Ruminant stomach pathology
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
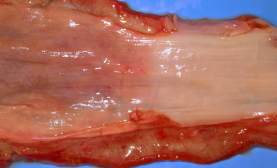
What is this and its cause?
Bloat line, caused by bloat/ruminal tympany
Pathogenesis of frothy bloat (primary)
Cattle at pasture that eat a large amount of leguminous plants, containing lots of soluble proteins (clover, alfalfa, rich lush pasture)
Soluble proteins released from chloroplasts, degraded by microflora and raised to surface where it stabilises foam and is insoluble/denatured.
Trapped gas cannot be eructated
Seen in multiple cows dying following turnout to lush pasture
Pathogenesis of free gas bloat (secondary) and list causes (8)
Caused by physical or functional defect in gas eructation produced by normal fermentation
oesophageal obstruction (tumour, stenosis)
choke
reticular adhesions
vagus indigestion
enlarged mediastinal lymph nodes (following pneumonia)
tetanus
milk fever
lateral recumbency causing blockage of cardia
How can bloat cause death?
Combined physical and metabolic effects
Increased intra-abdominal pressure on diaphragm impacts respiratory and cardiac functions
= hypoxia
Compression of caudal vena cava decreases venous flow to the heart
Altered vagosympathetic reflexes
7 gross findings of bloat death in ruminant
Bloat (hard to assess post mortem)
Dark blood clots poorly = death from anoxia
Oedema, congestion and haemorrhage of cervical muscles
Pale hind limb muscles
Bloat line
Voluminous frothy content/physical causes of impaired eructation - depending on the cause
Gross and histological findings of ruminal acidosis and its pathogenesis.
Increased starch/sugar fermentation decreases pH
Gross:
fermentative odour to rumen
ruminal epithelium adhered to submucousa
<5pH
hyperaemic lamina propria
Histo:
cytoplasmic vacuolation of epithelial cells
Neutrophils in mucousa and submucousa
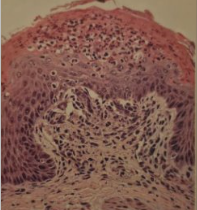
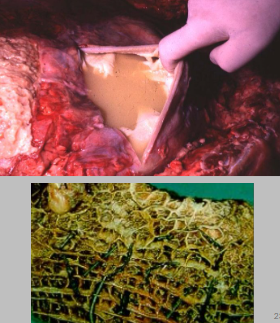
Diagnose this. What are the clinical signs (5), pathogenesis and diagnostic tests (3)
Traumatic reticulopericarditis
Wire or similar penetrates reticulum, causing inflammation and can lead to peritonitis and pericarditis
Signs:
ruminal tympany
pain on reticulorumen contraction
pyrexia
abdominal pain
heart failure
Diagnosis:
Withers pinch
Pole test
Eric Williams test (trachea should elicit grunt before ruminal contraction to indicate pain)
Pathophysiology and diagnosis of left displaced abomasum
Affects high producing cows within 6 weeks of calving
Poor management over transition - quick diet change, milk fever, retained foetal membrane
Diagnosis:
pings over left flank
reduced milk yield
reduced appetite…
Pathophysiology and pathogenesis of right displaced abomasum and its diagnosis
Twisting causing abomasal torsion or volvulus
Can occur any time during lactation
sick cow
shock
pain
Diagnosed = pings over right flank
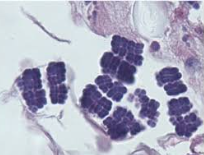
What is this and what does it cause
Sarcinia bacteria. Cause of abomasitis in calves
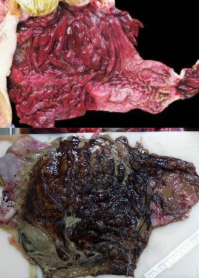
What is this condition. Explain its pathogenesis and give risk factors (4).
Abomasitis
Affects dairy calves < 3 weeks old
Usually Clostridium (septicum) or Sarcinia bacteria - produce toxins and rapid fermentation
Bacteria enter digestive system by ingestion. They replicate and produce gas and toxins,
Toxins irritate mucousa = inflammation
Gas = bloat
Risk factors:
overfeeding milk replacer
insufficient colostrum
rapid diet change
environmental fomites
List causative agents of abomasitis (7)
Clostridium septicum - cause Braxy in sheep and calves. Linked to cold weather.
Sarcinia
Bovine viral diarrhoea virus - viral mutation to cytopathic form = cell damage and ulceration of GIT. Diagnosed with antigen/antibody testing
Zygomycetes - hyphal invasion = infarction
Haemonchus
Ostertagia
Coccidia
(toxins)
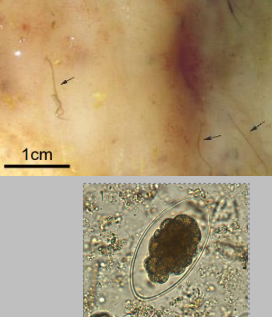
What is this abomasal parasite? How is it diagnosed (2)
Ostertagia ostertagia
Causes nodules on abomasal mucousa (especially in type II disease)
Diagnosis:
abomasal wash
FWEC
What are the three abomasal parasites of sheep?
Haemonchus contortus
Ostertagia circumcincta
Trichostrongylus axei

What is this parasite and its clinical signs? Diagnostic tests?
Haemonchus contortus
Pale mucous membranes/anaemia
Hypoproteinaemia
Damaged abomasal mucousa
Diagnosis:
abomasal wash (count number of worms)
FWEC - peanut agglutination test for H.contortus eggs
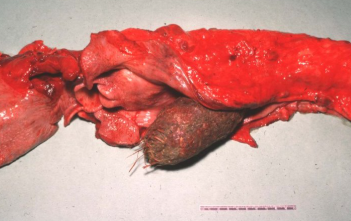
What is this condition?
Choke, caused by feed material obstructing oesophagus. Traumatic.