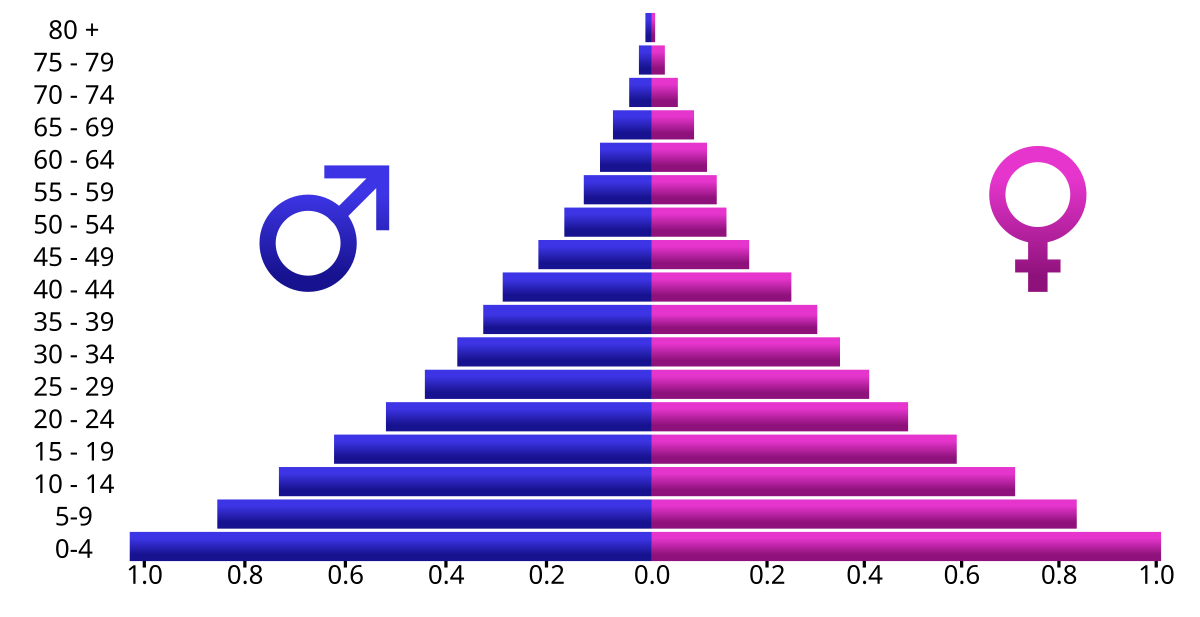
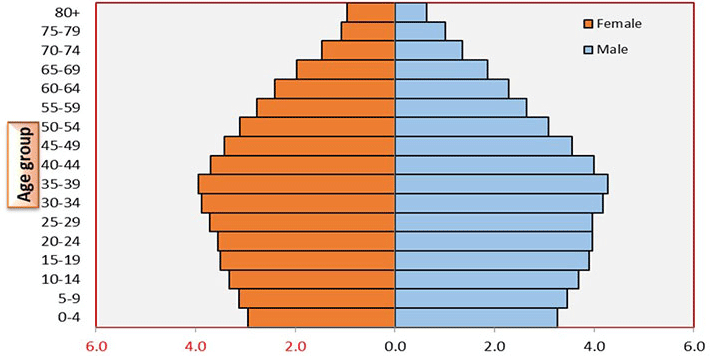
Age-sex composition graph
Definition: Graph based on only age and gender data. Can provide information on birth rates, death rates, how long people live on average and economic development. (population pyramid)
Sentence: "An age-sex composition graph can reveal population trends like aging or youth bulges."
Example Location: Useful in demographic studies for countries like Japan, where aging populations are common.
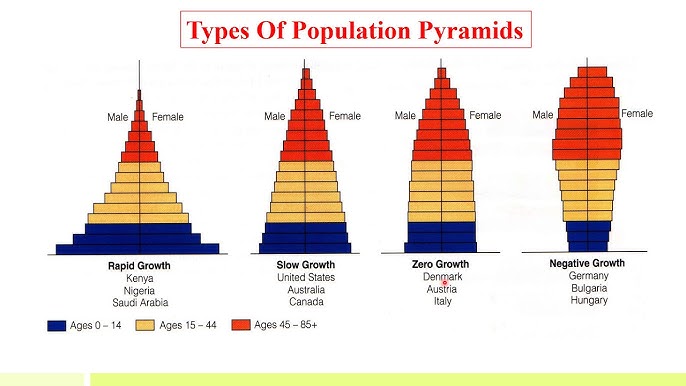
Population pyramid
Definition: Visual tool used to study population, also known as the age-sex composition.
Sentence: "The population pyramid of India shows a large number of young people."
Example Location: Countries with high birth rates have pyramid-shaped population structures.
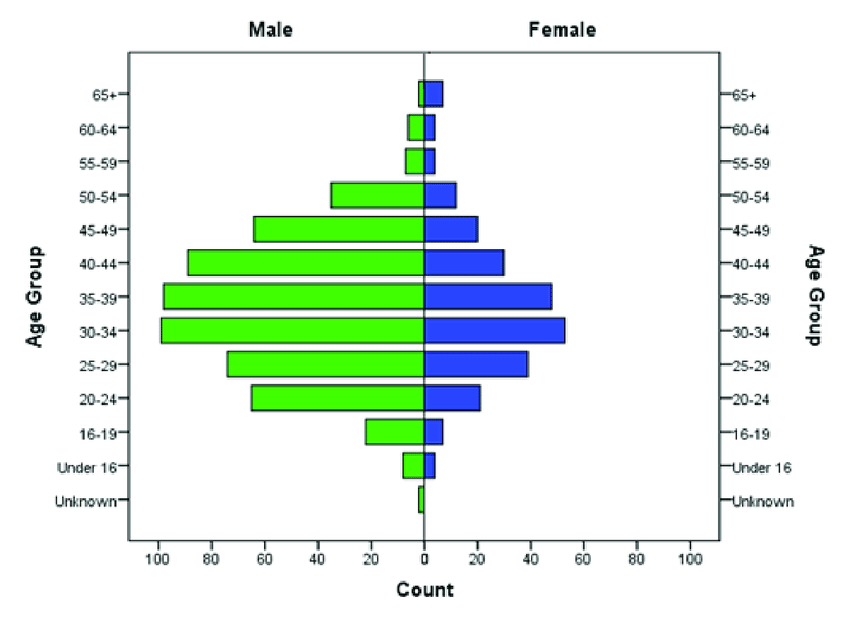
Cohort
Definition: Vertical axis on a pyramid that shows age groups. Often listed in the middle but can be shown on the left or right side.
Sentence: "The cohort of young adults in the U.S. is expected to grow in the coming years."
Example: Age cohort groups (like 0-4, 5-9) help analyze population structure.
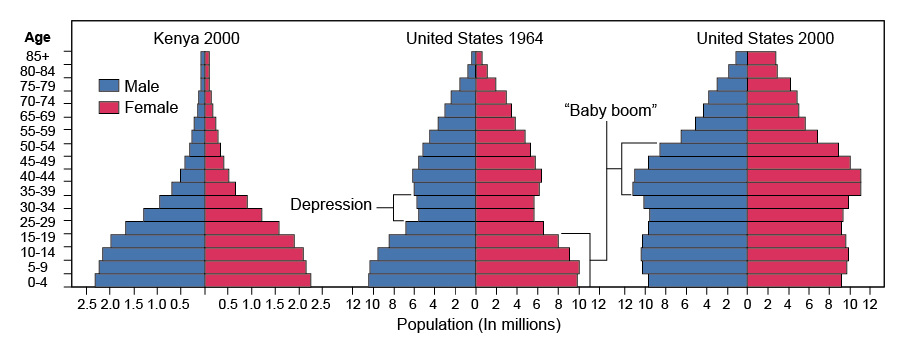
Birth deficit
Definition: The slow down of births.
Sentence: "After a long war, many countries experienced a birth deficit."
Example Location: Some European countries with low birth rates have a birth deficit.
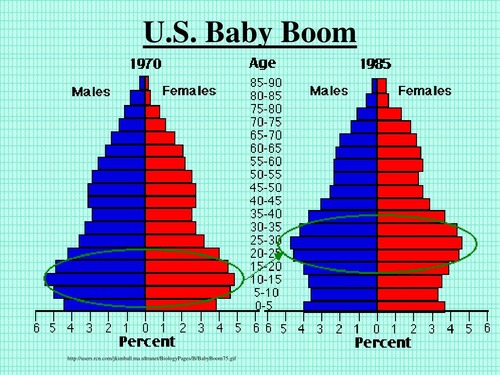
Baby boom
Definition: A spike (increase) in births.
Sentence: "The U.S. experienced a baby boom after World War II."
Example Location: Baby booms are common post-war in many nations.
Baby bust
Definition: The end of baby boom when births are lower until the boomers reach child-bearing age.
Sentence: "After the baby boom, there was a baby bust when families began to have fewer children."
Example Location: Often occurs after significant population growth periods, like in the U.S. in the 1970s.
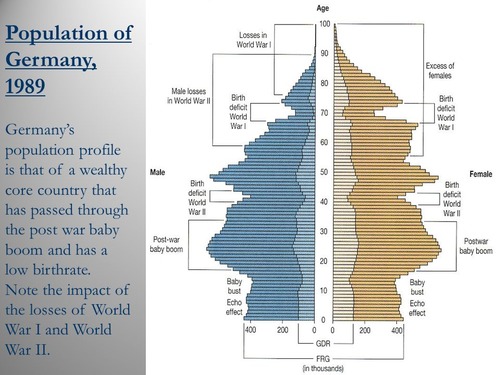
Echo
Definition: An increase in births reflecting an earlier baby boom.
Sentence: "The children of the baby boomers created an echo in population growth."
Example Location: Seen in demographic patterns when baby boomers’ children reach childbearing age.

Infrastructure
Definition: The facilities and structures that allows people to carry out typical activities.
Sentence: "Good infrastructure is crucial for economic growth."
Example Location: Urban infrastructure in cities like New York or London.
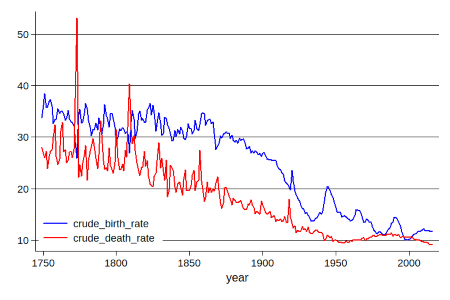
Crude birth rate (CBR)
Definition: The number of live births per year for every 1,000 people.
Sentence: "Countries with high crude birth rates often have younger populations."
Example Location: Often higher in developing countries with large family norms.
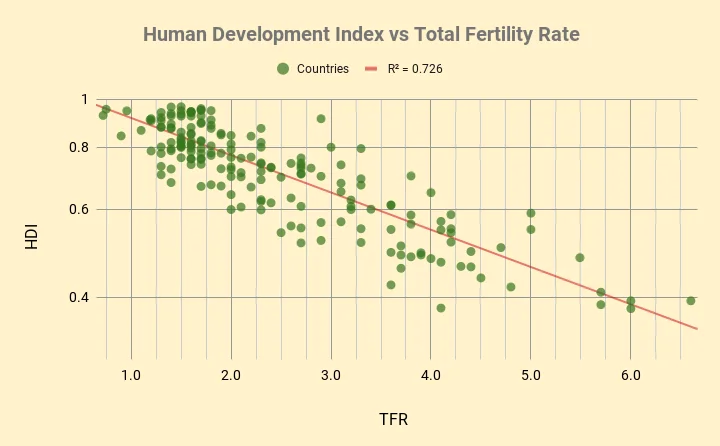
Total fertility rate (TFR)
Definition: The average number of children who would be born per woman aged 15 to 49 in a country, assuming every woman lived through her childbearing years.
Sentence: "A country’s total fertility rate often reflects its social and economic conditions."
Example Location: France, with a TFR of approximately 1.8, is below the replacement rate, leading to potential future population declines without migration.

Anti-natalist policies
Definition: Programs designed to decrease the number of births in a place.
Sentence: "China’s former one-child policy is an example of anti-natalist policies."
Example Location: China implemented anti-natalist policies in the 1980s to control population growth.

Pro-natalist policies
Definition: Programs designed to increase the fertility rate in a place.
Sentence: "Countries with low birth rates often introduce pro-natalist policies to encourage families to have more children."
Example Location: France offers financial incentives for families with multiple children as part of its pro-natalist policies.
Life expectancy
Definition: The number of years the average person will live.
Sentence: "Japan has one of the highest life expectancies in the world, with many citizens living well into their 80s and 90s."
Example Location: Japan, with an average life expectancy of around 85 years, is known for its aging population.
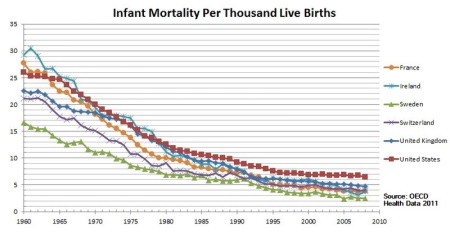
Infant mortality rate
Definition: The number of children who die before their first birthday.
Sentence: "Improving healthcare access has helped reduce the infant mortality rate in many developing nations."
Example Location: In Scandinavian countries, infant mortality rates are among the lowest globally due to advanced healthcare.
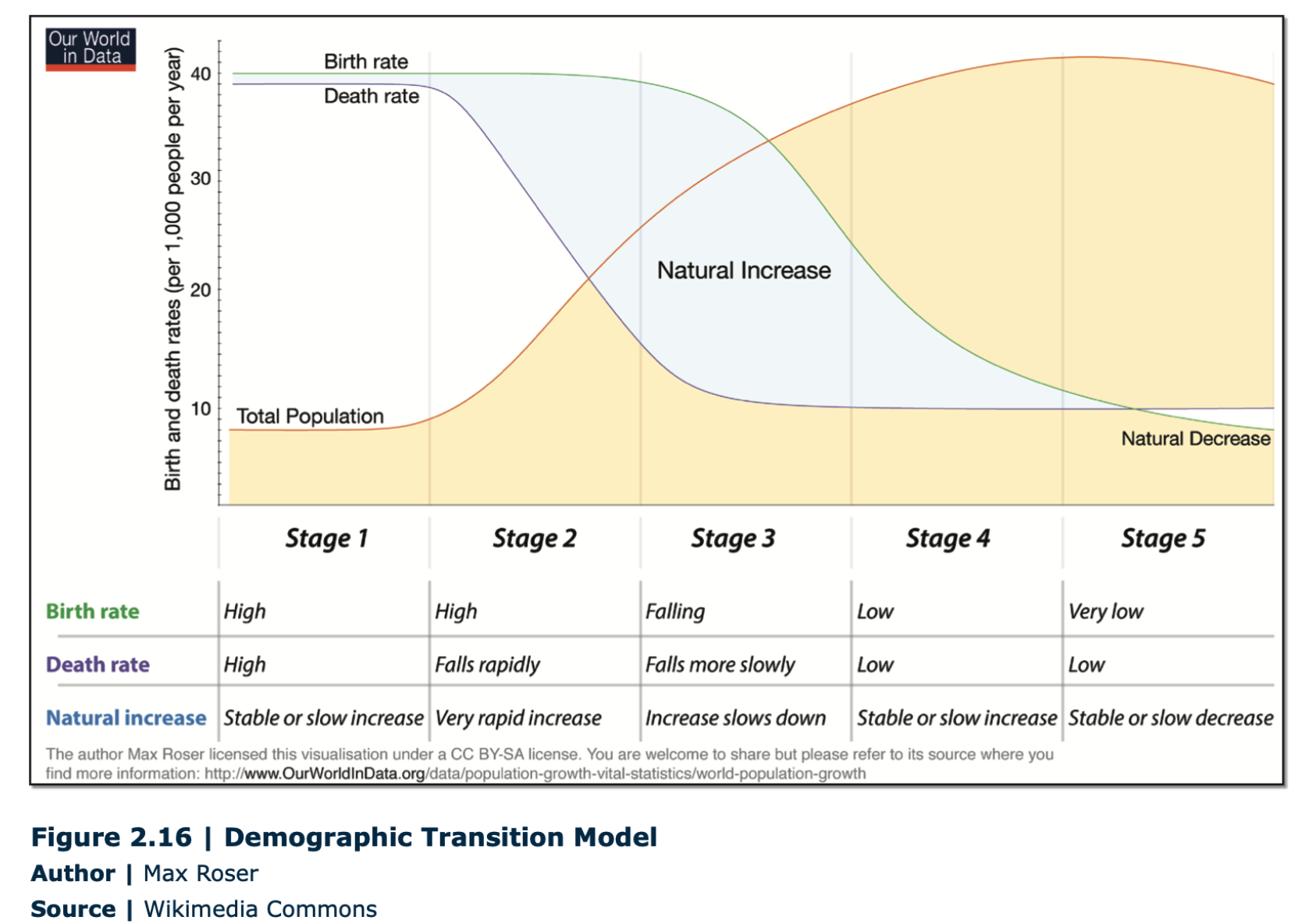
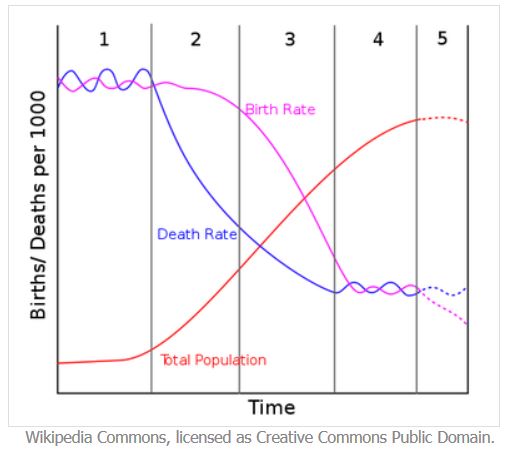
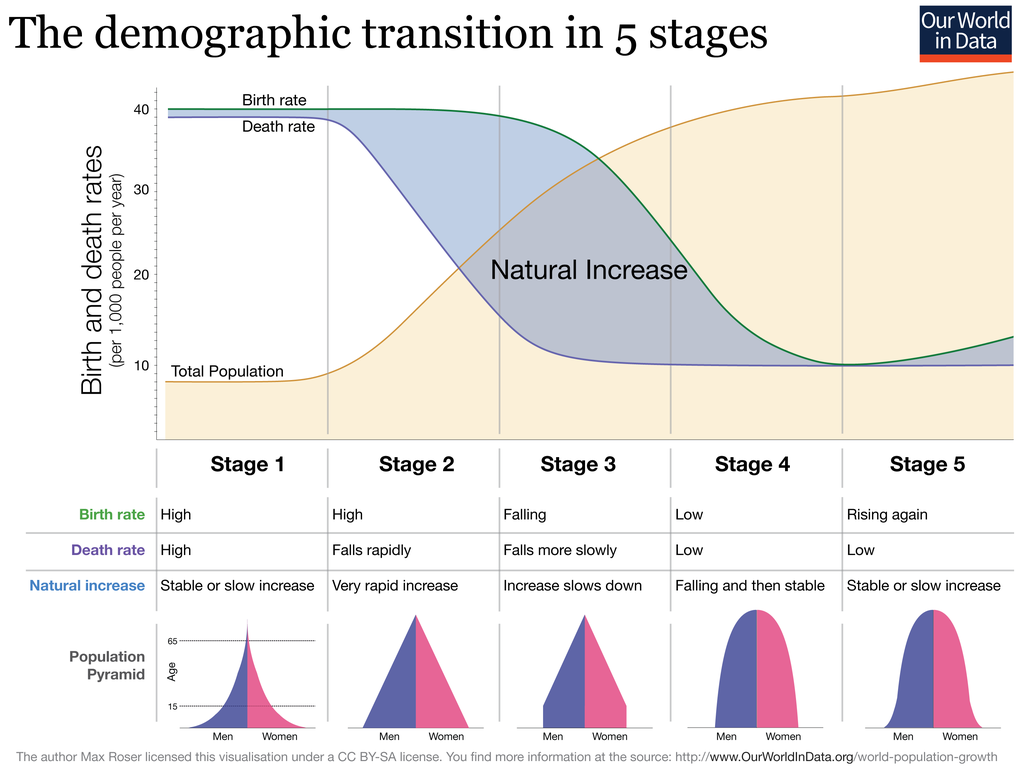
Demographic Transition Model
Definition: Model that shows five typical stages of population change that countries pass through as they modernize.
Sentence: "The demographic transition model explains why birth rates tend to decline in more developed countries."
Example Location: The United States and many European countries are in stage 4 of the demographic transition model, characterized by low birth and death rates.

Epidemiological Transition Model
Definition: Predictable stages in disease and life expectancy that countries experience as they develop, identified by Abdel Omran.
Sentence: "The epidemiological transition model illustrates how infectious diseases decline as chronic diseases increase in more developed societies."
Example Location: Many countries in Europe are in advanced stages of the epidemiological transition model, where lifestyle diseases are more prevalent.
Crude death rate (CBR)
Definition: The total number of deaths a year per 1,000 people.
Sentence: "Countries with older populations generally have a higher crude death rate."
Example Location: Japan’s aging population has contributed to a relatively high crude death rate.
Rate of natural increase
Definition: The percentage of which a country’s population is growing or declining without the impact of migration. Calculated by RNI = (CBR-CDR)/10 (%)
Sentence: "Countries with high rates of natural increase often face challenges in providing adequate resources."
Example Location: Sub-Saharan African countries often have high rates of natural increase due to high birth rates.

Immigrants
Definition: People who have moved into a country.
Sentence: "Immigrants contribute to the cultural diversity and economic strength of a country."
Example Location: The United States has a large immigrant population, contributing to its cultural mosaic.

Emigrants
Definition: People who have moved out of a country.
Sentence: "Economic hardship often causes people to become emigrants in search of better opportunities abroad."
Example Location: Many emigrants from Latin American countries move to the United States in search of economic stability.
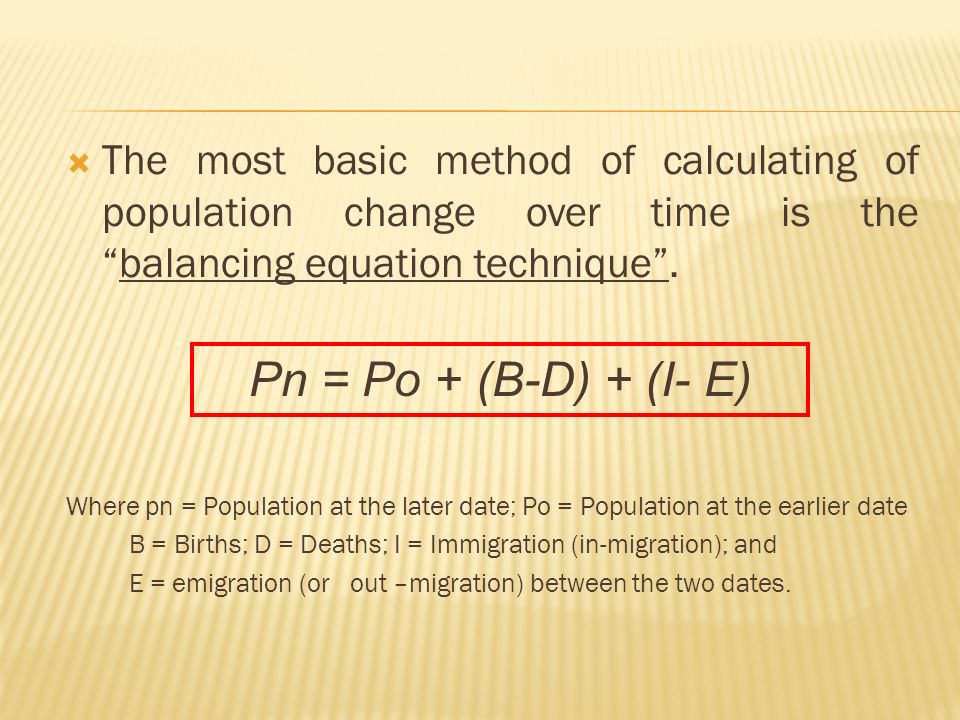
Demographic Balancing Equation
Definition: Used to calculate a country’s total population change. Equation as follows Total Population Change (TPC) = Births - Deaths + Immigrants - Emigrants
Sentence: "The demographic balancing equation helps policymakers understand population trends."
Example Location: Countries with positive net migration, such as Canada, see population growth due to the balancing equation.
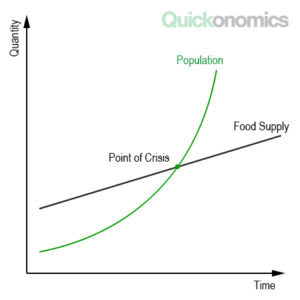
Malthusian Theory
Definition: The theory by Thomas Malthus that the world’s population was growing faster than the rate of food production, leading to mass starvation.
Sentence: "Malthusian theory predicted that unchecked population growth would lead to food shortages."
Example Location: Critics cite countries like India, which has managed to increase food production to match population growth, challenging Malthusian predictions.
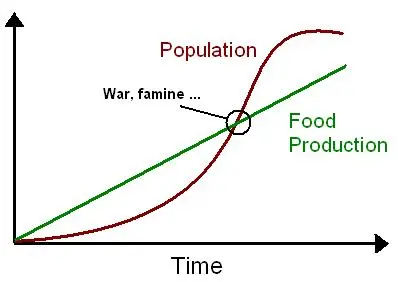
Neo-Malthusians
Definition: Those who have adapted Malthus’ ideas to modern conditions, arguing that global overpopulation is a serious problem and even greater threat for the future.
Sentence: "Neo-Malthusians warn about environmental degradation resulting from overpopulation."
Example Location: Neo-Malthusians highlight the environmental issues in densely populated areas like coastal China.
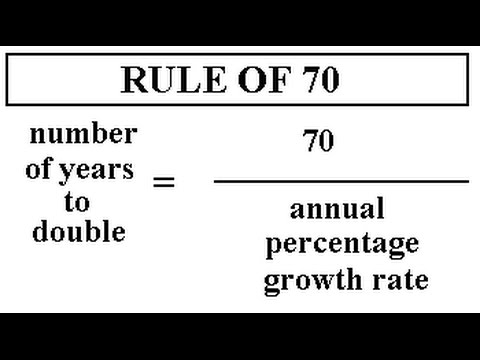
Doubling Time
Definition: The time it takes for a population to double in size, estimated with the Rule of 70: 70 / growth rate per year.
Sentence: "A population with a 2% growth rate has a doubling time of 35 years."
Example Location: Many African nations, with high growth rates, have shorter doubling times.
Demographic Momentum
Definition: Countries in transition from stage 3 to stage 4 experience an extended growth of population for at least one generation due to life expectancy increasing while fertility rate decrease.
Sentence: "Demographic momentum can lead to continued population growth even after fertility rates fall."
Example Location: Countries like Mexico, transitioning to lower birth rates, experience demographic momentum.
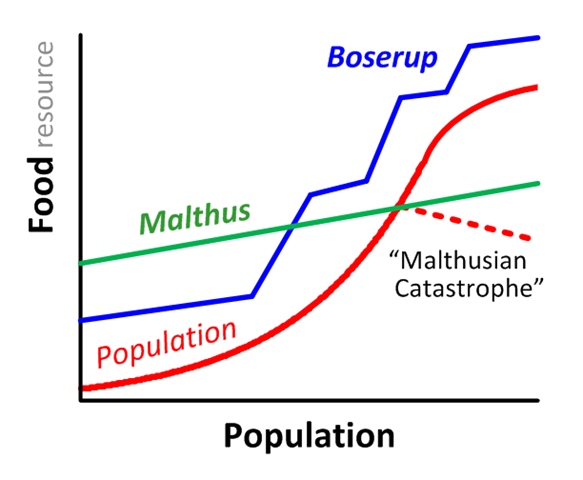
Boserup Theory
Definition: Opposing Malthus, a Danish economist suggested that the more people there are, the more hands there are to work, rather than just mouths to feed, As population increases, inventions are created to increase food population
Sentence: "The Boserup Theory argues that human innovation will keep food production in pace with population growth."
Example Location: The Green Revolution in India supports Boserup’s idea that necessity drives agricultural innovation.
Dependency ratio (DR)
Definition: A value comparing the working to the nonworking parts of a population.
Sentence: "An aging population increases a country’s dependency ratio, placing pressure on social services."
Example Location: Japan has a high dependency ratio due to its aging population.
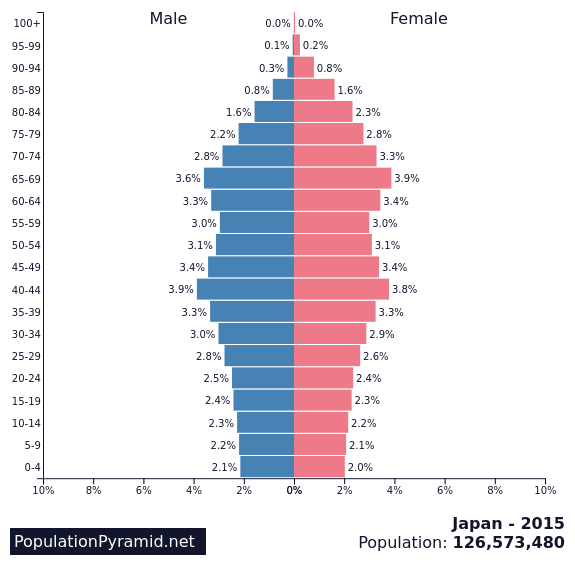
Dependent population
Definition: People under 15 or over 64 years old, considered too young or too old to work full-time.
Sentence: "Countries with a high dependent population may struggle with economic productivity."
Example Location: Many European nations have high proportions of elderly dependent populations.
Voluntary migration
Definition: Movement of people by choice.
Sentence: "People engage in voluntary migration to seek better economic opportunities."
Example Location: Many skilled workers migrate voluntarily to cities like Dubai for high-paying jobs.

Push factors
Definition: Negative circumstances, events, or conditions present where people live, reasons people decide to move away.
Sentence: "Political instability and lack of jobs are common push factors in many regions."
Example Location: Civil conflict in Syria created push factors leading many to seek refuge abroad.
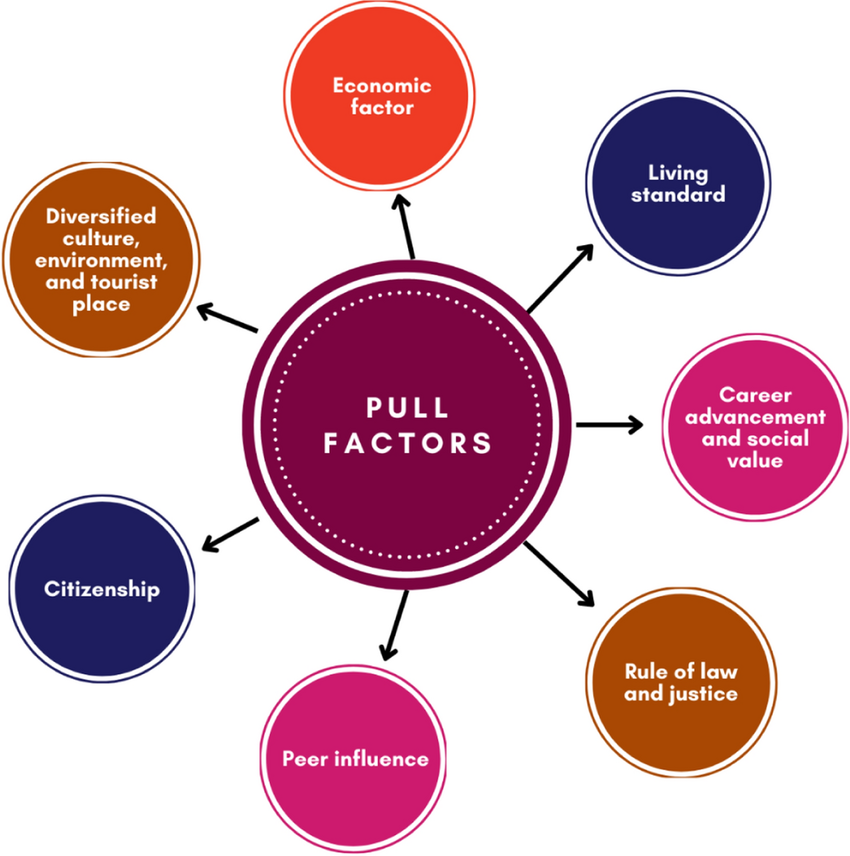
Pull factors
Definition: Positive conditions and circumstances of a place that people are drawn to once they decide to leave a place.
Sentence: "Good job prospects and quality education are pull factors drawing people to major cities."
Example Location: Many people are attracted to the United States by the pull factors of economic opportunities and personal freedom.
Asylum
Definition: Protection from the danger faced in one’s home country.
Sentence: "He applied for asylum in a neighboring country after facing persecution at home."
Example Location: Countries in Europe and North America often receive asylum applications from people fleeing political or religious persecution.
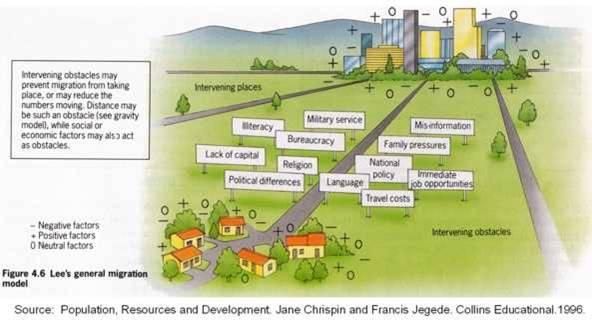
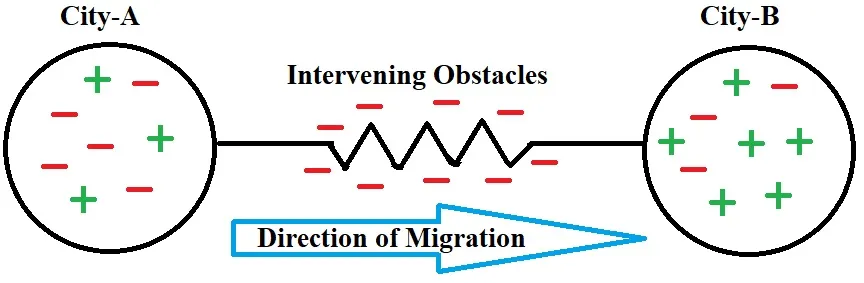
Intervening obstacles
Definition: Barriers that make reaching someone’s desired destination more difficult.
Sentence: "Intervening obstacles, like visa restrictions, can delay or prevent migration."
Example Location: Physical barriers like the Sahara Desert can be intervening obstacles for migrants moving northward in Africa.
Distance decay
Definition: The further apart two places are, the less likely it is that people will migrate between those places.
Sentence: "Distance decay affects family connections as people move to different countries."
Example Location: People may be less likely to move between distant countries like Japan and Brazil due to distance decay.
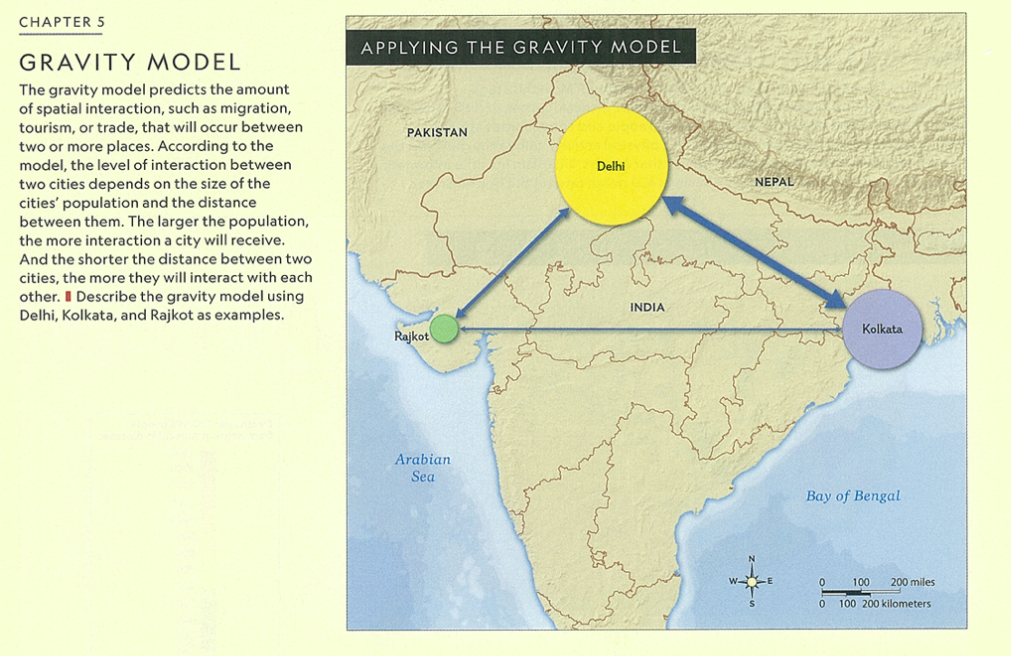
Gravity model of migration
Definition: The belief in the greater pull in larger communities and the assumption that more people are likely to migrate from a large community than a small one.
Sentence: "According to the gravity model of migration, people are more likely to move to large cities with more opportunities."
Example Location: New York City and London are major migration destinations due to their size and economic significance.
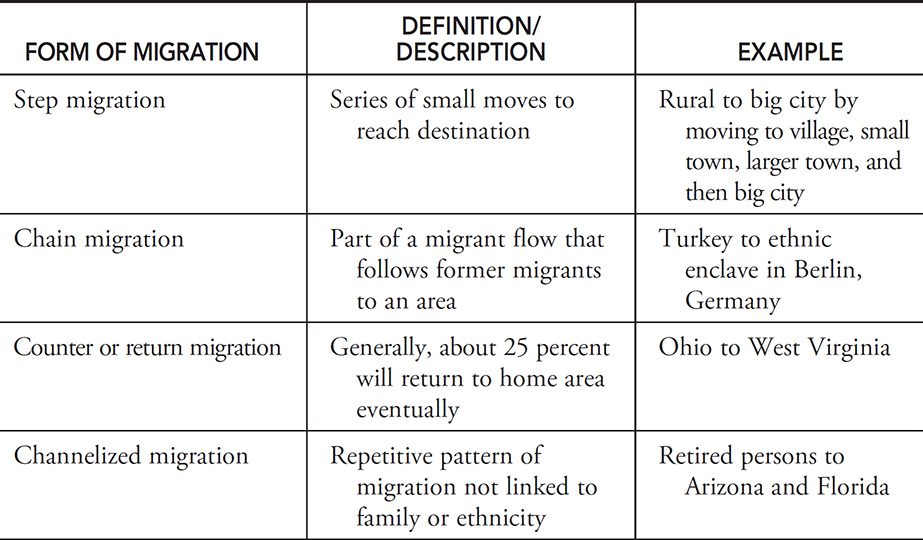
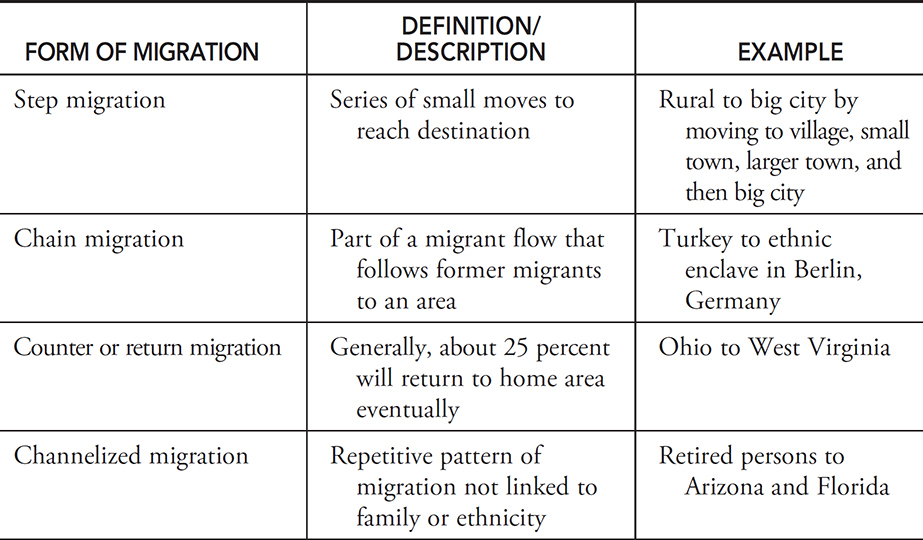
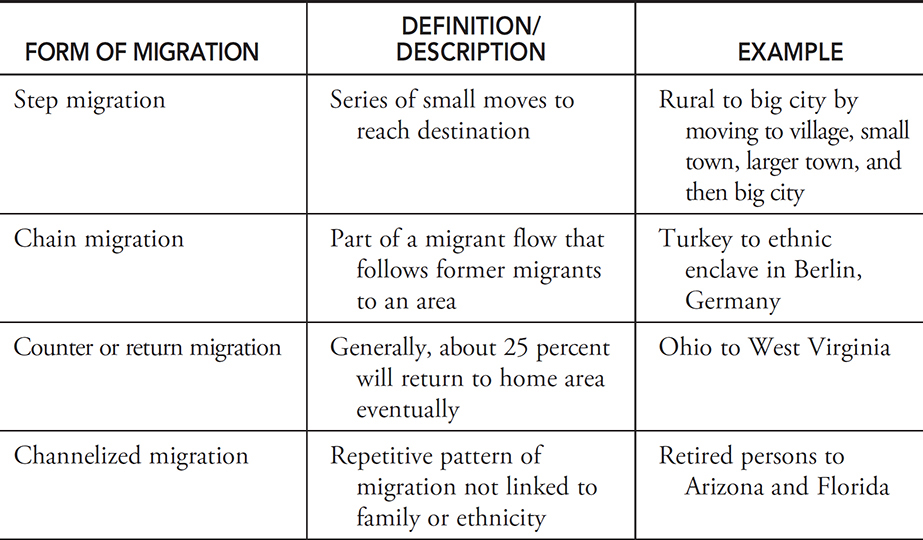
Step migration
Definition: A process in which migrants reach their eventual destination through a series of smaller moves.
Sentence: "Some people follow a pattern of step migration, moving from small towns to larger cities before reaching a major urban center."
Example Location: Migrants moving from rural Mexico may first relocate to a regional city before eventually moving to Mexico City or the U.S.
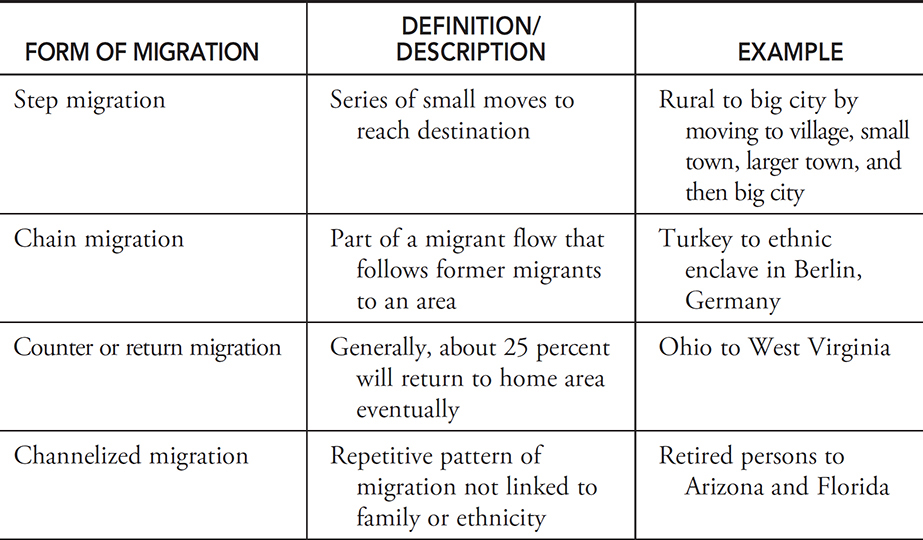
Counter migration
Definition: Each migration flow produces a movement in the opposite direction.
Sentence: "An increase in job opportunities back home led to counter migration as people returned."
Example Location: As job markets change, counter migration may bring people back to Eastern European countries from Western Europe.
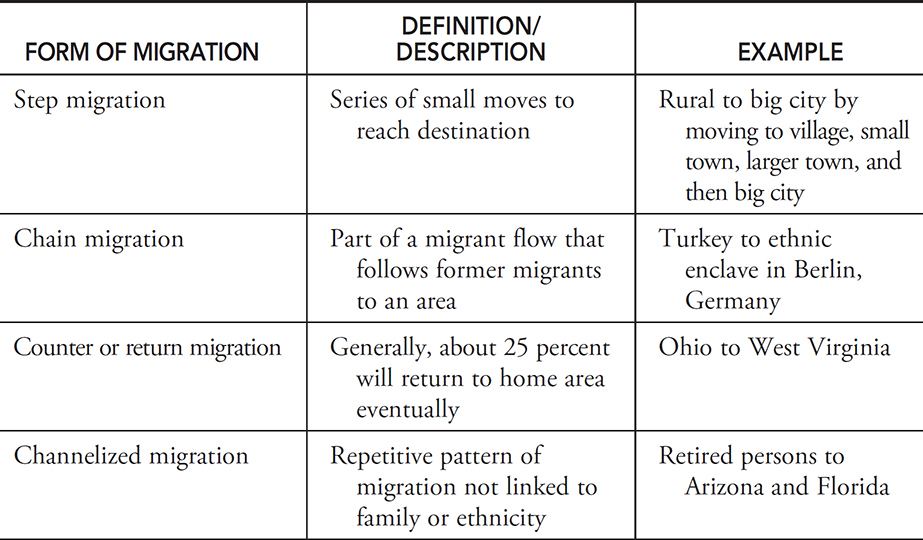
Return migration
Definition: When immigrants move back to their former home.
Sentence: "After several years abroad, she decided on return migration to be closer to family."
Example Location: Many Indian workers in the Middle East eventually participate in return migration to India.
Forced migration
Definition: A type of movement in which people do not choose to relocate, but do so under threat of violence.
Sentence: "Civil conflict led to forced migration as families sought safety elsewhere."
Example Location: The Rohingya community from Myanmar has experienced forced migration to Bangladesh.

Internally displaced person (IDPs)
Definition: Migrants who must flee to another part of the same country quickly in order to stay alive, without bringing their belongings, to get away from a political or environmental crisis in their home country. These individuals intend to return home when it is safe to do so.
Sentence: "Internally displaced persons often face challenges finding adequate resources within their country."
Example Location: In Colombia, many individuals are IDPs due to internal conflicts.

Refugees
Definition: Migrants who must flee across international borders in order to stay alive and get away from a political or environmental crisis in their home country. These individuals have a well-founded fear that they will be harmed if they return home.
Sentence: "The refugees sought safety in neighboring countries after conflict broke out at home."
Example Location: Refugees from South Sudan often cross into Uganda seeking refuge.
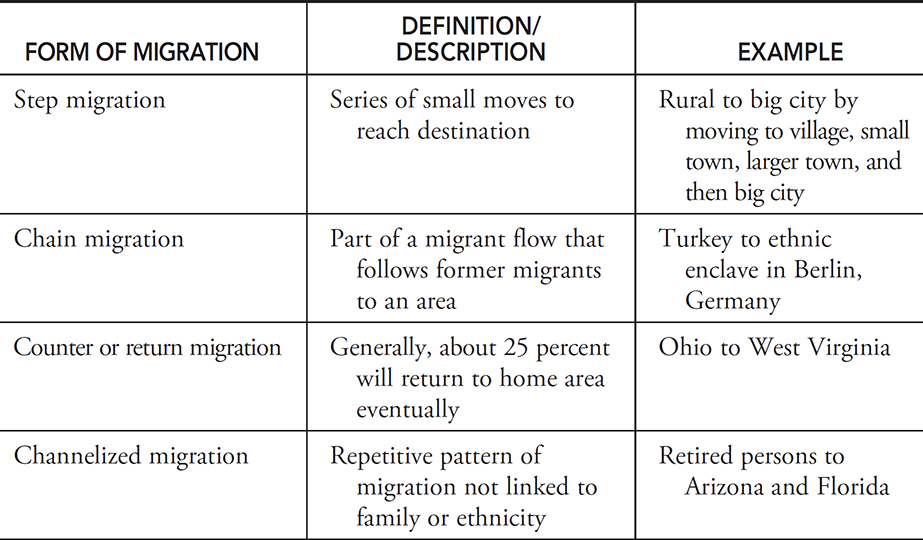
Chain migration
Definition: When people move to communities where relatives or friends migrated previously.
Sentence: "Chain migration allows families to reunite and form support networks in a new place."
Example Location: Many Central American migrants in the United States arrived through chain migration.

Ethnic enclaves
Definition: Neighborhoods filled primarily with people of the same ethnic group.
Sentence: "Ethnic enclaves provide cultural resources and familiarity for new immigrants."
Example Location: Koreatown in Los Angeles is an example of an ethnic enclave.

Xenophobia
Definition: A strong dislike of people who practice another culture.
Sentence: "Xenophobia can lead to social tensions and discrimination against newcomers."
Example Location: Xenophobic attitudes may rise in areas with recent large-scale immigration.
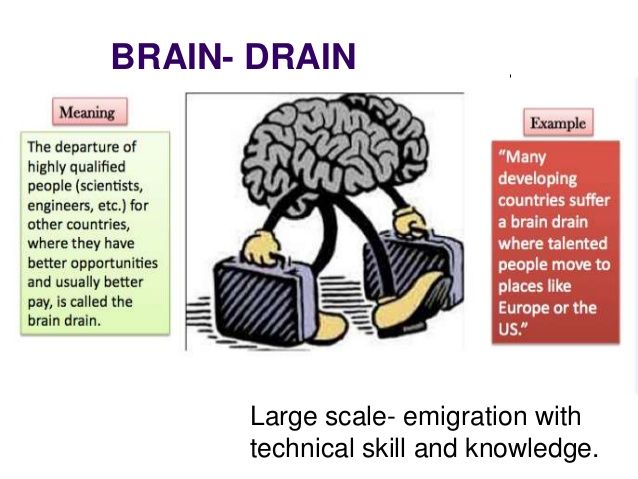
Brain drain
Definition: When migration out of a country is made up of many highly skilled people.
Sentence: "Brain drain affects the country's development as skilled professionals leave for better opportunities."
Example Location: Many skilled healthcare workers emigrate from Nigeria, contributing to brain drain.
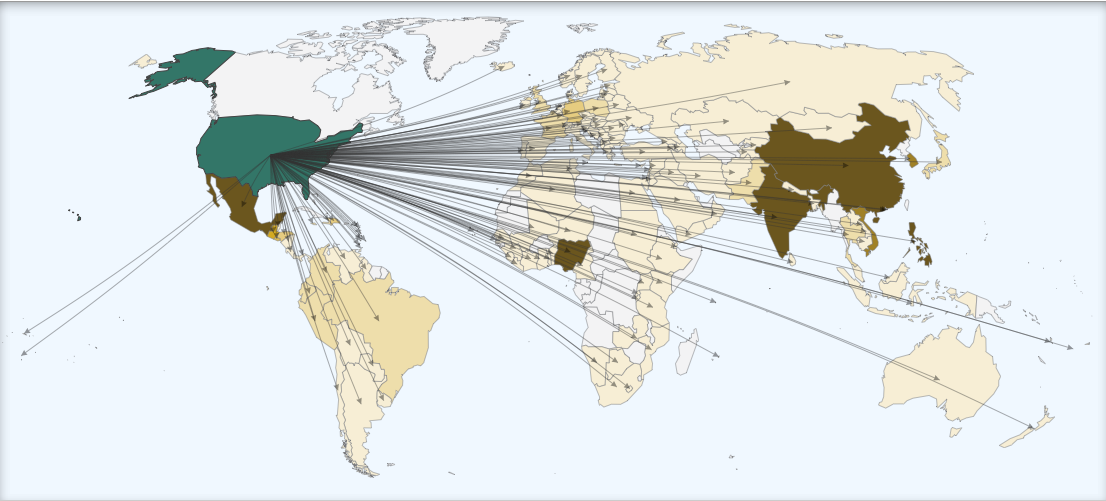
Remittances
Definition: Money immigrants send to their families and friends in the country they left.
Sentence: "Remittances play a vital role in supporting families and boosting local economies in developing countries."
Example Location: The Philippines receives significant remittances from overseas workers.
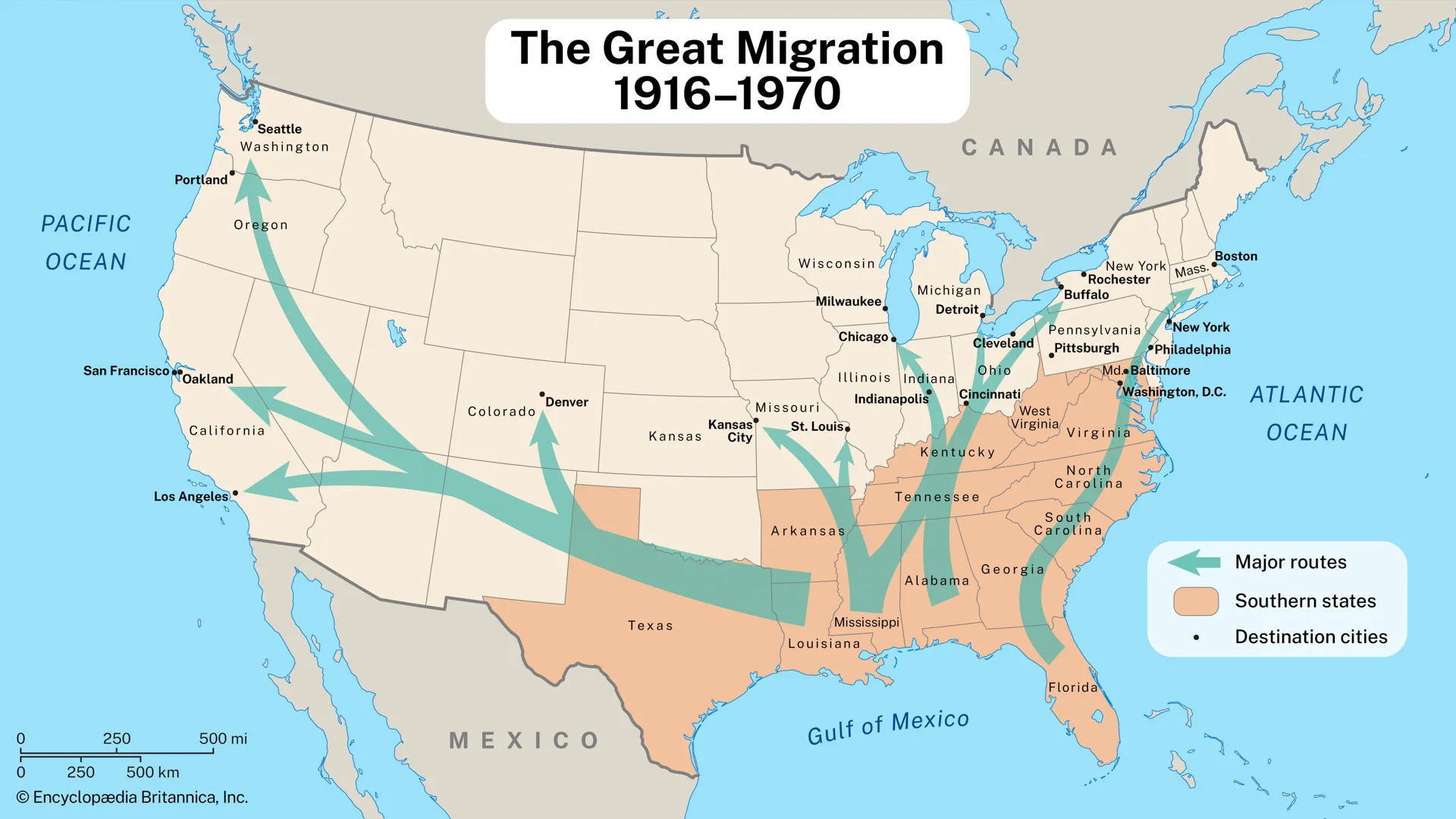
Migration
Definition: The permanent or semi-permanent relocation of people from one place to another.
Sentence: "Migration patterns can shape the demographics of urban areas as people move for work and education."
Example Location: Migration from rural regions to major Indian cities, like Mumbai, is common for job opportunities.
Emigrate
Definition: When people migrate away from somewhere.
Sentence: "High unemployment can lead people to emigrate in search of a better livelihood."
Example Location: Many people emigrate from Mexico to the United States seeking job opportunities.
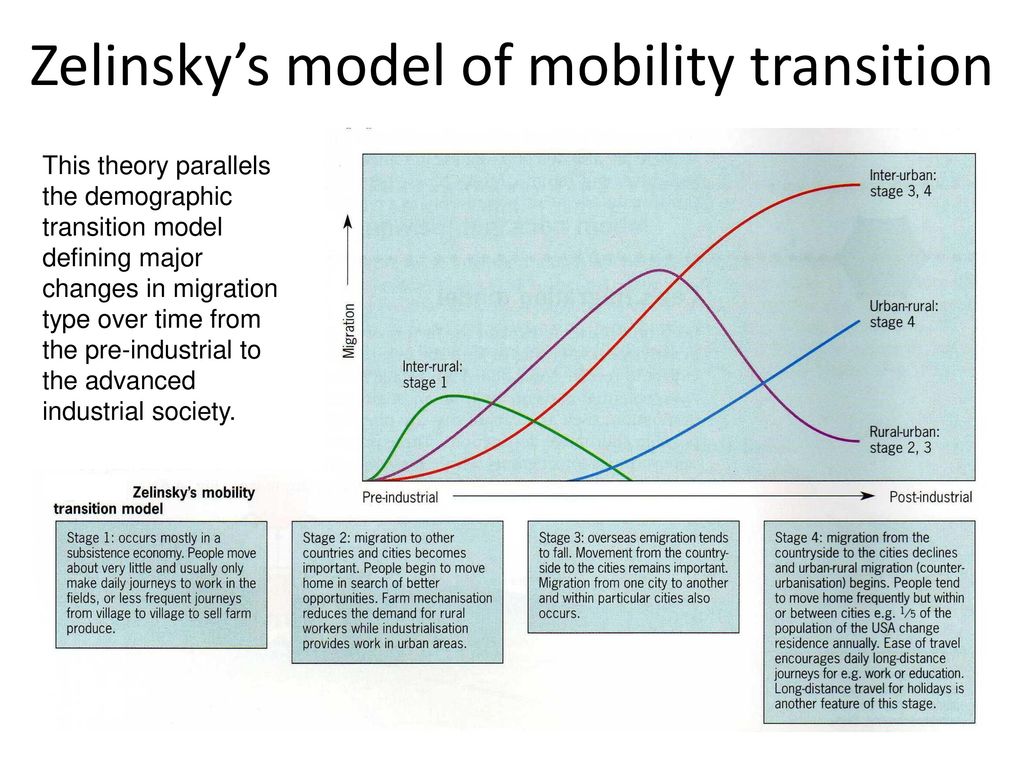
Migration transition model
Definition: Wilbur Zilensky’s theory that argues countries in stage 2 or stage 3 of the demographic transition model experience rapid population growth and overcrowding.
Sentence: "The migration transition model helps explain why people in developing countries move to urban areas."
Example Location: Many countries in Southeast Asia fit the migration transition model, experiencing high rates of urban migration.
Intervening opportunity
Definition: Opportunities en route of migration that disrupt the original migration plan.
Sentence: "An intervening opportunity, like finding employment, may lead migrants to settle in a different location than they planned."
Example Location: Migrants moving to Western Europe may settle in Spain if they find job opportunities there.
Rural-to-urban migration
Definition: Due to the need for more people to work, people are more likely to move from farming areas to cities.
Sentence: "Rural-to-urban migration has led to rapid growth in cities like Delhi as people seek jobs."
Example Location: China has experienced significant rural-to-urban migration, with millions moving to cities like Shanghai and Beijing for work.
Transnational migration
Definition: When people move from one country to another, or internationally rather than internally.
Sentence: "Transnational migration has become increasingly common, with people relocating to countries offering better job prospects and quality of life."
Example Location: Many skilled professionals from countries like India migrate to the United States to work in industries such as technology.

Transhumance
Definition: Process of herders moving with their animals to different pastures during different seasons.
Sentence: "Transhumance helps herders maintain livestock health by moving to seasonally available grazing lands."
Example Location: Transhumance is widely practiced in mountainous regions such as the Alps, where livestock is moved to highland pastures during summer months.

Guest workers
Definition: Transnational migrants who relocate to a new country to provide labor that isn’t available locally.
Sentence: "In the Gulf countries, guest workers make up a significant portion of the labor force, especially in sectors like construction."
Example Location: Guest workers from South Asia are often employed in construction and service sectors in the United Arab Emirates.

Guest worker policies
Definition: Policies that regulate the number of workers who can temporarily enter each country to work in specific industries for a defined amount of time.
Sentence: "Guest worker policies enable countries to manage labor shortages by allowing temporary migrant workers to fill specific roles."
Example Location: Germany has established guest worker policies for industries with labor shortages, allowing workers to come on fixed-term contracts.

Family reunification
Definition: Policies that allow migrants to sponsor family members who migrate to the country.
Sentence: "Family reunification policies support migrants in maintaining family connections by sponsoring relatives to join them in their new country."
Example Location: The United States offers family reunification visas, allowing permanent residents and citizens to bring spouses and children to the country.